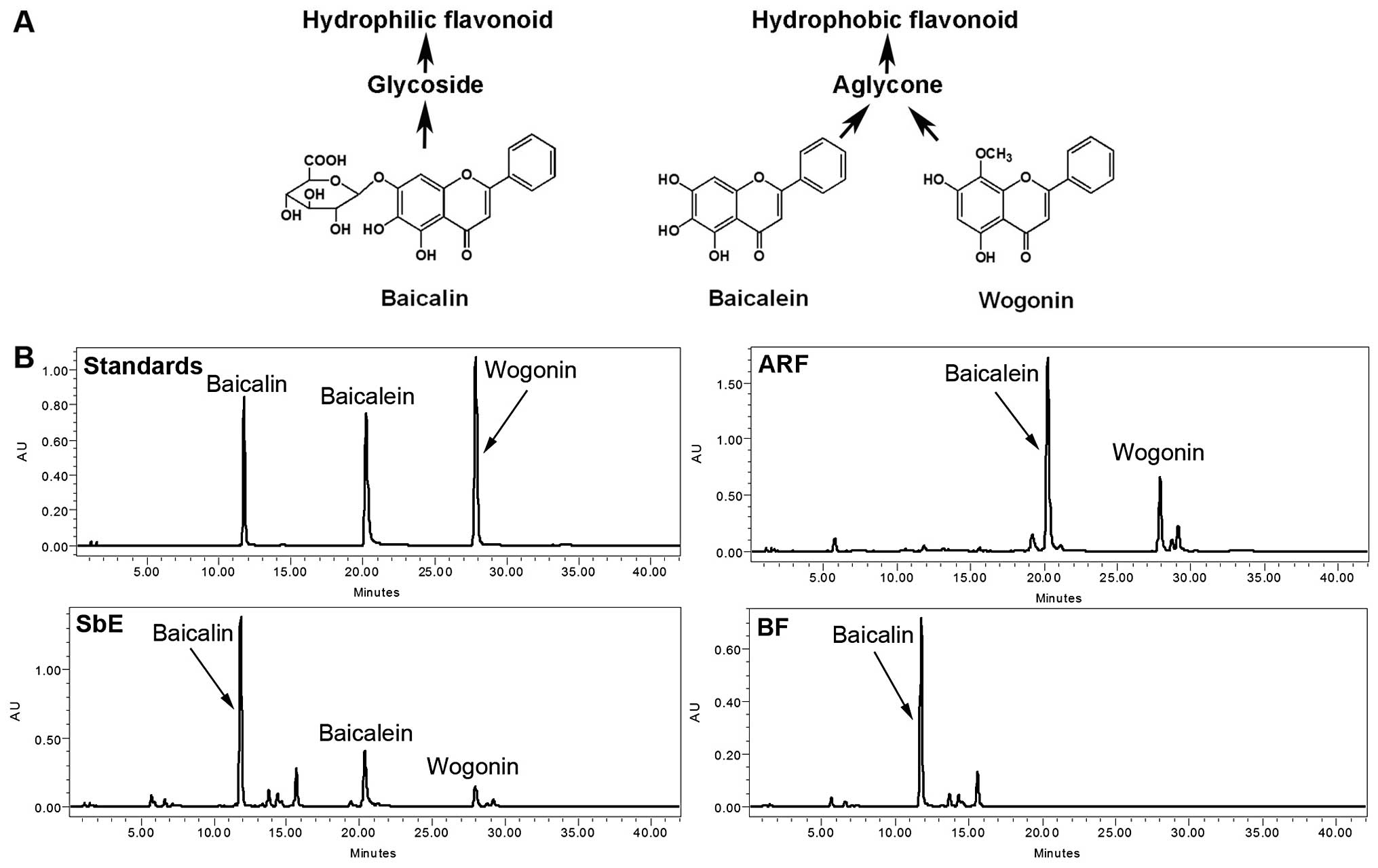
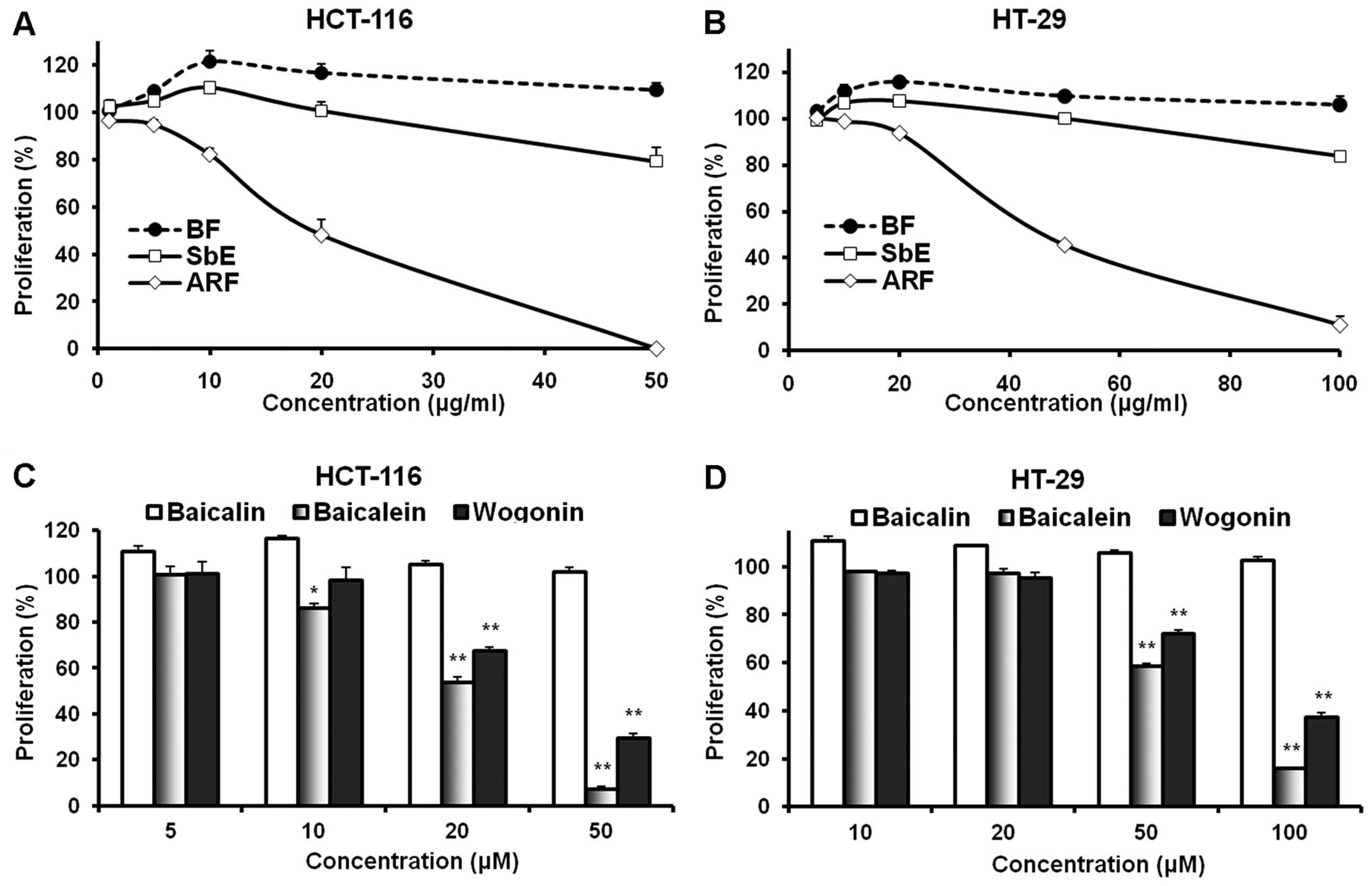
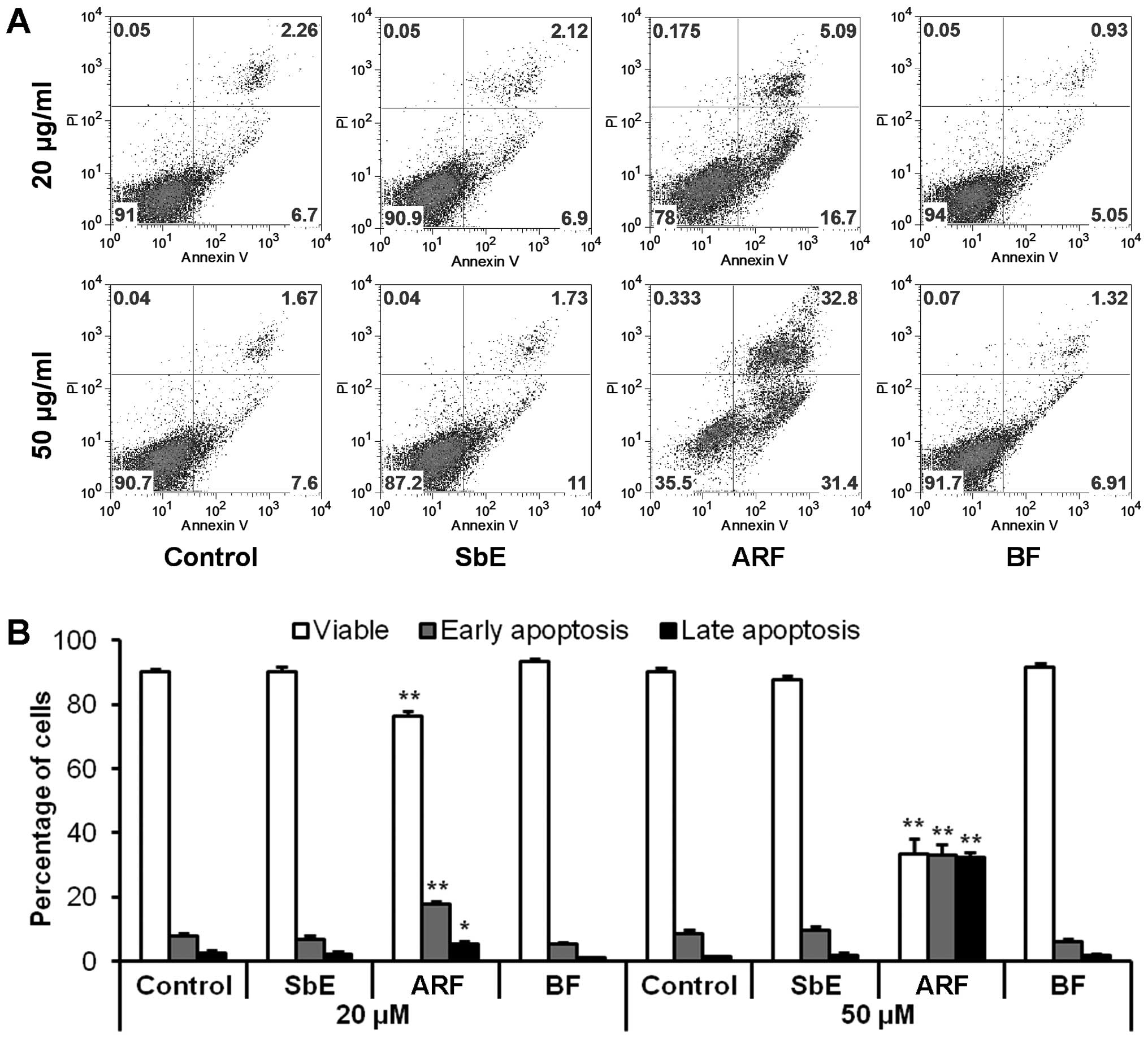
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Newman DJ and Cragg GM: Natural products
as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod.
70:461–477. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cassileth B, Yeung KS and Gubili J: Herbs
and other botanicals in cancer patient care. Curr Treat Options
Oncol. 9:109–116. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sengupta S, Toh SA, Sellers LA, et al:
Modulating angiogenesis: the yin and the yang in ginseng.
Circulation. 110:1219–1225. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Matthias A, Banbury L, Bone KM, et al:
Echinacea alkylamides modulate induced immune responses in
T-cells. Fitoterapia. 79:53–58. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Boyle SP, Doolan PJ, Andrews CE, et al:
