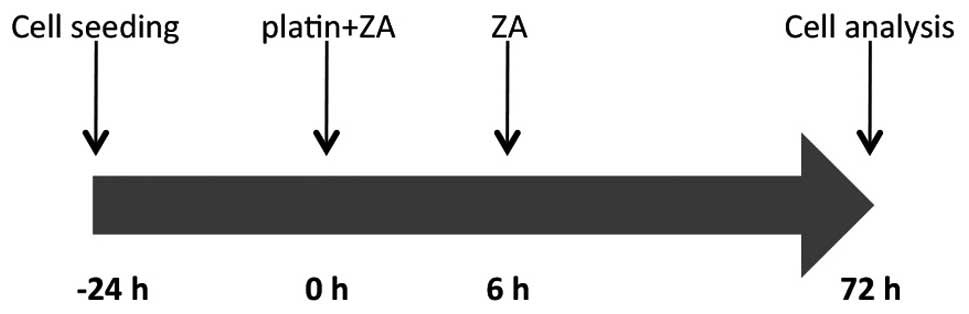
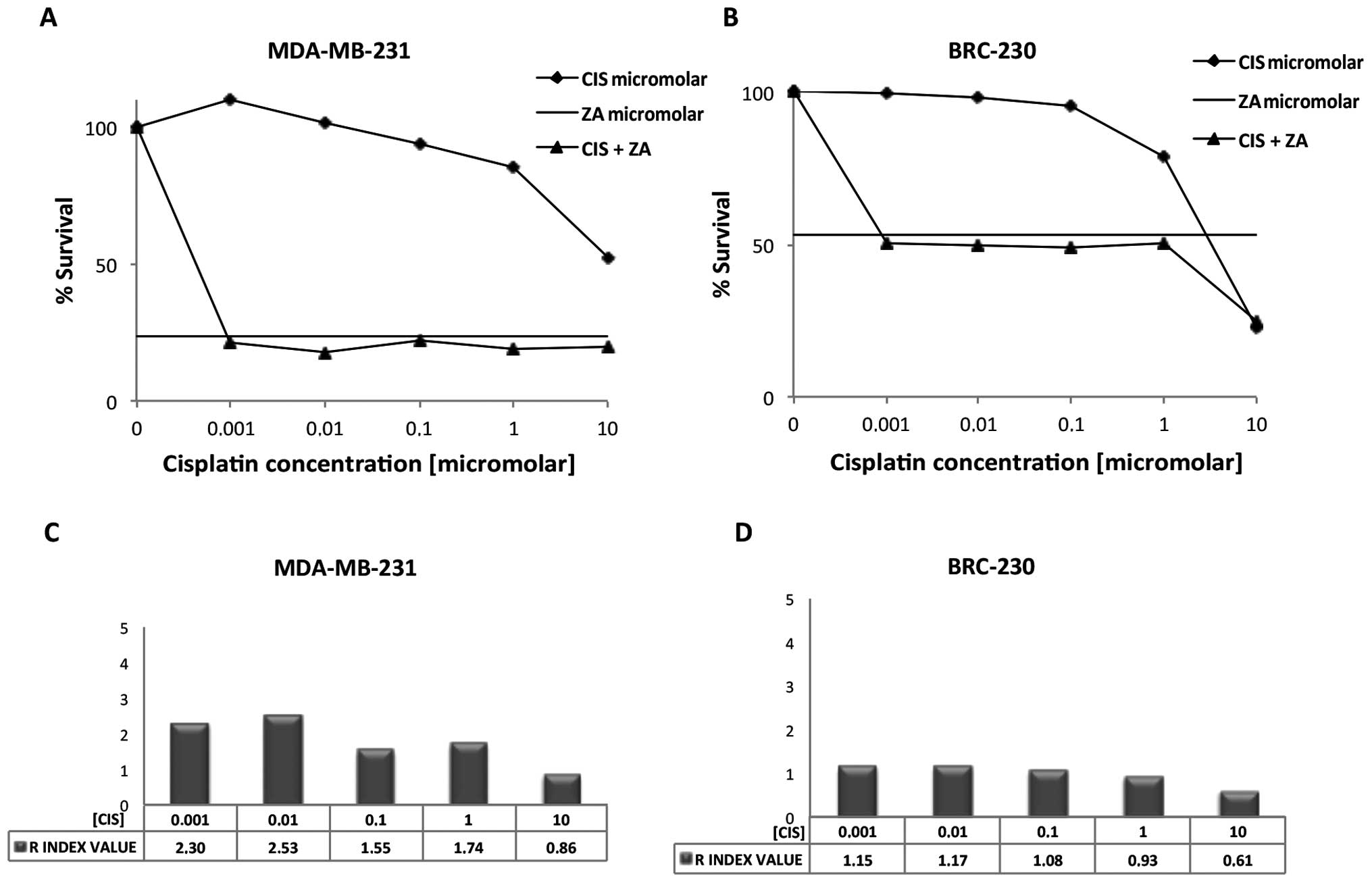
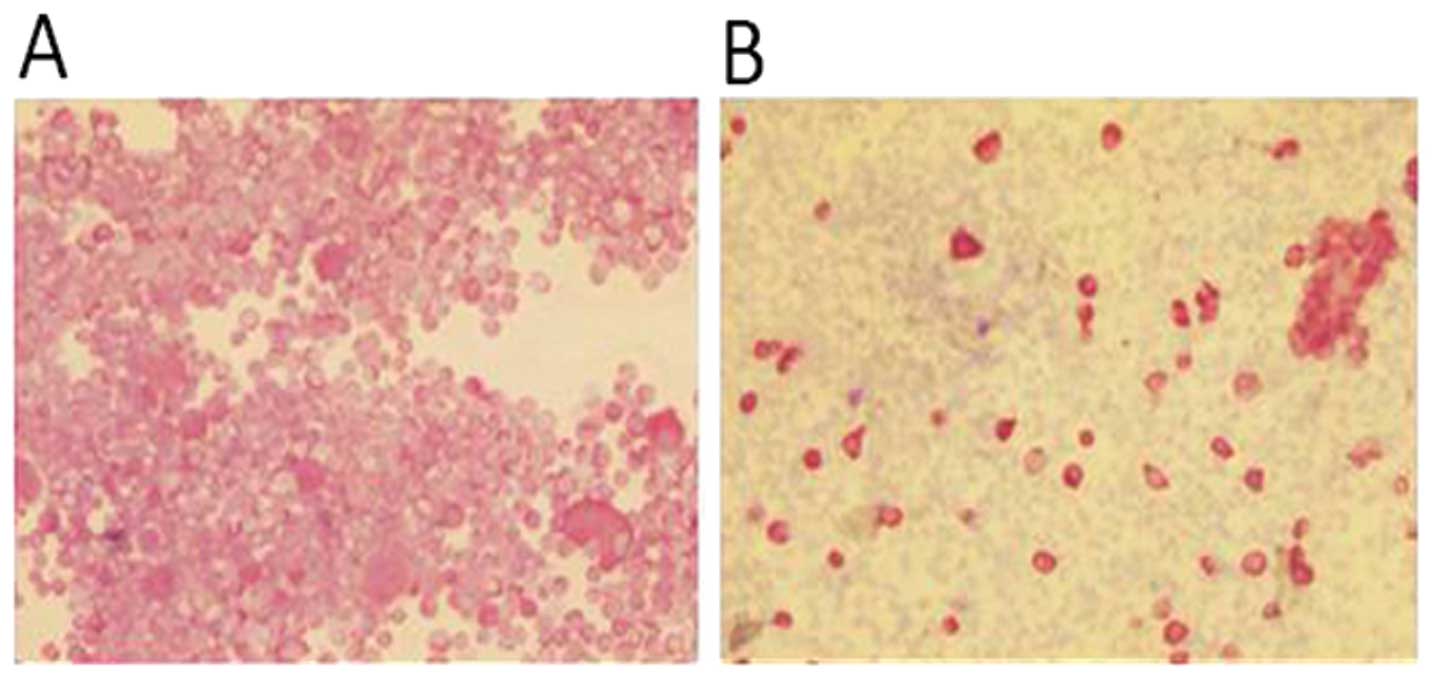
