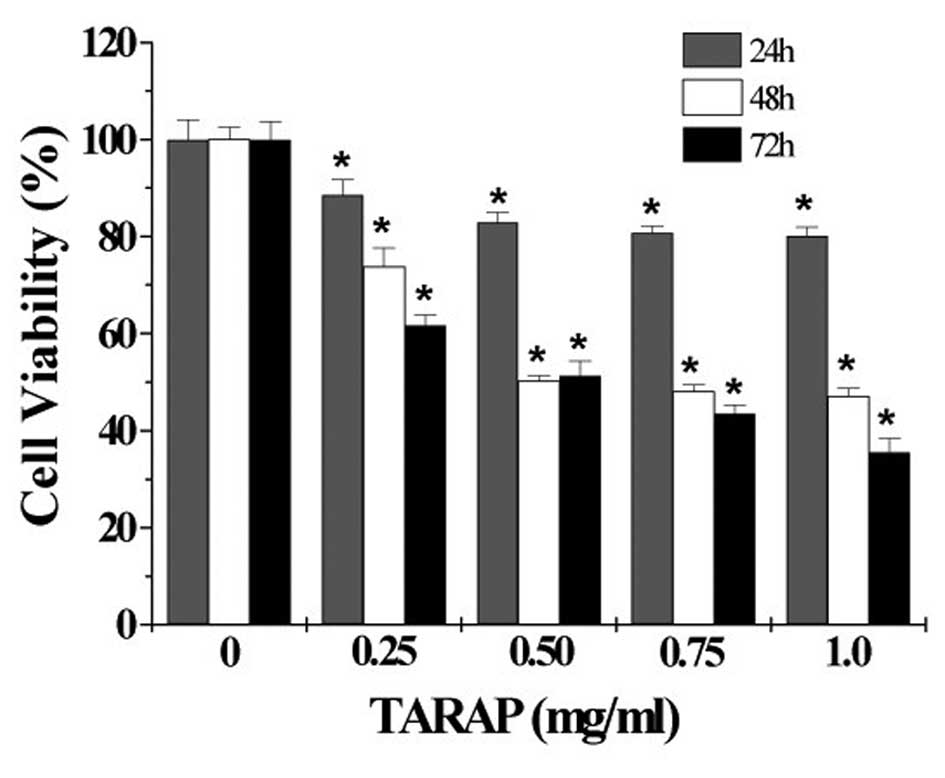
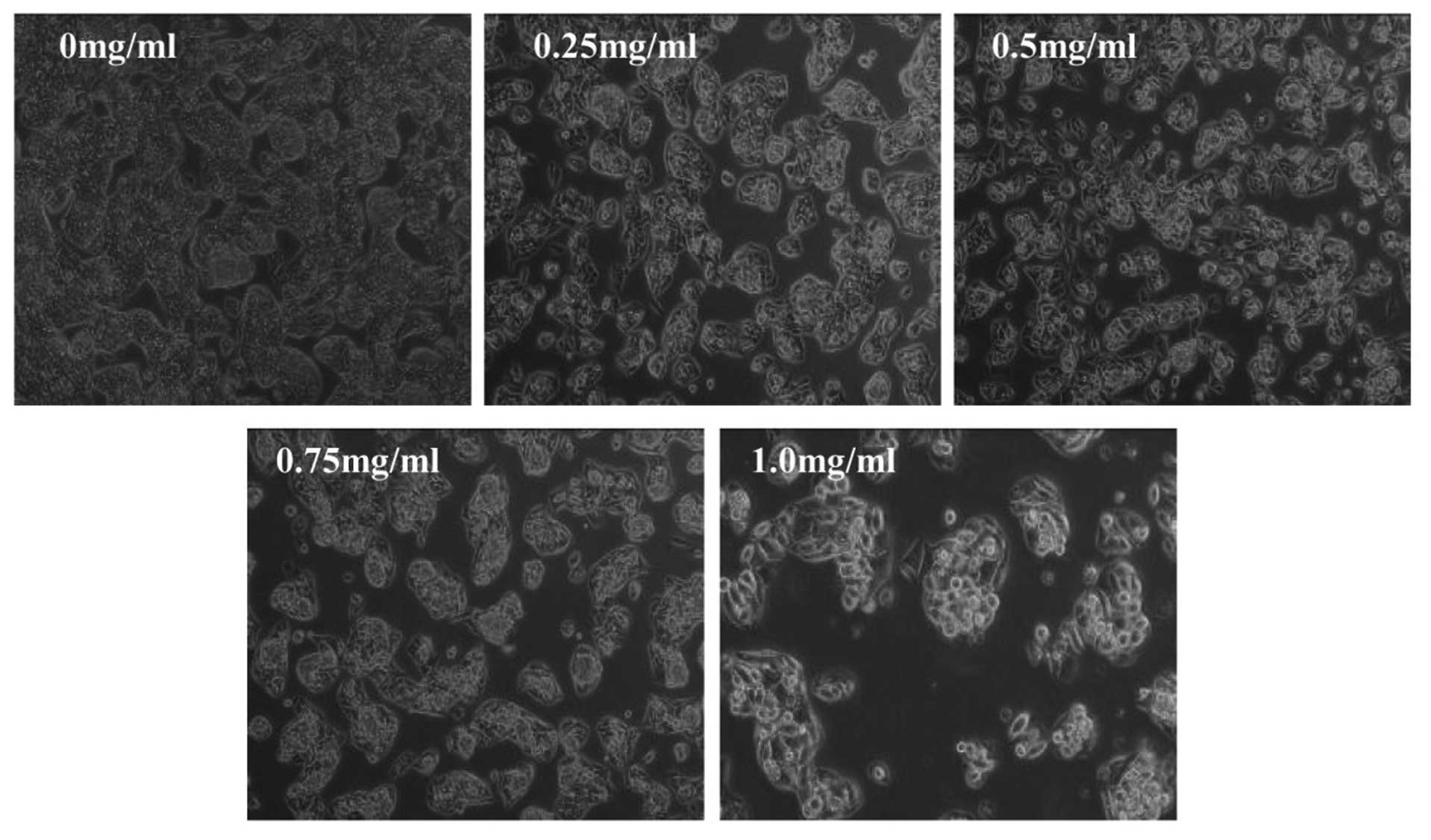
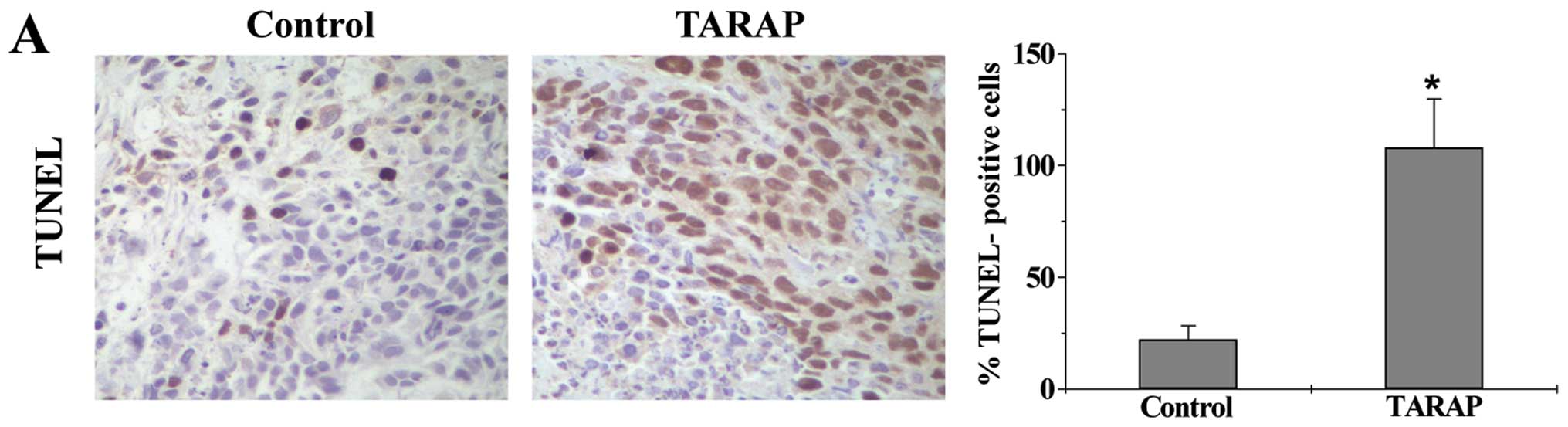
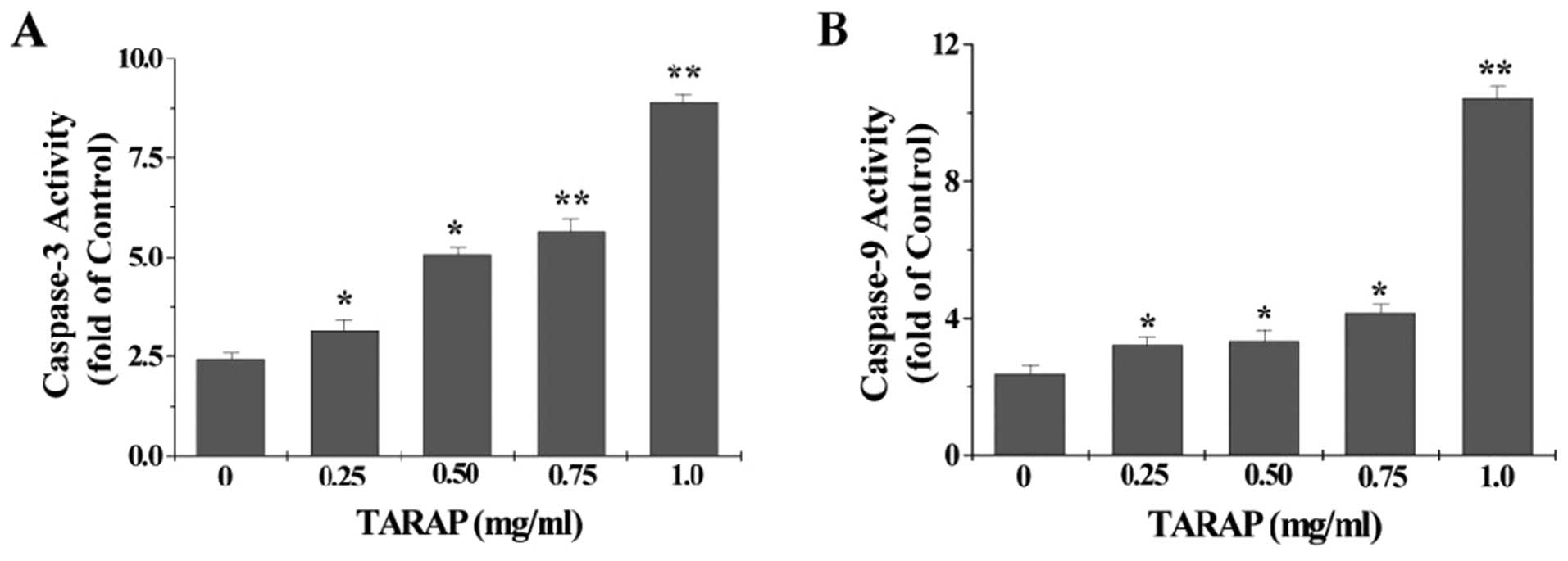
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer.
94:153–156. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Levin B and Amos C: Therapy of
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 332:1294–1296.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
El-Serag HB, Marrero JA, Rudolph L and
Reddy KR: Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Gastroenterol. 134:1752–1763. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thomas M: Molecular targeted therapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 44:136–141. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Newman DJ, Cragg GM and Snader KM: The
influence of natural products upon drug discovery. Nat Prod Rep.
