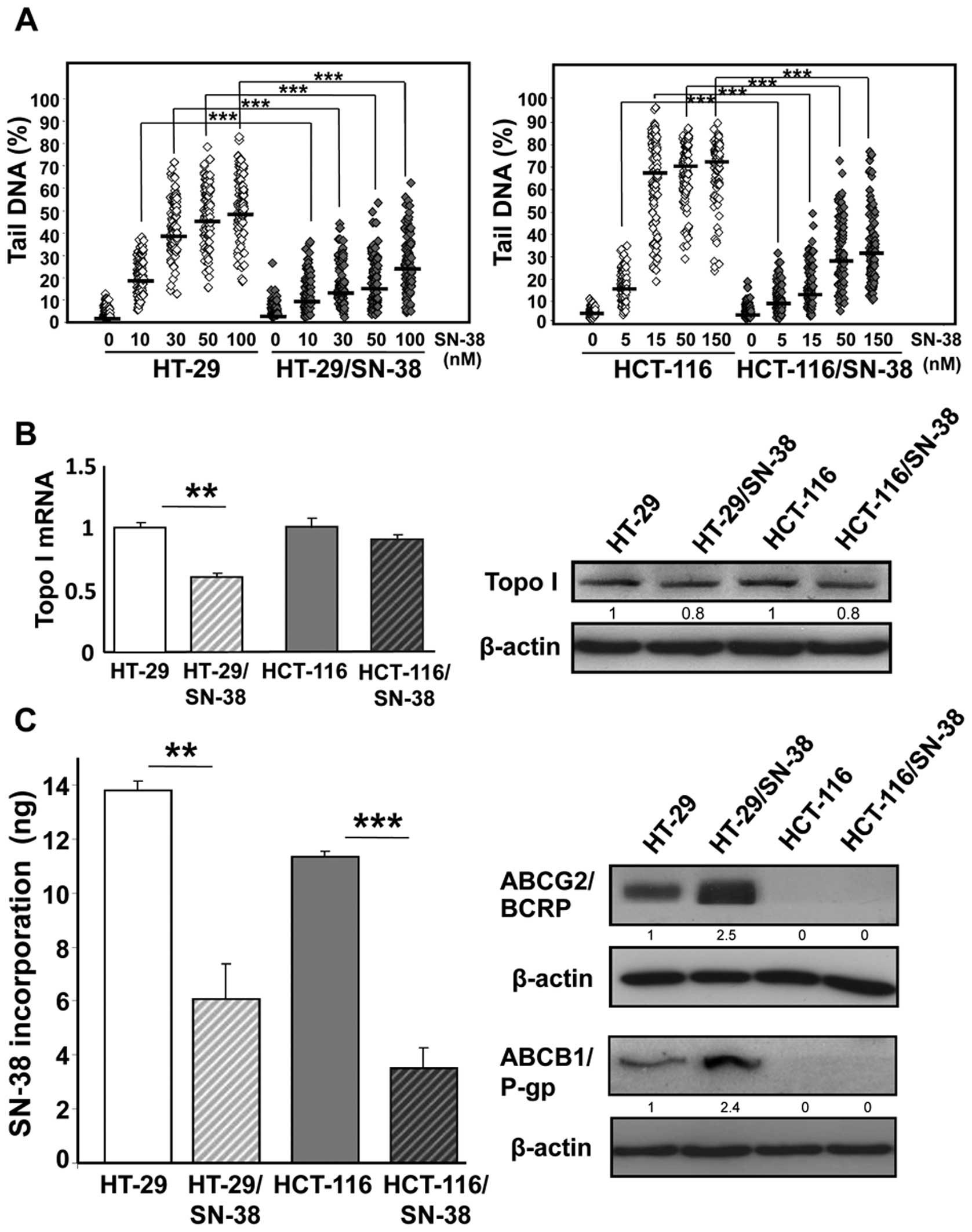
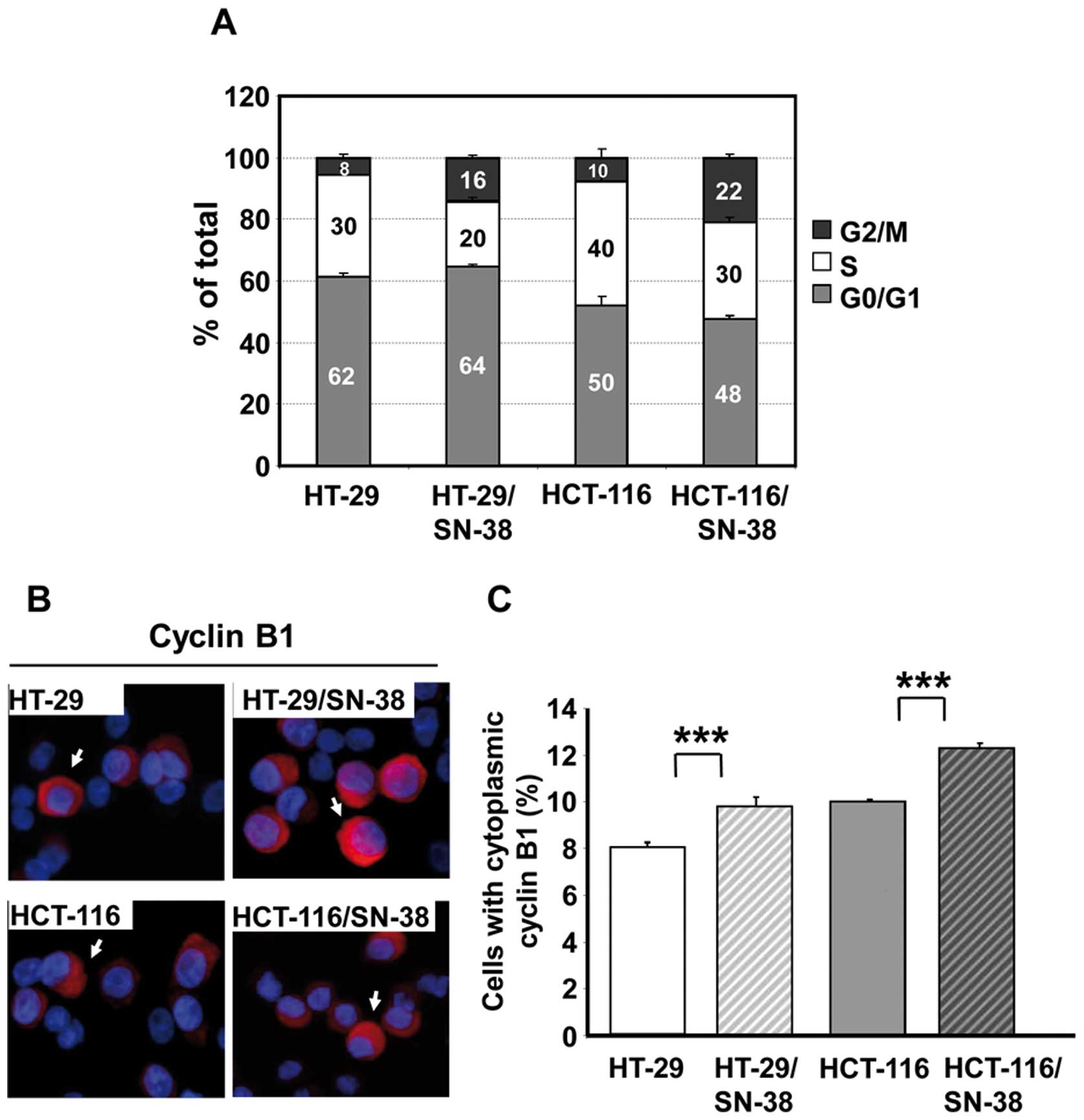
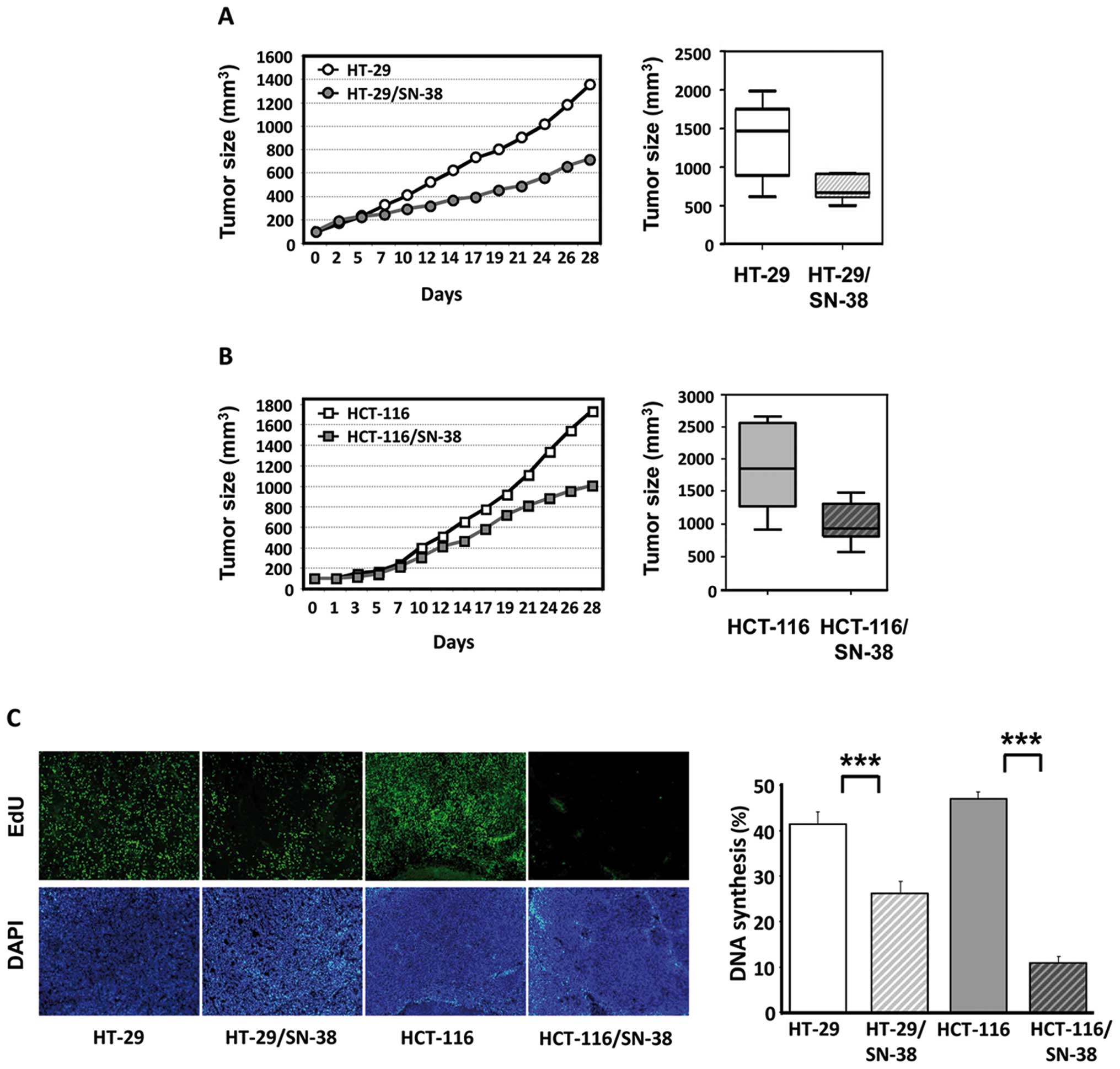
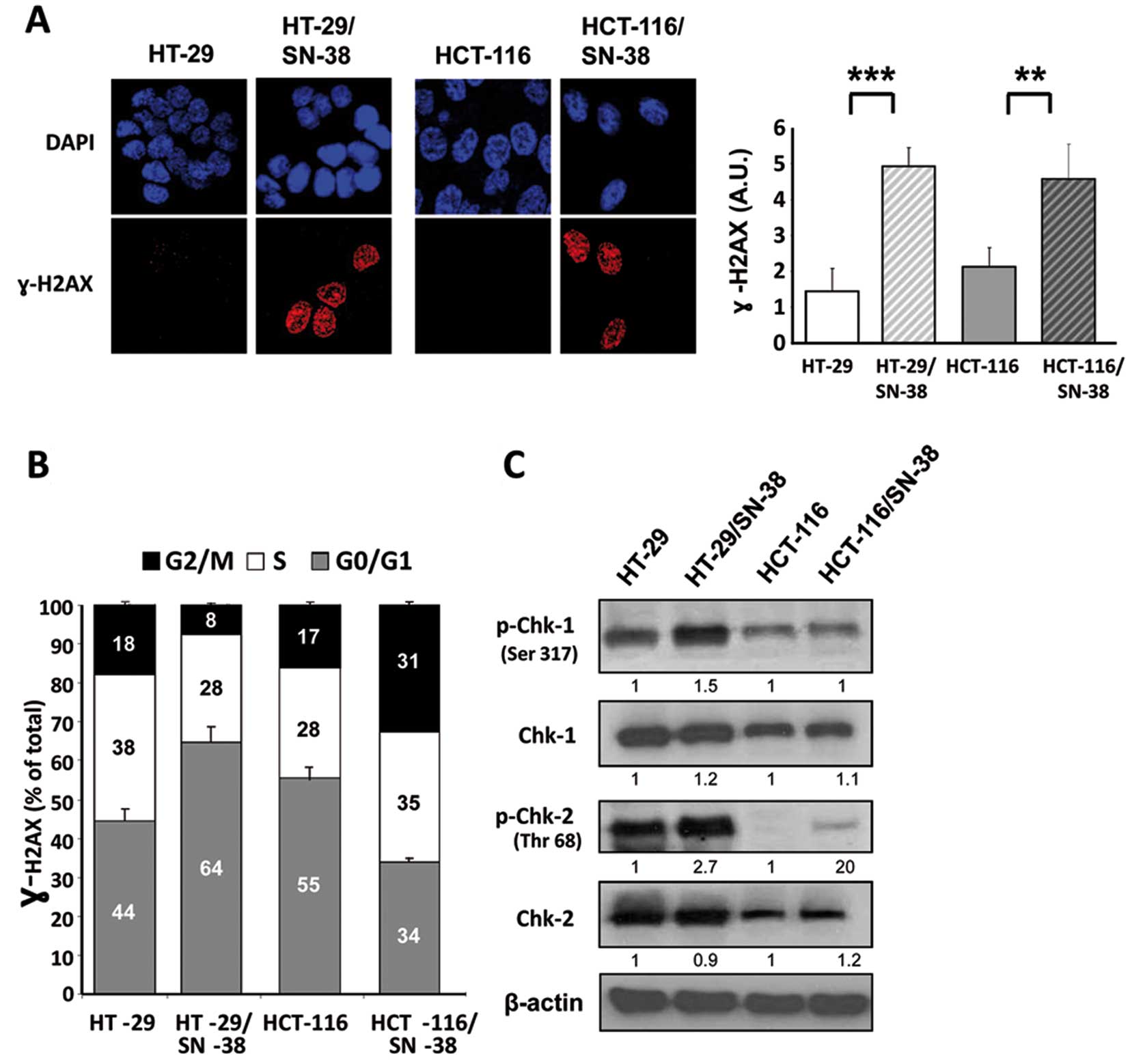
|
1.
|
Hsiang YH, Lihou MG and Liu LF: Arrest of
replication forks by drug-stabilized topoisomerase I-DNA cleavable
complexes as a mechanism of cell killing by camptothecin. Cancer
Res. 18:5077–5082. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Larsen AK, Gilbert C, Chyzak G, Plisov SY,
Naguibneva I, Lavergne O, Lesueur-Ginot L and Bigg DC: Unusual
potency of BN 80915, a novel fluorinated E-ring modified
camptothecin, toward human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res.
