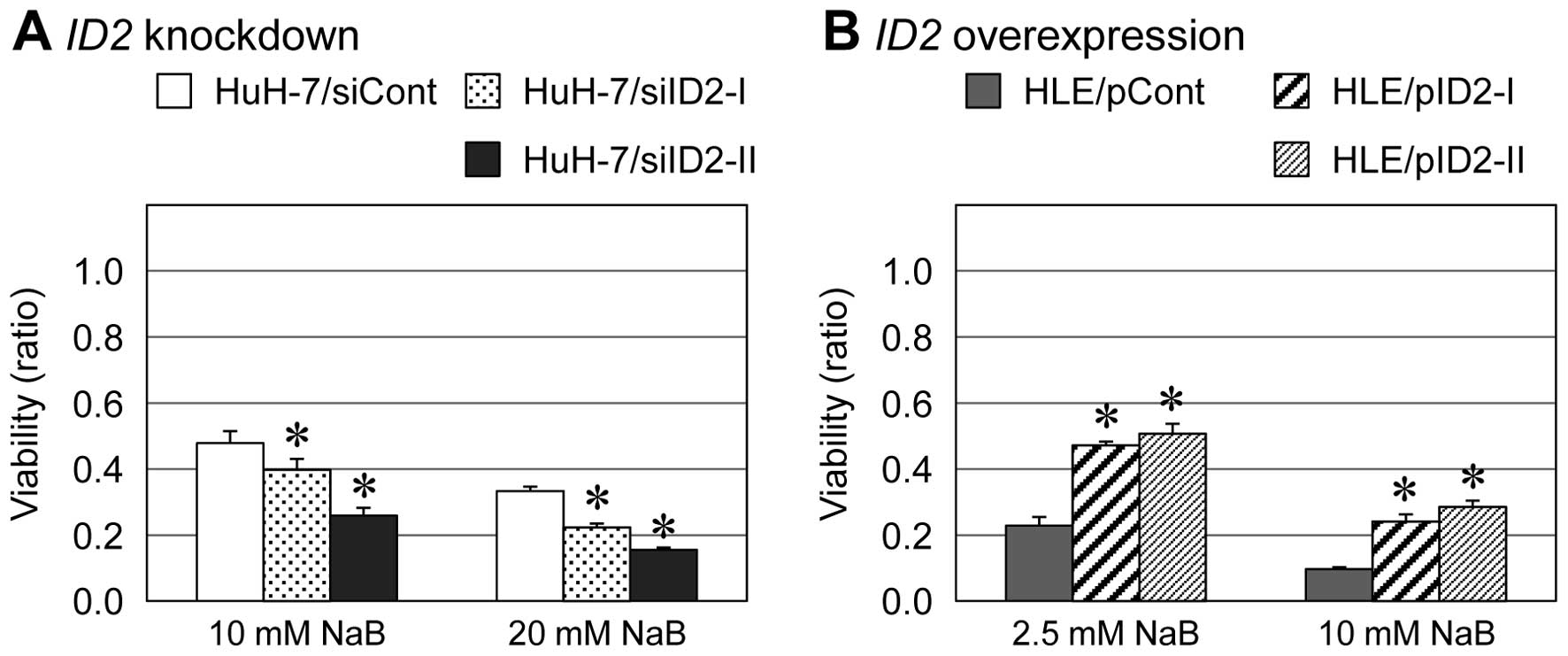
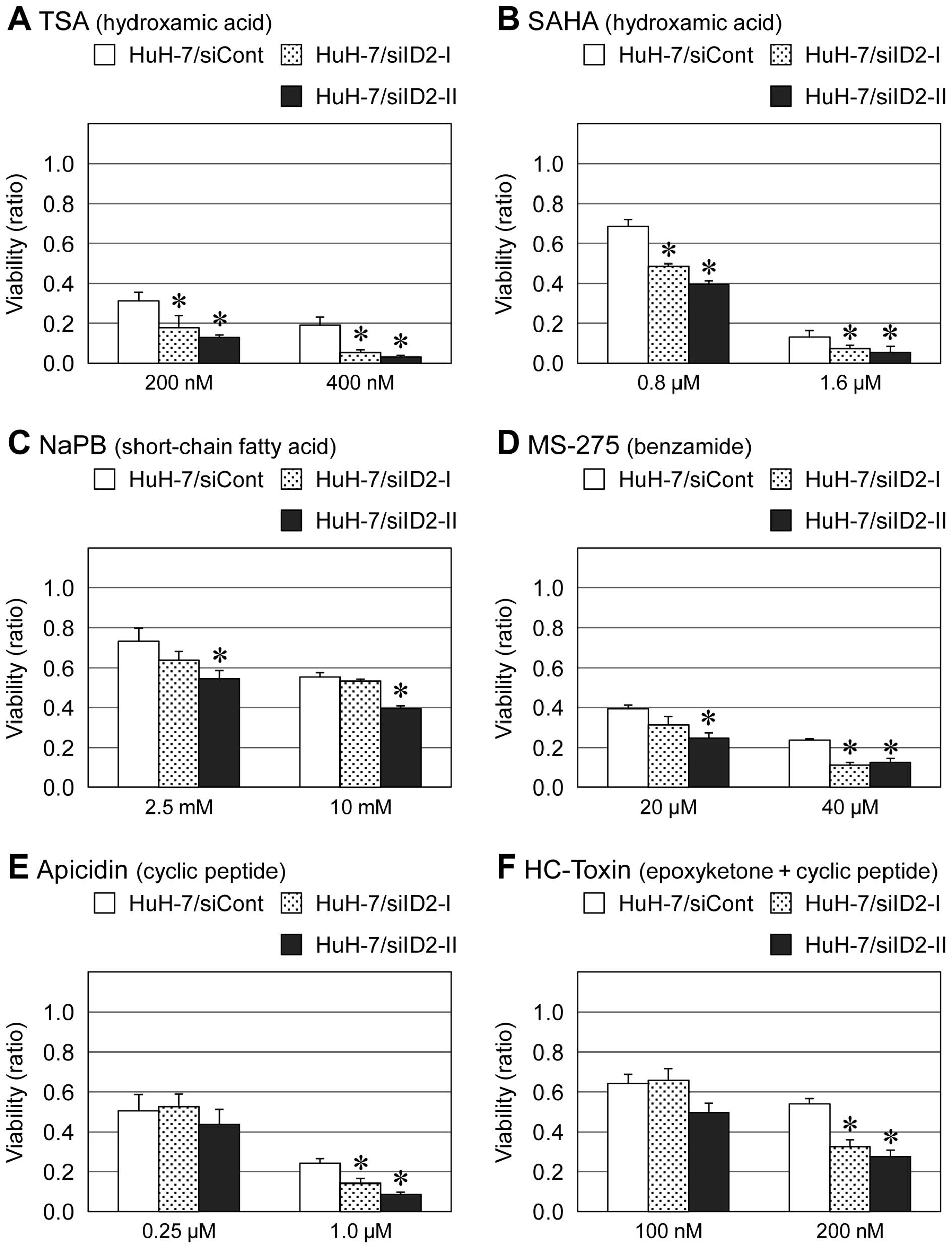
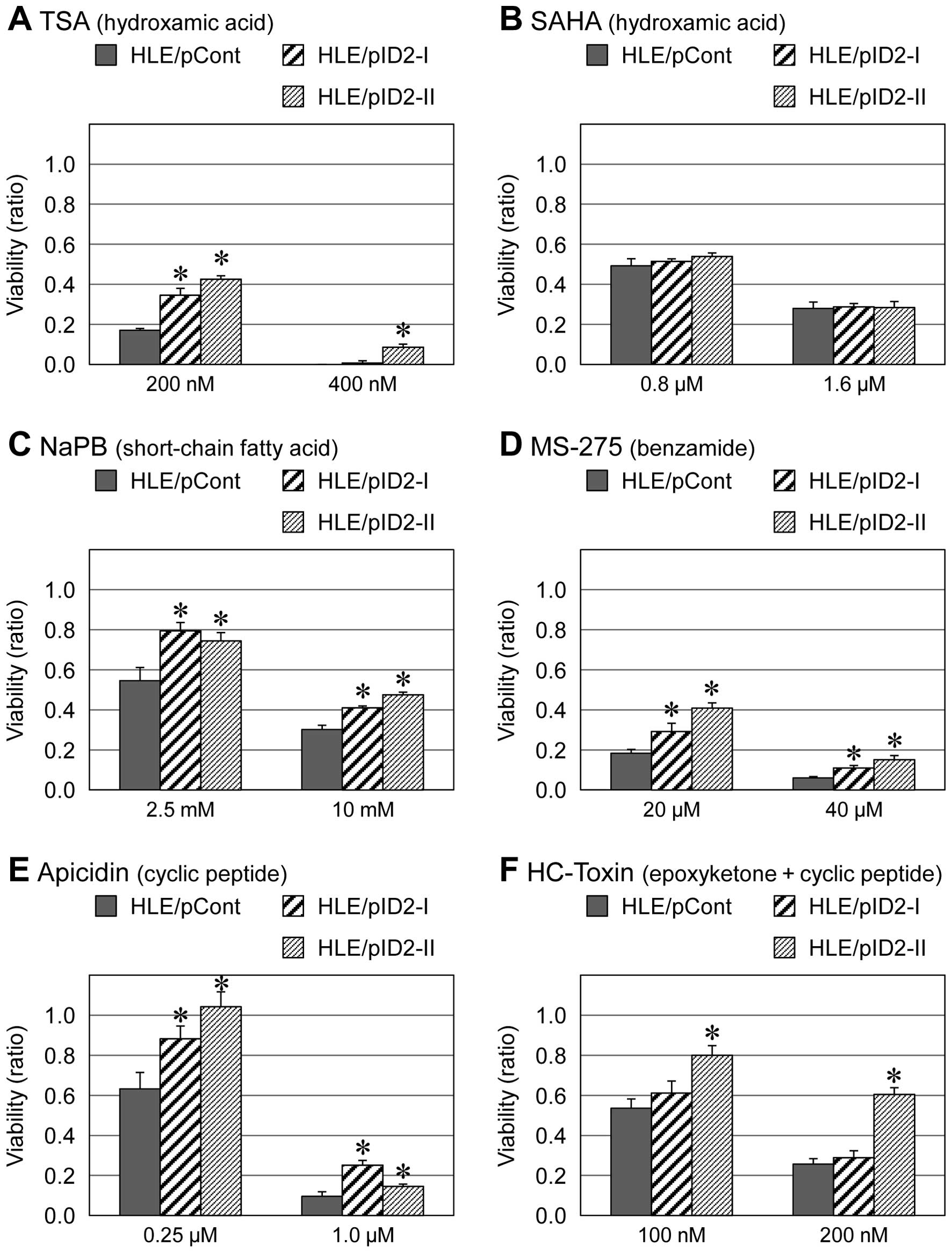
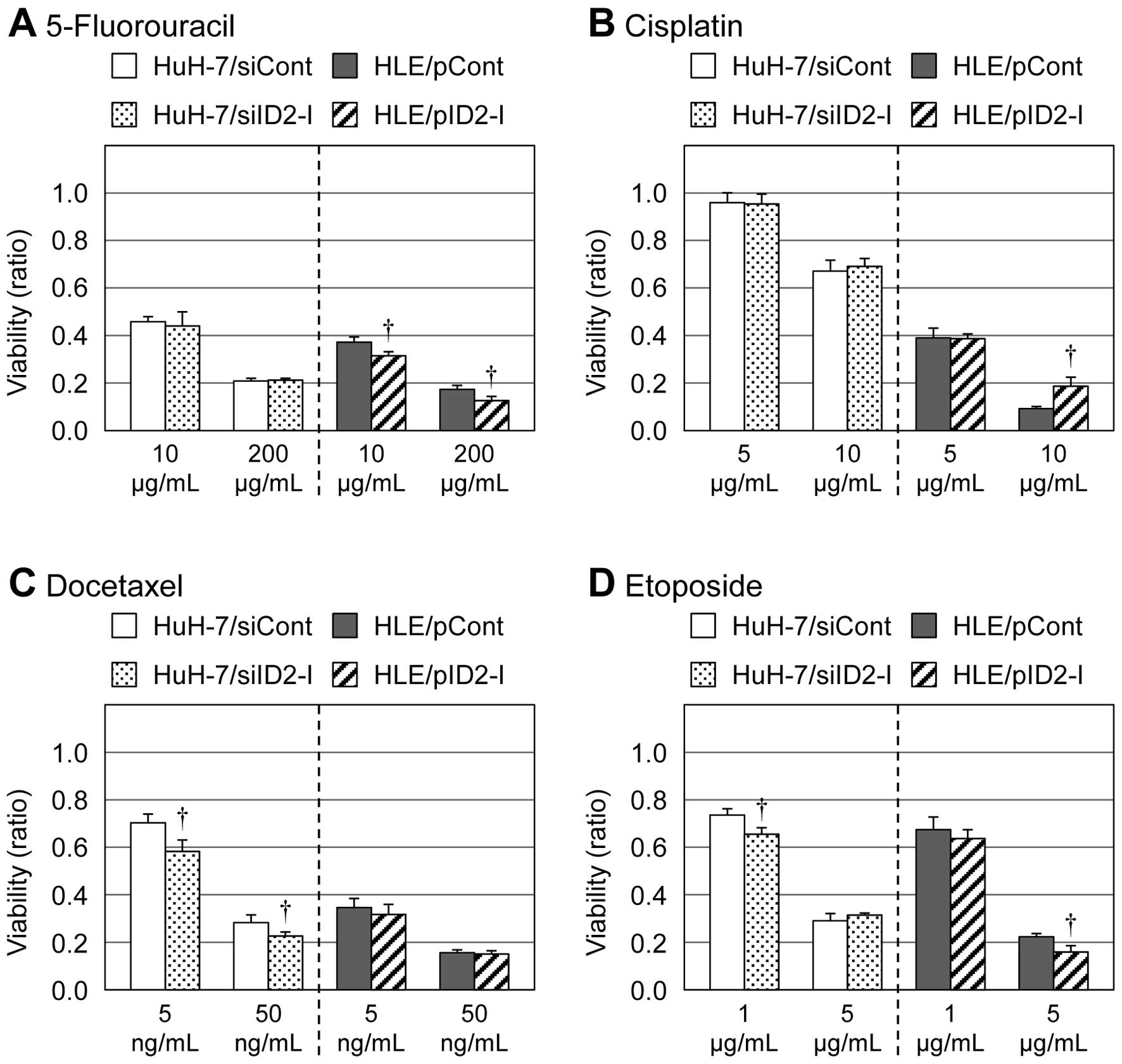
|
1
|
Thorgeirsson SS and Grisham JW: Molecular
pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet.
31:339–346. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005.55:74–108. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bruix J, Boix L, Sala M and Llovet JM:
Focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 5:215–219. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Iizuka N, Oka M, Yamada-Okabe H, Mori N,
