|
1.
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Kim SS, Ruiz VE, Carroll JD and Moss SF:
Helicobacter pylori in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer
and gastric lymphoma. Cancer Lett. 305:228–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Suerbaum S and Michetti P: Helicobacter
pylori infection. N Engl J Med. 347:1175–1186. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Fuccio L, Eusebi LH and Bazzoli F: Gastric
cancer, Helicobacter pylori infection and other risk
factors. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2:342–347. 2010.
|
|
5.
|
Conteduca V, Sansonno D, Ingravallo G, et
al: Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal cancer: an overview. Int J
Oncol. 41:414–424. 2012.
|
|
6.
|
Crew KD and Neugut AI: Epidemiology of
gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 12:354–362. 2006.
|
|
7.
|
Polk DB and Peek RM Jr: Helicobacter
pylori: gastric cancer and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:403–414.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Zullo A, Hassan C, Cristofari F, et al:
Effects of Helicobacter pylori eradication on early stage
gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:105–110. 2010.
|
|
9.
|
Fuccio L, Zagari RM, Eusebi LH, et al:
Meta-analysis: can Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment
reduce the risk for gastric cancer? Ann Intern Med. 151:121–128.
2009.
|
|
10.
|
Yaghoobi M, Bijarchi R and Narod SA:
Family history and the risk of gastric cancer. Br J Cancer.
102:237–242. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
IARC Working Group: Schistosomes, liver
flukes and Helicobacter pylori. IARC Working Group on the
Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans Lyon, 7–14 June 1994.
IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 61:1–241. 1994.
|
|
12.
|
De Vries AC, Haringsma J and Kuipers EJ:
The detection, surveillance and treatment of premalignant gastric
lesions related to Helicobacter pylori infection.
Helicobacter. 12:1–15. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Correa P: A human model of gastric
carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 48:3554–3560. 1998.
|
|
14.
|
Watanabe T, Tada M, Nagai H, Sasaki S and
Nakao M: Helicobacter pylori infection induces gastric
cancer in mongolian gerbils. Gastroenterology. 115:642–648. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Correa P and Houghton J: Carcinogenesis of
Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology. 133:659–672.
2007.
|
|
16.
|
Hatakeyama M: Helicobacter pylori
CagA-a bacterial intruder conspiring gastric carcinogenesis. Int J
Cancer. 119:1217–1223. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Konturek PC, Konturek SJ and Brzozowski T:
Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric cancerogenesis. J
Physiol Pharmacol. 60:3–21. 2009.
|
|
18.
|
Gianfagna F, De Feo E, van Duijn CM,
Ricciardi G and Boccia S: A systematic review of meta-analyses on
gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk. Curr Genomics.
9:361–374. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
González CA, Figueiredo C, Lic CB, et al:
Helicobacter pylori cagA and vacA genotypes as predictors of
progression of gastric preneoplastic lesions: a long-term follow-up
in a high-risk area in Spain. Am J Gastroenterol. 106:867–874.
2011.
|
|
20.
|
Liu D, He Q and Liu C: Correlations among
Helicobacter pylori infection and the expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor in gastric
mucosa with intestinal metaplasia or dysplasia. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 25:795–799. 2010.
|
|
21.
|
Hold GL, Rabkin CS, Chow WH, et al: A
functional polymorphism of toll-like receptor 4 gene increases risk
of gastric carcinoma and its precursors. Gastroenterology.
132:905–912. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Nobili S, Bruno L, Landini I, et al:
Genomic and genetic alterations influence the progression of
gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 17:290–299. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Lu XX, Yu JL, Ying LS, et al: Stepwise
cumulation of RUNX3 methylation mediated by Helicobacter
pylori infection contributes to gastric carcinoma progression.
Cancer. 118:5507–5517. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Rocco A, Compare D and Nardone G: Cancer
stem cell hypothesis and gastric carcinogenesis: Experimental
evidence and unsolved questions. World J Gastrointest Oncol.
4:54–59. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Suarez F, Lortholary O, Hermine O, et al:
Infection-associated lymphomas derived from marginal zone B cells:
a model of antigen-driven lymphoproliferation. Blood.
107:3034–3044. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Carmack SW, Genta RM, Graham DY and
Lauwers GY: Management of gastric polyps: a pathology-based guide
for gastroenterologists. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:331–341.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Kelly PJ and Lauwers GY: Clinical
guidelines: Consensus for the management of patients with gastric
polyps. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:7–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O’Morain C, et
al: Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter
pylori infection: the Maastricht III Consensus Report. Gut.
