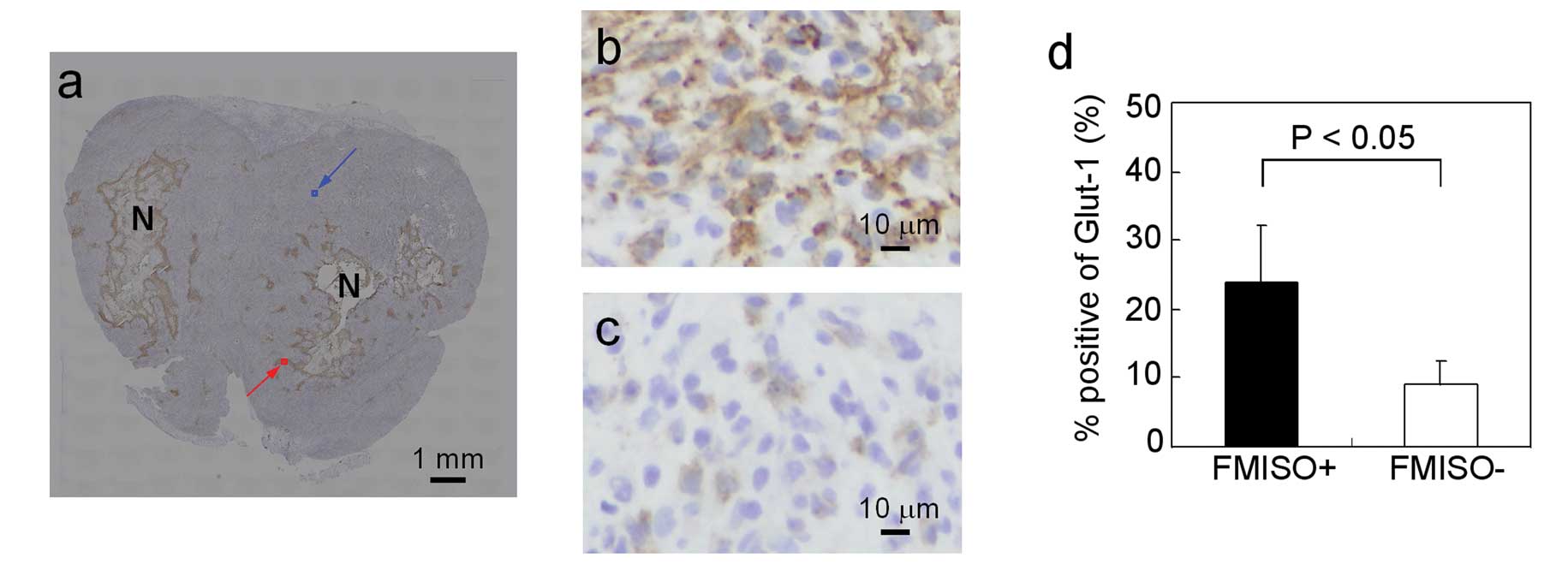
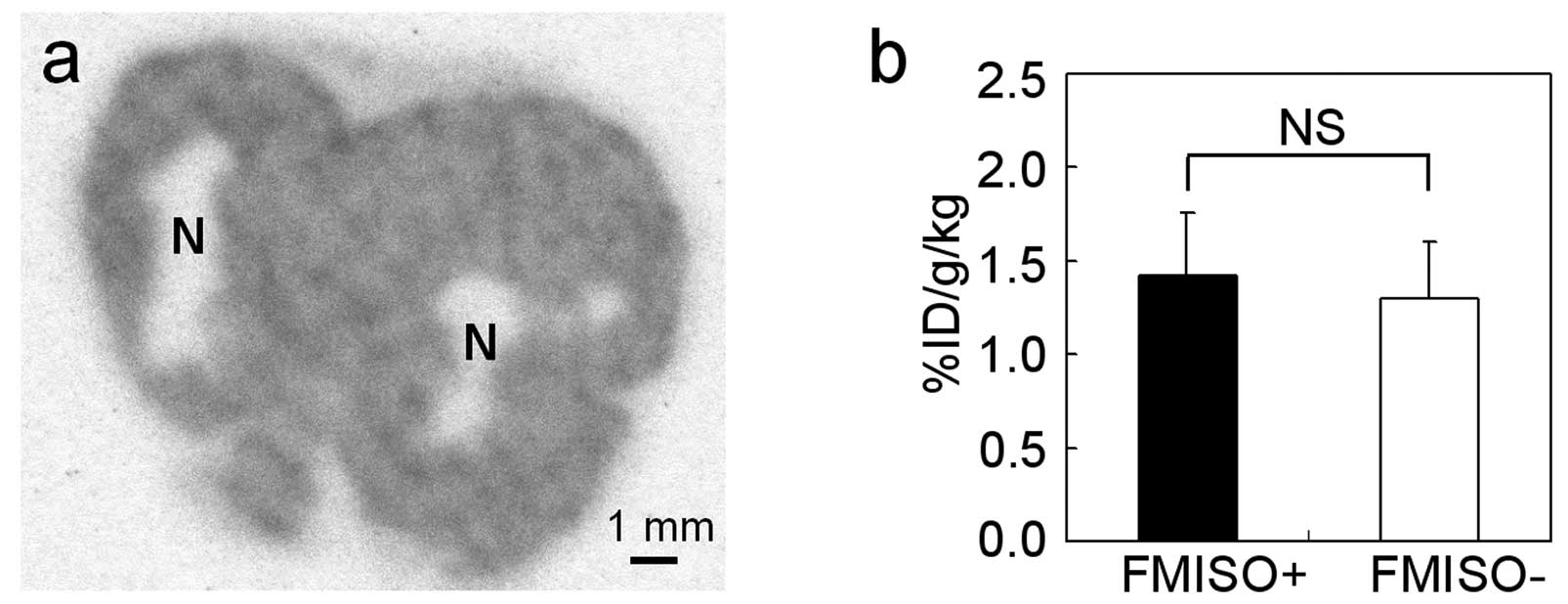
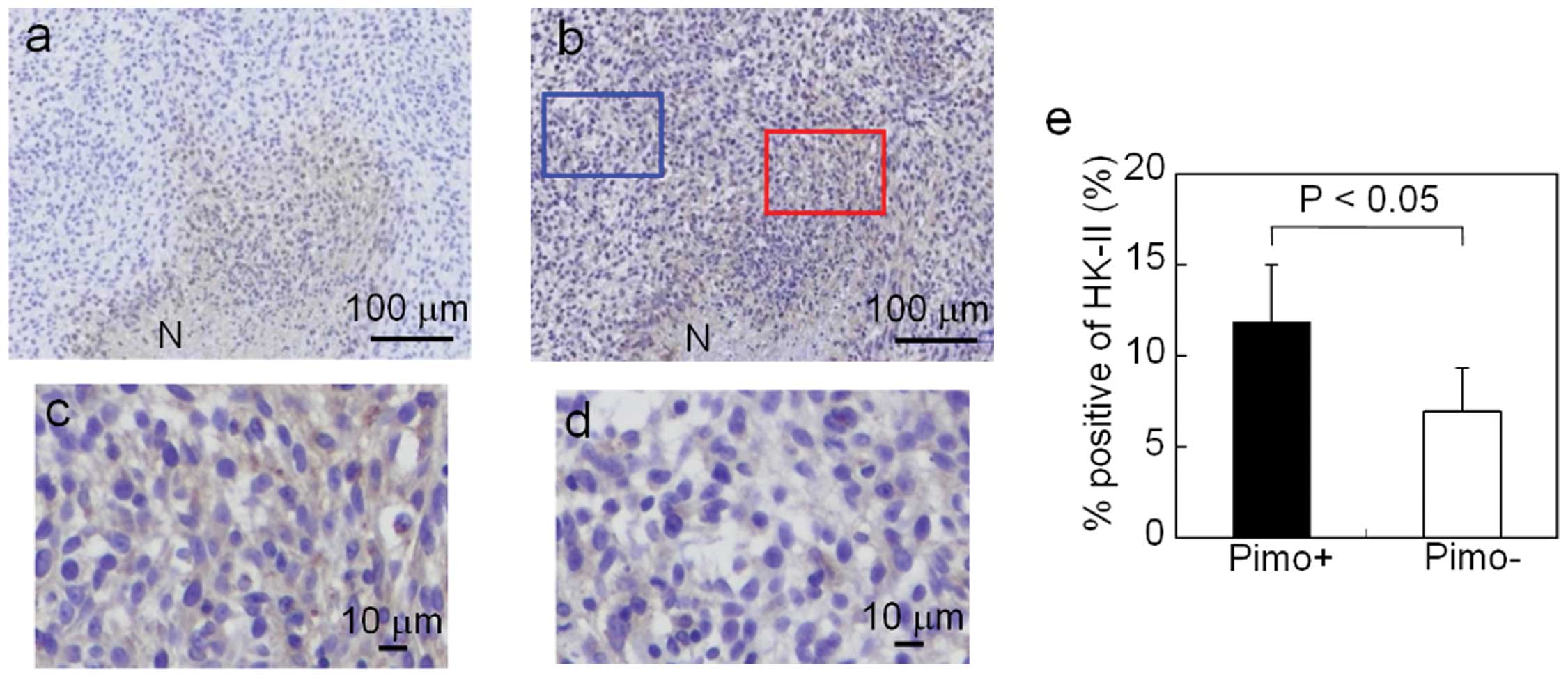
|
1
|
Brown JM and Giaccia AJ: The unique
physiology of solid tumors: opportunities (and problems) for cancer
therapy. Cancer Res. 58:1408–1416. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gray LH, Conger AD, Ebert M, Hornsey S and
Scott OC: The concentration of oxygen dissolved in tissues at the
time of irradiation as a factor in radiotherapy. Br J Radiol.
26:638–648. 1953. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Höckel M and Vaupel P: Tumor hypoxia:
definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 93:266–276. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Evans SM, Jenkins KW, Chen HI, Jenkins WT,
Judy KD, Hwang WT, Lustig RA, Judkins AR, Grady MS, Hahn SM and
Koch CJ: The relationship among hypoxia, proliferation, and outcome
in patients with de novo glioblastoma: A pilot study. Transl Oncol.
