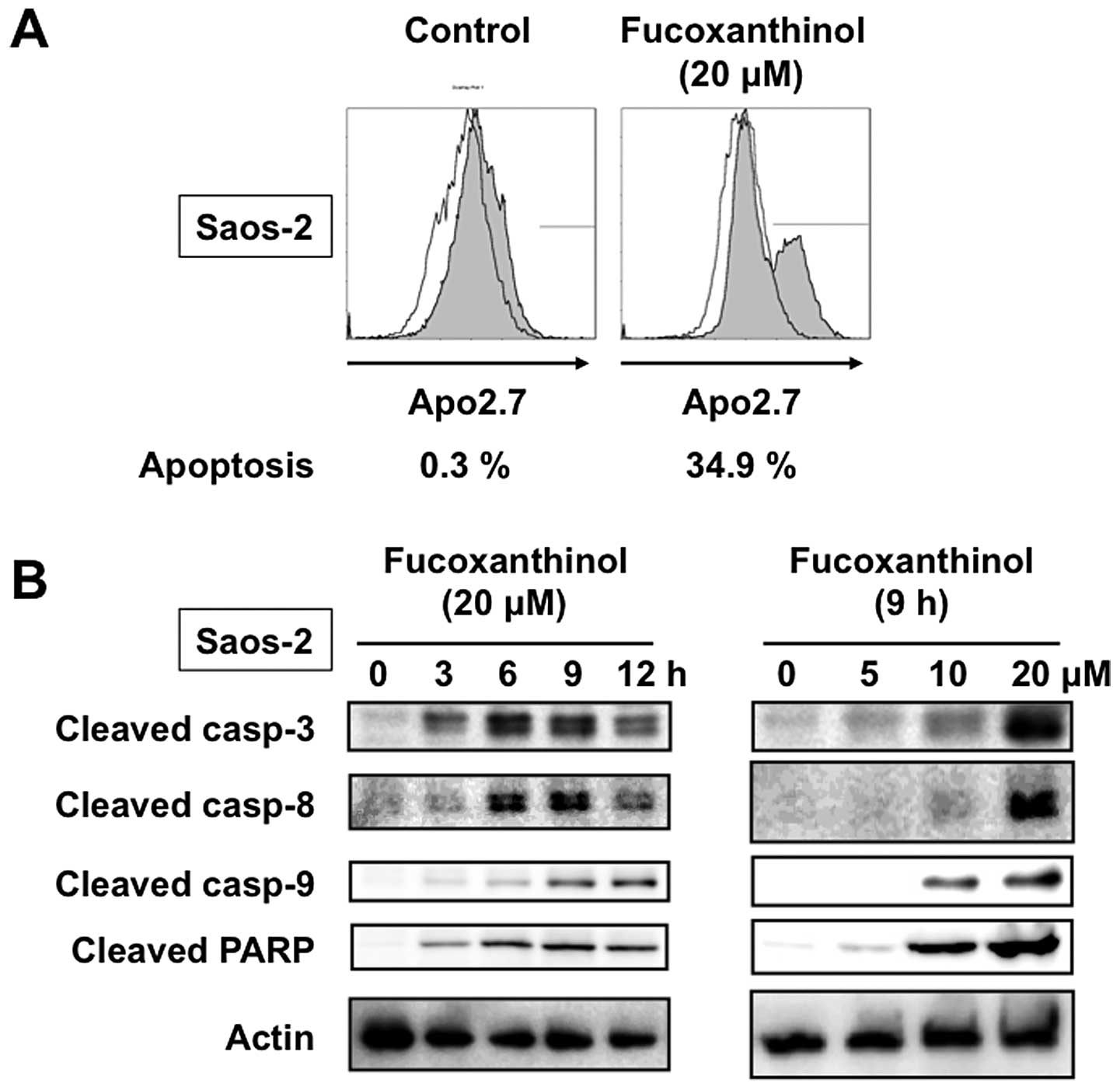
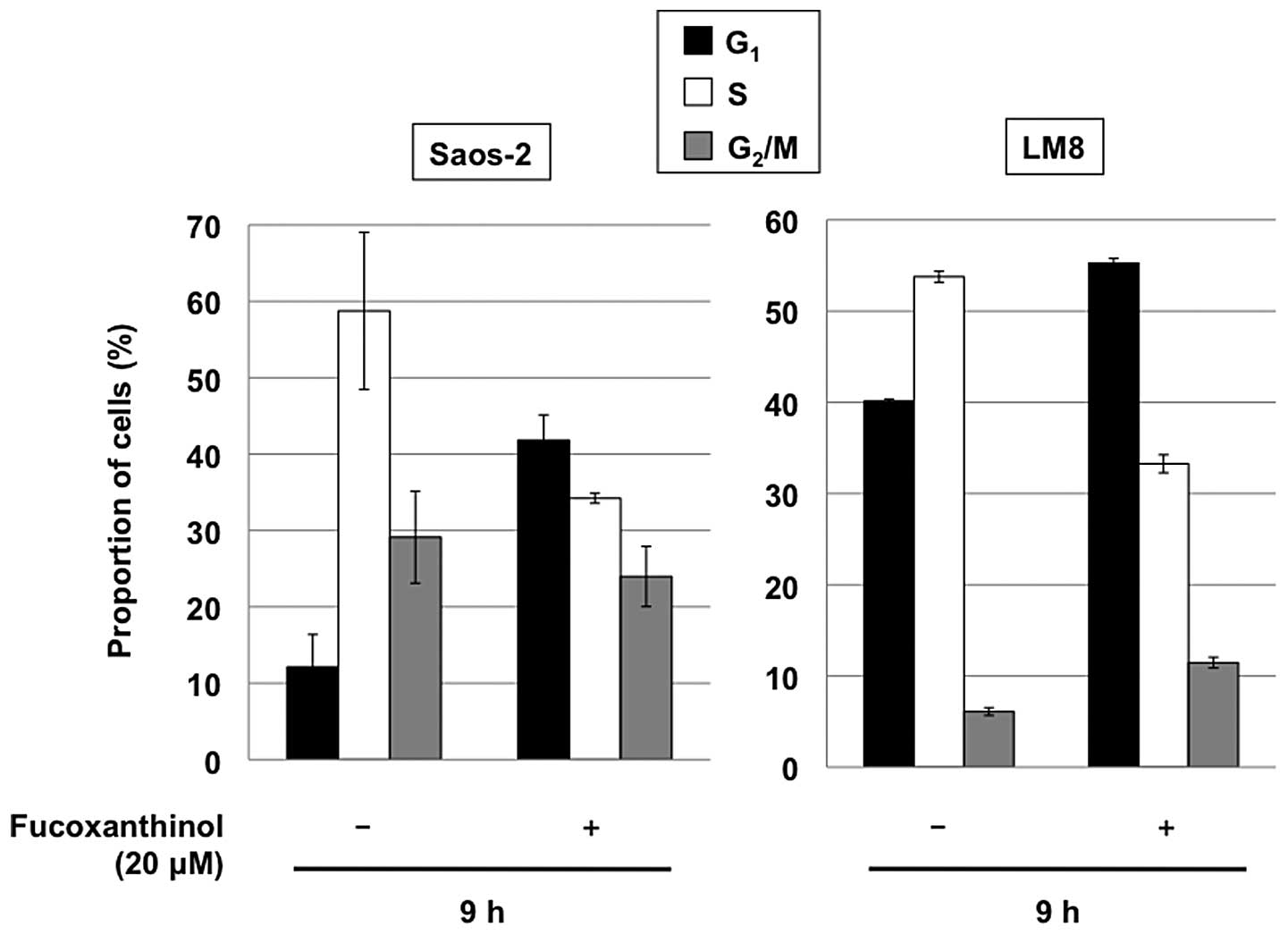
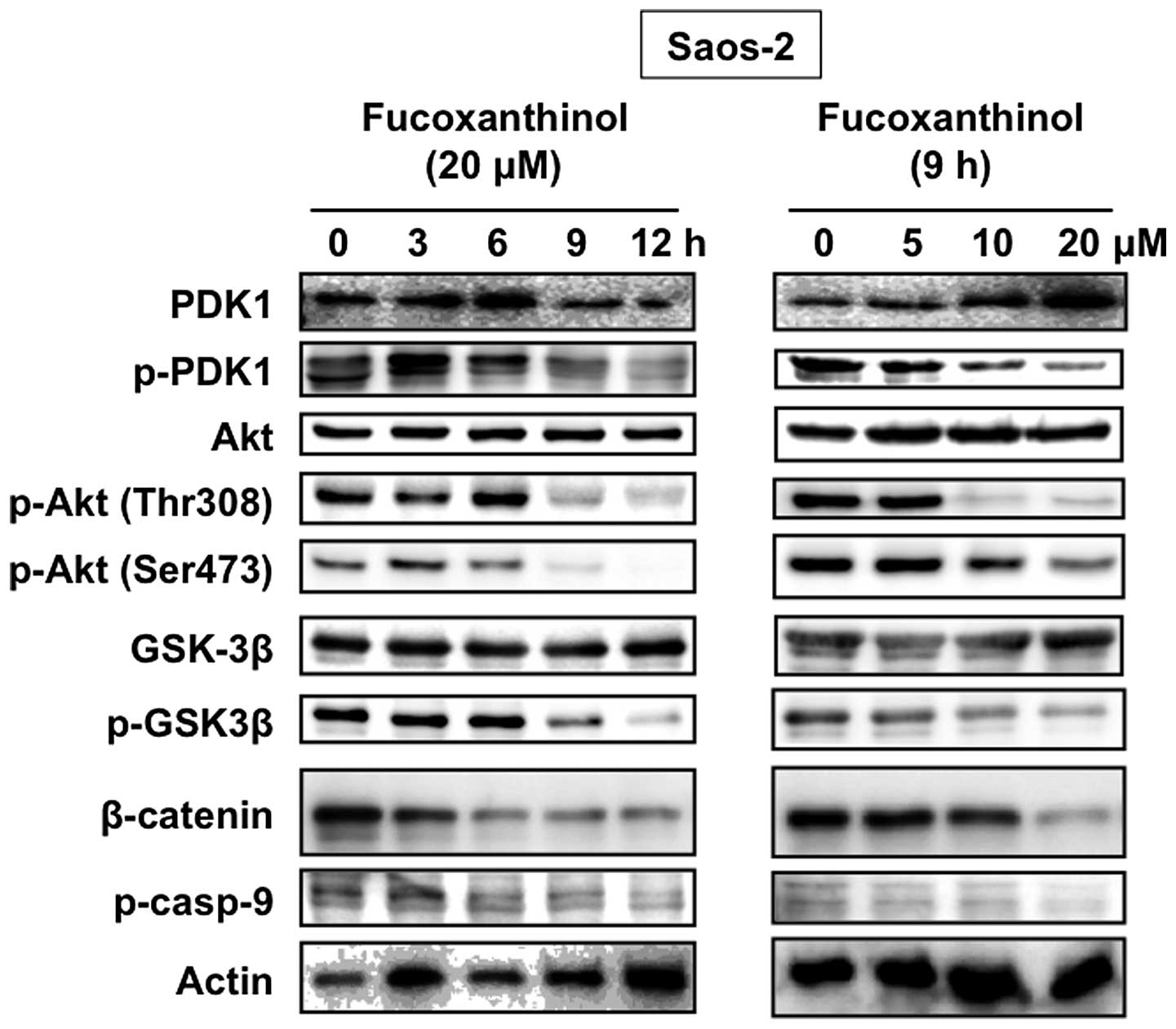
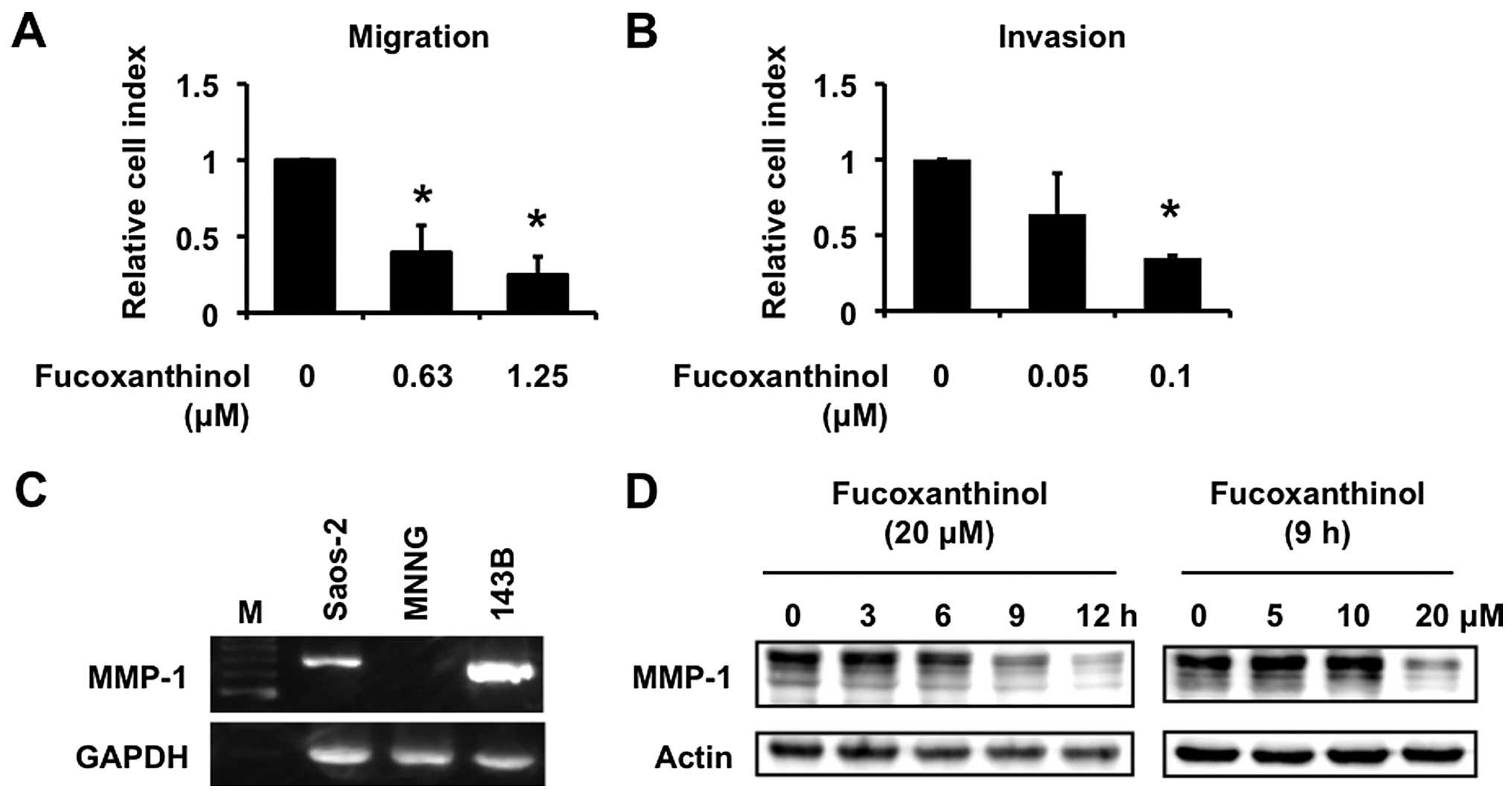
|
1.
|
Savage S and Mirabello L: Using
epidemiology and genomics to understand osteosarcoma etiology.
Sarcoma. 2011:5481512011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Anninga JK, Gelderblom H, Fiocco M, Kroep
JR, Taminiau AHM, Hogendoorn PCW and Egeler RM: Chemotherapeutic
adjuvant treatment for osteosarcoma: where do we stand? Eur J
Cancer. 47:2431–2445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Marina N, Gebhardt M, Teot L and Gorlick
R: Biology and therapeutic advances for pediatric osteosarcoma.
Oncologist. 9:422–441. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Musa-Veloso K, Card JW, Wong AW and Cooper
DA: Influence of observational study design on the interpretation
