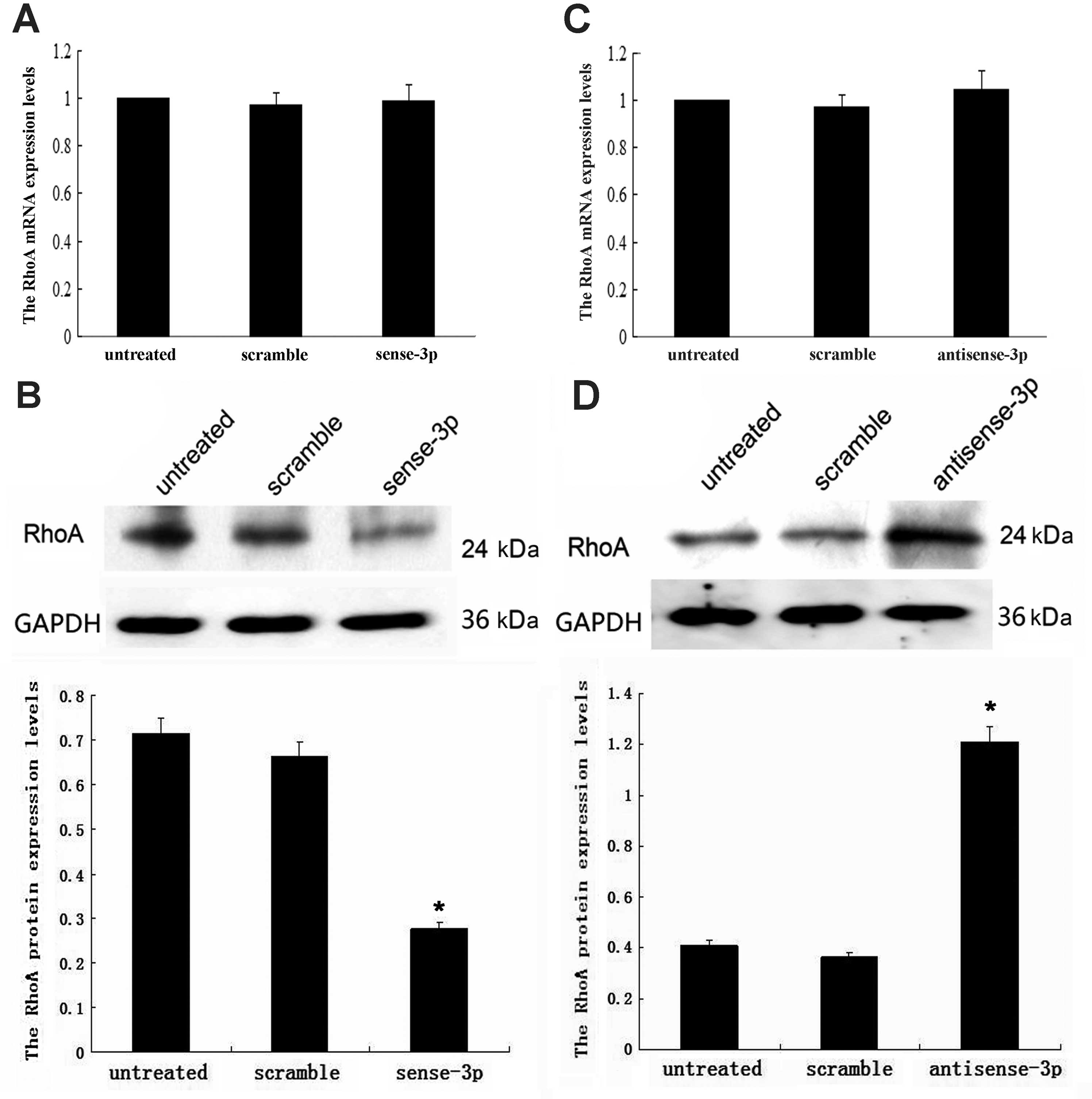
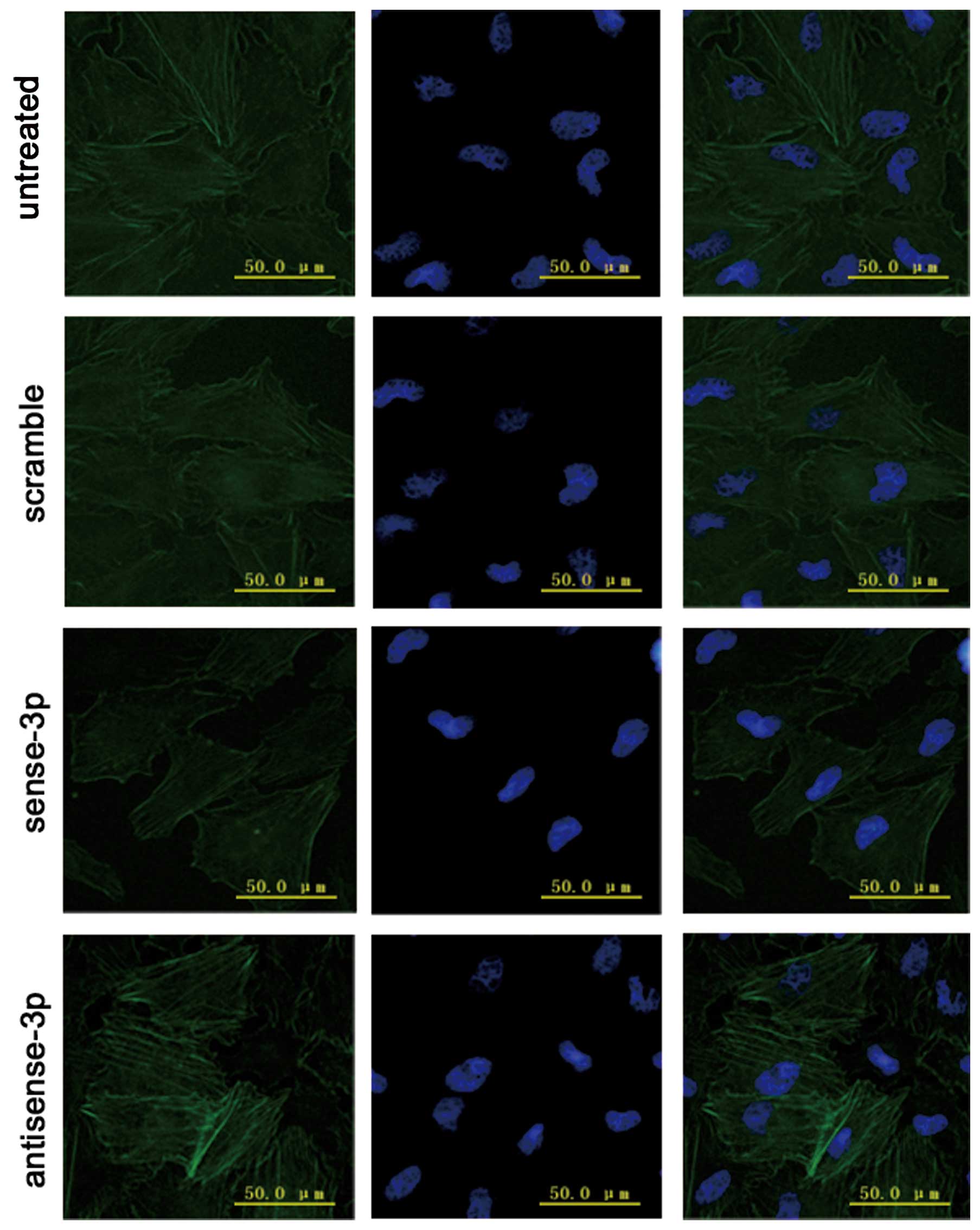
|
1.
|
Sporn MB: The war on cancer. Lancet.
