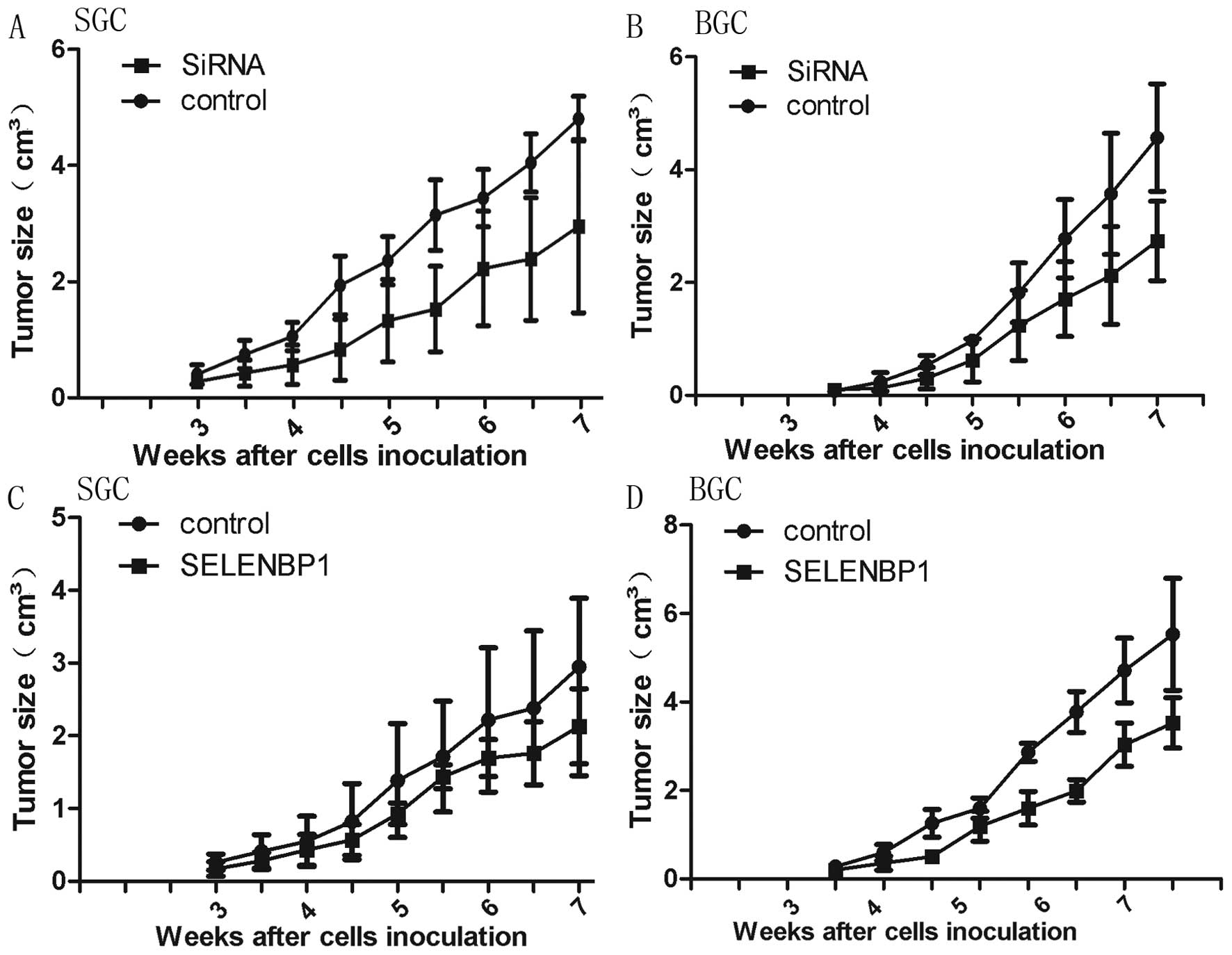