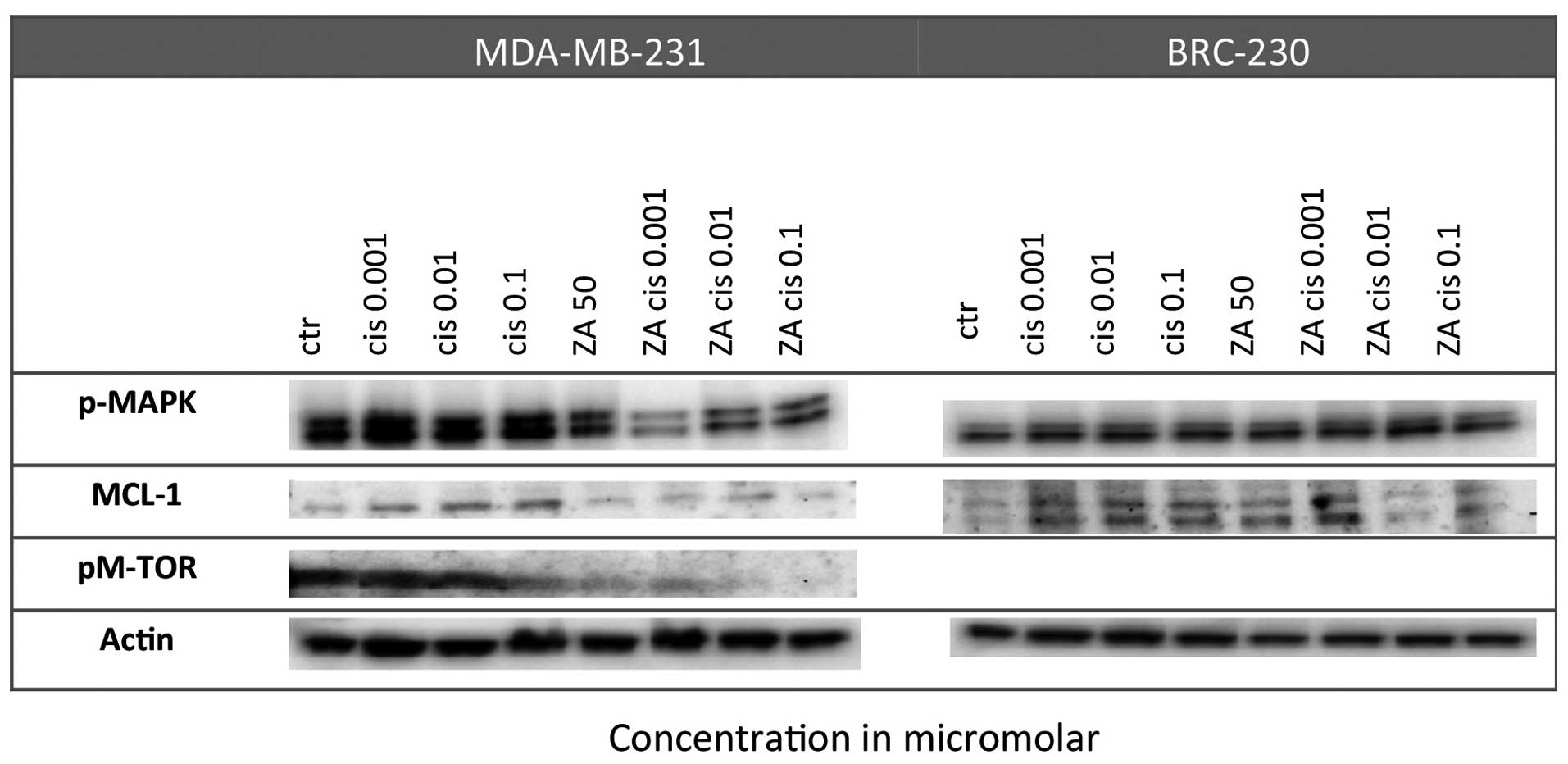
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Coleman RE and Rubens RD: The clinical
course of bone metastases from breast cancer. Br J Cancer.
