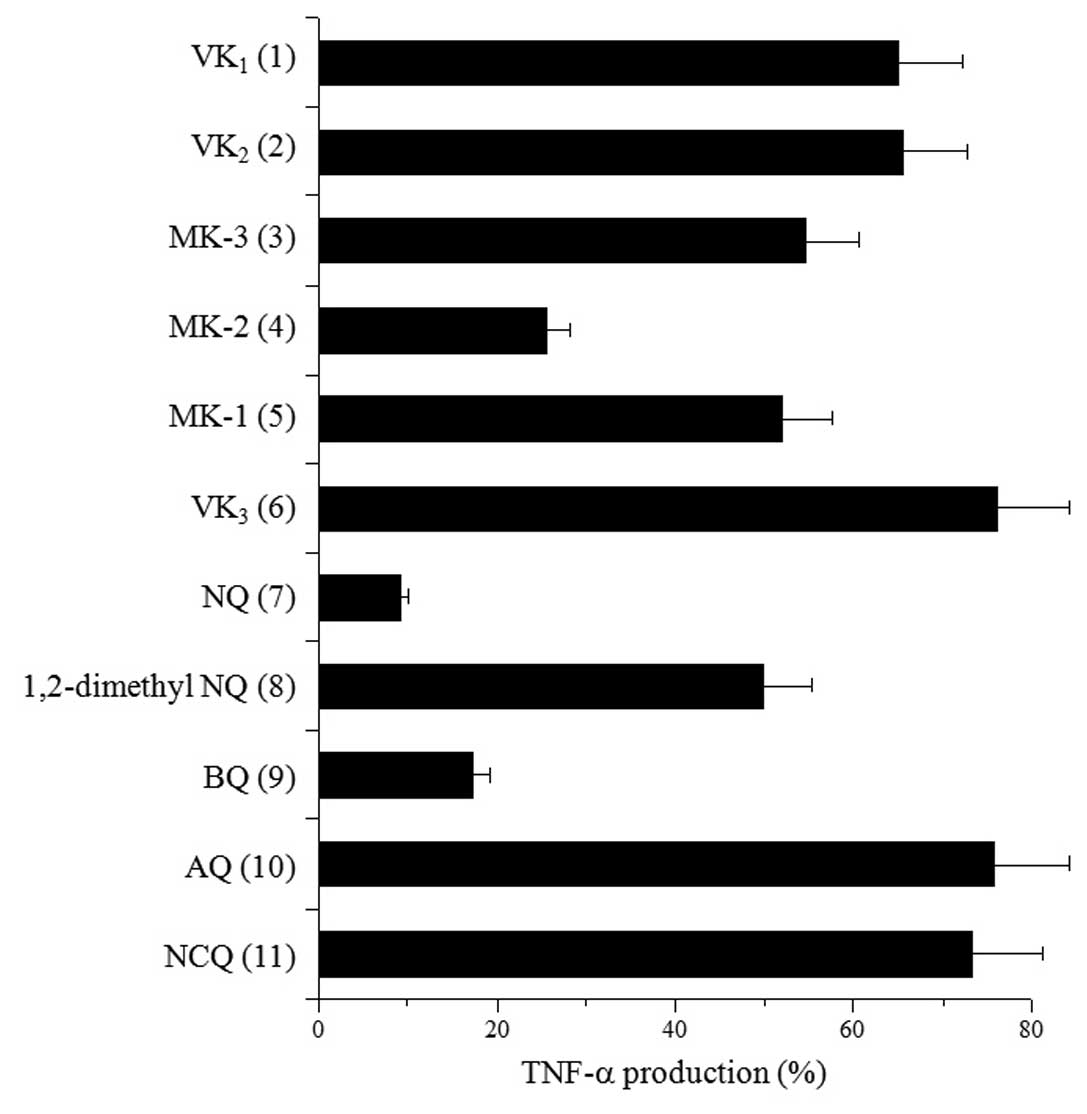
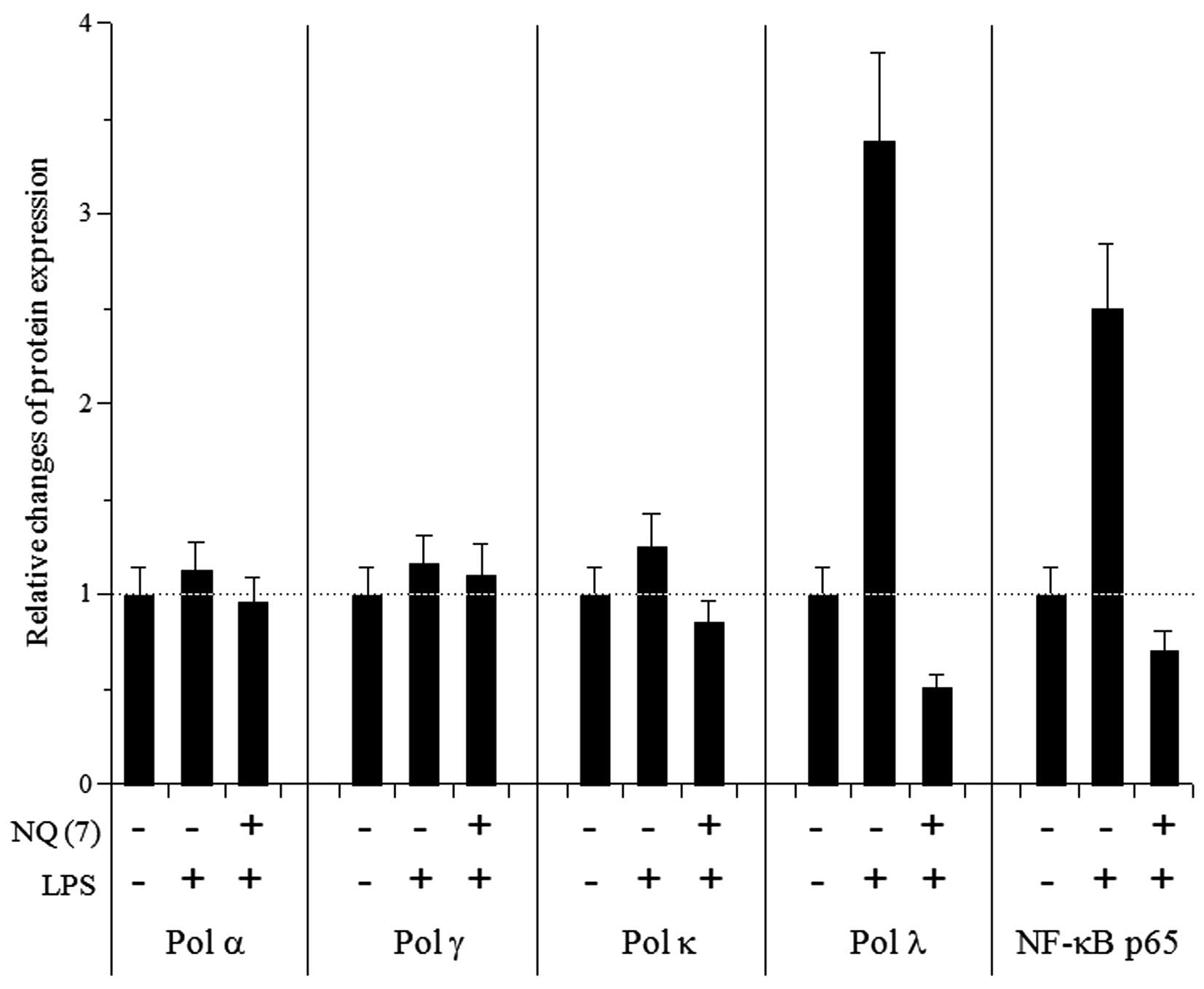
