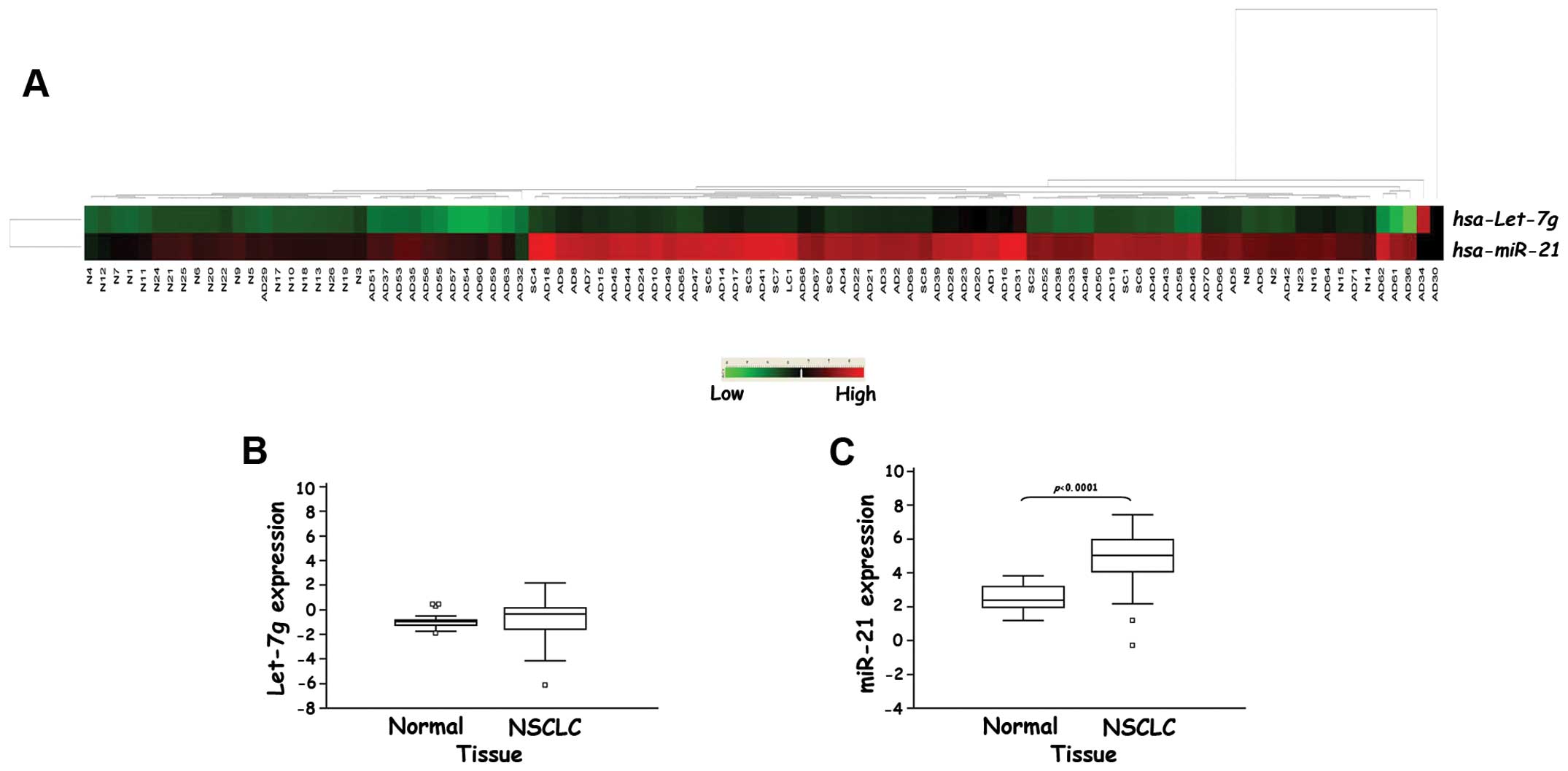
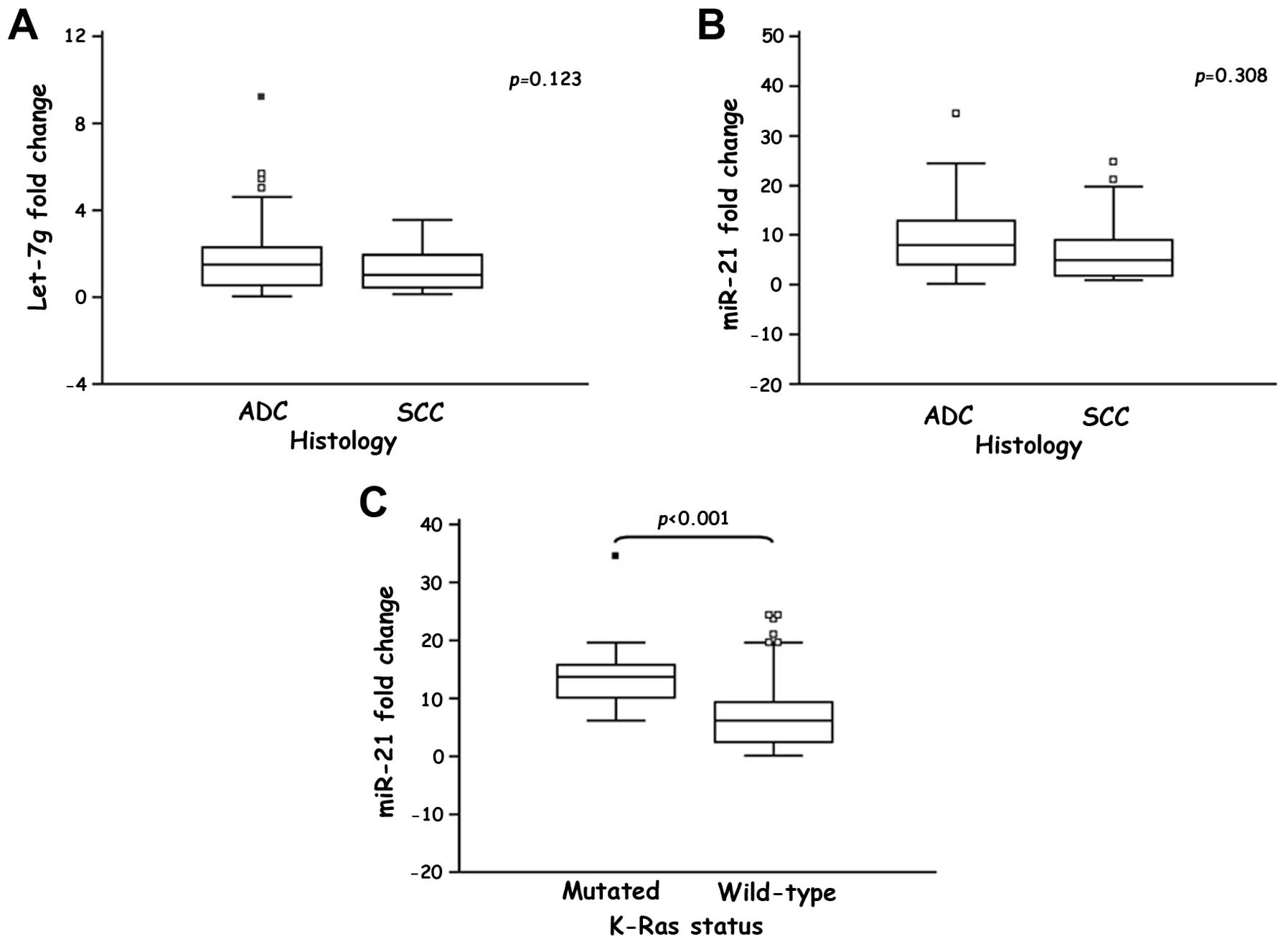
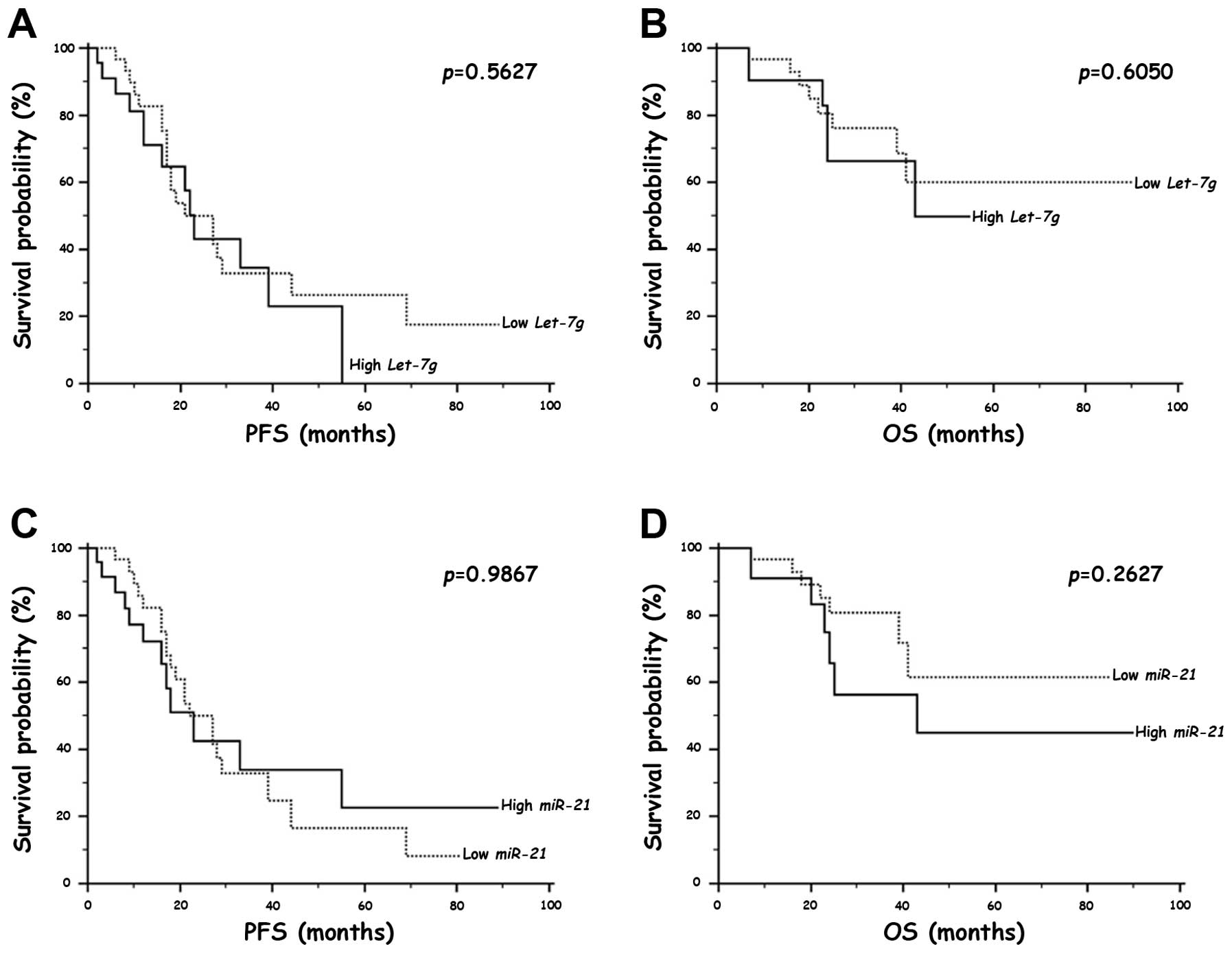
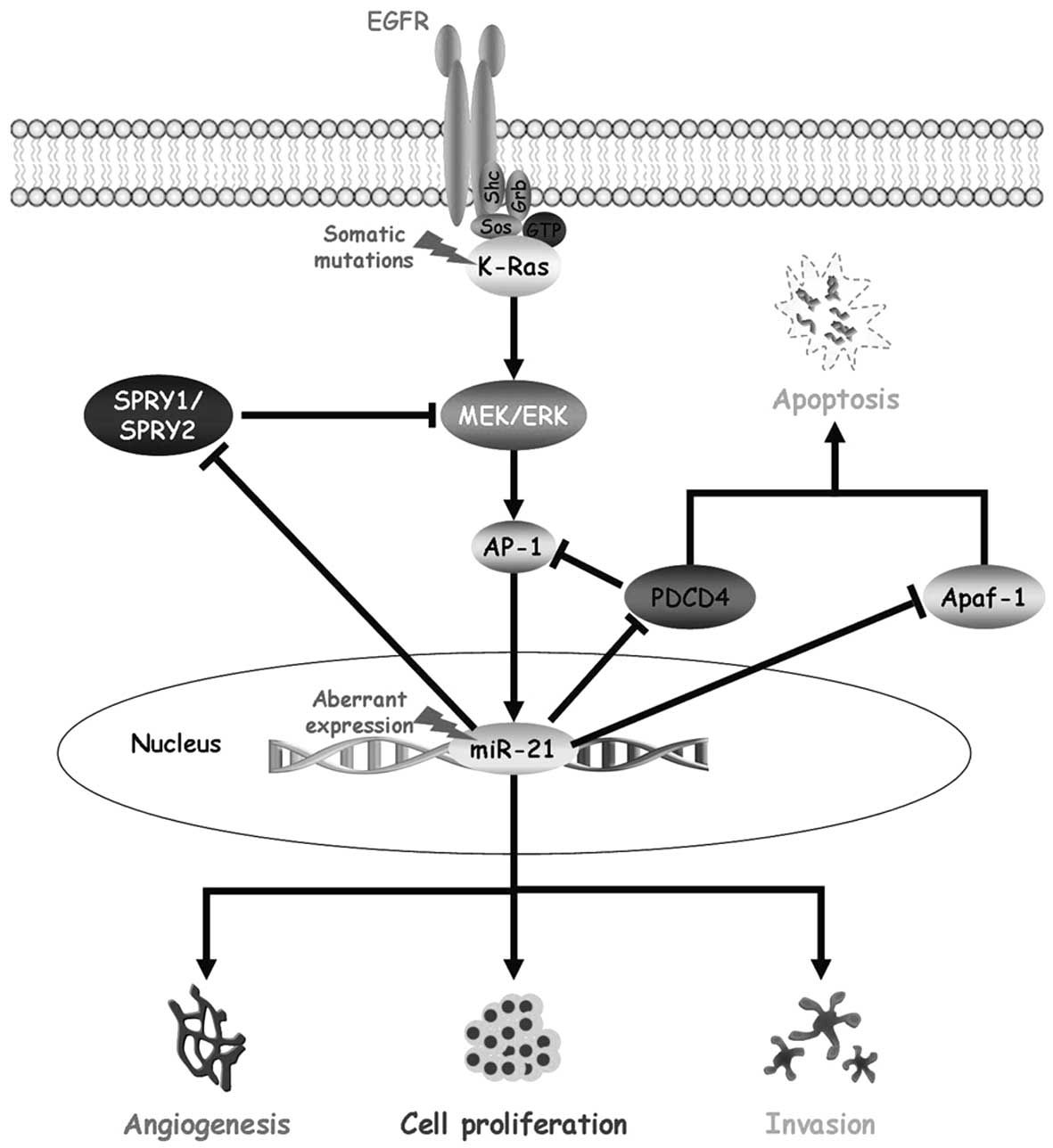
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Hemerlink
HK and Harris CC; World Health Organization Classification of
Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura,
Thymus and Heart. IARC Press; Lyon: 2004
|
|
3
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M,
Nicholson AG, Geisinger KR, Yatabe Y, Beer DG, Powell CA, Riely GJ,
Van Schil PE, Garg K, Austin JH, Asamura H, Rusch VW, Hirsch FR,
