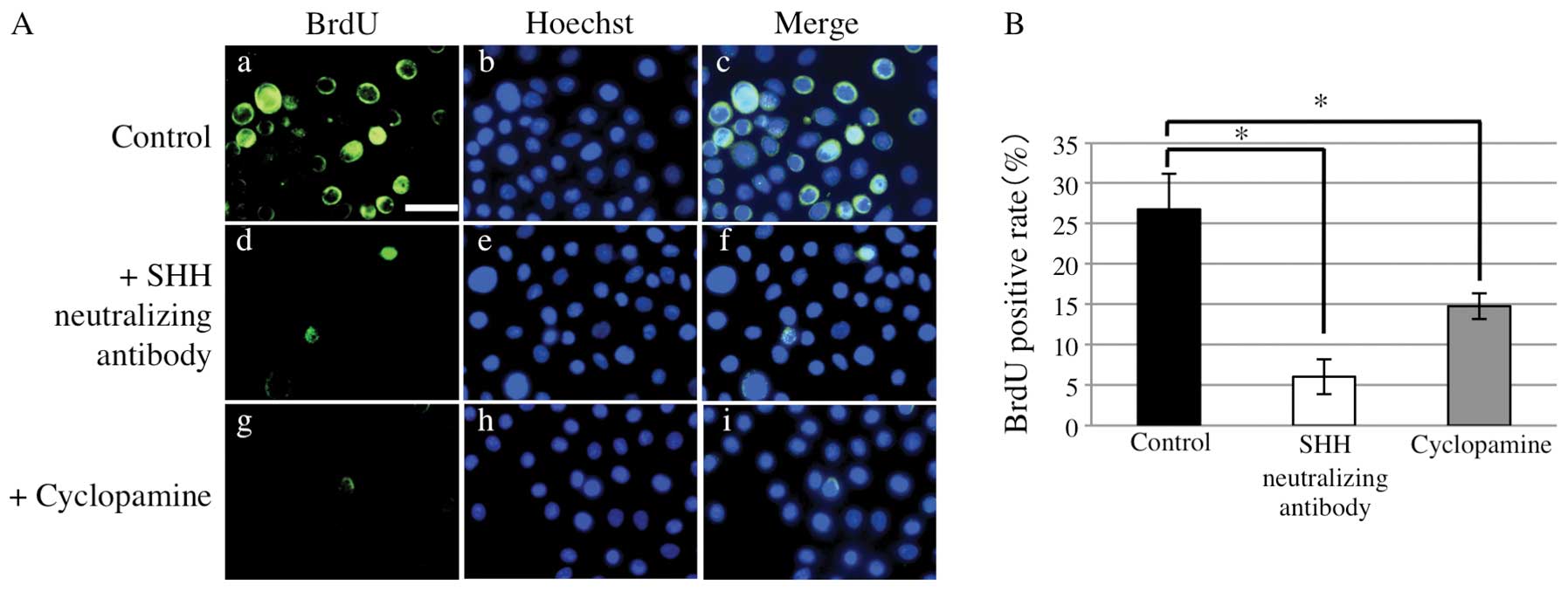
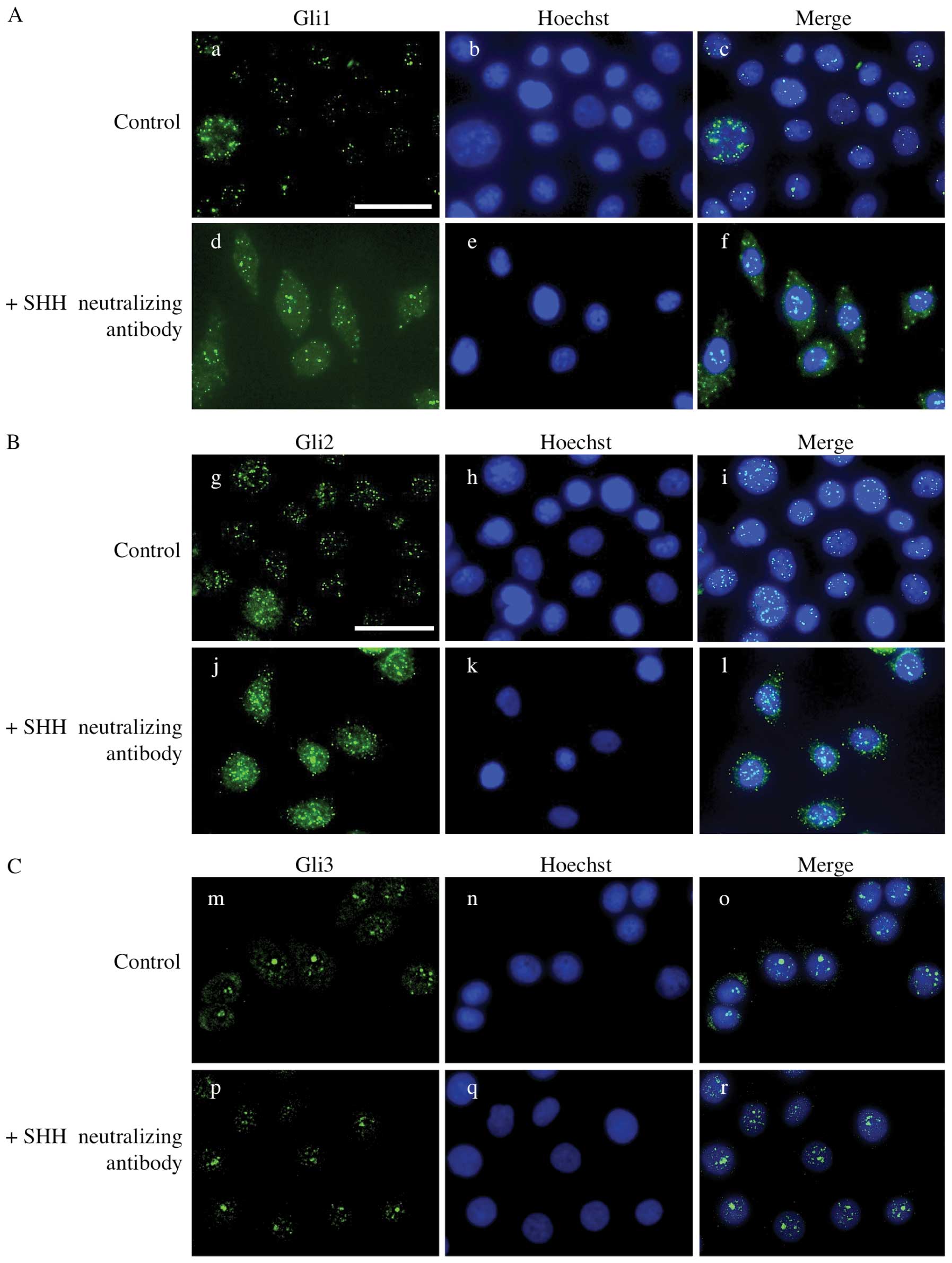
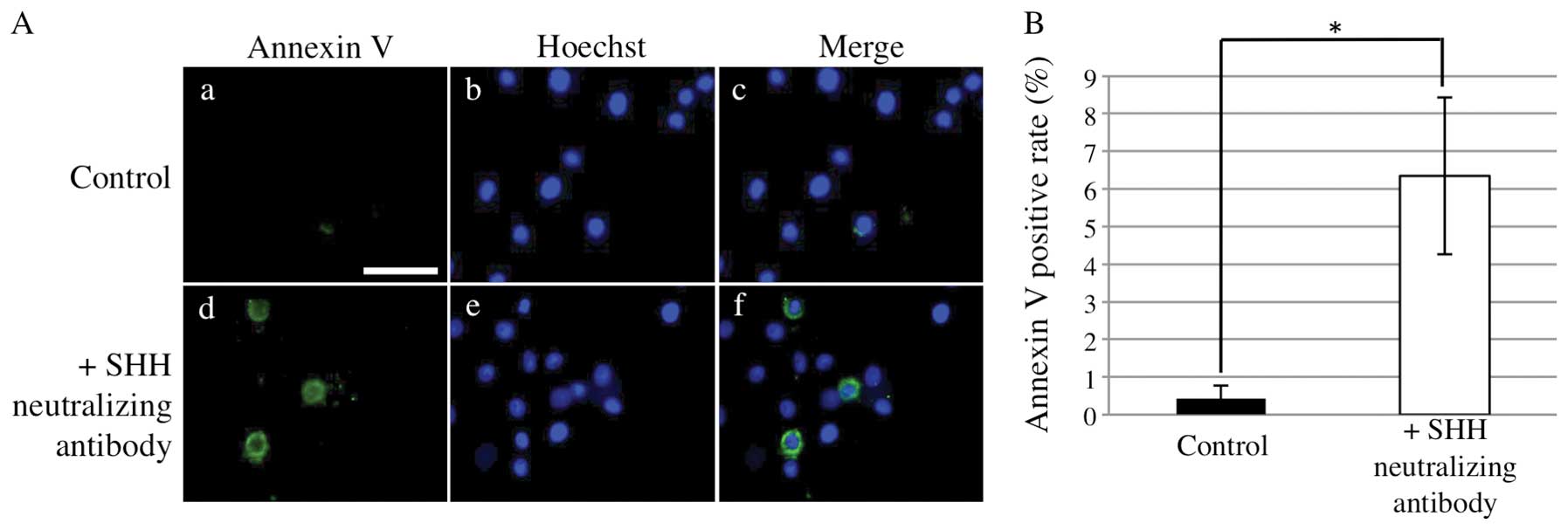
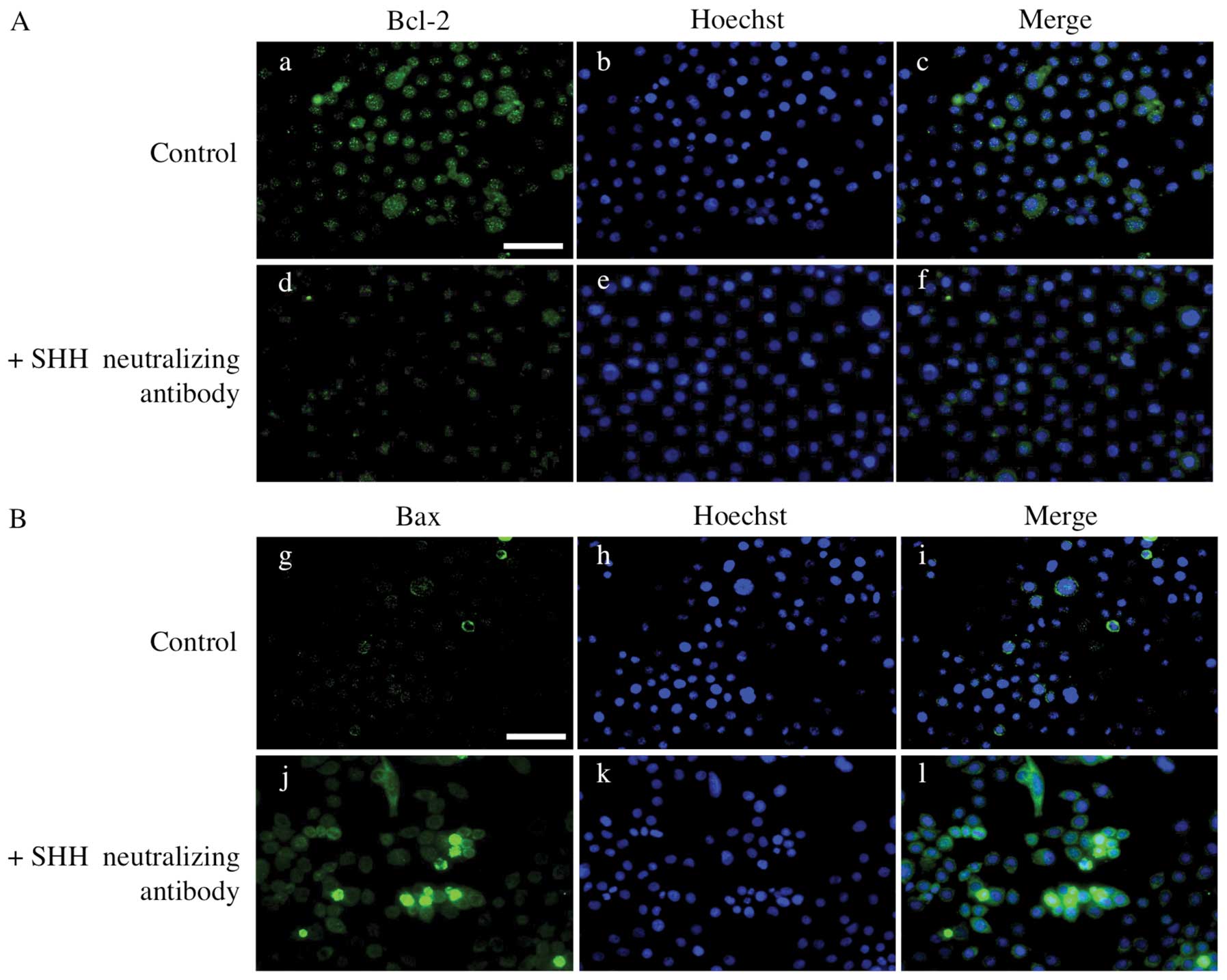
|
1
|
Ingham PW and McMahon AP: Hedgehog
signaling in animal development: paradigms and principals. Gens
Dev. 15:3059–3087. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Echelard Y, Epstein DJ, St-Jacques B, Shen
L, Mohler J, McMahon JA, et al: Sonic hedgehog, a member of a
family of putative signaling molecules, is implicated in the
regulation of CNS polarity. Cell. 75:1417–1430. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bitgood MJ and McMahon AP: Hedgehog and
Bmp genes are coexpressed at many diverse sites of cell-cell
interaction in the mouse embryo. Dev Biol. 172:126–138. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
NuÈsslein-Vohhard C and Wieschaus E:
Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in
Drosophila. Nature. 287:795–801. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stone DM, Hynes M, Armanini M, et al: The
tumour-suppressor gene patched encodes a candidate receptor for
Sonic hedgehog. Nature. 384:129–134. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alcedo J, Ayzenzon M, Von Ohlen T, Noll M
and Hooper JE: The Drosophila smoothened gene encodes a
seven-pass membrane protein, a putative receptor for the Hedgehog
signal. Cell. 86:221–232. 1996.