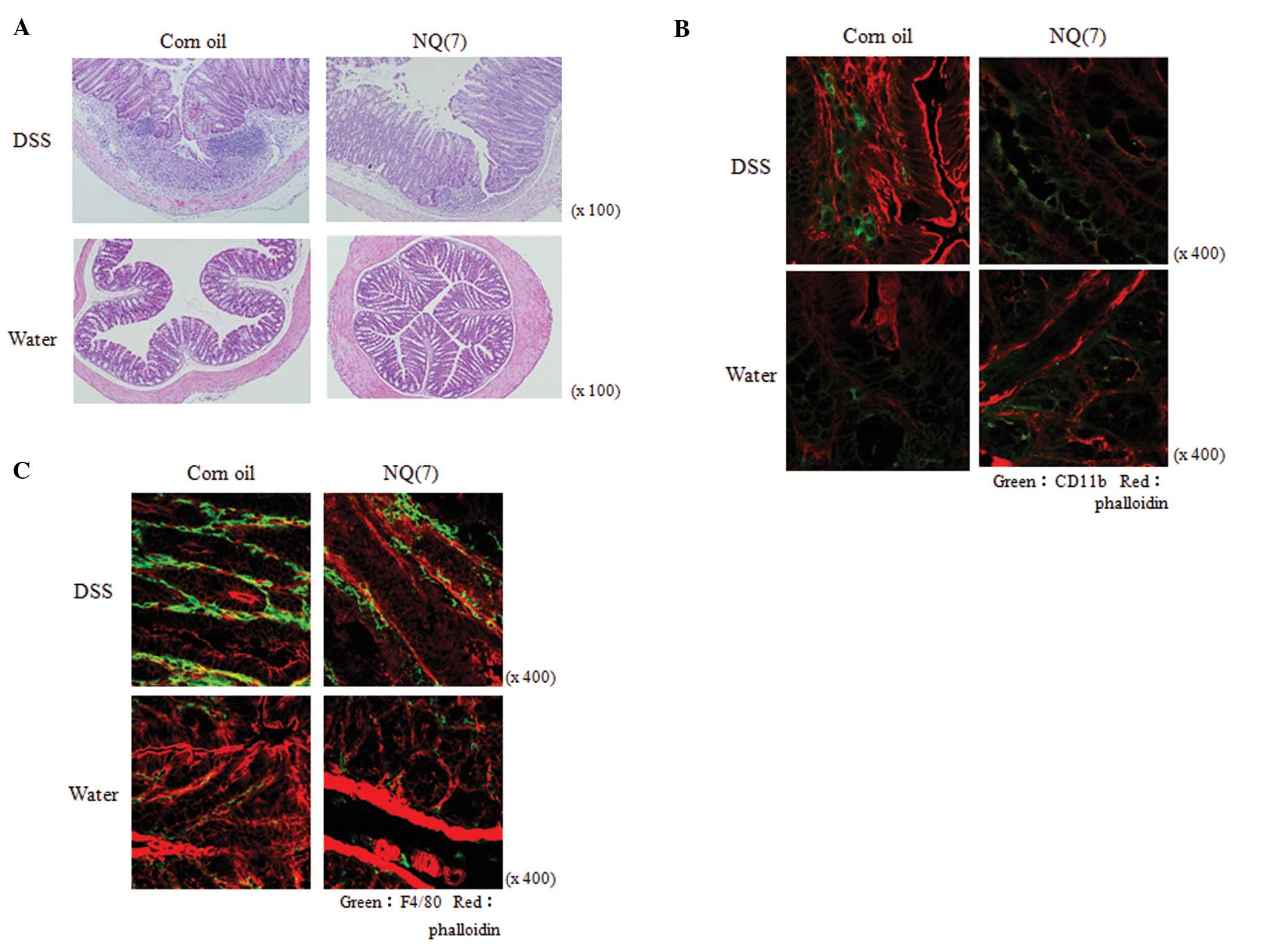
