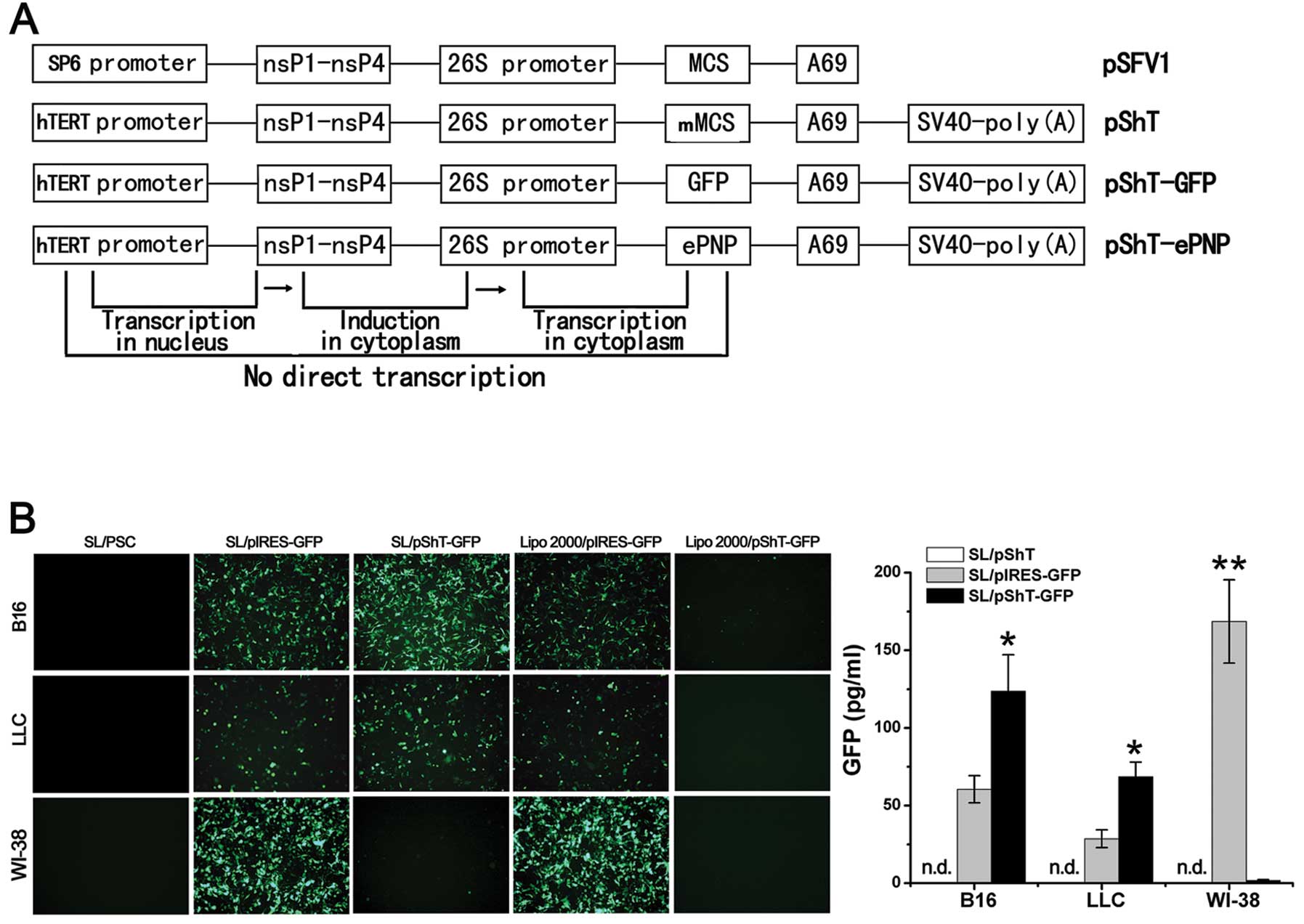
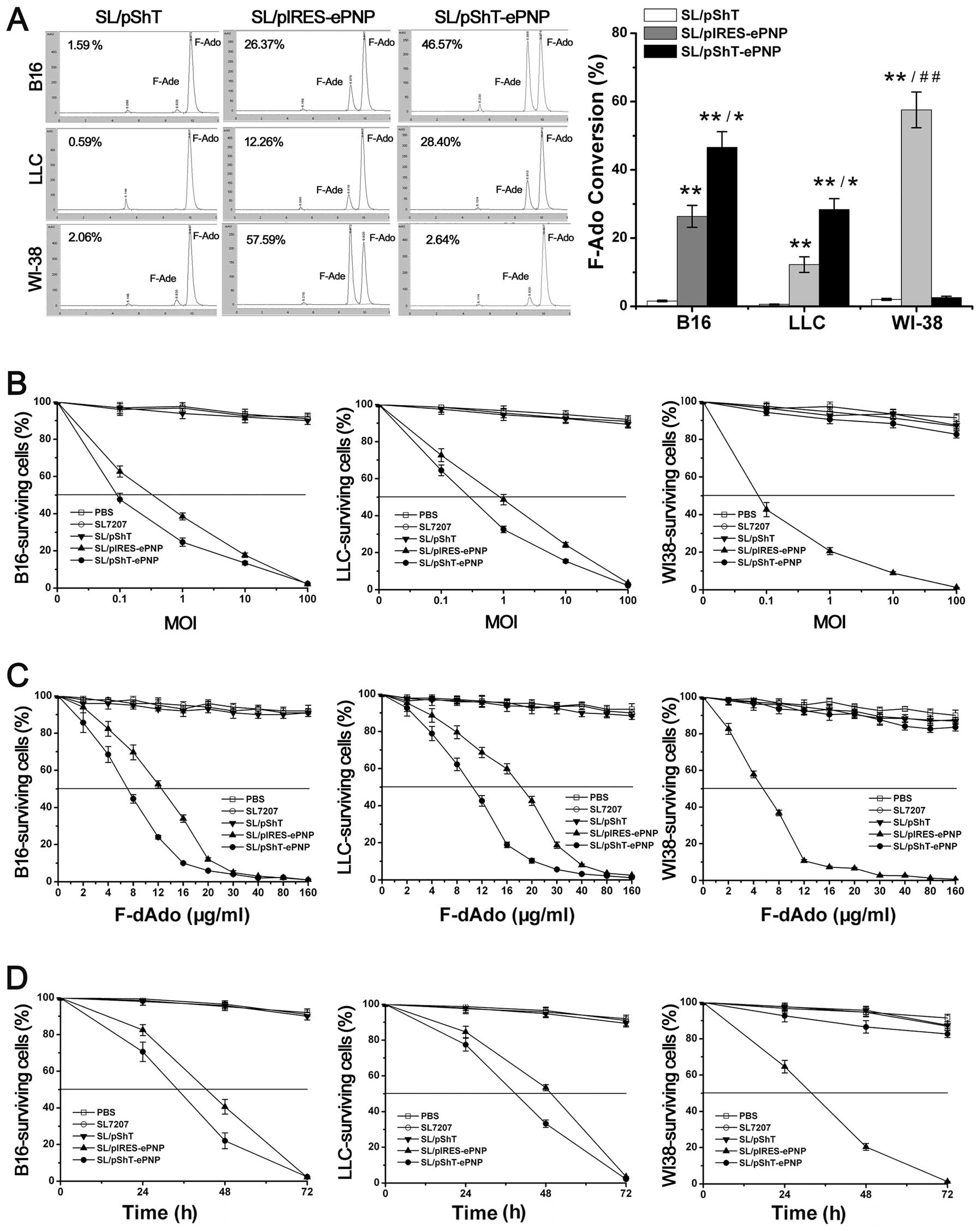
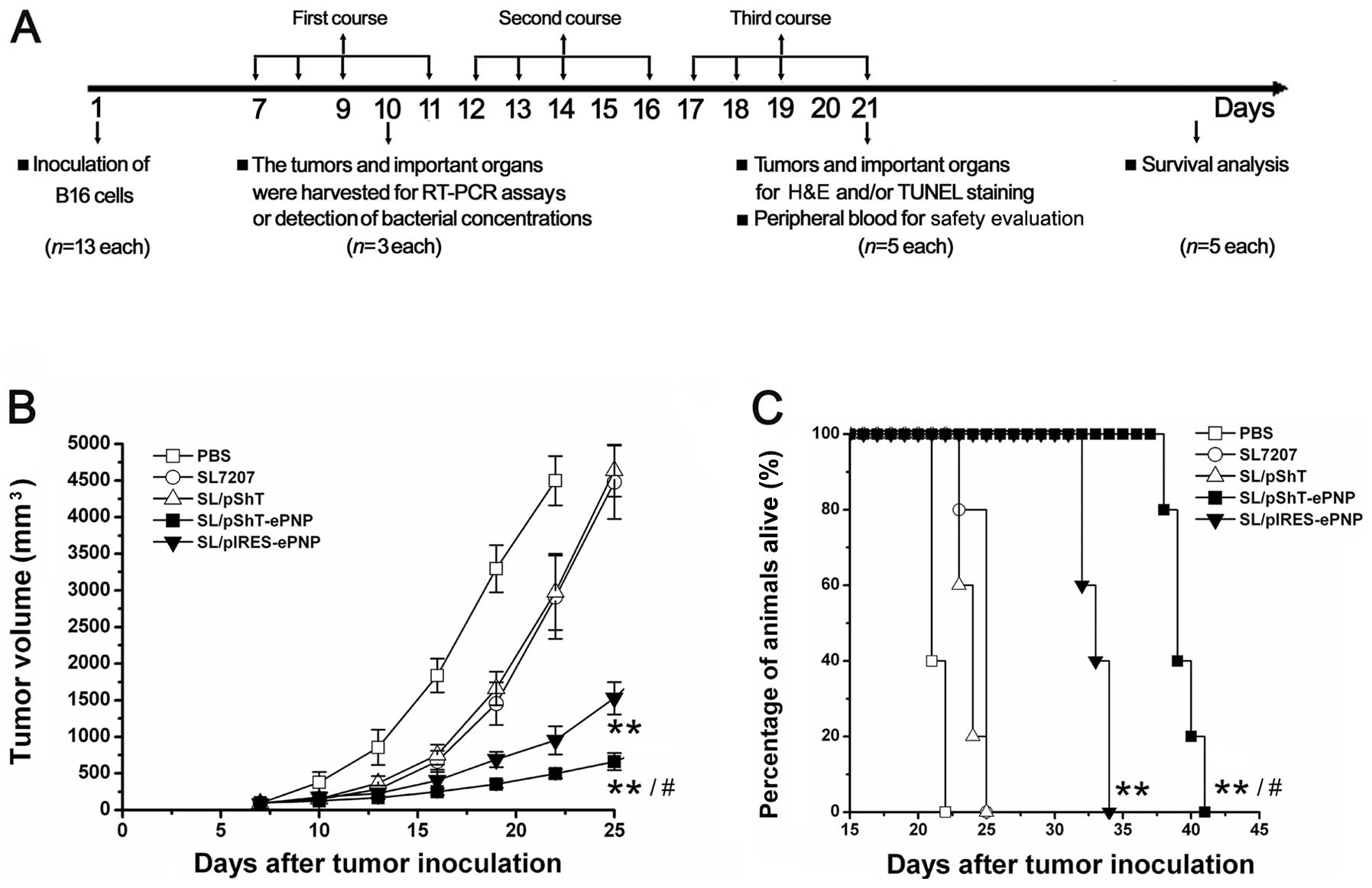
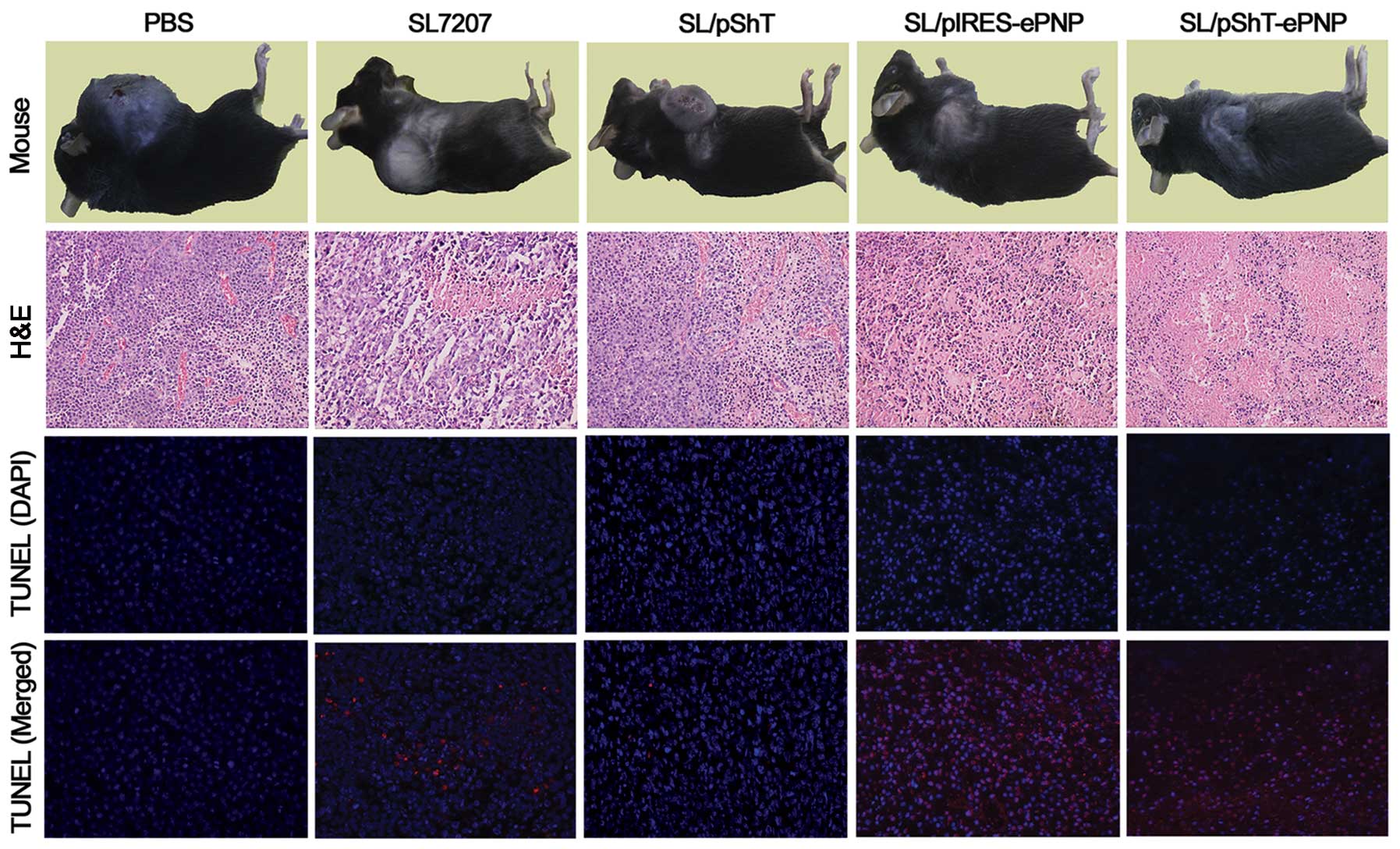
|
1
|
Afshar S, Olafsen T, Wu AM and Morrison
SL: Characterization of an engineered human purine nucleoside
phosphorylase fused to an anti-her2/neu single chain Fv for use in
ADEPT. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:1472009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fukazawa T, Matsuoka J, Yamatsuji T, Maeda
Y, Durbin ML and Naomoto Y: Adenovirus-mediated cancer gene therapy
and virotherapy (Review). Int J Mol Med. 25:3–10. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gu J, Kagawa S, Takakura M, Kyo S, Inoue
