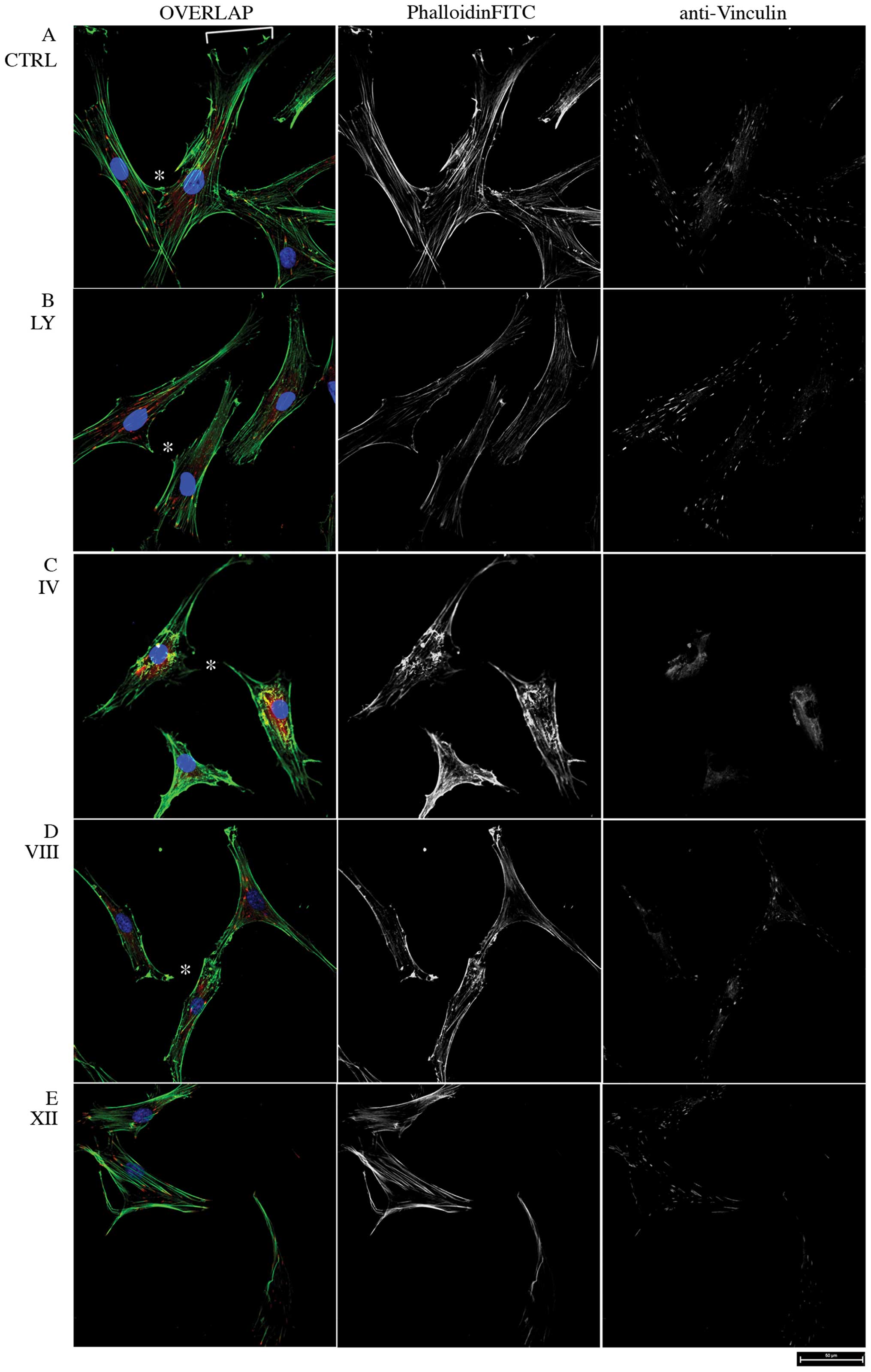
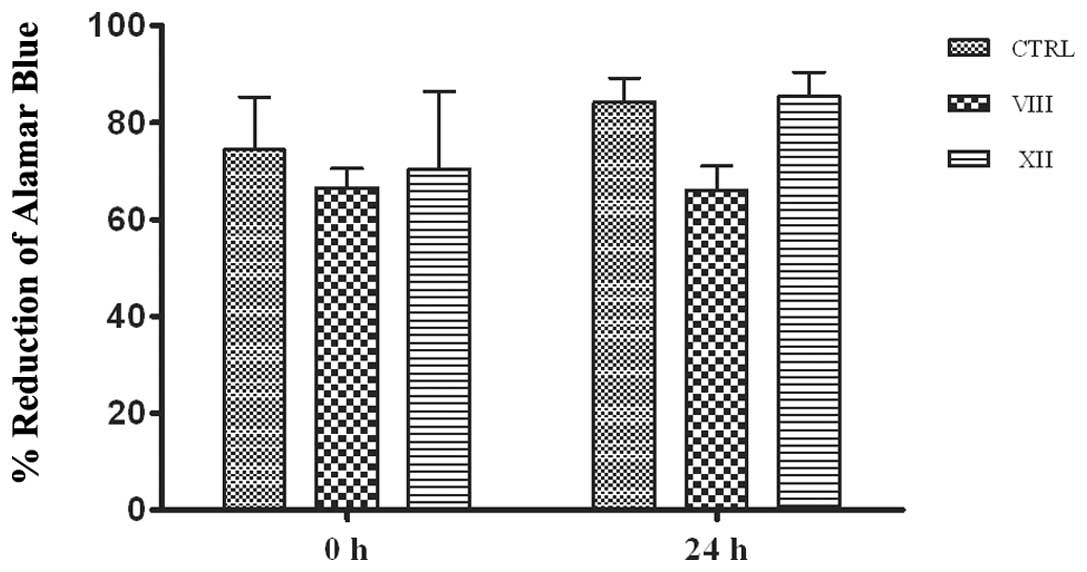
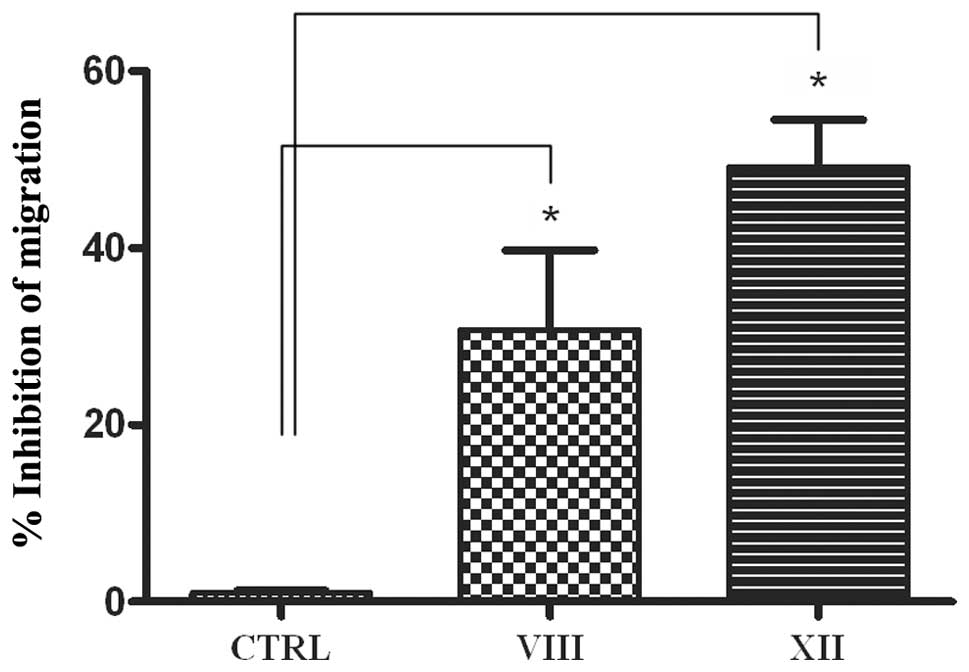
|
1.
|
Charbord P: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells: historical overview and concepts. Hum Gene Ther.
