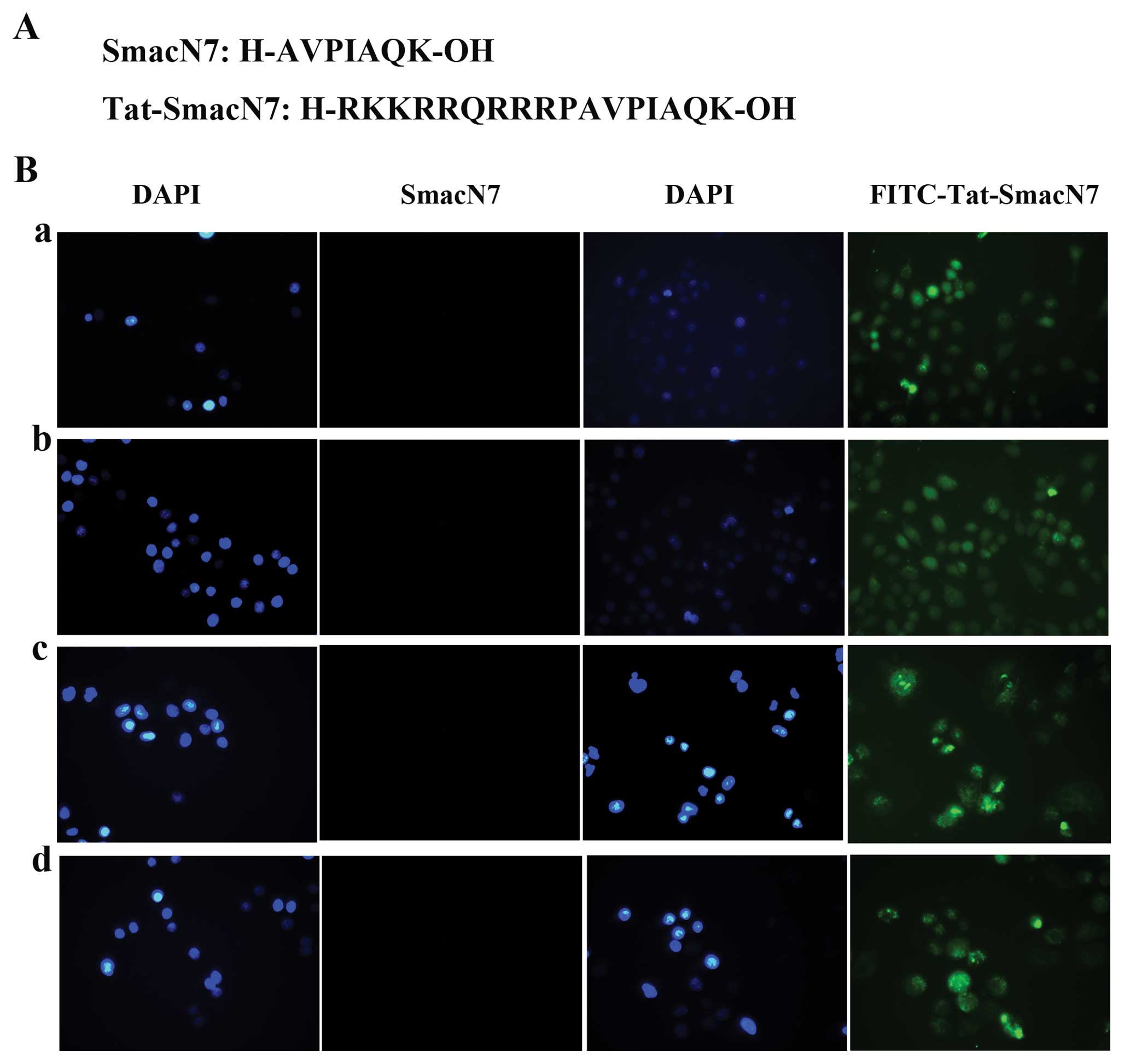
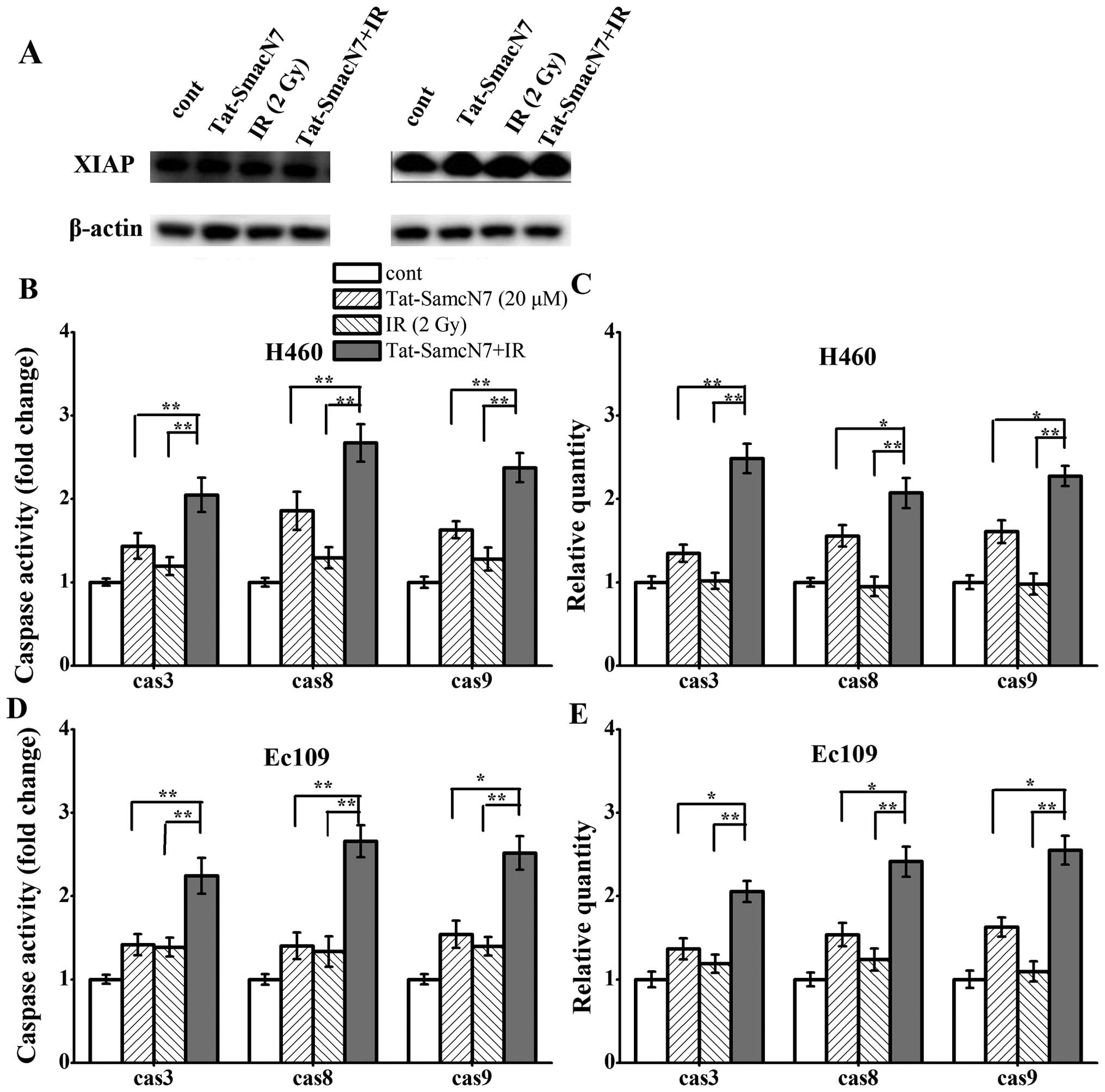
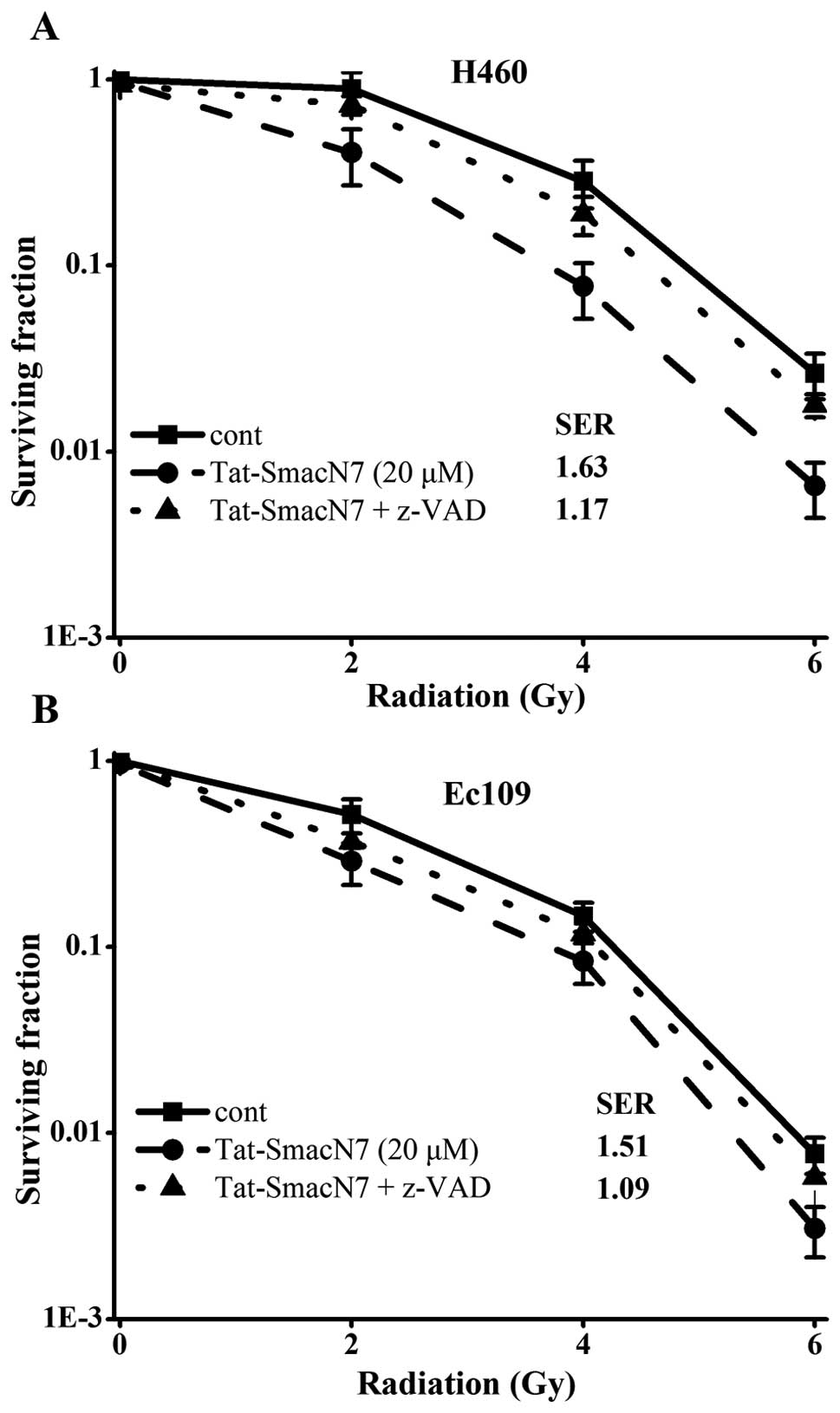
|
1
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hotchkiss RS, Strasser A, McDunn JE and
Swanson PE: Cell death. N Engl J Med. 361:1570–1583. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Death receptors:
signaling and modulation. Science. 281:1305–1308. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vaux DL and Korsmeyer SJ: Cell death in
development. Cell. 96:245–254. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Van Loo G, Saelens X, van Gurp M,
MacFarlane M, Martin SJ and Vandenabeele P: The role of
mitochondrial factors in apoptosis: a Russian roulette with more
than one bullet. Cell Death Differ. 9:1031–1042. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zou H, Li Y, Liu X and Wang X: An APAF-1.
cytochrome c multi meric complex is a functional apoptosome that
activates procaspase-9. J Biol Chem. 274:11549–11556. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kuida K, Haydar TF, Kuan CY, Gu Y, Taya C,
Karasuyama H, Su MS, Rakic P and Flavell RA: Reduced apoptosis and
cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation in mice lacking caspase 9.
Cell. 94:325–337. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gyrd-Hansen M and Meier P: IAPs: from
caspase inhibitors to modulators of NF-κB, inflammation and cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 10:561–574. 2010.
|
|
10
|
Altieri DC: Survivin and IAP proteins in
cell-death mechanisms. Biochem J. 430:199–205. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suzuki Y, Nakabayashi Y, Nakata K, Reed JC
and Takahashi R: X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP)
inhibits caspase-3 and -7 in distinct modes. J Biol Chem.