7:2961–2967. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Wu J, Yin MB, Hapke G, Tóth K and Rustum
YM: Induction of biphasic DNA double-strand breaks and activation
of multiple repair protein complexes by DNA topoisomerase I drug
7-ethyl-10-hydroxy-camptothecin. Mol Pharmacol. 4:742–748. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Regairaz M, Zhang YW, Fu H, Agama KK, Tata
N, Agrawal S, Aladjem MI and Pommier Y: Mus81-mediated DNA cleavage
resolves replication forks stalled by topoisomerase I-DNA
complexes. J Cell Biol. 195:739–749. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Horwitz SB and Horwitz MS: Effects of
camptothecin on the breakage and repair of DNA during the cell
cycle. Cancer Res. 33:2834–2836. 1973.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Cheng MF, Chatterjee S and Berger NA:
Schedule-dependent cytotoxicity of topotecan alone and in
combination chemotherapy regimens. Oncol Res. 6:269–279.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Huang X, Traganos F and Darzynkiewicz Z:
DNA damage induced by DNA topoisomerase I- and topoisomerase
II-inhibitors detected by histone H2AX phosphorylation in relation
to the cell cycle phase and apoptosis. Cell Cycle. 6:614–619.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Saltz LB, Cox JV, Blanke C, Rosen LS,
Fehrenbacher L, Moore MJ, Maroun JA, Ackland SP, Locker PK, Pirotta
N, Elfring GL and Miller LL: Irinotecan plus fluorouracil and
leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. Irinotecan Study Group
N Engl J Med. 13:905–914. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD,
Navarro M, James RD, Karasek P, Jandik P, Iveson T, Carmichael J,
Alakl M, Gruia G, Awad L and Rougier P: Irinotecan combined with
fluorouracil compared with fluorouracil alone as first-line
treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: a multicentre
randomised trial. Lancet. 9209:1041–1047. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Lengauer C, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B:
Genetic instabilities in human cancers. Nature. 6712:643–649. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network: Comprehensive
molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer.
Nature. 487:330–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Jiricny J: The multifaceted
mismatch-repair system. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 5:335–346. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Jacob S, Aguado M, Fallik D and Praz F:
The role of the DNA mismatch repair system in the cytotoxicity of
the topoisomerase inhibitors camptothecin and etoposide to human
colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 17:6555–6562. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Fallik D, Borrini F, Boige V, Viguier J,
Jacob S, Miquel C, Sabourin JC, Ducreux M and Praz F:
Microsatellite instability is a predictive factor of the tumor
response to irinotecan in patients with advanced colorectal cancer.
Cancer Res. 18:5738–5744. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Kanzawa F, Sugimoto Y, Minato K, Kasahara
K, Bungo M, Nakagawa K, Fujiwara Y, Liu LF and Saijo N:
Establishment of a camptothecin analogue (CPT-11)-resistant cell
line of human non-small cell lung cancer: characterization and
mechanism of resistance. Cancer Res. 18:5919–5924. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Maliepaard M, van Gastelen MA, de Jong LA,
Pluim D, van Waardenburg RC, Ruevekamp-Helmers MC, Floot BG and
Schellens JH: Overexpression of the BCRP/MXR/ABCP gene in a
topotecan-selected ovarian tumor cell line. Cancer Res.
18:4559–4563. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Kawabata S, Oka M, Shiozawa K, Tsukamoto
K, Nakatomi K, Soda H, Fukuda M, Ikegami Y, Sugahara K, Yamada Y,
Kamihira S, Doyle LA, Ross DD and Kohno S: Breast cancer resistance
protein directly confers SN-38 resistance of lung cancer cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 5:1216–1223. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Rasheed ZA and Rubin EH: Mechanisms of
resistance to topoisomerase I-targeting drugs. Oncogene.
22:7296–7304. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Boyer J, McLean EG, Aroori S, Wilson P,
McCulla A, Carey PD, Longley DB and Johnston PG: Characterization
of p53 wild-type and null isogenic colorectal cancer cell lines
resistant to 5-fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan. Clin
Cancer Res. 6:2158–2167. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Arakawa Y, Suzuki H, Saito S and Yamada H:
Novel missense mutation of the DNA topoisomerase I gene in
SN-38-resistant DLD-1 cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:502–508. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Takara K, Kitada N, Yoshikawa E, Yamamoto
K, Horibe S, Sakaeda T, Nishiguchi K, Ohnishi N and Yokoyama T:
Molecular changes to HeLa cells on continuous exposure to SN-38, an
active metabolite of irinotecan hydrochloride. Cancer Lett.
1:88–96. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Tagen M, Zhuang Y, Zhang F, Harstead KE,
Shen J, Schaiquevich P, Fraga CH, Panetta JC, Waters CM and Stewart
CF: P-glycoprotein, but not multidrug resistance protein 4, plays a
role in the systemic clearance of irinotecan and SN-38 in mice.