21:1045–1056. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Devine SM, Cobbs C, Jennings M,
Bartholomew A and Hoffman R: Mesenchymal stem cells distribute to a
wide range of tissues following systemic infusion into nonhuman
primates. Blood. 101:2999–3001. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Chamberlain G, Fox J, Ashton B and
Middleton J: Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells: their
phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and
potential for homing. Stem Cells. 25:2739–2749. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Kang SK, Shin IS, Ko MS, Jo JY and Ra JC:
Journey of mesenchymal stem cells for homing: strategies to enhance
efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy. Stem Cells Int.
2012:3429682012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Manning BD and Cantley LC: AKT/PKB
signaling: navigating downstream. Cell. 129:1261–1274. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Chin YR and Toker A: Akt isoform-specific
signaling in breast cancer: uncovering an anti-migratory role for
palladin. Cell Adh Migr. 5:211–214. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Worster DT, Schmelzle T, Solimini NL,
Lightcap ES, Millard B, Mills GB, Brugge JS and Albeck JG: Akt and
ERK control the proliferative response of mammary epithelial cells
to the growth factors IGF-1 and EGF through the cell cycle
inhibitor p57Kip2. Sci Signal. 5:ra192012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Kakinuma N, Roy BC, Zhu Y, Wang Y and
Kiyama R: Kank regulates RhoA-dependent formation of actin stress
fibers and cell migration via 14-3-3 in PI3K-Akt signaling. J Cell
Biol. 181:537–549. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Cenni V, Sirri A, Riccio M, Lattanzi G,
Santi S, de Pol A, Maraldi NM and Marmiroli S: Targeting of the
Akt/PKB kinase to the actin skeleton. Cell Mol Life Sci.
60:2710–2720. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Scita G, Tenca P, Frittoli E, Tocchetti A,
Innocenti M, Giardina G and Di Fiore PP: Signaling from Ras to Rac
and beyond: not just a matter of GEFs. EMBO J. 19:2393–2398. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Qian Y, Corum L, Meng Q, Blenis J, Zheng
JZ, Shi X, Flynn DC and Jiang BH: PI3K induced actin filament
remodeling through Akt and p70S6K1: implication of essential role
in cell migration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 286:C153–C163. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Enomoto A, Murakami H, Asai N, Morone N,
Watanabe T, Kawai K, Murakumo Y, Usukura J, Kaibuchi K and
Takahashi M: Akt/PKB regulates actin organization and cell motility
via Girdin/APE. Dev Cell. 9:389–402. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Yoeli-Lerner M, Yiu GK, Rabinovitz I,
Erhardt P, Jauliac S and Toker A: Akt blocks breast cancer cell
motility and invasion through the transcription factor NFAT. Mol
Cell. 20:539–550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Cenni V, Bavelloni A, Beretti F,
Tagliavini F, Manzoli L, Lattanzi G, Maraldi NM, Cocco L and
Marmiroli S: Ankrd2/ARPP is a novel Akt2 specific substrate and
regulates myogenic differentiation upon cellular exposure to
H(2)O(2). Mol Biol Cell. 22:2946–2956. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Irie HY, Pearline RV, Grueneberg D, Hsia
M, Ravichandran P, Kothari N, Natesan S and Brugge JS: Distinct
roles of Akt1 and Akt2 in regulating cell migration and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol. 171:1023–1034.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Pierini M, Dozza B, Lucarelli E, Tazzari
PL, Ricci F, Remondini D, di Bella C, Giannini S and Donati D:
Efficient isolation and enrichment of mesenchymal stem cells from
bone marrow. Cytotherapy. 14:686–693. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Maraldi T, Riccio M, Resca E, Pisciotta A,
La Sala GB, Ferrari A, Bruzzesi G, Motta A, Migliaresi C, Marzona L
and De Pol A: Human amniotic fluid stem cells seeded in fibroin
scaffold produce in vivo mineralized matrix. Tissue Eng Part A.