|
|
7
|
Kalderon D: Similarities between the
Hedgehog and Wnt signaling pathways. Trends Cell Biol. 12:523–531.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ruel L, Rodriguez R, Gallet A,
Lavenant-Staccini L and Thérond PP: Stability and association of
Smoothened, Costal2 and fused with Cubitus interruptus are
regulated by Hedgehog. Nat Cell Biol. 5:907–913. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hahn H, Wojnowski L, Miller G and Zimmer
A: The patched signaling pathway in tumorigenesis and development:
lessons from animal models. J Mol Med. 77:459–468. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Altaba AR, Sánchez P and Dahmane N: Gli
and Hedgehog in cancer: tumours, embryos and stem cells. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:361–372. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gailani MR, Ståhle-Bäckdahl M, Leffell DJ,
et al: The role of the human homologue of Drosophila patched
in sporadic basal cell carcinomas. Nat Genet. 14:78–81.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulos PG, et
al: Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in
the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell. 85:841–851.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Johnson RL, Rothman AL, Xie J, et al:
Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the basal cell nevus
syndrome. Science. 272:1668–1671. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Roessler E, Belloni E, Gaudenz K, et al:
Mutations human Sonic hedgehog gene cause holoprosencephaly. Nat
Genet. 14:357–360. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dahmane N, Lee J, Robins P, Heller P and
Altaba AR: Activation of the transcription factor Gli1 and the
Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway in skin tumours. Nature.
389:876–881. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reifenberger J, Wolter M, Weber RG, et al:
Missense mutations in SMOH in sporadic basal cell carcinomas of the
skin and primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the central nervous
system. Cancer Res. 58:1798–1803. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dassule HR and McMahon AP: Analysis of
epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in the initial morphogenesis of
the mammalian tooth. Dev Biol. 202:215–227. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hardcastle Z, Mo R, Hui C and Sharpe PT:
The Shh signaling pathway in tooth development. defects in Gli2 and
Gli3 mutants. Development. 125:2803–2811. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Barreto DC, Gomez RS, Bale AE, Boson WL