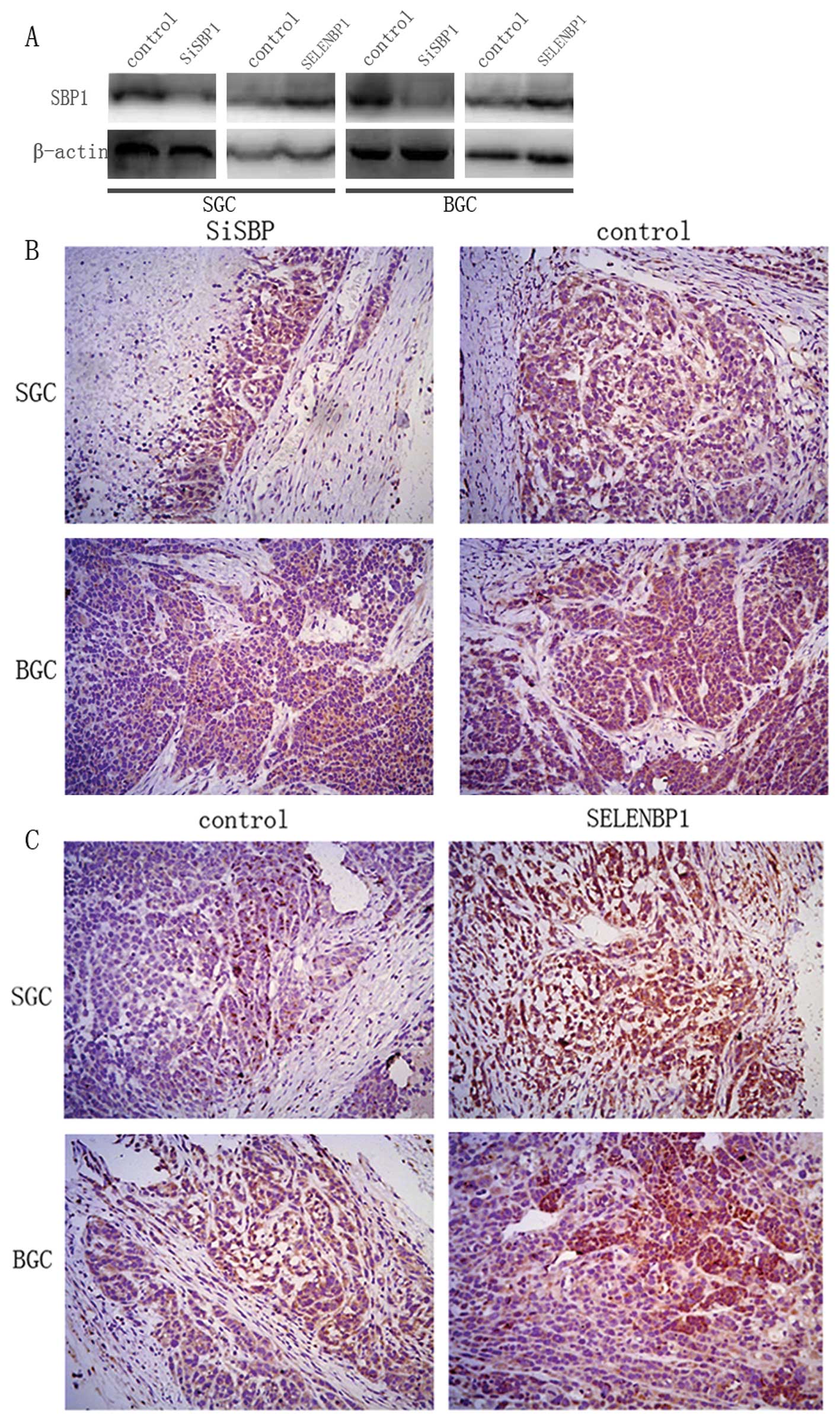