Tamesa T, Okada T, Takemoto N, Sakamoto K, Hamada K, Ishitsuka H,
Miyamoto T, Uchimura S and Hamamoto Y: Self-organizing-map-based
molecular signature representing the development of hepatocellular
carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 579:1089–1100. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Damdinsuren B, Nagano H, Kondo M, Yamamoto
H, Hiraoka N, Yamamoto T, Marubashi S, Miyamoto A, Umeshita K, Dono
K, Nakamori S, Wakasa K, Sakon M and Monden M: Expression of Id
proteins in human hepatocellular carcinoma: relevance to tumor
dedifferentiation. Int J Oncol. 26:319–327. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tsunedomi R, Iizuka N, Yamada-Okabe H,
Tamesa T, Okada T, Sakamoto K, Takashima M, Hamaguchi T, Miyamoto
T, Uchimura S, Hamamoto Y, Yamada M and Oka M: Identification of
ID2 associated with invasion of hepatitis C virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma by gene expression profile. Int J Oncol.
29:1445–1451. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tsunedomi R, Iizuka N, Tamesa T, Sakamoto
K, Hamaguchi T, Somura H, Yamada M and Oka M: Decreased ID2
promotes metastatic potentials of hepatocellular carcinoma by
altering secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:1025–1031. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Benezra R, Davis R, Lockshon D, Turner D
and Weintraub H: The protein ID: a negative regulator of
helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 61:49–59. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kadesch T: Consequences of heteromeric
interactions among helix-loop-helix proteins. Cell Growth Differ.
4:49–55. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Norton JD: ID helix-loop-helix proteins in
cell growth, differentiation and tumorigenesis. J Cell Sci.