Scagliotti G, Mitsudomi T, Huber RM, Ishikawa Y, Jett J,
Sanchez-Cespedes M, Sculier JP, Takahashi T, Tsuboi M,
Vansteenkiste J, Wistuba I, Yang PC, Aberle D, Brambilla C, Flieder
D, Franklin W, Gazdar A, Gould M, Hasleton P, Henderson D, Johnson
B, Johnson D, Kerr K, Kuriyama K, Lee JS, Miller VA, Petersen I,
Roggli V, Rosell R, Saijo N, Thunnissen E, Tsao M and Yankelewitz
D: International association for the study of lung cancer/American
thoracic society/European respiratory society international
multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac
Oncol. 6:244–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M,
Nicholson A, Geisinger K, Yatabe Y, Ishikawa Y, Wistuba I, Flieder
DB, Franklin W, Gazdar A, Hasleton PS, Henderson DW, Kerr KM,
Petersen I, Roggli V, Thunnissen E and Tsao M: Diagnosis of lung
cancer in small biopsies and cytology: implications of the 2011
International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American
Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Classification. Arch
Pathol Lab Med. 137:668–684. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bronte G, Rizzo S, La Paglia L, Adamo V,
Siragusa S, Ficorella C, Santini D, Bazan V, Colucci G, Gebbia N
and Russo A: Driver mutations and differential sensitivity to
targeted therapies: a new approach to the treatment of lung
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 36:S21–S29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pao W and Girard N: New driver mutations
in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 12:175–180. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Saintigny P and Burger JA: Recent advances
in non-small cell lung cancer biology and clinical management.
