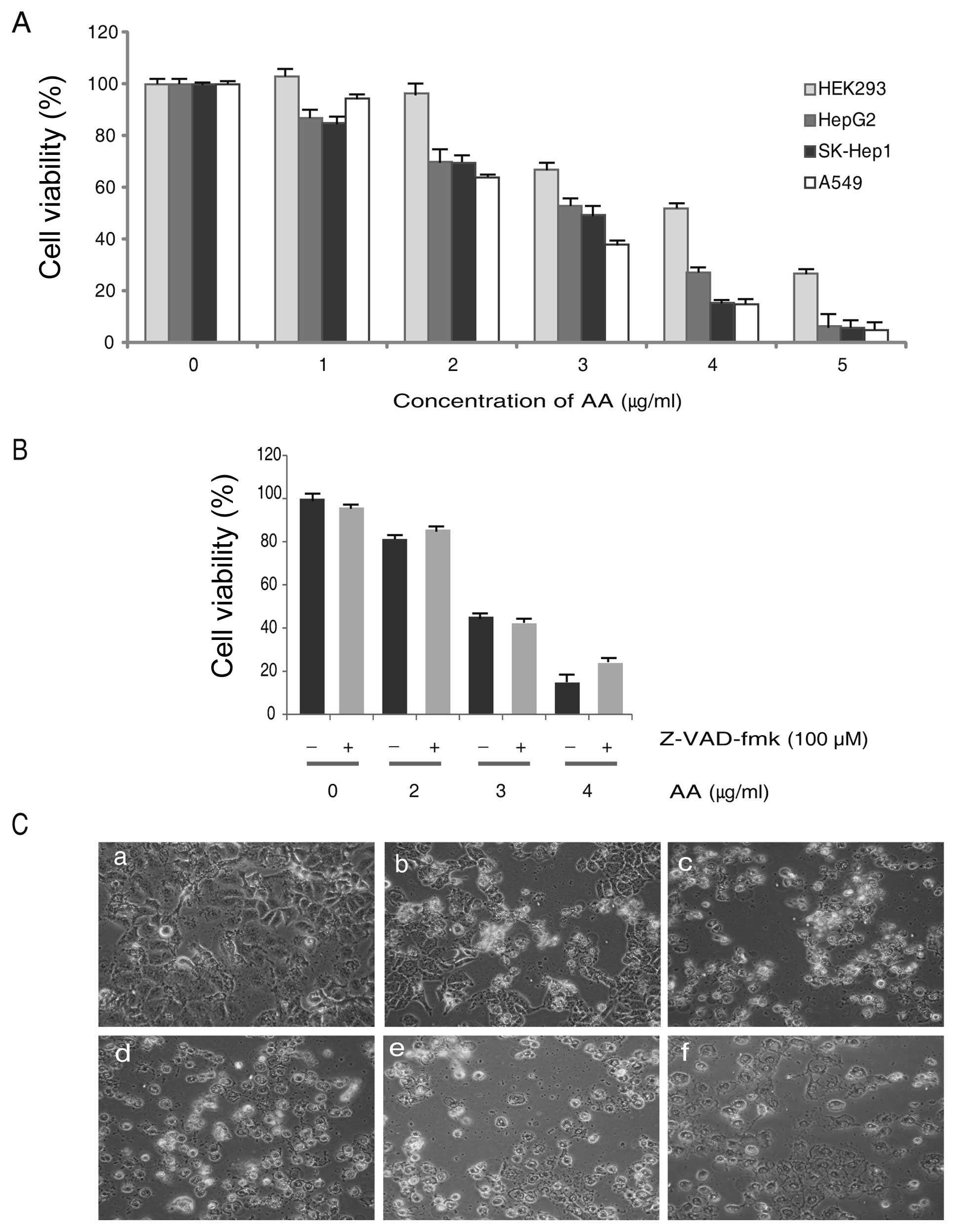
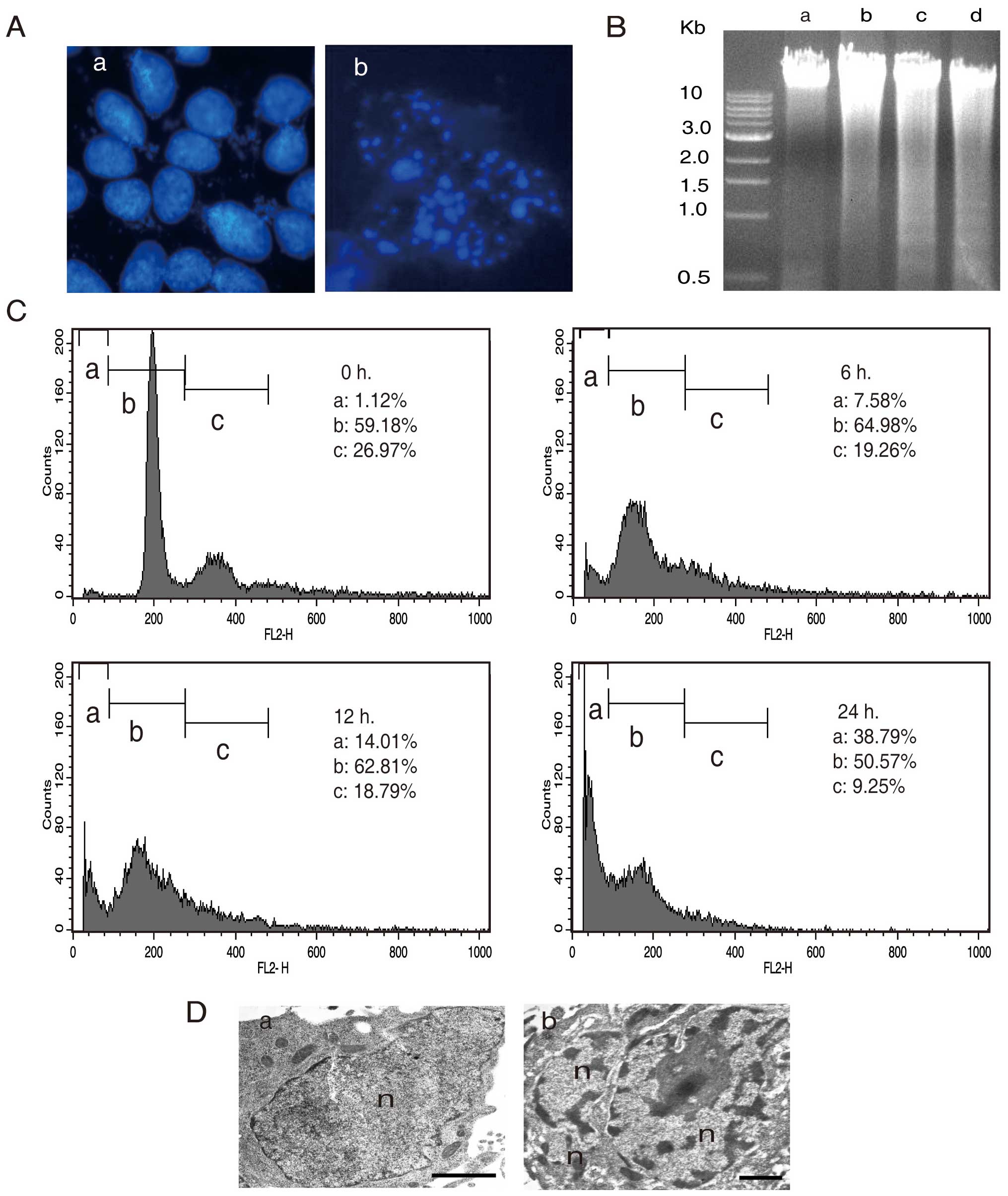
|
1
|
Kubo I, Kinst-Hori I and Yokokawa Y:
Tyrosinase inhibitors from Anacardium occidentale fruits. J Nat
Prod. 57:545–551. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Murata M, Irie J and Homma S: Inhibition
of lipid synthesis of bacteria, yeast and animal cells by anacardic
acids, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase inhibitors from Ginkgo.
Lebensm Wiss Technol. 30:458–463. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Grazzini R, Hesk D, Heininger E, et al:
Inhibition of lipoxygenase and prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase
by anacardic acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 176:775–780. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kishore AH, Vedamurthy BM, Mantelingu K,
et al: Specific small-molecule activator of aurora kinase A induces
autophosphorylation in a cell-free system. J Med Chem. 28:792–797.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun Y, Jiang X, Chen S and Price BD:
Inhibition of histone acetyltransferase activity by anacardic acid
sensitizes tumor cells to ionizing radiation. FEBS Lett.
580:4353–4356. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sung B, Pandey MK, Ahn KS, Yi T,
Chaturvedi MM, Liu M and Aggarwal BB: Anacardic acid (6-nonadecyl
salicylic acid), an inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase,
suppresses expression of nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated gene
products involved in cell survival, proliferation, invasion, and
inflammation through inhibition of the inhibitory subunit of
nuclear factor-kappaB alpha kinase, leading to potentiation of
apoptosis. Blood. 111:4880–4891. 2008.
|
|
7
|
Choi JG, Jeong SI, Ku CS, Sathishkumar M,
Lee JJ, Mun SP and Kim SM: Antibacterial activity of hydroxyalkenyl
salicylic acids from sarcotesta of Ginkgo biloba against
vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus. Fitoterapia. 80:18–20.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sukumari-Ramesh S, Singh N, Jensen MA,
Dhandapani KM and Vender JR: Anacardic acid induces
caspase-independent apoptosis and radiosensitizes pituitary adenoma
cells. J Neurosurg. 114:1681–1690. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P, et
al: Classification of cell death: recommendations of the
Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009. Cell Death Differ.