and De Marco L: PTCH gene mutations in odontogenic keratocysts. J
Dent Res. 79:1418–1422. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Diniz MG, Borges ER, Guimarães AL, Moreira
PR, Brito JA, Gomez MV, et al: PTCH1 isoforms in odontogenic
keratocysts. Oral Oncol. 45:291–295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sciubba JJ, Fantasia JE and Kahn LB:
Tumors and Cysts of the Jaw. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology;
Washington, DC: pp. 71–99. 2001
|
|
22
|
Harada H, Mitsuyasu T, Nakamura N, Higuchi
Y, Toyoshima K, Taniguchi A, et al: Establishment of ameloblastoma
cell line, AM-1. J Oral Pathol Med. 27:207–212. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
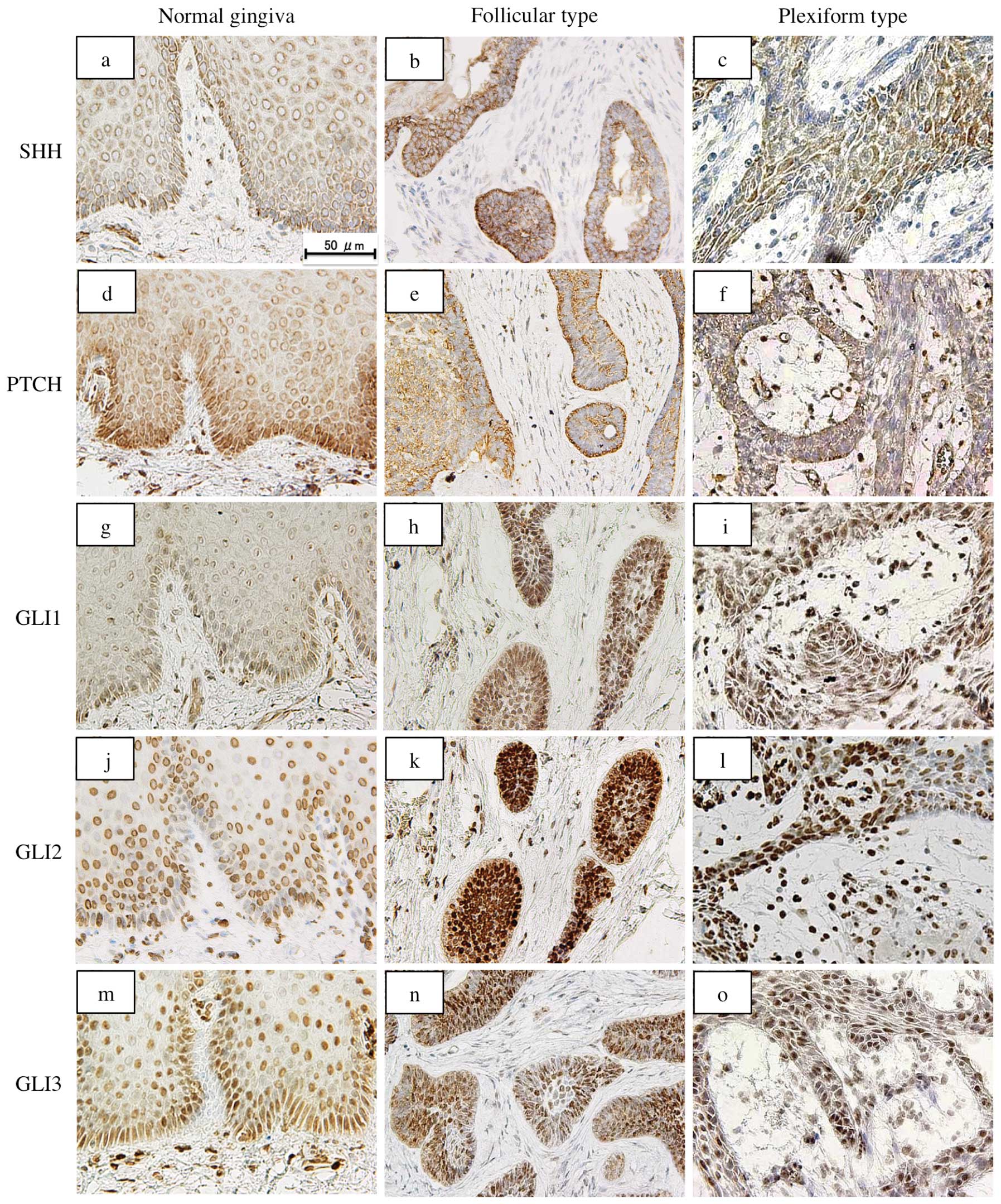
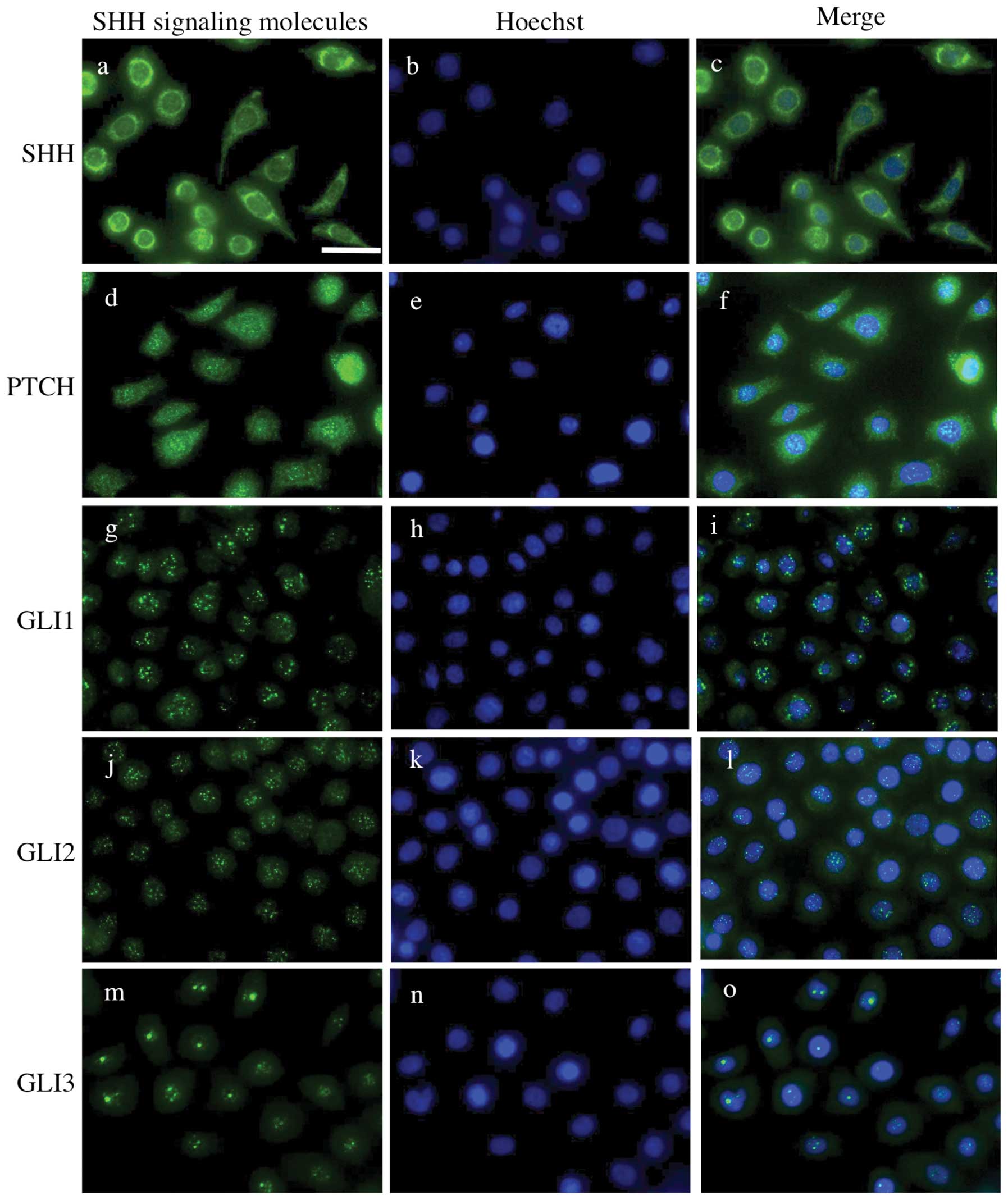
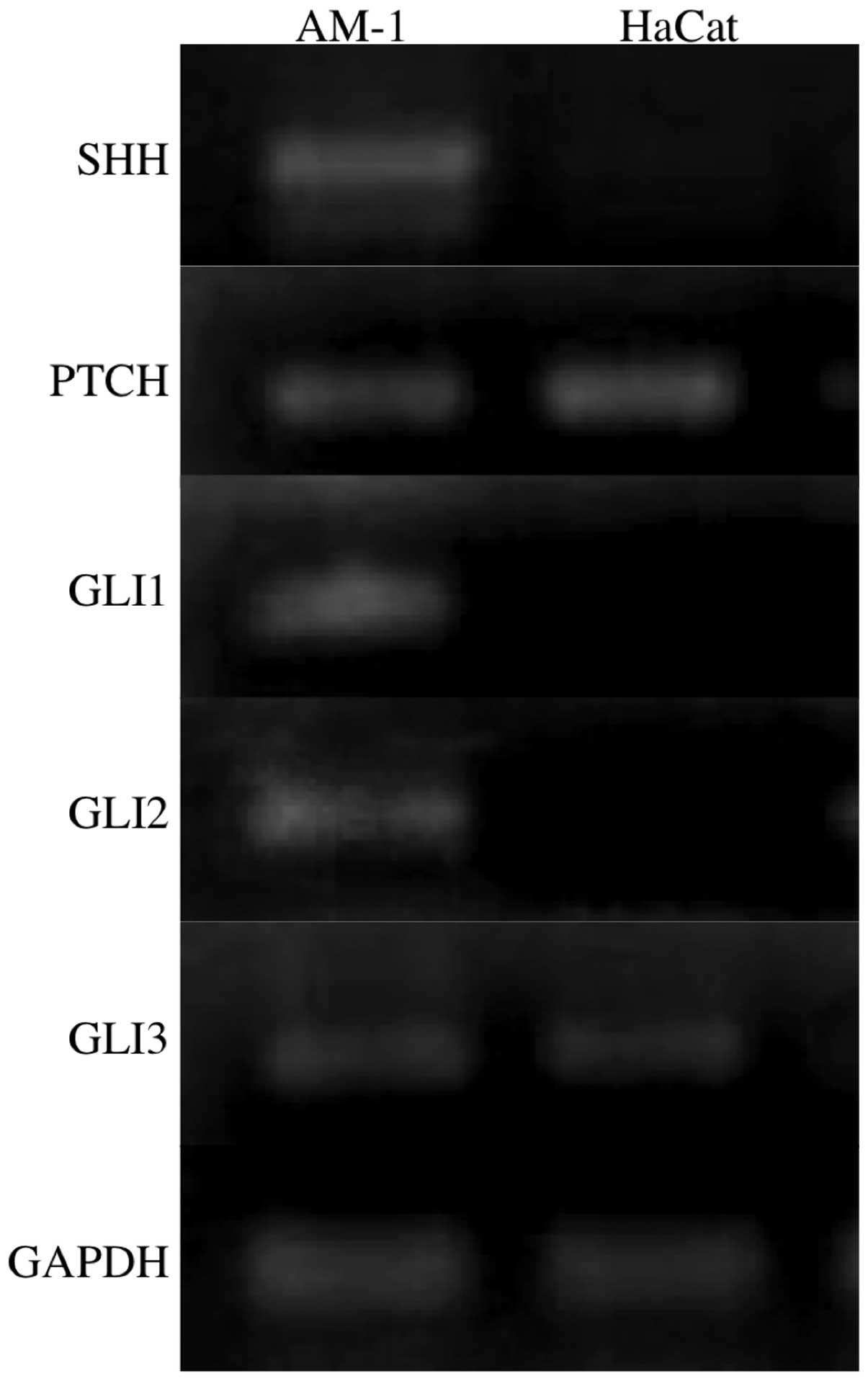
Kumamoto H, Ohki K and Ooya K: Expression
of sonic hedgehog (SHH) signaling molecules in ameloblastomas. J
Oral Pathol Med. 33:185–190. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang L, Chen XM, Sun ZJ, Bian Z, Fan MW
and Chen Z: Epithelial expression of SHH signaling pathway in
odontogenic tumors. Oral Oncol. 42:398–408. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vered M, Peleg O, Taicher S and Buchner A:
The immunoprofile of odontogenic keratocyst (keratocystic
odontogenic tumor) that includes expression of PTCH, SMO, GLI-1 and
bcl-2 is similar to ameloblastoma but different from odontogenic
cysts. J Oral Pathol Med. 38:597–604. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sandra F, Mitsuyasu T, Nakamura N,
Shiratsuchi Y and Ohishi M: Immunohistochemical evaluation of PCNA
and Ki-67 in ameloblastoma. Oral Oncol. 37:193–198. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Watkins DN, Berman DM, Burkholder SG, Wang
B, Beachy PA and Baylin SB: Hedgehog signalling within airway
epithelial progenitors and in small-cell lung cancer. Nature.
422:313–317. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Thayer SP, di Magliano MP, Heiser PW,
Nielsen CM, Roberts DJ, Lauwers GY, et al: Hedgehog is an early and
late mediator of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature.
425:851–856. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Maitra A, Montes
De Oca R, Gerstenblith MR, Briggs K, et al: Widespread requirement
for Hedgehog ligand stimulation in growth of digestive tract
tumours. Nature. 425:846–851. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yanai K, Nagai S, Wada J, Yamanaka N,
Nakamura M, Torata N, et al: Hedgehog signaling pathway is a
possible therapeutic target for gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol.