Discov Med. 13:287–297. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: small RNAs
with big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schmittgen TD: Regulation of microRNA
processing in development, differentiation and cancer. J Cell Mol
Med. 12:1811–1819. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang Y, Shen XJ, Zou Q, Wang SP, Tang SM
and Zhang GZ: Biological functions of microRNAs: a review. J
Physiol Biochem. 67:129–139. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M
and Croce CM: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at
fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bartels CL and Tsongalis GJ: MicroRNAs:
novel biomarkers for human cancer. Clin Chem. 55:623–631. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Farazi TA, Spitzer JI, Morozov P and
Tuschl T: miRNAs in human cancer. J Pathol. 223:102–115. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNA
dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics.
A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med. 4:143–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K,
Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H, Harano T, Yatabe Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y,
Mitsudomi T and Takahashi T: Reduced expression of the let-7
microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened
postoperative survival. Cancer Res. 64:3753–3756. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Johnson CD, Esquela-Kerscher A, Stefani G,
Byrom M, Kelnar K, Ovcharenko D, Wilson M, Wang X, Shelton J,
Shingara J, Chin L, Brown D and Slack FJ: The let-7 microRNA
represses cell proliferation pathways in human cells. Cancer Res.
67:7713–7722. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kumar MS, Erkeland SJ, Pester RE, Chen CY,
Ebert MS, Sharp PA and Jacks T: Suppression of non-small cell lung
tumor development by the let-7 microRNA family. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:3903–3908. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom
M, Jarvis R, Cheng A, Labourier E, Reinert KL, Brown D and Slack
FJ: RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell.
120:635–647. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roush S and Slack FJ: The let-7 family of
microRNAs. Trends Cell Biol. 18:505–516. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Krichevsky AM and Gabriely G: miR-21: a
small multi-faceted RNA. J Cell Mol Med. 13:39–53. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao W, Yu Y, Cao H, Shen H, Li X, Pan S
and Shu Y: Deregulated expression of miR-21, miR-143 and miR-181a
in non small cell lung cancer is related to clinicopathologic
characteristics or patient prognosis. Biomed Pharmacother.
64:399–408. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Moore LM and Zhang W: Targeting miR-21 in
glioma: a small RNA with big potential. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
14:1247–1257. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pan X, Wang ZX and Wang R: MicroRNA-21: a
novel therapeutic target in human cancer. Cancer Biol Ther.
10:1224–1232. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Seike M, Goto A, Okano T, Bowman ED,
Schetter AJ, Horikawa I, Mathe EA, Jen J, Yang P, Sugimura H, Gemma
A, Kudoh S, Croce CM and Harris CC: MiR-21 is an EGFR-regulated
anti-apoptotic factor in lung cancer in never-smokers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:12085–12090. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Selcuklu SD, Donoghue MT and Spillane C:
miR-21 as a key regulator of oncogenic processes. Biochem Soc
Trans. 37:918–925. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Capodanno A, Boldrini L, Alì G,
Pelliccioni S, Mussi A and Fontanini G:
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase α catalytic subunit gene somatic
mutations in bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine tumours. Oncol Rep.