Drug Metab Lett. 4:195–201. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Pastorino F, Loi M, Sapra P, Becherini P,
Cilli M, Emionite L, Ribatti D, Greenberger LM, Horak ID and
Ponzoni M: Tumor regression and curability of preclinical
neuroblastoma models by PEGylated SN38 (EZN-2208), a novel
topoisomerase I inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res. 19:4809–4821. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Waterhouse DN, Yapp D, Verreault M,
Anantha M, Sutherland B and Bally MB: Lipid-based nanoformulation
of irinotecan: dual mechanism of action allows for combination
chemo/angiogenic therapy. Nanomedicine (Lond). 9:1645–1654. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Petitprez A and Larsen AK: Irinotecan
resistance is accompanied by upregulation of EGFR and Src signaling
in human cancer models. Curr Pharm Des. Sep 7–2012.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
26.
|
Poindessous V, Koeppel F, Raymond E,
Comisso M, Waters S and Larsen AK: Marked activity of irofulven
(MGI-114) toward human carcinoma cells: comparison with cisplatin
and ecteinascidin (ET-743). Clin Cancer Res. 9:2817–2825.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Lemke K, Poindessous V, Skladanowski A and
Larsen AK: The antitumor triazoloacridone C-1305 is a topoisomerase
II poison with unusual properties. Mol Pharmacol. 4:1035–1042.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Poindessous V, Koeppel F, Raymond E,
Cvitkovic E, Waters SJ and Larsen AK: Enhanced antitumor activity
of irofulven in combination with 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin in
human colon and ovarian carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 23:1347–1355.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Larsen AK, Paoletti J, Belehradek J Jr and
Paoletti C: Uptake, cytofluorescence, and cytotoxicity of
oxazolopyridocarbazoles (amino acid-ellipticine conjugates) in
murine sarcoma cells. Cancer Res. 46:5236–5240. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Léonce S, Kraus-Berthier L, Golsteyn RM,
David-Cordonnier MH, Tardy C, Lansiaux A, Poindessous V, Larsen AK
and Pierré A: Generation of replication-dependent double-strand
breaks by the novel N2-G-alkylator S23906-1. Cancer Res.
14:7203–7210. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Rocca CJ, Poindessous V, Soares DG,
Ouadrani KE, Sarasin A, Guérin E, de Gramont A, Henriques JA,
Escargueil AE and Larsen AK: The NER proteins XPC and CSB, but not
ERCC1, regulate the sensitivity to the novel DNA binder S23906:
implications for recognition and repair of antitumor alkylators.
Biochem Pharmacol. 3:335–343. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Pencreach E, Guérin E, Nicolet C,
Lelong-Rebel I, Voegeli AC, Oudet P, Larsen AK, Gaub MP and Guenot
D: Marked activity of irinotecan and rapamycin combination toward
colon cancer cells in vivo and in vitro is mediated through
cooperative modulation of the mammalian target of
rapamycin/hypoxiainducible factor-1alpha axis. Clin Cancer Res.
15:1297–1307. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33.
|
Guérin E, Raffelsberger W, Pencreach E,
Maier A, Neuville A, Schneider A, Bachellier P, Rohr S, Petitprez
A, Poch O, Moras D, Oudet P, Larsen AK, Gaub MP and Guenot D: In
vivo topoisomerase I inhibition attenuates the expression of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1α target genes and decreases tumor
angiogenesis. Mol Med. 18:83–94. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Gil-Delgado MA, Bastian G, Guinet F, Spano
JP, Taillibert S, Rocher MA, Castaing D, Adam R, Urien S, Bismuth H
and Khayat D: Oxaliplatin plus irinotecan and FU-FOL combination
and pharmacokinetic analysis in advanced colorectal cancer
patients. Am J Clin Oncol. 27:294–298. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Escargueil AE, Poindessous V, Soares DG,
Sarasin A, Cook PR and Larsen AK: Influence of irofulven, a
transcription-coupled repair-specific antitumor agent, on RNA
polymerase activity, stability and dynamics in living mammalian
cells. J Cell Sci. 121:1275–1283. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Soares DG, Battistella A, Rocca CJ, Matuo
R, Henriques JA, Larsen AK and Escargueil AE: Ataxia telangiectasia
mutated-and Rad3-related kinase drives both the early and the late
DNA-damage response to the monofunctional antitumour alkylator
S23906. Biochem J. 1:63–73. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37.
|
Skladanowski A, Côme MG, Sabisz M,
Escargueil AE and Larsen AK: Down-regulation of DNA topoisomerase
II alpha leads to prolonged cell cycle transit in G2 and early M
phases and increased survival to microtubule-interacting agents.