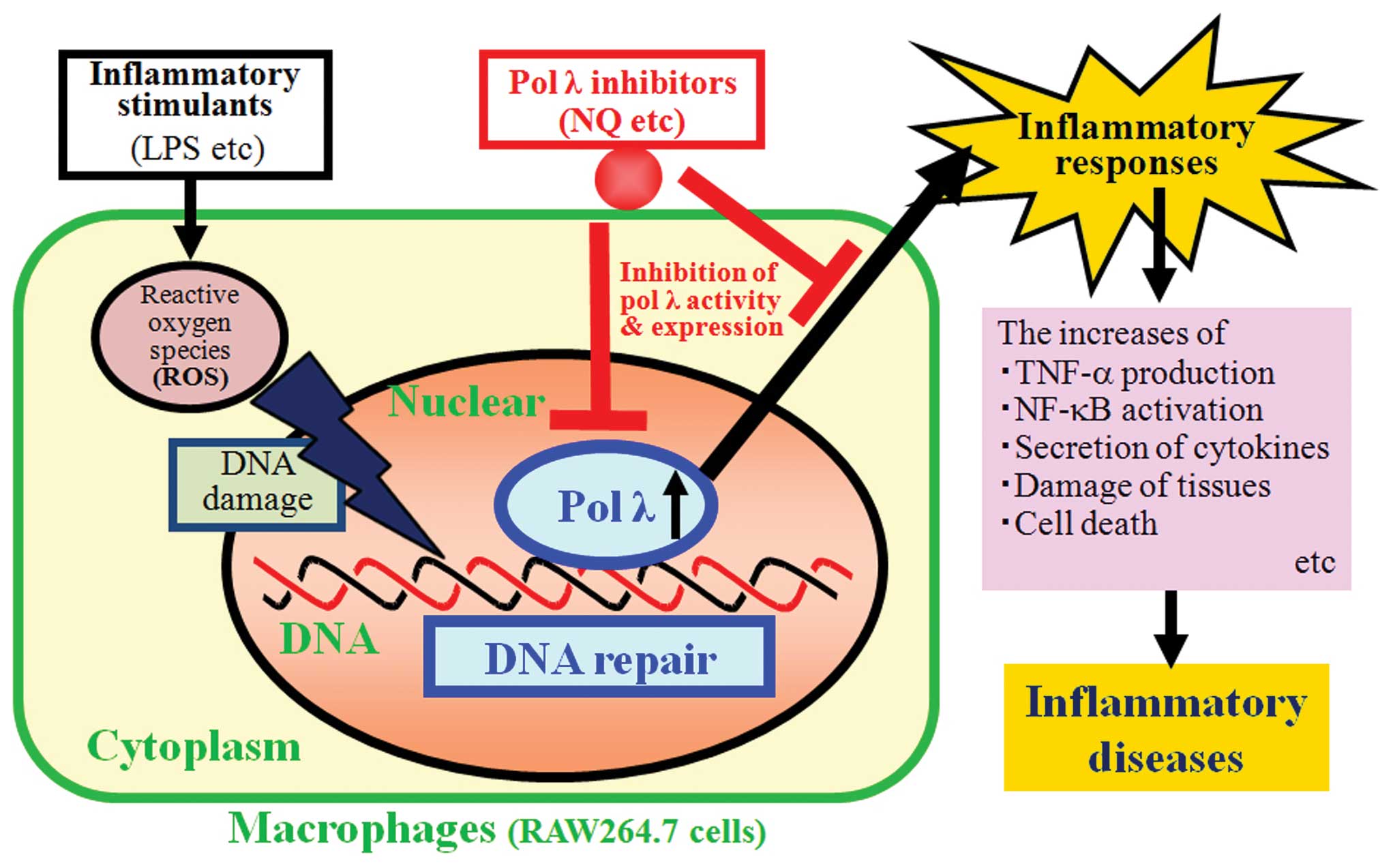
|
1
|
Furie B and Furie BC: Molecular basis of
vitamin K-dependent γ-carboxylation. Blood. 75:1753–1762. 1990.