56:772–781. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O’Morain CA,
et al: Management of Helicobacter pylori infection - the
Maastricht IV/ Florence Consensus Report. Gut. 61:646–664.
2012.
|
|
30.
|
De Vries AC and Kuipers EJ: Epidemiology
of premalignant gastric lesions: implications for the development
of screening and surveillance strategies. Helicobacter. 12:22–31.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Schlemper RJ, Itabashi M, Kato Y, et al:
Differences in diagnostic criteria for gastric carcinoma between
Japanese and western pathologists. Lancet. 349:1725–1729. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Schlemper RJ, Riddell RH, Kato Y, et al:
The Vienna classification of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia.
Gut. 47:251–255. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Dixon MF: Gastrointestinal epithelial
neoplasia: Vienna revisited. Gut. 51:130–131. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Rugge M, Pennelli G, Pilozzi E, et al:
Gastritis: the histology report. Dig Liver Dis. 43(Suppl 4):
S373–S384. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35.
|
Ohnita K, Isomoto H, Shikuwa S, et al:
Magnifying chromoendoscopic findings of early gastric cancer and
gastric adenoma. Dig Dis Sci. 56:2715–2722. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Yeh JM, Hur C, Kuntz KM, Ezzati M and
Goldie SJ: Cost-effectiveness of treatment and endoscopic
surveillance of precancerous lesions to prevent gastric cancer.
Cancer. 116:2941–2953. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Hamashima C, Shibuya D, Yamazaki H, et al:
The Japanese guidelines for gastric cancer screening. Jpn J Clin
Oncol. 38:259–267. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38.
|
Fock KM, Katelaris P, Sugano K, et al:
Second Asia-Pacific consensus guidelines for Helicobacter
pylori infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 24:1587–1600. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Zullo A, Hassan C, Cristofari F, Perri F
and Morini S: Gastric low-grade mucosal-associated lymphoid
tissue-lymphoma: Helicobacter pylori and beyond. World J
Gastrointest Oncol. 2:181–186. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Oh SY, Kim WS, Kim JS, et al: Multiple
mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue organs involving marginal zone B
cell lymphoma: organ-specific relationships and the prognostic
factors. Consortium for improving survival of lymphoma study. Int J
Hematol. 92:510–517. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41.
|
Shinagare AB, Ramaiya NH, O’Regan K,
Jagannathan JP, Hornick JL and LaCasce AS: Helicobacter
pylori-negative gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 29:297–300. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42.
|
Zucca E and Dreyling M; ESMO Guidelines
Working Group: Gastric marginal zone lymphoma of MALT type: ESMO
Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and
follow-up. Ann Oncol. 21(Suppl 5): v175–v176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43.
|
Ruskoné-Fourmestraux A, Fischbach W,
Aleman BM, et al: EGILS consensus report. Gastric extranodal
marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of MALT. Gut. 60:747–758.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Goddard AF, Badreldin R, Pritchard DM, et
al: British Society of Gastroenterology: The management of gastric
polyps. Gut. 59:1270–1276. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Fitzgeral RC, Hardwick R, Huntsman D, et
al: Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer: updated consensus guidelines
for clinical management and directions for future research. J Med
Genet. 47:436–444. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Guilford P, Humar B and Blair V:
Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer: translation of CDH1 germline
mutations into clinical practice. Gastric cancer. 13:1–10. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Bornschein J, Rokkas T, Selgrad M and
Malfertheiner P: Helicobacter pylori and clinical aspects of
gastric cancer. Helicobacter. 14(Suppl 1): 41–45. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48.