17:215–234. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gordaliza M: Natural products as leads to
anticancer drugs. Clin Transl Oncol. 9:767–776. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang W and Eisenbrand G: Chinese Drugs of
Plant Origin: Chemistry, Pharmacology and Use in Traditional and
Modern Medicine. Springer-Verlag; Berlin: 1992, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Huang KC: The Pharmacology of Chinese
Herbs. 2nd edition. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL: 1999
|
|
9
|
Hong ZF: Hepatoprotective effects of
Rubus aleaefolius Poir and identification of its active
constituents. J Hepatol. 129:267–272. 2010.
|
|
10
|
Xue H, Aziz RM and Sun N: Inhibition of
cellular transformation by berry extracts. Carcinogenesis.
22:351–356. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee JH: Activity of crude extract of
Rubus crataegifolius roots as a potent apoptosis inducer and
DNA to topoisomerase 1 inhibitor. Arch Pharm Res. 23:338–343.
2000.
|
|
12
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 apoptotic
switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene. 26:1324–1337.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Borner C: Bcl-2 family members integrators
of survival and death. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1644:71–72. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cory S and Adams JM: The Bcl-2 family:
regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:647–656. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hsu YT, Wolter K and Youle RJ: Cytosol to
membrane redistribution of members of the Bcl-2 family during
apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:3668–3672. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wolter KG: Movement of Bax from the
cytosol to mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 139:1281–1292. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado
AM, Cai J, Peng TI, Jones DP and Wang X: Prevention of apoptosis by
Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science.
275:1129–1132. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Antonsson B, Montessuit S, Lauper S, Eskes
R and Martinou JC: Bax oligomerization is required for
channel-forming activity in liposomes and to trigger cytochrome c
release from mitochondria. Biochem J. 345:271–278. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jürgensmeier JM, Xie Z, Deveraux Q,
Ellerby L, Bredesen D and Reed JC: Bax directly induces release of
cytochrome c from isolated mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:4997–5002. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR and
Newmeyer DD: The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a
primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science.
275:1132–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thomenius MJ, Wang NS, Reineks EZ, Wang Z
and Distelhorst CW: Bcl-2 on the endoplasmic reticulum regulates
Bax activity by binding to BH3-only proteins. J Biol Chem.
278:6243–6250. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Antonsson B, Conti F and Ciavatta A:
Inhibition of Bax channel-forming activity by Bcl-2. Science.
277:370–372. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yip KW and Reed JC: Bcl-2 family proteins
and cancer. Oncogene. 27:6398–6406. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin JM, Zhao JY, Li TJ, Zhou JH, Hu J and
Hong ZF: Hepatoprotection in a rat model of acute liver damage
through inhibition of CY2E1 activity by total alkaloids extracted
from Rubus alceifolius Poir. Int J Toxicol. 30:237–243.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Singh RP, Dhanalakshmi S, Tyagi AK, Chan
DCF, Agarwal C and Agarwal R: Dietary feeding of silibinin inhibits
advance human prostate carcinoma growth in athymic nude mice, and
increases plasma insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3
levels. Cancer Res. 62:3063–3069. 2002.
|
|
28
|
Resendes AR, Majó N, Segalés J, Espadamala
J, Mateu E, Chianini F, Nofrarías M and Domingo M: Apoptosis in
normal lymphoid organs from healthy normal, conventional pigs at
different ages detected by TUNEL and cleaved caspase-3
immunohistochemistry in paraffin-embedded tissues. Vet Immunol
Immunopathol. 99:203–213. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yang JX, Wang YL, Bao Y and Guo J: The
total flavones from Semen cuscutae reverse the reduction of
testosterone level and the expression of androgen receptor gene in
kidney-yang deficient mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 119:166–171.
2008.
|
|
30
|
Boose G and Stopper H: Genotoxicity of
several clinically used topoisomerase II inhibitors. Toxicol Lett.
116:7–16. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Borner C: The Bcl-2 protein family:
sensors and checkpoints for life-or-death decisions. Mol Immunol.
39:615–647. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ow YP, Green DR, Hao Z and Mak TW:
Cytochrome c: functions beyond respiration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
9:532–542. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|