347:1377–1381. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Nguyen DX, Bos PD and Massague J:
Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:274–284. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Crawford M, Brawner E, Batte K, et al:
MicroRNA-126 inhibits invasion in non-small cell lung carcinoma
cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 373:607–612. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Xiong BH, Cheng Y, Ma L and Zhang CQ:
Mir-21 regulates biological behavior through the PTEN/PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
42:219–228. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Tavazoie SF, Alarcón C, Oskarsson T, et
al: Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer
metastasis. Nature. 451:147–152. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Nicoloso MS, Spizzo R, Shimizu M, et al:
MicroRNAs - the micro steering wheel of tumour metastases. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:293–302. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Valastyan S, Reinhardt F, Benaich N, et
al: A pleiotropically acting microRNA, miR-31, inhibits breast
cancer metastasis. Cell. 137:1032–1046. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, et
al: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor
suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 27:2128–2136. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
He XY, Chen JX and Zhang Z: The let-7a
microRNA protects from growth of lung carcinoma by suppression of
k-Ras and c-Myc in nude mice. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
136:1023–1028. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Wu L and Belasco JG: Micro-RNA regulation
of the mammalian lin-28 gene during neuronal differentiation of
embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 25:9198–9208. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Laneve P, Di Marcotullio L, Gioia U, et
al: The interplay between microRNAs and the neurotrophin receptor
tropomyosin-related kinase C controls proliferation of human
neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:7957–7962. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Cowden Dahl KD, Dahl R, Kruichak JN, et
al: The epidermal growth factor receptor responsive miR-125a
represses mesenchymal morphology in ovarian cancer cells.
Neoplasia. 11:1208–1215. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Jiang L, Huang Q, Zhang S, et al:
Hsa-125a-3p and hsa-miR-125a-5p are downregulated in non-small cell
lung cancer and have inverse effects on invasion and migration of
lung cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 10:3182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Chambers AF, Groom AC and MacDonald IC:
Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:563–572. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Woodhouse EC, Chuaqui RF and Liotta LA:
General mechanisms of metastasis. Cancer. 80(Suppl 8): 1529–1537.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Ho TT, Merajver SD, Lapiere CM, et al:
RhoA-GDP regulates RhoB protein stability. J Biol Chem.
283:21588–21598. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Ming J, Liu N, Gu Y, et al: PRL-3
facilitates angiogenesis and metastasis by increasing ERK
phosphorylation and up-regulating the levels and activities of
Rho-A/C in lung cancer. Pathology. 41:118–126. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Etienne-Manneville S and Hall A: Rho
GTPases in cell biology. Nature. 420:629–635. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Yoshioka K, Matsumura F and Akedo H: Small
GTP-binding protein Rho stimulates the actomyosin system, leading
to invasion of tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 273:5146–5154. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Paterson HF, Self AJ, Garrett MD, et al:
Microinjection of recombinant p21rho induces rapid changes in cell
morphology. J Cell Biol. 111:1001–1007. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Takaishi K, Kikuchi A, Kuroda S, et al:
Involvement of rho p21 and its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein
(rho GDI) in cell motility. Mol Cell Biol. 13:72–79.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Kishi K, Sasaki T, Kuroda S, et al:
Regulation of cytoplasmic division of Xenopus embryo by rho
p21 and its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (rho GDI). J Cell
Biol. 120:1187–1195. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Mabuchi I, Hamaguchi Y, Fujimoto H, et al:
A rho-like protein is involved in the organisation of the
contractile ring in dividing sand dollar eggs. Zygote. 1:325–331.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Perona R, Esteve P, Jimenez B, et al:
Tumorigenic activity of rho genes from Aplysia californica.
Oncogene. 8:1285–1292. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Prendergast GC, Khosravi-Far R, Solski P,
et al: Critical role of Rho in cell transformation by oncogenic
Ras. Oncogene. 10:2289–2296. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Fritz G, Just I and Kaina B: Rho GTPases
were over-expressed in human tumors. Int J Cancer. 81:682–687.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Horiuchi A, Kikuchi N, Osada R, et al:
Overexpression of RhoA enhances peritoneal dissemination: RhoA
suppression with Lovastatin may be useful for ovarian cancer.
Cancer Sci. 12:2532–2539. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Yoshioka K, Nakamori S and Itoh K:
Overexpression of small GTP-binding protein RhoA promotes invasion
of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 59:2004–2010. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|