95:55–62. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Litingtung Y, Dahn RD, Li Y, Fallon JF and
Chiang C: Shh and Gli3 are dispensable for limb skeleton formation
but regulate digit number and identity. Nature. 418:979–983. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang B, Fallon JF and Beachy PA:
Hedgehog-regulated processing of Gli3 produces an
anterior/posterior repressor gradient in the developing vertebrate
limb. Cell. 100:423–434. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mitsuyasu T, Harada H, Higuchi Y, Kimura
K, Nakamura N, Katsuki T, et al: Immunohistochemical demonstration
of bcl-2 protein in ameloblastoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 26:345–348.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
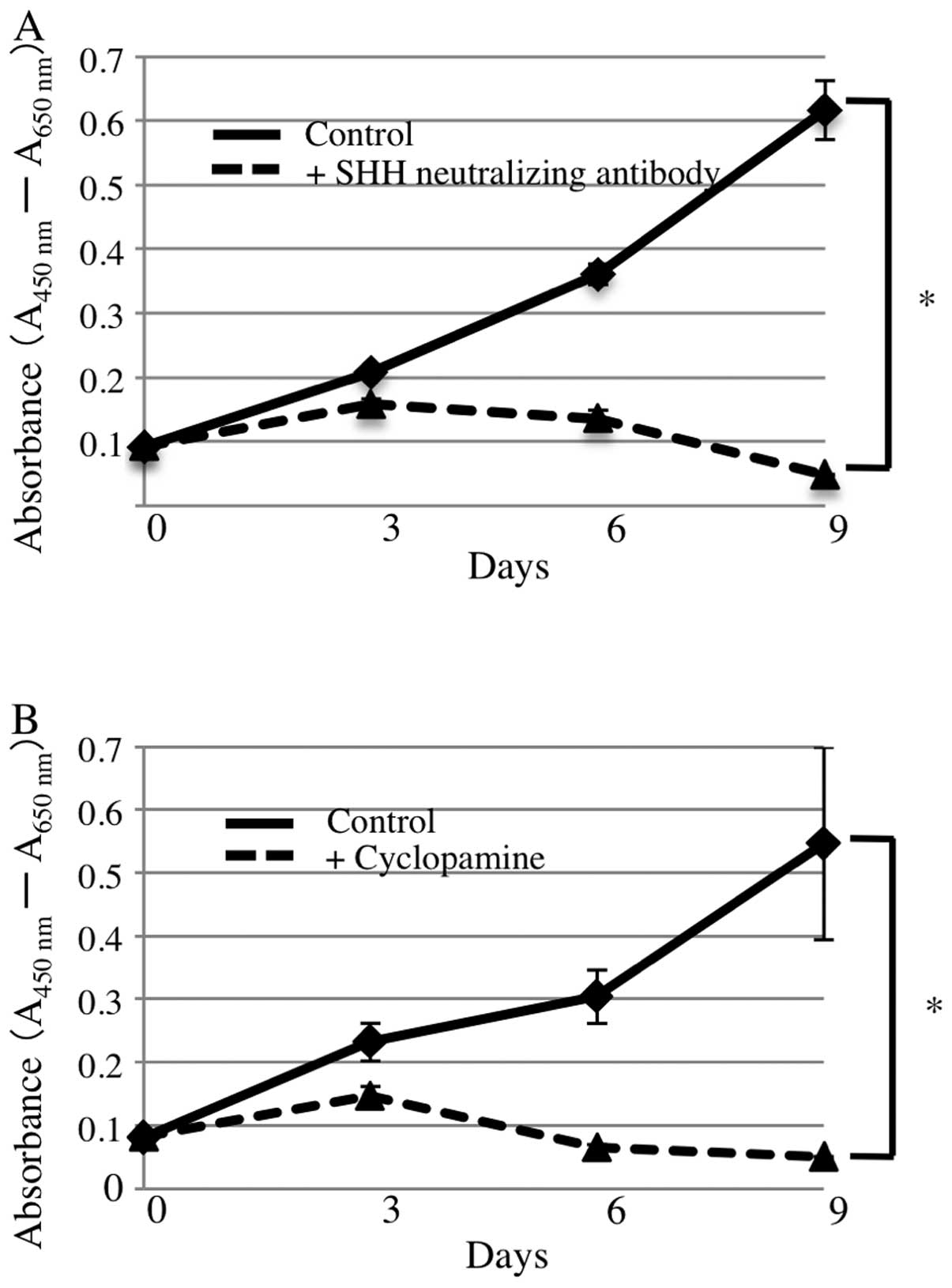
Qualtrough D, Buda A, Gaffield W, Williams
AC and Paraskeva C: Hedgehog signaling in colorectal tumor cells:
induction of apoptosis with cyclopamine treatment. Int J Cancer.
110:831–837. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fujita E, Khoroku Y, Urase K, Tsukahara T,
Momoi MY, Kumagai H, et al: Involvement of Sonic hedgehog in the
cell growth of LK-2 cells, human lung squamous carcinoma cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 238:658–664. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oro AE, Higgins KM, Hu Z, Bonifas JM,
Epstein EH Jr and Scott MP: Basal cell carcinomas in mice
overexpressing Sonic hedgehog. Science. 276:817–821. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|