3:160–169. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Evans SM, Hahn SM, Magarelli DP and Koch
CJ: Hypoxic heterogeneity in human tumors: EF5 binding,
vasculature, necrosis, and proliferation. Am J Clin Oncol.
24:467–472. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Troost EG, Laverman P, Philippens ME, et
al: Correlation of [18F]FMISO autoradiography and
pimonidazole immunohistochemistry in human head and neck carcinoma
xenografts. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 35:1803–1811. 2008.
|
|
7
|
Troost EG, Laverman P, Kaanders JH,
Philippens M, Lok J, Oyen WJ, van der Kogel AJ, Boerman OC and
Bussink J: Imaging hypoxia after oxygenation-modification:
comparing [18F]FMISO autoradiography with pimonidazole
immunohistochemistry in human xenograft tumors. Radiother Oncol.
80:157–164. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Spence AM, Muzi M, Swanson KR, O’Sullivan
F, Rockhill JK, Rajendran JG, Adamsen TC, Link JM, Swanson PE,
Yagle KJ, Rostomily RC, Silbergeld DL and Krohn KA: Regional
hypoxia in glioblastoma multiforme quantified with
[18F]fluoromisonidazole positron emission tomography
before radiotherapy: correlation with time to progression and
survival. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2623–2630. 2008.
|
|
9
|
Eschmann SM, Paulsen F, Reimold M,
Dittmann H, Welz S, Reischl G, Machulla HJ and Bares R: Prognostic
impact of hypoxia imaging with 18F-misonidazole PET in
non-small cell lung cancer and head and neck cancer before
radiotherapy. J Nucl Med. 46:253–260. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rajendran JG, Schwartz DL, O’Sullivan J,
Peterson LM, Ng P, Scharnhorst J, Grierson JR and Krohn KA: Tumor
hypoxia imaging with [F-18] fluoromisonidazole positron emission
tomography in head and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:5435–5441.
2006.
|
|
11
|
Overgaard J: Clinical evaluation of
nitroimidazoles as modifiers of hypoxia in solid tumors. Oncol Res.