28:1559–1566. 2012.
|
|
29
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M,
Prueitt RL, Yanaihara N, Lanza G, Scarpa A, Vecchione A, Negrini M,
Harris CC and Croce CM: A microRNA expression signature of human
solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:2257–2261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Landi MT, Zhao Y, Rotunno M, Koshiol J,
Liu H, Bergen AW, Rubagotti M, Goldstein AM, Linnoila I, Marincola
FM, Tucker MA, Bertazzi PA, Pesatori AC, Caporaso NE, McShane LM
and Wang E: MicroRNA expression differentiates histology and
predicts survival of lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:430–441.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mitsudomi T, Oyama T, Nishida K, Ogami A,
Osaki T, Sugio K, Yasumoto K, Sugimachi K and Gazdar AF: Loss of
heterozygosity at 3p in non-small cell lung cancer and its
prognostic implication. Clin Cancer Res. 2:1185–1189.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zabarovsky ER, Lerman MI and Minna JD:
Tumor suppressor genes on chromosome 3p involved in the
pathogenesis of lung and other cancers. Oncogene. 21:6915–6935.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Riely GJ, Marks J and Pao W: KRAS
mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Proc Am Thorac Soc.
6:201–205. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mao C, Qiu LX, Liao RY, Du FB, Ding H,
Yang WC, Li J and Chen Q: KRAS mutations and resistance to
EGFR-TKIs treatment in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a
meta-analysis of 22 studies. Lung Cancer. 69:272–278. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yatabe Y and Mitsudomi T: Epidermal growth
factor receptor mutations in lung cancers. Pathol Int. 57:233–244.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ladanyi M and Pao W: Lung adenocarcinoma:
guiding EGFR-targeted therapy and beyond. Mod Pathol. 21:S16–S22.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dacic S: Molecular diagnostics of lung
carcinomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 135:622–629. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dacic S, Kelly L, Shuai Y and Nikiforova
MN: miRNA expression profiling of lung adenocarcinomas: correlation
with mutational status. Mod Pathol. 23:1577–1582. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chin LJ, Ratner E, Leng S, Zhai R, Nallur
S, Babar I, Muller RU, Straka E, Su L, Burki EA, Crowell RE, Patel
R, Kulkarni T, Homer R, Zelterman D, Kidd KK, Zhu Y, Christiani DC,
Belinsky SA, Slack FJ and Weidhaas JB: A SNP in a let-7 microRNA
complementary site in the KRAS 3′ untranslated region increases
non-small cell lung cancer risk. Cancer Res. 68:8535–8540.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Boutros T, Chevet E and Metrakos P:
Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/MAP kinase phosphatase
regulation: roles in cell growth, death and cancer. Pharmacol Rev.
60:261–310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hatley ME, Patrick DM, Garcia MR,
Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R, van Rooij E and Olson EN: Modulation
of K-Ras-dependent lung tumorigenesis by MicroRNA-21. Cancer Cell.
18:282–293. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lu Z, Liu M, Stribinskis V, Klinge CM,
Ramos KS, Colburn NH and Li Y: MicroRNA-21 promotes cell
transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene.
Oncogene. 27:4373–4379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hwang SK, Jin H, Kwon JT, Chang SH, Kim
TH, Cho CS, Lee KH, Young MR, Colburn NH, Beck GR Jr, Yang HS and
Cho MH: Aerosol-delivered programmed cell death 4 enhanced
apoptosis, controlled cell cycle and suppressed AP-1 activity in
the lungs of AP-1 luciferase reporter mice. Gene Ther.
14:1353–1361. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Talotta F, Cimmino A, Matarazzo MR,
Casalino L, De Vita G, D'Esposito M, Di Lauro R and Verde P: An
autoregulatory loop mediated by miR-21 and PDCD4 controls the AP-1
activity in RAS transformation. Oncogene. 28:73–84. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Markou A, Tsaroucha EG, Kaklamanis L,
Fotinou M, Georgoulias V and Lianidou ES: Prognostic value of
mature microRNA-21 and microRNA-205 overexpression in non-small
cell lung cancer by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Clin Chem.
54:1696–1704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|