16:3–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Millan A and Huerta S: Apoptosis-inducing
factor and colon cancer. J Surg Res. 151:163–170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Slee EA, Adrain C and Martin SJ:
Executioner caspase-3, -6, and -7 perform distinct, non-redundant
roles during the demolition phase of apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
276:7320–7326. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Walczak H and Krammer PH: The CD95
(APO-1/Fas) and the TRAIL (APO-2L) apoptosis systems. Exp Cell Res.
256:58–66. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zamzami N, Susin SA, Marchetti P, Hirsch
T, Gómez-Monterrey I, Castedo M and Kroemer G: Mitochondrial
control of nuclear apoptosis. J Exp Med. 183:1533–1544. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schultz DR and Harrington WJ Jr:
Apoptosis: programmed cell death at a molecular level. Semin
Arthritis Rheum. 32:345–369. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Adrain C and Martin SJ: The mitochondrial
apoptosome: a killer unleashed by the cytochrome seas. Trends
Biochem Sci. 26:390–397. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, et al:
Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing
factor. Nature. 397:441–446. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ye H, Cande C, Stephanou NC, et al: DNA
binding is required for the apoptogenic action of apoptosis
inducing factor. Nat Struct Biol. 9:680–684. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
O’Connor L, Strasser A, O’Reilly LA,
Hausmann G, Adams JM, Cory S and Huang DC: Bim: a novel member of
the Bcl-2 family that promotes apoptosis. EMBO J. 17:384–395.
1998.
|
|
20
|
Beckmann RP, Mizzen LE and Welch WJ:
Interaction of Hsp70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications
for protein folding and assembly. Science. 248:850–854. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Obexer P, Geiger K, Ambros PF, Meister B
and Ausserlechner MJ: FKHRL1-mediated expression of Noxa and Bim
induces apoptosis via the mitochondria in neuroblastoma cells. Cell
Death Differ. 14:534–547. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR and
Newmeyer DD: The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a
primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science.
275:1132–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, et al: Prevention
of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria
blocked. Science. 275:1129–1132. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Green DR and Amarante-Mendes GP: The point
of no return: mitochondria, caspases, and the commitment to cell
death. Results Probl Cell Differ. 24:45–61. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c and
dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an
apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nutt LK, Pataer A, Pahler J, Fang B, Roth
J, McConkey DJ and Swisher SG: Bax and Bak promote apoptosis by
modulating endoplasmic reticular and mitochondrial Ca2+
stores. J Biol Chem. 277:9219–9225. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Oda E, Ohki R, Murasawa H, et al: Noxa, a
BH3-only member of the Bcl-2 family and candidate mediator of
p53-induced apoptosis. Science. 288:1053–1058. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang H and Tindall DJ: Dynamic FoxO
transcription factors. J Cell Sci. 120:2479–2487. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Leung HW, Wu CH, Lin CH and Lee HZ:
Luteolin induced DNA damage leading to human lung squamous
carcinoma CH27 cell apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 508:77–83. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang X, Chen J, Graham SH, et al:
Intranuclear localization of apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) and
large scale DNA fragmentation after traumatic brain injury in rats
and in neuronal cultures exposed to peroxynitrite. J Neurochem.
82:181–191. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cregan SP, Dawson VL and Slack RS: Role of
AIF in caspase-dependent and caspase-independent cell death.
Oncogene. 23:2785–2796. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu SW, Wang H, Poitras MF, et al:
Mediation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-dependent cell death by
apoptosis-inducing factor. Science. 297:259–263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gurbuxani S, Schmitt E, Cande C, et al:
Heat shock protein 70 binding inhibits the nuclear import of
apoptosis-inducing factor. Oncogene. 22:6669–6678. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li CY, Lee JS, Ko YG, Kim JI and Seo JS:
Heat shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis downstream of cytochrome c
release and upstream of caspase-3 activation. J Biol Chem.
275:25665–25671. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Saleh A, Srinivasula SM, Balkir L, Robbins
PD and Alnemri ES: Negative regulation of the Apaf-1 apoptosome by
Hsp70. Nat Cell Biol. 2:476–483. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Creagh EM, Carmody RJ and Cotter TG: Heat
shock protein 70 inhibits caspase-dependent and -independent
apoptosis in Jurkat T cells. Exp Cell Res. 257:58–66. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nylandsted J, Wick W, Hirt UA, et al:
Eradication of glioblastoma, and breast and colon carcinoma
xenografts by Hsp70 depletion. Cancer Res. 62:7139–7142.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu D, Zalmas LP and La Thangue NB: A
transcription cofactor required for the heat-shock response. EMBO
Rep. 9:662–669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|