6:509–518. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Overgaard J and Horsman MR: Modification
of hypoxia-induced radioresistance in tumors by the use of oxygen
and sensitizers. Semin Radiat Oncol. 6:10–21. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moeller BJ and Dewhirst MW: HIF-1 and
tumour radiosensitivity. Br J Cancer. 95:1–5. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Moeller BJ, Dreher MR, Rabbani ZN,
Schroeder T, Cao Y, Li CY and Dewhirst MW: Pleiotropic effects of
HIF-1 blockade on tumor radiosensitivity. Cancer Cell. 8:99–110.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dang CV and Semenza GL: Oncogenic
alterations of metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci. 24:68–72. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kamlah F, Eul BG, Li S, Lang N, Marsh LM,
Seeger W, Grimminger F, Rose F and Hänze J: Intravenous injection
of siRNA directed against hypoxia-inducible factors prolongs
survival in a Lewis lung carcinoma cancer model. Cancer Gene Ther.
16:195–205. 2009.
|
|
17
|
Le QT and Courter D: Clinical biomarkers
for hypoxia targeting. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27:351–362. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Reske SN, Grillenberger KG, Glatting G,
Port M, Hildebrandt M, Gansauge F and Beger HG: Overexpression of
glucose transporter 1 and increased FDG uptake in pancreatic
carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 38:1344–1348. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Aloj L, Caracó C, Jagoda E, Eckelman WC
and Neumann RD: Glut-1 and hexokinase expression: relationship with
2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake in A431 and T47D cells in
culture. Cancer Res. 59:4709–4714. 1999.
|
|
20
|
Semenza GL: Targeting HIF-1 for cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:721–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhao S, Kuge Y, Yi M, Zhao Y, Hatano T,
Magota K, Nishijima K, Kohanawa M and Tamaki N: Dynamic
11C-methionine PET analysis has an additional value for
differentiating tumors from granulomas: An experimental study using
small animal PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 38:1876–1886. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang G, Wang M, Tang X, Gan M and Luo L:
Fully automated one-pot synthesis of
[18F]fluoromisonidazole. Nucl Med Biol. 32:553–558.
2005.
|
|
23
|
Oh SJ, Chi DY, Mosdzianowski C, Kim JY,
Gil HS, Kang SH, Ryu JS and Moon DH: Fully automated synthesis of
[18F]fluoromisonidazole using a conventional
[18F]FDG module. Nucl Med Biol. 32:899–905. 2005.
|
|
24
|
Brown RS, Leung JY, Fisher SJ, Frey KA,
Ethier SP and Wahl RL: Intratumoral distribution of tritiated
fluorodeoxyglucose in breast carcinoma: I. Are inflammatory cells
important? J Nucl Med. 36:1854–1861. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Toyama H, Ichise M, Liow JS, Modell KJ,
Vines DC, Esaki T, Cook M, Seidel J, Sokoloff L, Green MV and Innis
RB: Absolute quantification of regional cerebral glucose
utilization in mice by 18F-FDG small animal PET scanning
and 2-14C-DG autoradiography. J Nucl Med. 45:1398–1405.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hatanaka Y, Imaoka Y, Torisu K, Kamihara
Y, Hashizume K, Ichimura K, Yoshino T and Tani Y: A simplified,
sensitive immunohistochemical detection system employing signal
amplification based on fluorescyl-tyramide/antifluorescein antibody
reaction: its application to pathologic testing and research. Appl
Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 16:87–93. 2008.
|
|
27
|
Sorger D, Patt M, Kumar P, Wiebe LI,
Barthel H, Seese A, Dannenberg C, Tannapfel A, Kluge R and Sabri O:
[18F] Fluoroazomycinarabinofuranoside
(18FAZA) and [18F]Fluoromisonidazole
(18FMISO): a comparative study of their selective uptake
in hypoxic cells and PET imaging in experimental rat tumors. Nucl
Med Biol. 30:317–326. 2003.
|
|
28
|
Buatti J, Ryken TC, Smith MC, Sneed P, Suh
JH, Mehta M and Olson JJ: Radiation therapy of pathologically
confirmed newly diagnosed glioblastoma in adults. J Neurooncol.
89:313–337. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kaanders JH, Wijffels KI, Marres HA,
Ljungkvist AS, Pop LA, van den Hoogen FJ, de Wilde PC, Bussink J,
Raleigh JA and van der Kogel AJ: Pimonidazole binding and tumor
vascularity predict for treatment outcome in head and neck cancer.
