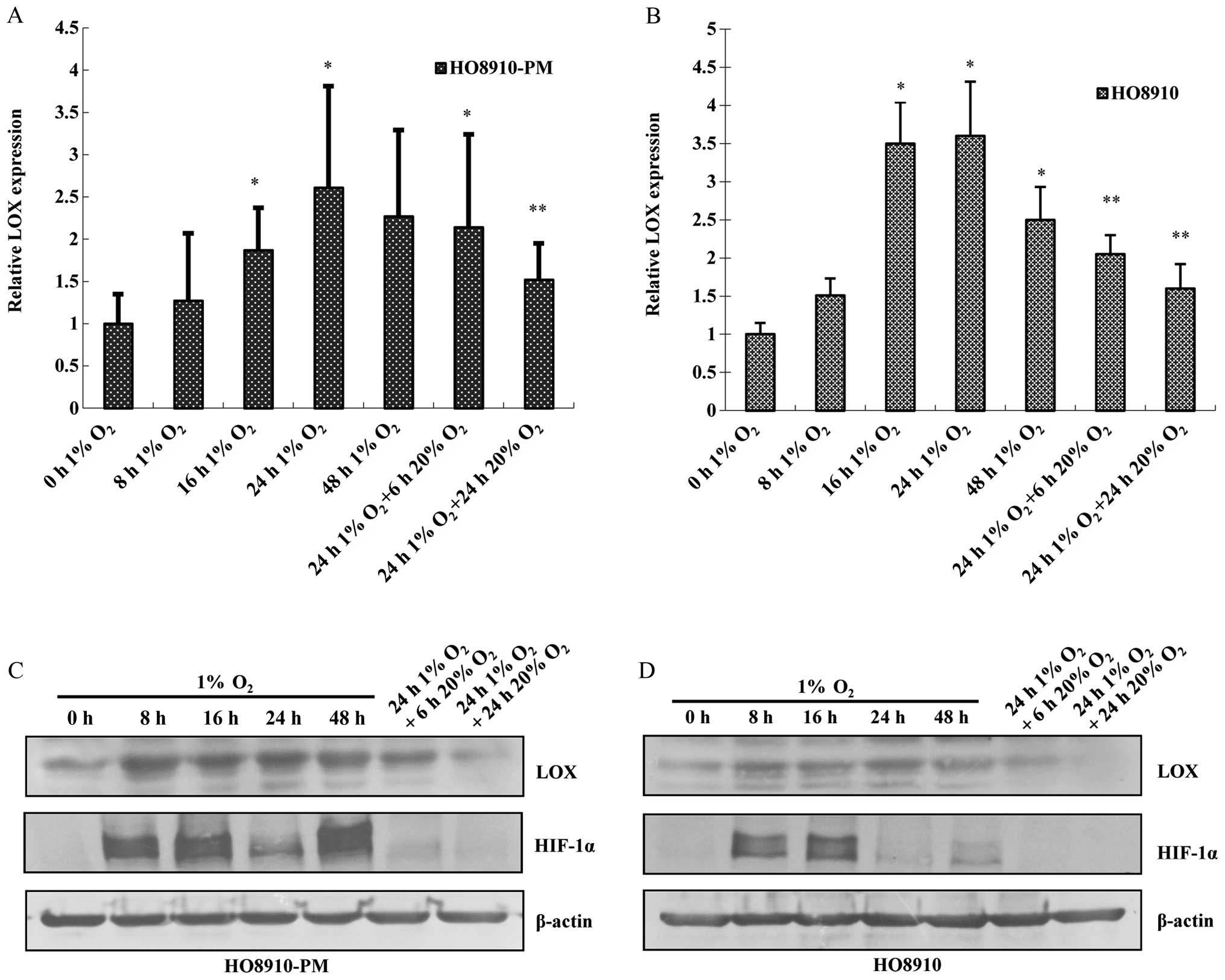
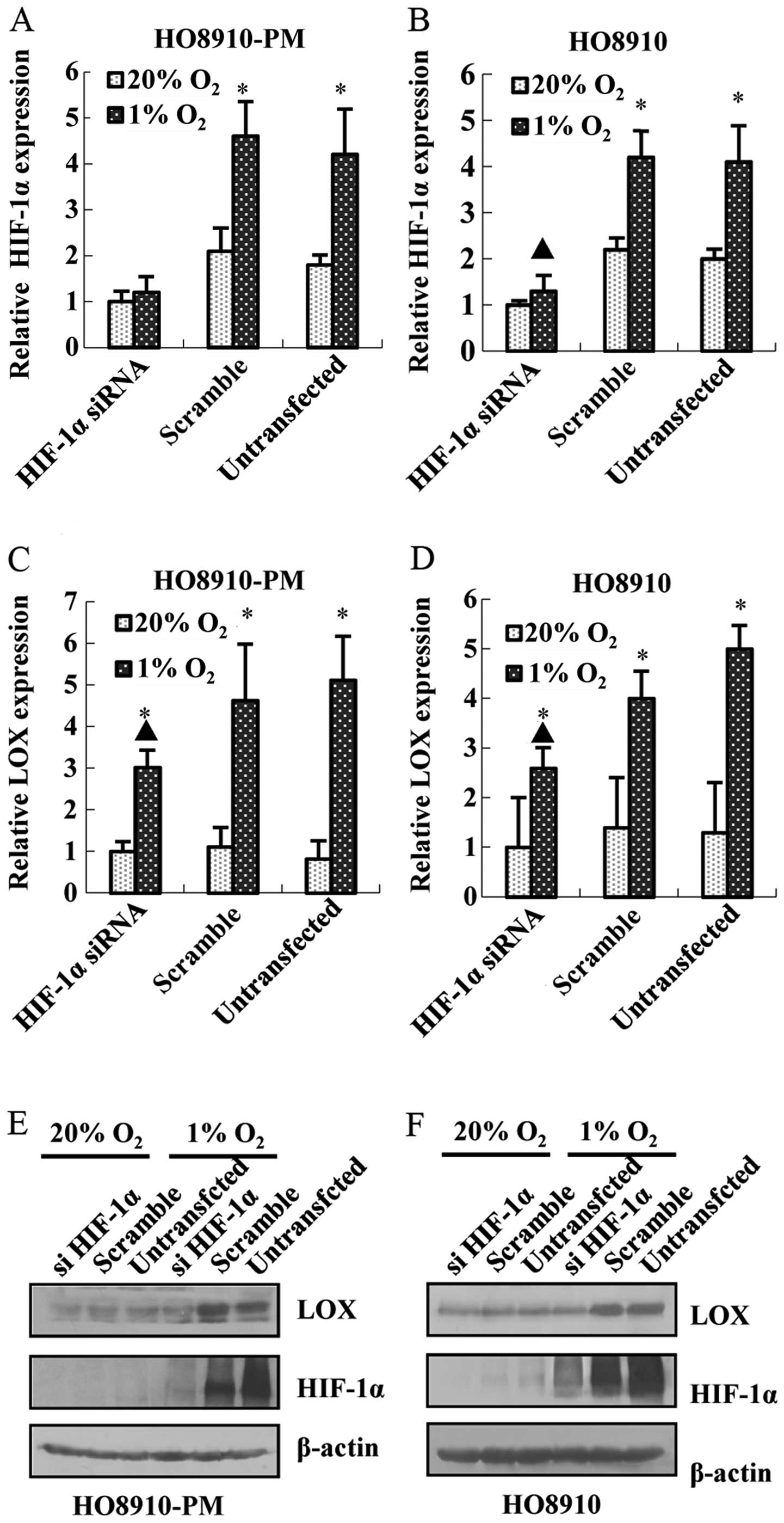
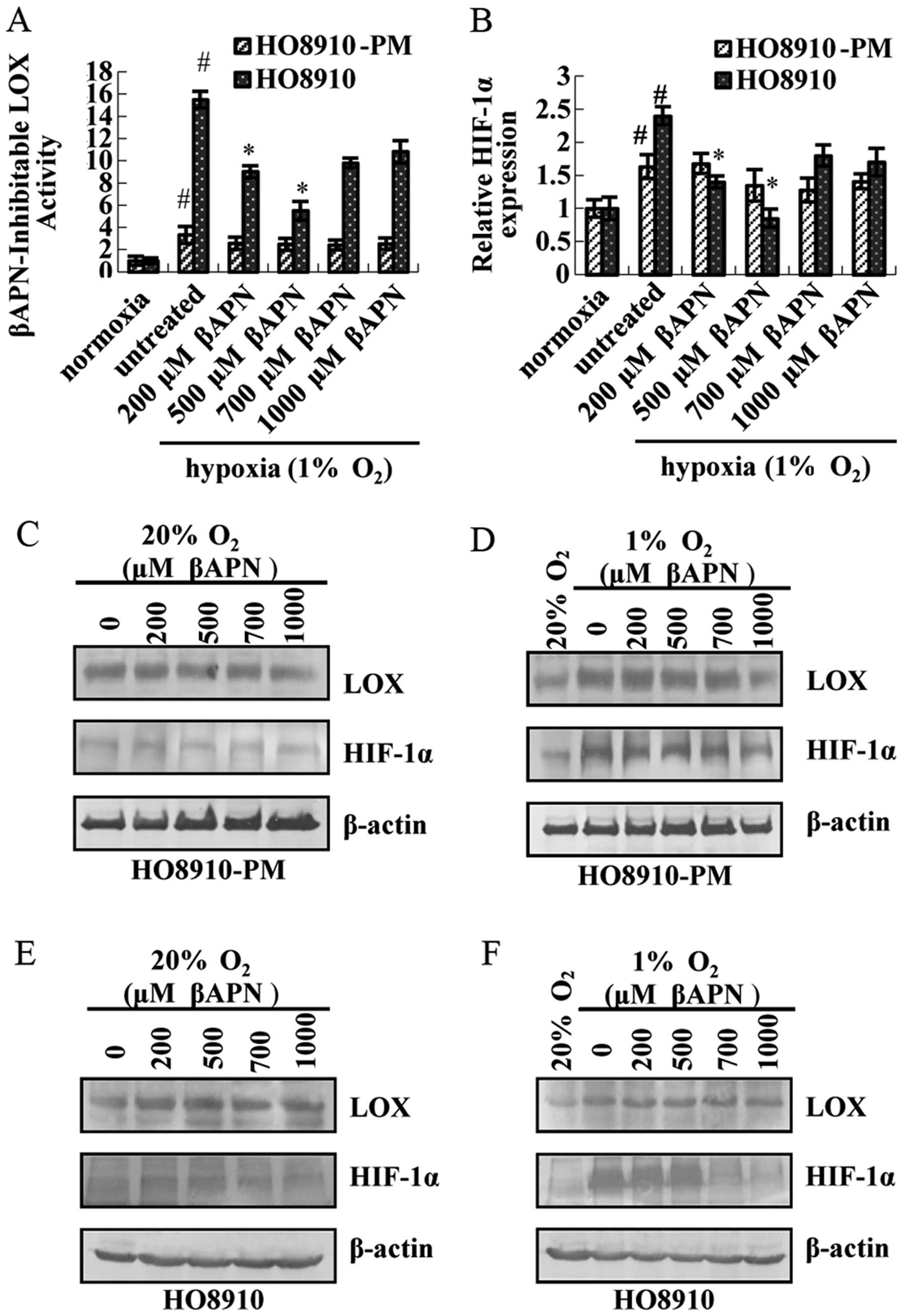
|
1.
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J
and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 57:43–66.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Rustin G, van der Burg M, Griffin C, Qian
W and Swart AM: Early versus delayed treatment of relapsed ovarian
cancer. Lancet. 377:380–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Vergara D, Merlot B, Lucot JP, Collinet P,
Vinatier D, Fournier I and Salzet M: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 291:59–66. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Ricciardelli C and Oehler MK: Diverse
molecular pathways in ovarian cancer and their clinical
significance. Maturitas. 62:270–275. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Choi JY, Jang YS, Min SY and Song JY:
Overexpression of MMP-9 and HIF-1α in breast cancer cells under
hypoxic conditions. J Breast Cancer. 14:88–95. 2011.
|
|
7.
|
Dayan F, Mazure NM, Brahimi-Horn MC and
Pouyssegur J: A dialogue between the hypoxia-inducible factor and
the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Microenviron. 1:53–68. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Allen M and Louise Jones J: Jekyll and
Hyde: the role of the microenvironment on the progression of
cancer. J Pathol. 223:162–176. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Semenza GL: Defining the role of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics.