|
|
2
|
Suttie JW: Synthesis of vitamin
K-dependent proteins. FASEB J. 7:445–452. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shearer MJ: Role of vitamin K and Gla
proteins in the pathophysiology of osteoporosis and vascular
calcification. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 3:433–438. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ohsaki Y, Shirakawa H, Hiwatashi K,
Furukawa Y, Mizutani T and Komai M: Vitamin K suppresses
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in the rat. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 70:926–932. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Seegers WH and Bang NU: Blood Clotting
Enzymology. Academic Press; New York, NY: 1967
|
|
6
|
Elder SJ, Haytowitz DB, Howe J, Peterson
JW and Booth SL: Vitamin K contents of meat, dairy, and fast food
in the U.S. diet. J Agric Food Chem. 54:463–467. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tsukamoto Y, Ichise H, Kakuda H and
Yamaguchi M: Intake of fermented soybean (natto) increases
circulating vitamin K2 (menaquinone-7) and γ-carboxylated
osteocalcin concentration in normal individuals. J Bone Miner
Metab. 18:216–222. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suttie JW: The importance of menaquinone
in human nutrition. Annu Rev Nutr. 15:399–417. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Booth SL: Dietary vitamin K guidance: an
effective strategy for stable control of oral anticoagulation? Nutr
Rev. 68:178–181. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Billeter M, Bolliger W and Martius C:
Untersuchungen uber die umwandlung von verfutterten K-vitamin durch
austausch der seitenkette und die rolle der darmbakterien hierbei.
Biochem Z. 340:290–303. 1964.(In German).
|
|
11
|
Davidson RT, Foley AL, Engelke JA and
Suttie JW: Conversion of dietary phylloquinone to tissue
menaquinone-4 in rats is not dependent on gut bacteria. J Nutr.
128:220–223. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Budavari S, O’Neil MJ, Smith A and
Heckelman PE: The Merck Index. Merck & Co. Inc; Rahway, NJ:
1989
|
|
13
|
Taggart WV and Matschiner JT: Metabolism
of menadione-6,7-3H in the rat. Biochemistry. 8:1141–1146. 1969.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Monks TJ, Hanzlik RP, Cohen GM, Ross D and
Graham DG: Quinone chemistry and toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
112:2–16. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
O’Brien PJ: Molecular mechanisms of
quinone cytotoxicity. Chem Biol Interact. 80:1–41. 1991.
|
|
16
|
Bolton JL, Trush MA, Penning TM, Dryhurst
G and Monks TJ: Role of quinones in toxicology. Chem Res Toxicol.
13:135–160. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cho AK, Schmitz DA, Ying Y, Rodriguez CE,
DiStefano EW, Kumagai Y, Miguel A, Eiguren A, Kobayashi T, Avol E
and Froines JR: Determination of four quinones in diesel exhaust
particles, SRM 1649a, and atmospheric PM2.5. Aerosol Sci Technol.
38:68–81. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kornberg A and Baker TA: DNA replication
Chaprter. 6 2nd edition. WD Freeman and Co; New York, NY: pp.
197–225. 1992
|
|
19
|
Hubscher U, Maga G and Spadari S:
Eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 71:133–163. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bebenek K and Kunkel TA: DNA repair and
replication. Adv Protein Chem. 69:137–165. 2004.
|
|
21
|
Takata K, Shimizu T, Iwai S and Wood RD:
Human DNA polymerase N (POLN) is a low fidelity enzyme capable of
error-free bypass of 5S-thymine glycol. J Biol Chem.
281:23445–23455. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Loeb LA and Monnat RJ Jr: DNA polymerases
and human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 9:594–604. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mizushina Y, Tanaka N, Yagi H, Kurosawa T,
Onoue M, Seto H, Horie T, Aoyagi N, Yamaoka M, Matsukage A, Yoshida
S and Sakaguchi K: Fatty acids selectively inhibit eukaryotic DNA
polymerase activities in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1308:256–262.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mizushina Y, Yoshida S, Matsukage A and
Sakaguchi K: The inhibitory action of fatty acids on DNA polymerase
β. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1336:509–521. 1997.