|
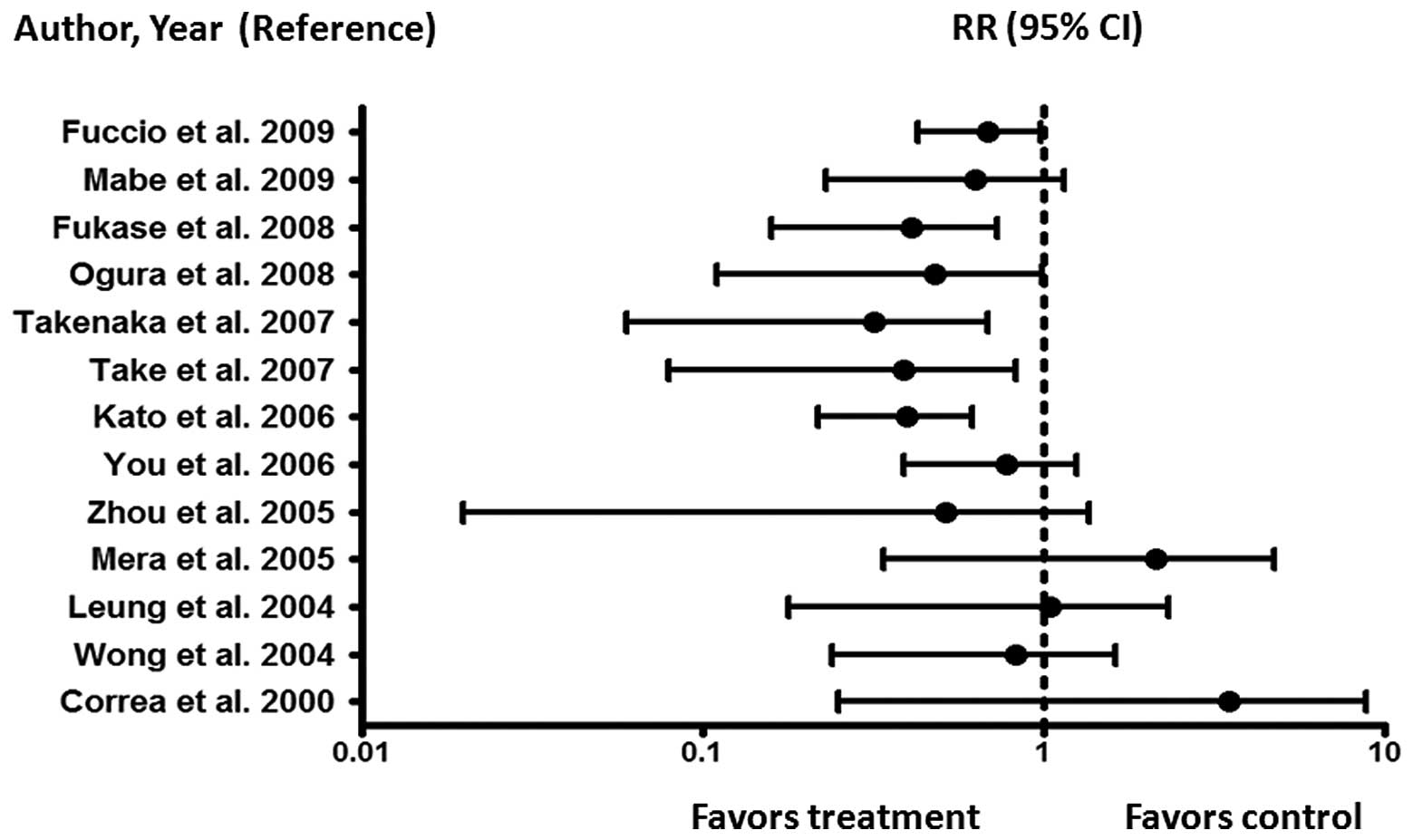
Fukase K, Kato M, Kikuchi S, et al: Effect
of eradication of Helicobacter pylori on incidence of
metachronous gastric carcinoma after endoscopic resection of early
gastric cancer: an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet.
372:392–397. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Take S, Mizuno M, Ishiki K, et al: The
long-term risk of gastric cancer after the successful eradication
of Helicobacter pylori. J Gastroenterol. 46:318–324. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Kodama M, Murakami K, Okimoto T, et al:
Helicobacter pylori eradication improves gastric atrophy and
intestinal metaplasia in long-term observation. Digestion.
85:126–130. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51.
|
Correa P, Fontham ET, Bravo JC, et al:
Chemoprevention of gastric dysplasia: randomized trial of
antioxidant supplements and anti-Helicobacter pylori
therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:1881–1888. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Wong BC, Lam SK, Wong WM, et al:
Helicobacter pylori eradication to prevent gastric cancer in
a high-risk region of China: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA.
291:187–194. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53.
|
Leung WK, Lin SR, Ching JY, et al: Factors
predicting progression of gastric intestinal metaplasia: results of
a randomised trial on Helicobacter pylori eradication. Gut.