Oncogene. 29:625–634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Chen CL, Chu JS, Su WC, Huang SC and Lee
WY: Hypoxia and metabolic phenotypes during breast carcinogenesis:
expression of HIF-1alpha, GLUT1, and CAIX. Virchows Arch.
457:53–61. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Lucero HA and Kagan HM: Lysyl oxidase: an
oxidative enzyme and effector of cell function. Cell Mol Life Sci.
63:2304–2316. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Payne SL, Hendrix MJ and Kirschmann DA:
Paradoxical roles for lysyl oxidases in cancer - a prospect. J Cell
Biochem. 101:1338–1354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Postovit LM, Abbott DE, Payne SL, Wheaton
WW, Margaryan NV, Sullivan R, Jansen MK, Csiszar K, Hendrix MJ and
Kirschmann DA: Hypoxia/reoxygenation: a dynamic regulator of lysyl
oxidase-facilitated breast cancer migration. J Cell Biochem.
103:1369–1378. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Nagaraja GM, Othman M, Fox BP, Alsaber R,
Pellegrino CM, Zeng Y, Khanna R, Tamburini P, Swaroop A and Kandpal
RP: Gene expression signatures and biomarkers of noninvasive and
invasive breast cancer cells: comprehensive profiles by
representational difference analysis, microarrays and proteomics.
Oncogene. 25:2328–2338. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Nicolau M,
Dornhofer N, Kong C, Le QT, Chi JT, Jeffrey SS and Giaccia AJ:
Lysyl oxidase is essential for hypoxia-induced metastasis. Nature.
440:1222–1226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Payne SL, Fogelgren B, Hess AR, Seftor EA,
Wiley EL, Fong SF, Csiszar K, Hendrix MJ and Kirschmann DA: Lysyl
oxidase regulates breast cancer cell migration and adhesion through
a hydrogen peroxide-mediated mechanism. Cancer Res. 65:11429–11436.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Polgar N, Fogelgren B, Shipley JM and
Csiszar K: Lysyl oxidase interacts with hormone placental lactogen
and synergistically promotes breast epithelial cell proliferation
and migration. J Biol Chem. 282:3262–3272. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Fogelgren B, Polgar N, Szauter KM,
Ujfaludi Z, Laczko R, Fong KS and Csiszar K: Cellular fibronectin
binds to lysyl oxidase with high affinity and is critical for its
proteolytic activation. J Biol Chem. 280:24690–24697. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Bouez C, Reynaud C, Noblesse E, Thepot A,
Gleyzal C, Kanitakis J, Perrier E, Damour O and Sommer P: The lysyl
oxidase LOX is absent in basal and squamous cell carcinomas and its
knockdown induces an invading phenotype in a skin equivalent model.
Clin Cancer Res. 12:1463–1469. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21.
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22.
|
Cassavaugh J and Lounsbury KM:
Hypoxia-mediated biological control. J Cell Biochem. 112:735–744.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Gort EH, Groot AJ, van der Wall E, van
Diest PJ and Vooijs MA: Hypoxic regulation of metastasis via
hypoxia-inducible factors. Curr Mol Med. 8:60–67. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Rofstad EK: Microenvironment-induced
cancer metastasis. Int J Radiat Biol. 76:589–605. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Ruan K, Song G and Ouyang G: Role of
hypoxia in the hallmarks of human cancer. J Cell Biochem.
107:1053–1062. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Pez F, Dayan F, Durivault J, Kaniewski B,
Aimond G, Le Provost GS, Deux B, Clezardin P, Sommer P, Pouyssegur
J and Reynaud C: The HIF-1-inducible lysyl oxidase activates HIF-1
via the Akt pathway in a positive regulation loop and synergizes
with HIF-1 in promoting tumor cell growth. Cancer Res.
71:1647–1657. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Denko NC, Fontana LA, Hudson KM, Sutphin
PD, Raychaudhuri S, Altman R and Giaccia AJ: Investigating hypoxic
tumor physiology through gene expression patterns. Oncogene.
22:5907–5914. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Choi YK, Kim CK, Lee H, Jeoung D, Ha KS,
Kwon YG, Kim KW and Kim YM: Carbon monoxide promotes VEGF
expression by increasing HIF-1alpha protein level via two distinct
mechanisms, translational activation and stabilization of
HIF-1alpha protein. J Biol Chem. 285:32116–32125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|