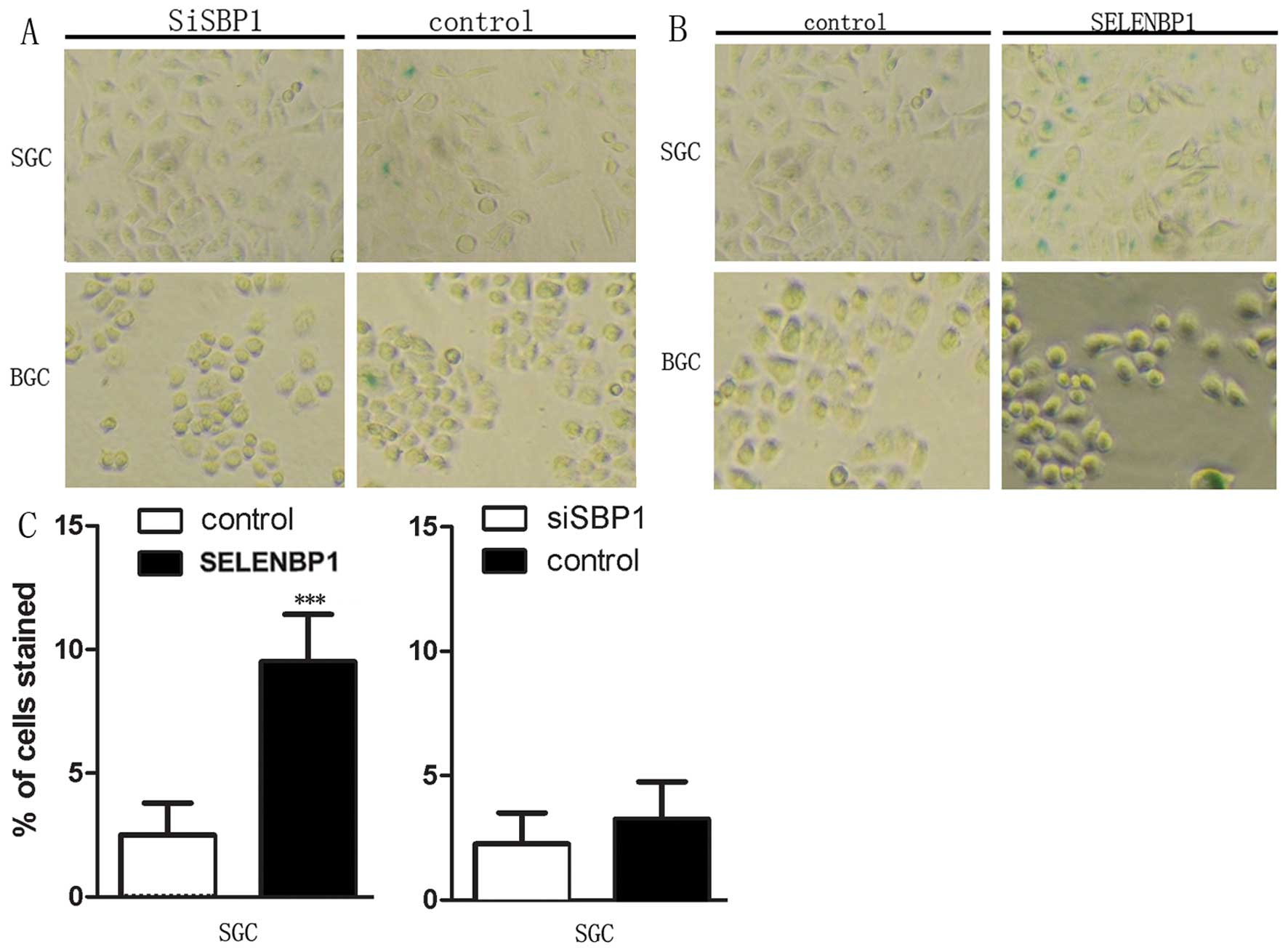
|
1.