Evaluation of quality control strategies in Scutellaria
herbal medicines. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 54:951–957. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang CZ, Mehendale SR, Calway T, et al:
Botanical flavonoids on coronary heart disease. Am J Chin Med.
39:661–671. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhen Z, Chang B, Li M, et al:
Anti-diabetic effects of a Coptis chinensis containing new
traditional Chinese medicine formula in type 2 diabetic rats. Am J
Chin Med. 39:53–63. 2011.
|
|
9
|
Park HJ, Lee YW, Park HH, et al: Induction
of quinone reductase by a methanol extract of Scutellaria
baicalensis and its flavonoids in murine Hepa 1c1c7 cells. Eur
J Cancer Prev. 7:465–471. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bonham M, Posakony J, Coleman I, et al:
Characterization of chemical constituents in Scutellaria
baicalensis with antiandrogenic and growth-inhibitory
activities toward prostate carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
11:3905–3914. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ye F, Xui L, Yi J, et al: Anticancer
activity of Scutellaria baicalensis and its potential
mechanism. J Altern Complement Med. 8:567–572. 2002.
|
|
12
|
Goh D, Lee YH and Ong ES: Inhibitory
effects of a chemically standardized extract from Scutellaria
barbata in human colon cancer cell lines, LoVo. J Agric Food
Chem. 53:8197–8204. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kuntz S, Wenzel U and Daniel H:
Comparative analysis of the effects of flavonoids on proliferation,
cytotoxicity, and apoptosis in human colon cancer cell lines. Eur J
Nutr. 38:133–142. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Po LS, Chen ZY, Tsang DS, et al: Baicalein
and genistein display differential actions on estrogen receptor
(ER) transactivation and apoptosis in MCF-7 cells. Cancer Lett.