276:27058–27063. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shiozaki EN, Chai J, Rigotti DJ, Riedl SJ,
Li P, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Fairman R and Shi Y: Mechanism of
XIAP-mediated inhibition of caspase-9. Mol Cell. 11:519–527. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Deveraux QL and Reed JC: IAP family
proteins-suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 13:239–252. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wagenknecht B, Glaser T, Naumann U, Kügler
S, Isenmann S, Bähr M, Korneluk R, Liston P and Weller M:
Expression and biological activity of X-linked inhibitor of
apoptosis (XIAP) in human malignant glioma. Cell Death Differ.
6:370–376. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L and Wang X: Smac,
a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent
caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell. 102:33–42.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, Silke J,
Connolly LM, Reid GE, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ and Vaux DL:
Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes
apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell.
102:43–53. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Srinivasula SM, Hegde R, Saleh A, Datta P,
Shiozaki E, Chai J, Lee RA, Robbins PD, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Shi Y
and Alnemri ES: A conserved XIAP-interaction motif in caspase-9 and
Smac/DIABLO regulates caspase activity and apoptosis. Nature.
410:112–116. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chai J, Du C, Wu JW, Kyin S, Wang X and
Shi Y: Structural and biochemical basis of apoptotic activation by
Smac/DIABLO. Nature. 406:855–862. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Green DR: Apoptotic pathways: paper wraps
stone blunts scissors. Cell. 102:1–4. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu G, Chai J, Suber TL, Wu JW, Du C, Wang
X and Shi Y: Structural basis of IAP recognition by Smac/DIABLO.
Nature. 408:1008–1012. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Giagkousiklidis S, Vogler M, Westhoff MA,
Kasperczyk H, Debatin KM and Fulda S: Sensitization for
gamma-irradiation-induced apoptosis by second mitochondria-derived
activator of caspase. Cancer Res. 65:10502–10513. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Giagkousiklidis S, Vellanki SH, Debatin KM
and Fulda S: Sensitization of pancreatic carcinoma cells for
gamma-irradiation-induced apoptosis by XIAP inhibition. Oncogene.
26:7006–7016. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vellanki SH, Grabrucker A, Liebau S,
Proepper C, Eramo A, Braun V, Boeckers T, Debatin KM and Fulda S:
Small-molecule XIAP inhibitors enhance gamma-irradiation-induced
apoptosis in glioblastoma. Neoplasia. 11:743–752. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu J, Bai L, Sun H, Nikolovska-Coleska Z,
McEachern D, Qiu S, Miller RS, Yi H, Shangary S, Sun Y, Meagher JL,
Stuckey JA and Wang S: SM-164: a novel, bivalent Smac mimetic that
induces apoptosis and tumor regression by concurrent removal of the
blockade of cIAP-1/2 and XIAP. Cancer Res. 68:9384–9393. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun H, Nikolovska-Coleska Z, Lu J, Meagher
JL, Yang CY, Qiu S, et al: Design, synthesis and characterization
of a potent, nonpeptide, cell-permeable, bivalent Smac mimetic that
concurrently targets both the BIR2 and BIR3 domains in XIAP. J Am
Chem Soc. 129:15279–15294. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang J, McEachern D, Li W, Davis MA, Li H,
Morgan MA, Bai L, Sebolt JT, Sun H, Lawrence TS, Wang S and Sun Y:
Radiosensitization of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by a
SMAC-mimetic compound, SM-164, requires activation of caspases. Mol
Cancer Ther. 10:658–669. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fulda S, Wick W, Weller M and Debatin KM:
Smac agonists sensitize for Apo2L/TRAIL- or anticancer drug-induced
apoptosis and induce regression of malignant glioma in vivo. Nat
Med. 8:808–815. 2002.
|
|
28
|
Qin L, Tong T, Song Y, Xue L, Fan F and
Zhan Q: Aurora-A interacts with Cyclin B1 and enhances its
stability. Cancer Lett. 275:77–85. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bockbrader KM, Tan M and Sun Y: A small
molecule Smac-mimic compound induces apoptosis and sensitizes
TRAIL-and etoposide-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells.
Oncogene. 24:7381–7388. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Herr I and Debatin KM: Cellular stress
response and apoptosis in cancer therapy. Blood. 98:2603–2614.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mow BM, Blajeski AL, Chandra J and
Kaufmann SH: Apoptosis and the response to anticancer therapy. Curr
Opin Oncol. 13:453–462. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lowe SW and Lin AW: Apoptosis in cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 21:485–495. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of
apoptosis. Nature. 407:770–776. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tait SW and Green DR: Mitochondria and
cell death: outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 11:621–632. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|