|
|
25
|
Mizushina Y, Motoshima H, Yamaguchi Y,
Takeuchi T, Hirano K, Sugawara F and Yoshida H: 3-O-methylfunicone,
a selective inhibitor of mammalian Y-family DNA polymerases from an
Australian sea salt fungal strain. Mar Drugs. 7:624–639. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sakaguchi K, Sugawara F and Mizushina Y:
Inhibitors of eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Seikagaku. 74:244–251.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mizushina Y: Specific inhibitors of
mammalian DNA polymerase species. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
73:1239–1251. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mizushina Y: Screening of novel bioactive
compounds from food components and nutrients. J Jpn Soc Nutr Food
Sci. 64:377–384. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Mizushina Y, Yonezawa Y and Yoshida Y:
Selective inhibition of animal DNA polymerases by fat-soluble
vitamins A, D, E and K, and their related compounds. Curr Enzyme
Inhibition. 3:61–75. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sasaki R, Suzuki Y, Yonezawa Y, Ota Y,
Okamoto Y, Demizu Y, Huang P, Yoshida H, Sugimura K and Mizushina
Y: DNA polymerase γ inhibition by vitamin K3 induces
mitochondria-mediated cytotoxicity in human cancer cells. Cancer
Sci. 99:1040–1048. 2008.
|
|
31
|
Matsubara K, Kayashima T, Mori M, Yoshida
H and Mizushina Y: Inhibitory effects of vitamin K3 on
DNA polymerase and angiogenesis. Int J Mol Med. 22:381–387.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tanaka S, Nishiumi S, Nishida M, Mizushina
Y, Kobayashi K, Masuda A, Fujita T, Morita Y, Mizuno S, Kutsumi H,
Azuma T and Yoshida M: Vitamin K3 attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through inhibition of
nuclear factor-κB activation. Clin Exp Immunol. 160:283–292.
2010.
|
|
33
|
Chinzei R, Masuda A, Nishiumi S, Nishida
M, Onoyama M, Sanki T, Fujita T, Moritoh S, Itoh T, Kutsumi H,
Mizuno S, Azuma T and Yoshida M: Vitamin K3 attenuates
cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis through inhibition of the
autophagic pathway. Pancreas. 40:84–94. 2011.
|
|
34
|
Mizushina Y, Maeda J, Irino Y, Nishida M,
Nishiumi S, Kondo Y, Nishio K, Kuramochi K, Tsubaki K, Kuriyama I,
Azuma T, Yoshida H and Yoshida M: Effects of intermediates between
vitamins K(2) and K(3) on mammalian DNA polymerase inhibition and
anti-inflammatory activity. Int J Mol Sci. 12:1115–1132. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kobayashi K, Nishiumi S, Nishida M, Hirai
M, Azuma T, Yoshida H, Mizushina Y and Yoshida M: Effects of
quinone derivatives, such as 1,4-naphthoquinone, on DNA polymerase
inhibition and anti-inflammatory action. Med Chem. 7:37–44. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Aoganghua A, Nishiumi S, Kobayashi K,
Nishida M, Kuramochi K, Tsubaki K, Hirai M, Tanaka S, Azuma T,
Yoshida H, Mizushina Y and Yoshida M: Inhibitory effects of vitamin
K3 derivatives on DNA polymerase and inflammatory
activity. Int J Mol Med. 28:937–945. 2011.
|
|
37
|
Huang TT and Wuerzberger-Davis SM:
Sequential modification of NEMO/IKKÁ by SUMO-1 and ubiquitin
mediates NF-κB activation by genotoxic stress. Cell. 115:565–576.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hayden M and Ghosh S: Signaling to NF-κB.
Genes Dev. 18:2195–2224. 2004.
|
|
39
|
Bonizzi G and Karin M: The two NF-κB
activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity.
Trends Immunol. 25:280–288. 2004.
|
|
40
|
Wajant H, Pfizenmaier K and Scheurich P:
Tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell Death Differ. 10:45–65. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Elson CO, Sartor RB, Tennyson GS and
Riddell RH: Experimental models of inflammatory bowel disease.