187:33–40. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yam CH, Fung TK and Poon RY: Cyclin A in
cell cycle control and cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 59:1317–1326.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Egloff AM, Vella LA and Finn OJ: Cyclin B1
and other cyclins as tumor antigens in immunosurveillance and
immunotherapy of cancer. Cancer Res. 66:6–9. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kobayashi S, Kajino S, Takahashi N, et al:
53BP2 induces apoptosis through the mitochondrial death pathway.
Genes Cells. 10:253–260. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Takahashi N, Kobayashi S, Kajino S, et al:
Inhibition of the 53BP2S-mediated apoptosis by nuclear factor
kappaB and Bcl-2 family proteins. Genes Cells. 10:803–811. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fiorucci G, Vannucchi S, Chiantore MV, et
al: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) as a
pro-apoptotic signal transducer with cancer therapeutic potential.
Curr Pharm Des. 11:933–944. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cretney E, Shanker A, Yagita H, et al:
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand as a therapeutic agent in
autoimmunity and cancer. Immunol Cell Biol. 84:87–98. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Majors BS, Betenbaugh MJ and Chiang GG:
Links between metabolism and apoptosis in mammalian cells:
applications for anti-apoptosis engineering. Metab Eng. 9:317–326.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Willis SN and Adams JM: Life in the
balance: how BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 17:617–625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
DiGianni LM, Garber JE and Winer EP:
Complementary and alternative medicine use among women with breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 20:S34–S38. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tian JH, Liu LS, Shi ZM, et al: A
randomized controlled pilot trial of ‘Feiji Recipe’ on quality of
life of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Am J Chin Med.
38:15–25. 2010.
|
|
25
|
Randhawa MA and Alghamdi MS: Anticancer
activity of Nigella sativa (black seed) - a review. Am J
Chin Med. 39:1075–1091. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Richardson MA and Straus SE: Complementary
and alternative medicine: opportunities and challenges for cancer
management and research. Semin Oncol. 29:531–545. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Olaku O and White JD: Herbal therapy use
by cancer patients: a literature review on case reports. Eur J
Cancer. 47:508–514. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Da Rocha AB, Lopes RM and Schwartsmann G:
Natural products in anticancer therapy. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
1:364–369. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mann J: Natural products in cancer
chemotherapy: past, present and future. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:143–148.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee KH: Novel antitumor agents from higher
plants. Med Res Rev. 19:569–596. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ye F, Jiang S, Volshonok H, et al:
Molecular mechanism of anti-prostate cancer activity of
Scutellaria baicalensis extract. Nutr Cancer. 57:100–110.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen S, Ruan Q, Bedner E, et al: Effects
of the flavonoid baicalin and its metabolite baicalein on androgen
receptor expression, cell cycle progression and apoptosis of
prostate cancer cell lines. Cell Prolif. 34:293–304. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chang WH, Chen CH and Lu FJ: Different
effects of baicalein, baicalin and wogonin on mitochondrial
function, glutathione content and cell cycle progression in human
hepatoma cell lines. Planta Med. 68:128–132. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hong T, Jin GB, Cho S, et al: Evaluation
of the anti-inflammatory effect of baicalein on dextran sulfate
sodium-induced colitis in mice. Planta Med. 68:268–271. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Christopher R, Dhiman A, Fox J, et al:
Data-driven computer simulation of human cancer cell. Ann NY Acad
Sci. 1020:132–153. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tomida A, Yun J and Tsuruo T:
Glucose-regulated stresses induce resistance to camptothecin in
human cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 68:391–396. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Akhdar H, Loyer P, Rauch C, et al:
Involvement of Nrf2 activation in resistance to 5-fluorouracil in
human colon cancer HT-29 cells. Eur J Cancer. 45:2219–2227. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Qi LW, Wang CZ and Yuan CS: American
ginseng: potential structure-function relationship in cancer
chemoprevention. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:947–954. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|