17:2833–2843. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Dozza B, Gobbi G, Lucarelli E, Pierini M,
Bella CD, Frisoni T, Tazzari PL, Ricci F, Mirandola P, Carubbi C,
Giannini S, Donati D and Vitale M: A rapid method for obtaining
mesenchymal stem cells and platelets from bone marrow aspirate. J
Tissue Eng Regen Med. June 19–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Maraldi T, Riccio M, Sena P, Marzona L,
Nicoli A, La Marca A, Marmiroli S, Bertacchini J, La Sala G and De
Pol A: MATER protein as substrate of PKCepsilon in human cumulus
cells. Mol Hum Reprod. 15:499–506. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Cenni V, Sabatelli P, Mattioli E,
Marmiroli S, Capanni C, Ognibene A, Squarzoni S, Maraldi NM, Bonne
G, Columbaro M, Merlini L and Lattanzi G: Lamin A N-terminal
phosphorylation is associated with myoblast activation: impairment
in Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet. 42:214–220.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Duca M, Dozza B, Lucarelli E, Santi S, Di
Giorgio A and Barbarella G: Fluorescent labeling of human
mesenchymal stem cells by thiophene fluorophores conjugated to a
lipophilic carrier. Chem Commun (Camb). 46:7948–7950. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Maraldi T, Bertacchini J, Benincasa M,
Guida M, De Pol A, Liotta LA, Petricoin E, Cocco L and Marmiroli S:
Reverse-phase protein microarrays (RPPA) as a diagnostic and
therapeutic guide in multidrug resistant leukemia. Int J Oncol.
38:427–435. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Gebäck T, Schulz MM, Koumoutsakos P and
Detmar M: TScratch: a novel and simple software tool for automated
analysis of monolayer wound healing assays. Biotechniques.
46:265–274. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Mirandola P, Sponzilli I, Gobbi G,
Marmiroli S, Rinaldi L, Binazzi R, Piccari GG, Ramazzotti G,
Gaboardi GC, Cocco L and Vitale M: Anticancer agents sensitize
osteosarcoma cells to TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
downmodulating IAP family proteins. Int J Oncol. 28:127–133.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Martelli AM, Evangelisti C, Follo MY,
Ramazzotti G, Fini M, Giardino R, Manzoli L, McCubrey JA and Cocco
L: Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target
of rapamycin signaling network in cancer stem cells. Curr Med Chem.
18:2715–2726. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Wu W-I, Voegtli WC, Sturgis HL, Dizon FP,
Vigers GPA and Brandhuber BJ: Crystal structure of human AKT1 with
an allosteric inhibitor reveals a new mode of kinase inhibition.
PLoS One. 5:e129132010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Chin YR and Toker A: The actin-bundling
protein palladin is an Akt1-specific substrate that regulates
breast cancer cell migration. Mol Cell. 38:333–344. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Nocentini S, Reginensi D, Garcia S,
Carulla P, Moreno-Flores MT, Wandosell F, Trepat X, Bribian A and
Del Río JA: Myelin-associated proteins block the migration of
olfactory ensheathing cells: an in vitro study using single-cell
tracking and traction force microscopy. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Fox JM, Chamberlain G, Ashton BA and
Middleton J: Recent advances into the understanding of mesenchymal
stem cell trafficking. Br J Haematol. 137:491–502. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Stambolic V and Woodgett JR: Functional
distinctions of protein kinase B/AKT isoforms defined by their
influence on cell migration. Trends Cell Biol. 16:461–466. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Toker A: Achieving specificity in Akt
signaling in cancer. Adv Enzyme Regul. 52:78–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Virtakoivu R, Pellinen T, Rantala JK,
Perälä M and Ivaska J: Distinct roles of AKT isoforms in regulating
β1-integrin activity, migration, and invasion in prostate cancer.
Mol Biol Cell. 23:3357–3369. 2012.
|
|
33.
|
Moritz A, Li Y, Guo A, Villén J, Wang Y,
MacNeill J, Kornhauser J, Sprott K, Zhou J, Possemato A, Ren JM,
Hornbeck P, Cantley LC, Gygi SP, Rush J and Comb MJ: AKT-RSK-S6
kinase signaling networks activated by oncogenic receptor tyrosine
kinases. Sci Signal. 3:ra642010.PubMed/NCBI
|