113:3897–3905. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Biggs J, Murphy EV and Israel MA: Id-like
helix-loop-helix protein expressed during early development. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:1512–1516. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hara E, Yamaguchi T, Nojima H, Ide T,
Campisi J, Okayama H and Oda K: Id-related genes encoding
helix-loop-helix proteins are required for G1 progression and are
repressed in senescent human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem.
269:2139–2145. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rivera R and Murre C: The regulation and
function of the Id proteins inlymphocyte development. Oncogene.
20:8308–8316. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zebedee Z and Hara E: Id proteins in cell
cycle control and cellular senescence. Oncogene. 20:8317–8325.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Benezra R, Rafii S and Lyden D: The Id
proteins and angiogenesis. Oncogene. 20:8334–8341. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ellmeier W, Aguzzi A, Kleiner E, Kurzbauer
R and Weith A: Mutually exclusive expression of a helix-loop-helix
gene and N-myc in human neuroblastomas and in normal development.
EMBO J. 11:2563–2571. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Israel MA, Hernandez MC, Florio M,
Andres-Barquin PJ, Mantani A, Carter JH and Julin CM: Id gene
expression as a key mediator of tumor cell biology. Cancer Res.
59:1726s–1730s. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lyden D, Young AZ, Zagzag D, Yan W, Gerald
W, O’Reilly R, Bader BL, Hynes RO, Zhuang Y, Manova K and Benezra
R: Id1 and Id3 are required for neurogenesis, angiogenesis and
vascularization of tumour xenografts. Nature. 401:670–677. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Maruyama H, Kleeff J, Wildi S, Friess H,
Büchler MW, Israel MA and Korc M: Id-1 and Id-2 are overexpressed
in pancreatic cancer and in dysplastic lesions in chronic
pancreatitis. AmJ Pathol. 155:815–822. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lin CQ, Singh J, Murata K, Itahana Y,
Parrinello S, Liang SH, Gillett CE, Campisi J and Desprez PY: A
role for Id-1 in the aggressive phenotype and steroid hormone
response of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 60:1332–1340.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Langlands K, Down GA and Kealey T: Id
proteins are dynamically expressed in normal epidermis and
dysregulated in squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 60:5929–5933.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wilson JW, Deed RW, Inoue T, Balzi M,
Becciolini A, Faraoni P, Potten CS and Norton JD: Expression of Id
helix-loop-helix proteins in colorectal adenocarcinoma correlates
with p53 expression and mitotic index. Cancer Res. 61:8803–8810.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schindl M, Schoppmann SF, Ströbel T,
Heinzl H, Leisser C, Horvat R and Birner P: Level of Id-1protein
expression correlates with poor differentiation, enhanced malignant
potential and more aggressive clinical behavior of epithelial
ovarian tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 9:779–785. 2003.
|
|
24
|
Itahana Y, Singh J, Sumida T, Coppe JP,
Parrinello S, Bennington JL and Desprez PY: Role of Id-2 in the
maintenance of a differentiated and noninvasive phenotype in breast
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 63:7098–7105. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Coppe JP, Itahana Y, Moore DH, Bennington
JL and Desprez PY: Id-1 and Id-2 proteins as molecular markers for
human prostate cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2044–2051.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Umetani N, Takeuchi H, Fujimoto A,
Shinozaki M, Bilchik AJ and Hoon DS: Epigenetic inactivation of ID4
in colorectal carcinomas correlates with poor differentiation and
unfavorable prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 10:7475–7483. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
de Candia P, Benera R and Solit DB: A role
for Id proteins in mammary gland physiology and tumorigenesis. Adv
Cancer Res. 92:81–94. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stighall M, Manetopoulos C, Axelson H and
Landberg G: High ID2 protein expression correlates with a
favourable prognosis in patients with primary breast cancer and
reduces cellular invasiveness of breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
115:403–411. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Umetani N, Mori T, Koyanagi K, Shinozaki
M, Kim J, Giuliano AE and Hoon DS: Aberrant hypermethylation of ID4
gene promoter region increases risk of lymph node metastasis in T1
breast cancer. Oncogene. 24:4721–4727. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matsuda Y, Yamagiwa S, Takamura M, Honda
Y, Ishimoto Y, Ichida T and Aoyagi Y: Overexpressed Id-1 is
associated with a high risk of hepatocellular carcinoma development
in patients with cirrhosis without transcriptional repression of
p16. Cancer. 104:1037–1044. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee TK, Poon RT, Yuen AP, Ling MT, Wang
XH, Wong YC, Guan XY, Man K, Tang ZY and Fan ST: Regulation of
angiogenesis by Id-1 through hypoxia-inducible factor-1a-mediated
vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulation in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6910–6919. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Drummond DC, Noble CO, Kirpotin DB, Guo Z,
Scott GK and Benz CC: Clinical development of histone deacetylase
inhibitors as anticancer agents. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
45:495–528. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu T, Kuljaca S, Tee A and Marshall GM:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: multifunctional anticancer agents.