53:1244–1249. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Mera R, Fontham ET, Bravo LE, et al: Long
term follow up of patients treated for Helicobacter pylori
infection. Gut. 54:1536–1540. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Zhou LY, Lin SR, Ding SG, et al: The
changing trends of the incidence of gastric cancer after
Helicobacter pylori eradication in Shandong area. Chin J Dig
Dis. 6:114–115. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
You WC, Brown LM, Zhang L, et al:
Randomized double-blind factorial trial of three treatments to
reduce the prevalence of precancerous gastric lesions. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 98:974–983. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57.
|
Kato M, Asaka M, Nakamura T, et al:
Helicobacter pylori eradication prevents the development of
gastric cancer - results of a long-term retrospective study in
Japan. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 24:203–206. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58.
|
Take S, Mizuno M, Ishiki K, et al:
Baseline gastric mucosal atrophy is a risk factor associated with
the development of gastric cancer after Helicobacter pylori
eradication therapy in patients with peptic ulcer diseases. J
Gastroenterol. 42(Suppl 17): 21–27. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Takenaka R, Okada H, Kato J, et al:
Helicobacter pylori eradication reduced the incidence of
gastric cancer, especially of the intestinal type. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 25:805–812. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60.
|
Ogura K, Hirata Y, Yanai A, et al: The
effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on reducing the
incidence of gastric cancer. J Clin Gastroenterol. 42:279–283.
2008.
|
|
61.
|
Mabe K, Takahashi M, Oizumi H, et al: Does
Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy for peptic ulcer
prevent gastric cancer? World J Gastroenterol. 15:4290–4297.
2009.
|
|
62.
|
Kuo SH, Yeh KH, Wu MS, et al:
Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy is effective in the
treatment of early-stage H pylori-positive gastric diffuse large
B-cell lymphomas. Blood. 119:4838–4844. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Park HS, Kim YJ, Yang WI, Suh CO and Lee
YC: Treatment and outcome of localized Helicobacter
pylori-negative low-grade gastric MALT lymphoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 16:2158–2162. 2010.
|
|
64.
|
Gill H, Chim CS, Au WY, et al: Non-gastric
marginal zone B cell lymphoma: clinicopathologic features and
treatment results. Ann Hematol. 90:1399–1407. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65.
|
Owens SR and Smith LB: Molecular aspects
of H. pylori-related MALT lymphoma. Patholog Res Int.
2011:1931492011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66.
|
O’Connor A, Gisbert JP, McNamara D and
O’Morain C: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection 2010.
Helicobacter. 15:46–52. 2010.
|
|
67.
|
Graham DY and Fischbach L: Helicobacter
pylori treatment in the era of increasing antibiotic
resistance. Gut. 59:1143–1153. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68.
|
Malfertheiner P, Bazzoli F, Delchier JC,
et al: Helicobacter pylori eradication with a capsule
containing bismuth subcitrate potassium, metronidazole and
tetracycline given with omeprazole versus clarithromycin-based
triple therapy: a randomised, open-label, non-inferiority, phase 3
trial. Lancet. 377:905–913. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69.
|
Kang JM, Kim N, Lee DH, et al: Effect of
the CYP2C19 polymorphism on the eradication rate of Helicobacter
pylori infection by 7-day triple therapy with regular proton
pump inhibitor dosage. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:1287–1291.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70.
|
Perri F, Manes G, Neri M, Vaira D and
Nardone G: Helicobacter pylori antigen stool test and
13C-Urea breath test in patients after eradication
treatments. Am J Gastroenterol. 97:2756–2762. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71.
|
World Gastroenterology Organisation: World
Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guideline: Helicobacter
pylori in developing countries. J Clin Gastroenterol.
45:383–388. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72.
|
Czinn SJ and Blanchard T: Vaccinating
against Helicobacter pylori infection. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 8:133–140. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73.
|
Moss SF, Moise L, Lee DS, et al:
HelicoVax: epitope-based therapeutic Helicobacter pylori
vaccination in a mouse model. Vaccine. 29:2085–2091. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74.
|
Othman MO and Wallace MB: Endoscopic
mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD)
in 2011, a Western perspective. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol.
35:288–294. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75.
|
Pandalai PK, Lauwers GY, Chung DC, Patel D
and Yoon SS: Prophylactic total gastrectomy for individuals with
germline CDH1 mutation. Surgery. 149:347–355. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76.
|
Wu CY, Wu MS, Kuo KN, Wang CB, Chen YJ and
Lin JT: Effective reduction of gastric cancer risk with regular use
of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in Helicobacter
pylori-infected patients. J Clin Oncol. 28:2952–2957. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77.
|
Navarro Silvera SA, Mayne ST, Risch HA, et
al: Principal component analysis of dietary and lifestyle patterns
in relation to risk of subtypes of esophageal and gastric cancer.
Ann Epidemiol. 21:543–550. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|