Cancer Res. 62:7066–7074. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Airley R, Loncaster J, Davidson S, Bromley
M, Roberts S, Patterson A, Hunter R, Stratford I and West C:
Glucose transporter glut-1 expression correlates with tumor hypoxia
and predicts metastasis-free survival in advanced carcinoma of the
cervix. Clin Cancer Res. 7:928–934. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Thorwarth D, Eschmann SM, Holzner F,
Paulsen F and Alber M: Combined uptake of [18F]FDG and
[18F]FMISO correlates with radiation therapy outcome in
head-and-neck cancer patients. Radiother Oncol. 80:151–156.
2006.
|
|
32
|
Wyss MT, Honer M, Schubiger PA and
Ametamey SM: NanoPET imaging of [18F]fluoromisonidazole
uptake in experimental mouse tumours. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
33:311–318. 2006.
|
|
33
|
Zimny M, Gagel B, DiMartino E, Hamacher K,
Coenen HH, Westhofen M, Eble M, Buell U and Reinartz P: FDG - a
marker of tumour hypoxia? A comparison with
[18F]fluoromisonidazole and pO2-polarography
in metastatic head and neck cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
33:1426–1431. 2006.
|
|
34
|
Gagel B, Piroth M, Pinkawa M, Reinartz P,
Zimny M, Kaiser HJ, Stanzel S, Asadpour B, Demirel C, Hamacher K,
Coenen HH, Scholbach T, Maneschi P, DiMartino E and Eble MJ:
pO2 polarography, contrast enhanced color duplex
sonography (CDS), [18F] fluoromisonidazole and
[18F] fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography:
validated methods for the evaluation of therapy-relevant tumor
oxygenation or only bricks in the puzzle of tumor hypoxia? BMC
Cancer. 7:1132007.
|
|
35
|
Rajendran JG, Mankoff DA, O’Sullivan F,
Peterson LM, Schwartz DL, Conrad EU, Spence AM, Muzi M, Farwell DG
and Krohn KA: Hypoxia and glucose metabolism in malignant tumors:
evaluation by [18F]fluoromisonidazole and
[18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography
imaging. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2245–2252. 2004.
|
|
36
|
Cherk MH, Foo SS, Poon AM, Knight SR,
Murone C, Papenfuss AT, Sachinidis JI, Saunder TH, O’Keefe GJ and
Scott AM: Lack of correlation of hypoxic cell fraction and
angiogenesis with glucose metabolic rate in non-small cell lung
cancer assessed by 18F-Fluoromisonidazole and
18F-FDG PET. J Nucl Med. 47:1921–1926. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Riesterer O, Honer M, Jochum W, Oehler C,
Ametamey S and Pruschy M: Ionizing radiation antagonizes tumor
hypoxia induced by antiangiogenic treatment. Clin Cancer Res.
12:3518–3524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wijffels KI, Marres HA, Peters JP, Rijken
PF, van der Kogel AJ and Kaanders JH: Tumour cell proliferation
under hypoxic conditions in human head and neck squamous cell
carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 44:335–344. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rajendran JG, Wilson DC, Conrad EU,
Peterson LM, Bruckner JD, Rasey JS, Chin LK, Hofstrand PD, Grierson
JR, Eary JF and Krohn KA: [18F]FMISO and
[18F]FDG PET imaging in soft tissue sarcomas:
correlation of hypoxia, metabolism and VEGF expression. Eur J Nucl
Med Mol Imaging. 30:695–704. 2003.
|
|
40
|
Kubota K, Tada M, Yamada S, Hori K, Saito
S, Iwata R, Sato K, Fukuda H and Ido T: Comparison of the
distribution of fluorine-18 fluoromisonidazole, deoxyglucose and
methionine in tumour tissue. Eur J Nucl Med. 26:750–757. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dewhirst MW: Intermittent hypoxia furthers
the rationale for hypoxia-inducible factor-1 targeting. Cancer Res.
67:854–855. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Søvik A, Malinen E and Olsen DR:
Strategies for biologic image-guided dose escalation: a review. Int
J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 73:650–658. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|