M, Roth JA and Fang B: Tumor-specific transgene expression from the
human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter enables targeting
of the therapeutic effects of the Bax gene to cancers. Cancer Res.
60:5359–5364. 2000.
|
|
4
|
Fakhoury J, Nimmo GA and Autexier C:
Harnessing telomerase in cancer therapeutics. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 7:475–483. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Song JS: Activity of the human telomerase
catalytic subunit (hTERT) gene promoter could be increased by the
SV40 enhancer. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 68:1634–1639. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liljeström P and Garoff H: A new
generation of animal cell expression vectors based on the Semliki
Forest virus replicon. Biotechnology. 9:1356–1361. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Diciommo DP and Bremner R: Rapid, high
level protein production using DNA-based Semliki Forest virus
vectors. J Biol Chem. 273:18060–18066. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kohno A, Emi N, Kasai M, Tanimoto M and
Saito H: Semliki Forest virus-based DNA expression vector:
transient protein production followed by cell death. Gene Ther.
5:415–418. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Quetglas JI, Ruiz-Guillen M, Aranda A,
Cassales E, Bezunartea J and Smerdou C: Alphavirus vectors for
cancer therapy. Virus Res. 153:179–196. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang WL, Xu HL, Lu RJ and Ruan L: A
comparative study on SFV-based DNA vaccine and the conventional DNA
vaccine. Chin J Virol. 18:325–331. 2002.
|
|
11
|
Juárez-Rodríguez MD, Arteaga-Cortés LT,
Kader R, Curtiss R III and Clark-Curtiss JE: Live attenuated
Salmonella vaccines against Mycobacterium
tuberculosis with antigen delivery via the type III secretion
system. Infect Immun. 80:798–814. 2012.