|
Wagner AD, Grothe W, Haerting J, Kleber G,
Grothey A and Fleig WE: Chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer: a
systematic review and meta-analysis based on aggregate data. J Clin
Oncol. 24:2903–2909. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Lee JH, Kim KM, Cheong JH and Noh SH:
Current management and future strategies of gastric cancer. Yonsei
Med J. 53:248–257. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Xia YJ, Ma YY, He XJ, Wang HJ, Ye ZY and
Tao HQ: Suppression of selenium-binding protein 1 in gastric cancer
is associated with poor survival. Hum Pathol. 42:1620–1628. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Zhang J, Dong WG and Lin J: Reduced
selenium-binding protein 1 is associated with poor survival rate in
gastric carcinoma. Med Oncol. 28:481–487. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Zhang P, Zhang C, Wang X, et al: The
expression of selenium-binding protein 1 is decreased in uterine
leiomyoma. Diagn Pathol. 5:802010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Silvers AL, Lin L, Bass AJ, et al:
Decreased selenium-binding protein 1 in esophageal adenocarcinoma
results from posttranscriptional and epigenetic regulation and
affects chemosensitivity. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2009–2021. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Zhang C, Wang YE, Zhang P, et al:
Progressive loss of selenium-binding protein 1 expression
correlates with increasing epithelial proliferation and papillary
complexity in ovarian serous borderline tumor and low-grade serous
carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 41:255–261. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Wu C, Luo Z, Chen X, et al:
Two-dimensional differential in-gel electrophoresis for
identification of gastric cancer-specific protein markers. Oncol
Rep. 21:1429–1437. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Pohl NM, Tong C, Fang W, Bi X, Li T and
Yang W: Transcriptional regulation and biological functions of
selenium-binding protein 1 in colorectal cancer in vitro and in
nude mouse xenografts. PLoS One. 4:e77742009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Li T, Yang W, Li M, et al: Expression of
selenium-binding protein 1 characterizes intestinal cell maturation
and predicts survival for patients with colorectal cancer. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 52:1289–1299. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Chen G, Wang H, Miller CT, et al: Reduced
selenium-binding protein 1 expression is associated with poor
outcome in lung adenocarcinomas. J Pathol. 202:321–329. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Kim H, Kang HJ, You KT, et al: Suppression
of human selenium-binding protein 1 is a late event in colorectal
carcinogenesis and is associated with poor survival. Proteomics.
6:3466–3476. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Pan S, Cheng L, White JT, et al:
Quantitative proteomics analysis integrated with microarray data
reveals that extracellular matrix proteins, catenins, and p53
binding protein 1 are important for chemotherapy response in
ovarian cancers. OMICS. 13:345–354. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Huang C, Ding G, Gu C, et al: Decreased
selenium-binding protein 1 enhances glutathione peroxidase 1
activity and down-regulates HIF-1alpha to promote hepatocellular
carcinoma invasiveness. Clin Cancer Res. 18:3042–3053. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Jeong JY, Wang Y and Sytkowski AJ: Human
selenium binding protein-1 (hSP56) interacts with VDU1 in a
selenium-dependent manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 379:583–588.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Raucci R, Colonna G, Guerriero E, et al:
Structural and functional studies of the human selenium binding
protein-1 and its involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1814:513–522. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Porat A, Sagiv Y and Elazar Z: A 56-kDa
selenium-binding protein participates in intra-Golgi protein
transport. J Biol Chem. 275:14457–14465. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Rayman MP: Selenium and human health.
Lancet. 379:1256–1268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Scortegagna M, Martin RJ, Kladney RD,
Neumann RG and Arbeit JM: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha
suppresses squamous carcinogenic progression and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 69:2638–2646. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
He QY, Cheung YH, Leung SY, Yuen ST, Chu
KM and Chiu JF: Diverse proteomic alterations in gastric
adenocarcinoma. Proteomics. 4:3276–3287. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Zhang J, Zhan N and Dong WG: Altered
expression of selenium-binding protein 1 in gastric carcinoma and
precursor lesions. Med Oncol. 28:951–957. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Blot WJ, Li JY, Taylor PR, et al:
Nutrition intervention trials in Linxian, China: supplementation
with specific vitamin/mineral combinations, cancer incidence, and
disease-specific mortality in the general population. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 85:1483–1492. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Cho YM, Bae SH, Choi BK, et al:
Differential expression of the liver proteome in senescence
accelerated mice. Proteomics. 3:1883–1894. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|