55:61–66. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saad F, Adachi JD, Brown JP, Canning LA,
Gelmon KA, Josse RG and Pritchard KL: Cancer treatment-induced bone
loss in breast and prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:5465–5476.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coleman RE: Risks and benefits of
bisphosphonates. Br J Cancer. 98:1736–1740. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Coleman RE and McCloskey EV:
Bisphosphonates in oncology. Bone. 49:71–76. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Amin D, Cornell SA, Gustafson SK, Needle
SJ, Ullrich JW, Bilder GE and Perrone MH: Bisphosphonates used for
the treatment of bone disorders inhibit squalene synthase in
cholesterol biosynthesis. J Lipid Res. 33:1657–1663.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Van Beek E, Pieterman E, Cohen L, Lowick C
and Papapoulos S: Farnesyl pyrophosphatase synthase is the
molecular target of nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 264:108–111. 1999.
|
|
8
|
Coxon FP, Helfrich MH, Van't Hof R, Sebti
S, Ralston SH, Hamilton A and Rogers MJ: Protein
geranylgeranylation is required for osteoclast formation, function
and survival: inhibition by bisphosphonates and GGTI-298. J Bone
Miner Res. 15:1467–1476. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rogers MJ, Gordon S, Benford HL, Coxon FP,
Luckman SP, Monkkonen J and Frith JC: Cellular and molecular
mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Cancer. 88:2961–2978.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Benford HL, McGowan NW, Helfrich MH,
Nuttall ME and Rogers MJ: Visualization of bisphosphonate-induced
caspase-3 activity in apoptotic osteoclasts in vitro. Bone.
28:465–473. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jagdev SP, Coleman RE, Shipman CM, Rostami
HA and Croucher PI: The bisphosphonate, ZA, induces apoptosis of
breast cancer cells: evidence for synergy with paclitaxel. Br J
Cancer. 84:1126–1134. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Senaratne SG, Pirianov G, Mansi JL, Arnett
T and Colston KW: Bisphosphonates induce apoptosis in human breast
cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer. 82:1459–1468. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Derenne S, Amiot M, Barille S, et al:
Zoledronate is a potent inhibitor of myeloma cell growth and
secretion of IL-6 and MMP-1 by the tumoral environment. J Bone
Miner Res. 14:2048–2056. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee MV, Fong EM, Singer FR and Guenette
RS: Bisphosphonate treatment inhibits the growth of prostate cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 61:2602–2608. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shipman CM, Rogers MJ, Apperley JF,
Russell RG and Croucher PI: Bisphosphonates induce apoptosis in
human myeloma cell lines: a novel anti-tumour activity. Br J
Haematol. 98:665–672. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Van der Pluijm G, Vloedgraven H, van Beek
EJ, van der Wee-Pals L, Lowik C and Papapoulos S: Bisphosphonates
inhibit the adhesion of breast cancer cells to bone matrices in
vitro. J Clin Invest. 98:698–705. 1996.
|
|
17
|
Boissier S, Magnetto S, Frappart L, Cuzin
B, Ebetino FH, Delmas PD and Clezardin P: Bisphosphonates inhibit
prostate and breast carcinoma cell adhesion to unmineralized and
mineralized bone extracellular matrices. Cancer Res. 57:3890–3894.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Boissier S, Ferreras M, Peyruchaud O, et
al: Bisphosphonates inhibit breast and prostate carcinoma cell
invasion, an early event in the formation of bone metastases.
Cancer Res. 60:2949–2954. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wood J, Bonjean K, Ruetz S, Bellahcene A,
Devy L and Foidart JM: Novel antiangiogenic effects of the
bisphosphonate compound zoledronic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
302:1055–1061. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Neville-Webbe HL, Rostami-Hodjegan A,
Evans CA, Coleman RE and Holen I: Sequence- and schedule-dependent
enhancement of ZA induced apoptosis by doxorubicin in breast and
prostate cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 113:364–371. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Neville-Webbe HL, Evans CA, Coleman RE and
Holen I: Mechanisms of the synergistic interaction between the
bisphosphonate ZA and the chemotherapy agent paclitaxel in breast
cancer cells in vitro. Tumour Biol. 27:92–103. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vogt U, Bielawski KP, Bosse U and
Schlotter CM: Breast tumour growth inhibition in vitro
through the combination of
cyclophosphamide/metotrexate/5-fluorouracil,
epirubicin/cyclophosphamide, epirubicin/paclitaxel, and
epirubicin/docetaxel with the bisphosphonates ibandronate and
zoledronic acid. Oncol Rep. 12:1109–1114. 2004.
|
|
23
|
Zhao X, Xu X, Guo L, et al: Biomarker
alterations with metronomic use of low-dose ZA for breast cancer
patients with bone metastases and potential clinical significance.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 124:733–743. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Valentin MD, da Silva SD, Privat M,
Alaoui-Jamali M and Bignon YJ: Molecular insights on basal-like
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 134:21–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sirohi B, Arnedos M, Popat S, et al:
Platinum-based chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann
Oncol. 19:1847–1852. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Amadori D, Bertoni L, Flamigni A, et al:
Establishment and characterization of a new cell line from primary
human breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 28:251–260. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, et al:
New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 82:1107–1112. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Monks A, Scudiero D, Skehan P, et al:
Feasibility of a high-flux anticancer drug screen using a diverse
panel of cultured human tumor cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst.