Cancer Treat Rev. 32:157–165. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Khan O and La Thangue NB: HDAC inhibitors
in cancer biology: Emerging mechanisms and clinical applications.
Immunol Cell Biol. 90:85–94. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rosato RR, Almenara JA, Dai Y and Grant S:
Simultaneous activation of the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways by
histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors and tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) synergistically
induces mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in human leukemia cells.
Mol Cancer Ther. 2:1273–1284. 2003.
|
|
36
|
Emanuele S, Lauricella M and Tesoriere G:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Apoptotic effects and clinical
implications. Int J Oncol. 33:637–646. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang J, Kan S, Huang B, Hao Z, Mak TW and
Zhong Q: Mule determines the apoptotic response to HDAC inhibitors
by targeted ubiquitination and destruction of HDAC2. Genes Dev.
25:2610–2618. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vigushin DM and Coombes RC: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors in cancer treatment. Anticancer Drugs.
13:1–13. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lin HY and Chen CS, Lin SP, Weng JR and
Chen CS: Targeting histone deacetylase in cancer therapy. Med Res
Rev. 26:397–413. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xu WS, Parmigiani RB and Marks PA: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors: molecular mechanisms of action. Oncogene.
26:5541–5552. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tsunedomi R, Ogawa Y, Iizuka N, Sakamoto
K, Tamesa T, Moribe T and Oka M: The assessment of methylated BASP1
and SRD5A2 levels in the detection of early hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 36:205–212. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kouzarides T: Histone acetylases and
deacetylases in cell proliferation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 9:40–48.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Marks PA, Richon VM and Rifkind RA:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors:inducers of differentiation or
apotosis of transformed cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:1210–1216.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Timmermann S, Lehrmann H, Polesskaya A and
Harel-Bellan A: Histone acetylation and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci.
58:728–736. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ogawa K, Yasumura S, Atarashi Y, Minemura
M, Miyazaki T, Iwamoto M, Higuchi K and Watanabe A: Sodium butyrate
enhances Fas-mediated apoptosis of human hepatoma cells. J Hepatol.
40:278–284. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Joseph J, Mudduluru G, Antony S, Vashistha
S, Ajitkumar P and Somasundaram K: Expression profiling of sodium
butyrate (NaB)-treated cells: identification of regulation of genes
related to cytokine signaling and cancer metastasis by NaB.
Oncogene. 23:6304–6315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Chiba T, Yokosuka O, Arai M, Tada M, Fukai
K, Imazeki F, Kato M, Seki N and Saisho H: Identification of genes
up-regulated by histone deacetylase inhibition with cDNA microarray
and exploration of epigenetic alterations on hepatoma cells. J
Hepatol. 41:436–445. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen J, Saha P, Kornbluth S, Dynlacht BD
and Dutta A: Cyclin-binding motifs are essential for the function
of p21CIP1. Mol Cell Biol. 16:4673–4682. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Shin JY, Kim HS, Park J, Park JB and Lee
JY: Mechanism for inactivation of the KIP family cyclin-dependent
kinase inhibitor genes in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Res.
60:262–265. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Han JW, Ahn SH, Kim YK, Bae GU, Yoon JW,
Hong S, Lee HY, Lee YW and Lee HW: Activation of
p21WAF1/Cip1 transcription through Sp1 sites by histone
deacetylase inhibitor apicidin. J Biol Chem. 276:42084–42090.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|