|
|
12
|
Hegazy WA and Hensel M: Salmonella
enterica as a vaccine carrier. Future Microbiol. 7:111–127.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Loessner H and Weiss S: Bacteria-mediated
DNA transfer in gene therapy and vaccination. Expert Opin Biol
Ther. 4:157–168. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jarosz M, Jazowiecka-Rakus J, Cichoń T, et
al: Therapeutic antitumor potential of endoglin-based DNA vaccine
combined with immunomodulatory agents. Gene Ther. 12:1038–1046.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moreno M, Kramer MG, Yim L and Chabalgoity
JA: Salmonella as live Trojan horse for vaccine development and
cancer gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 10:56–76. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sorscher EJ, Peng S, Bebok Z, Allan PW,
Bennett LL Jr and Parker WB: Tumor cell bystander killing in
colonic carcinoma utilizing the E. coli Deo D gene and generation
of toxic purines. Gene Ther. 1:233–238. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:551983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Parker WB, Allan PW, Hassan AE, Secrist JA
III, Sorscher EJ and Waud WR: Antitumor activity of
2-fluoro-2’-deoxyadenosine against tumors that express
Escherichia coli purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Cancer
Gene Ther. 10:23–29. 2003.
|
|
19
|
Wang W, Jin B, Li W, et al: Targeted
antitumor effect induced by hTERT promoter mediated ODC antisense
adenovirus. Mol Biol Rep. 37:3239–3247. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hashimoto Y, Tazawa H, Teraishi F, et al:
The hTERT promoter enhances the antitumor activity of an oncolytic
adenovirus under a hypoxic microenvironment. PLoS One.
7:e392922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang J, Wild J, Bieler K and Graf M:
Comparative study of expression and humoral immunogenicity of HIV-1
group specific antigen Pr55∼(gag) by conventional plasmid vectors
versus semliki forest virus-derived vectors. Chin J Virol.
18:529–536. 2002.
|
|
22
|
Brown A, Hormaeche CE, Demarco de
Hormaeche R, Winther M, Dougan G, Maskell DJ and Stocker BA: An
attenuated aroA Salmonella typhimurium vaccine elicits
humoral and cellular immunity to cloned beta-galactosidase in mice.
J Infect Dis. 155:86–92. 1987.
|
|
23
|
Hoiseth SK and Stocker BA:
Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent
and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 291:238–239.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Darji A, Guzman CA, Gerstel B, et al: Oral
somatic transgene vaccination using attenuated S.
typhimurium. Cell. 91:765–775. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zeng S, Zhang J, Zhang J, et al:
Suppression of murine melanoma growth by a vaccine of attenuated
Salmonella carrying heat shock protein 70 and Herpes simplex
virus-thymidine kinase genes. Oncol Rep. 27:798–806.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fu W, Lan H, Li S, Han X, Gao T and Ren D:
Synergistic antitumor efficacy of suicide/ePNP gene and
6-methylpurine 2′-deoxyriboside via Salmonella against murine
tumors. Cancer Gene Ther. 15:474–484. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leitner WW, Hwang LN, deVeer MJ, et al:
Alphavirus-based DNA vaccine breaks immunological tolerance by
activating innate antiviral pathways. Nat Med. 9:33–39. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gil J, Alcami J and Esteban M: Induction
of apoptosis by double-stranded-RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR)
involves the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation
factor 2 and NF-kappaB. Mol Cell Biol. 19:4653–4663. 1999.
|
|
29
|
Xie X, Guo J, Kong Y, et al: Targeted
expression of Escherichia coli purine nucleoside
phosphorylase and Fludara® for prostate cancer therapy.
J Gene Med. 13:680–691. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ueki H, Watanabe M, Kaku H, et al: A novel
gene expression system for detecting viable bladder cancer cells.
Int J Oncol. 41:135–140. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ambade AV, Joshi GV and Mulherkar R:
Effect of suicide gene therapy in combination with immunotherapy on
antitumour immune response and tumour regression in a xenograft
mouse model for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Indian J Med
Res. 132:415–422. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kuriyama S, Tsujinoue H and Yoshiji H:
Immune response to suicide gene therapy. Methods Mol Med.
90:353–369. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dong B, Sun L, Wu X, et al: Vaccination
with TCL plus MHSP65 induces anti-lung cancer immunity in mice.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 59:899–908. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yamazaki M, Straus FH, Messina M, et al:
Adenovirus-mediated tumor-specific combined gene therapy using
Herpes simplex virus thymidine/ganciclovir system and murine
interleukin-12 induces effective antitumor activity against
medullary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 11:8–15. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|