Gastroenterology. 109:1344–1367. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Aggarwal BB: Signalling pathways of the
TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:745–756.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rahman I, Biswas SK and Kirkham PA:
Regulation of inflammation and redox signaling by dietary
polyphenols. Biochem Pharmacol. 72:1439–1452. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Corda S, Laplace C, Vicaut E and Duranteau
J: Rapid reactive oxygen species production by mitochondria in
endothelial cells exposed to tumor necrosis factor-α is mediated by
ceramide. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 24:762–768. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS and
Sedergran DJ: Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium
experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest. 69:238–249.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bhattacharyya S, Dudeja PK and Tobacman
JK: ROS, Hsp27, and IKKβ mediate dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)
activation of IκBα, NFκB, and IL-8. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 15:673–683.
2009.
|
|
47
|
Mizushina Y, Hirota M, Murakami C, Ishidoh
T, Kamisuki S, Shimazaki N, Takemura M, Perpelescu M, Suzuki M,
Yoshida H, Sugawara F, Koiwai O and Sakaguchi K: Some anti-chronic
inflammatory compounds are DNA polymerase λ-specific inhibitors.
Biochem Pharmacol. 66:1935–1944. 2003.
|
|
48
|
Mizushina Y, Takeuchi T, Kuramochi K,
Kobayashi S, Sugawara F, Sakaguchi K and Yoshida H: Study on the
molecular structure and bio-activity (DNA polymerase inhibitory
activity, anti-inflammatory activity and anti-oxidant activity)
relationship of curcumin derivatives. Curr Bioactive Compounds.
3:171–177. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Garcia-Diaz M, Bebenek K, Sabariegos R,
Dominguez O, Rodriguez J, Kirchhoff T, Garcia-Palomero E, Picher
AJ, Juarez R, Ruiz JF, Kunkel TA and Blanco L: DNA polymerase λ, a
novel DNA repair enzyme in human cells. J Biol Chem.
277:13184–13191. 2002.
|
|
50
|
Singhal RK and Wilson SH: Short
gap-filling synthesis by DNA polymerase β is processive. J Biol
Chem. 268:15906–15911. 1993.
|
|
51
|
Matsumoto Y and Kim K: Excision of
deoxyribose phosphate residues by DNA polymerase β during DNA
repair. Science. 269:699–702. 1995.
|
|
52
|
Sobol RW, Horton JK, Kuhn R, Gu H, Singhal
RK, Prasad R, Rajewsky K and Wilson SH: Requirement of mammalian
DNA polymerase-β in base-excision repair. Nature. 379:183–186.
1996.
|
|
53
|
Ramadan K, Shevelev IV, Maga G and
Hubscher U: DNA polymerase λ from calf thymus preferentially
replicates damaged DNA. J Biol Chem. 277:18454–18458. 2002.
|
|
54
|
Sugo N, Aratani Y, Nagashima Y, Kubota Y
and Koyama H: Neonatal lethality with abnormal neurogenesis in mice
deficient in DNA polymerase β. EMBO J. 19:1397–1404.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Garcia-Diaz M, Bebenek K, Kunkel TA and
Blanco L: Identification of an intrinsic 5′-deoxyribose-5-phosphate
lyase activity in human DNA polymerase λ: a possible role in base
excision repair. J Biol Chem. 276:34659–34663. 2001.
|
|
56
|
Hirose F, Hotta Y, Yamaguchi M and
Matsukage A: Difference in the expression level of DNA polymerase β
among mouse tissues: high expression in the pachytene spermatocyte.
Exp Cell Res. 181:169–180. 1989.
|
|
57
|
Garcia-Diaz M, Dominguez O,
Lopez-Fernandez LA, De Lera LT, Saniger ML, Ruiz JF, Parraga M,
Garcia-Ortiz MJ, Kirchhoff T, Del Mazo J, Bernad A and Blanco L:
DNA polymerase λ, a novel DNA repair enzyme in human cells. J Mol
Biol. 301:851–867. 2000.
|
|
58
|
Bertocci B, De Smet A, Flatter E, Dahan A,
Bories JC, Landreau C, Weill JC and Reynaud CA: Cutting edge: DNA
polymerases μ and λ are dispensable for Ig gene hypermutation. J
Immunol. 168:3702–3706. 2002.
|