Mol Pharmacol. 68:625–634. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Skladanowski A, Bozko P, Sabisz M and
Larsen AK: Dual inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling and the DNA damage
checkpoint in p53-deficient cells with strong survival signaling:
implications for cancer therapy. Cell Cycle. 18:2268–2275. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Soares DG, Escargueil AE, Poindessous V,
Sarasin A, de Gramont A, Bonatto D, Henriques JA and Larsen AK:
Replication and homologous recombination repair regulate DNA
double-strand break formation by the antitumor alkylator
ecteinascidin 743. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 32:13062–13067. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Soares DG, Machado MS, Rocca CJ,
Poindessous V, Ouaret D, Sarasin A, Galmarini CM, Henriques JA,
Escargueil AE and Larsen AK: Trabectedin and its C subunit modified
analogue PM01183 attenuate nucleotide excision repair and show
activity toward platinum-resistant cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
8:1481–1489. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41.
|
Poindessous V, Ouaret D, El Ouadrani K,
Battistella A, Mégalophonos VF, Kamsu-Kom N, Petitprez A,
Escargueil AE, Boudou P, Dumont S, Cervera P, Fléjou JF, André T,
Tournigand C, Chibaudel B, de Gramont A and Larsen AK: EGFR- and
VEGF(R)-targeted small molecules show synergistic activity in
colorectal cancer models refractory to combinations of monoclonal
antibodies. Clin Cancer Res. 20:6522–6530. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Godard T, Deslandes E, Sichel F, Poul JM
and Gauduchon P: Detection of topoisomerase inhibitor-induced DNA
strand breaks and apoptosis by the alkaline comet assay. Mutat
Resgg. 1–2:47–56. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Hans F and Dimitrov S: Histone H3
phosphorylation and cell division. Oncogene. 20:3021–3027. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Pines J and Hunter T: Cyclin-dependent
kinases: a new cell cycle motif? Trends Cell Biol. 5:117–121. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Ookata K, Hisanaga S, Okano T, Tachibana K
and Kishimoto T: Relocation and distinct subcellular localization
of p34cdc2-cyclin B complex at meiosis reinitiation in starfish
oocytes. EMBO J. 5:1763–1772. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Escargueil AE, Plisov SY, Skladanowski A,
Borgne A, Meijer L, Gorbsky GJ and Larsen AK: Recruitment of cdc2
kinase by DNA topoisomerase II is coupled to chromatin remodeling.
FASEB J. 12:2288–2290. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Bartkova J, Horejsí Z, Koed K, Krämer A,
Tort F, Zieger K, Guldberg P, Sehested M, Nesland JM, Lukas C,
Ørntoft T, Lukas J and Bartek J: DNA damage response as a candidate
anti-cancer barrier in early human tumorigenesis. Nature.
7035:864–870. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Gorgoulis VG, Vassiliou LV, Karakaidos P,
Zacharatos P, Kotsinas A, Liloglou T, Venere M, Ditullio RA Jr,
Kastrinakis NG, Levy B, Kletsas D, Yoneta A, Herlyn M, Kittas C and
Halazonetis TD: Activation of the DNA damage checkpoint and genomic
instability in human precancerous lesions. Nature. 434:907–913.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Jazayeri A, Falck J, Lukas C, Bartek J,
Smith GC, Lukas J and Jackson SP: ATM- and cell cycle-dependent
regulation of ATR in response to DNA double-strand breaks. Nat Cell
Biol. 8:37–45. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Reinhardt HC and Yaffe MB: Kinases that
control the cell cycle in response to DNA damage: Chk1, Chk2 and
MK2. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:245–255. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Soza S, Leva V, Vago R, Ferrari G, Mazzini
G, Biamonti G and Montecucco A: DNA ligase I deficiency leads to
replication-dependent DNA damage and impacts cell morphology
without blocking cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol.
29:2032–2041. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Li J and Stern DF: Regulation of CHK2 by
DNA-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 280:12041–12050. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|