83:757–766. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kern DH, Morgan CR and Hildebrand-Zanki
SU: In vitro pharmacodynamics of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine:
synergy of antitumor activity with
cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Cancer Res. 48:117–121.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Romanelli S, Perego P, Pratesi G, Carenini
N, Tortoreto M and Zunino F: In vitro and in vivo interaction
between cisplatin and topotecan in ovarian carcinoma systems.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 41:385–390. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hahnel A, Wichmann H, Kappler M, Kotzsch
M, Vordermark D, Taubert H and Bache M: Effects of osteopontin
inhibition on radiosensitivity of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.
Radiat Oncol. 5:822010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Senaratne SG, Mansi JL and Colston KW: The
bisphosphonate ZA impairs Ras membrane [correction of impairs
membrane] localisation and induces cytochrome c release in breast
cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 86:1479–1486. 2002.
|
|
33
|
Rachner TD, Singh SK, Schoppet M, et al:
ZA induces apoptosis and changes the TRAIL/OPG ratio in breast
cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 287:109–116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guise TA: Antitumor effects of
bisphosphonates: promising preclinical evidence. Cancer Treat Rev.
34:19–24. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fabbri F, Brigliadori G, Carloni S, et al:
Zoledronic acid increases docetaxel cytotoxicity through pMEK and
Mcl-1 inhibition in a hormone-sensitive prostate carcinoma cell
line. J Transl Med. 6:432008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Curigliano G and Goldhirsch A:
Triple-negative subtype: new ideas for the poorest prognosis breast
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 108–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME,
Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y and Pietenpol JA: Identification of human
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for
selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 121:2750–2767.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Benassi MS, Chiechi A, Ponticelli F, et
al: Growth inhibition and sensitization to cisplatin by zoledronic
acid in osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Lett. 250:194–205. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ozturk OH, Bozcuk H, Burgucu D, Ekinci D,
Ozdogan M, Akca S and Yildiz M: Cisplatin cytotoxicity is enhanced
with zoledronic acid in A549 lung cancer cell line: preliminary
results of an in vitro study. Cell Biol Int. 31:1069–1071. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fujise K, Zhang D, Liu J and Yeh ET:
Regulation of apoptosis and cell cycle progression by MCL1.
Differential role of proliferating cell nuclear antigen. J Biol
Chem. 275:39458–39465. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ellard SL, Clemons M, Gelmon KA, et al:
Randomized phase II study comparing two schedules of everolimus in
patients with recurrent/metastatic breast cancer: NCI Clinical
Trials Group IND.163. J Clin Oncol. 27:4536–4541. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Steelman LS, Navolanic P, Chappell WH, et
al: Involvement of Akt and mTOR in chemotherapeutic- and
hormonal-based drug resistance and response to radiation in breast
cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 10:3003–3015. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gaur S, Chen L, Yang L, Wu X, Un F and Yen
Y: Inhibitors of mTOR overcome drug resistance from topoisomerase
II inhibitors in solid tumors. Cancer Lett. 311:20–28. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Moriceau G, Ory B, Mitrofan L, et al:
Zoledronic acid potentiates mTOR inhibition and abolishes the
resistance of osteosarcoma cells to RAD001 (Everolimus): pivotal
role of the prenylation process. Cancer Res. 70:10329–10339. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ottewell PD, Deux B, Mönkkönen H, Cross S,
Coleman RE, Clezardin P and Holen I: Differential effect of
doxorubicin and zoledronic acid on intraosseous versus extraosseous
breast tumor growth in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 14:4658–4666. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Coleman RE, Winter MC, Cameron D, et al:
The effects of adding zoledronic acid to neoadjuvant chemotherapy
on tumour response: exploratory evidence for direct anti-tumour
activity in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 102:1099–1105. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|