of cancer risk reduction by carotenoids. Nutr Rev. 67:527–545.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Peng J, Yuan J-P, Wu C-F and Wang J-H:
Fucoxanthin, a marine carotenoid present in brown seaweeds and
diatoms: metabolism and bioactivities relevant to human health. Mar
Drugs. 9:1806–1828. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Yamamoto K, Ishikawa C, Katano H, Yasumoto
T and Mori N: Fucoxanthin and its deacetylated product,
fucoxanthinol, induce apoptosis of primary effusion lymphomas.
Cancer Lett. 300:225–234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Rhim JS, Putman DL, Arnstein P, Huebner RJ
and McAllister RM: Characterization of human cells transformed in
vitro by N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Int J Cancer.
19:505–510. 1977.
|
|
8.
|
Hensler PJ, Annab LA, Barrett JC and
Pereira-Smith OM: A gene involved in control of human cellular
senescence on human chromosome 1q. Mol Cell Biol. 14:2291–2297.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Zhang C, Ao Z, Seth A and Schlossman SF: A
mitochondrial membrane protein defined by a novel monoclonal
antibody is preferentially detected in apoptotic cells. J Immunol.
157:3980–3987. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Antalis TM and Godbolt D: Isolation of
intact nuclei from hematopoietic cell types. Nucleic Acids Res.
19:43011991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Mori N and Prager D: Transactivation of
the interleukin-1α promoter by human T-cell leukemia virus type I
and type II Tax proteins. Blood. 87:3410–3417. 1996.
|
|
12.
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: Living with or
without cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev.
18:2699–2711. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Cheng L, Rossi F, Fang W, Mori T and
Cobrinik D: Cdk2-dependent phosphorylation and functional
inactivation of the pRB-related p130 protein in pRB(−),
p16INK4A(+) tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 275:30317–30325.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Perkins ND: The diverse and complex roles
of NF-κB subunits in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:121–132. 2012.
|
|
15.
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Shared principles
in NF-κB signaling. Cell. 132:344–362. 2008.
|
|
16.
|
Iwanaga R, Ohtani K, Hayashi T and
Nakamura M: Molecular mechanism of cell cycle progression induced
by the oncogene product Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type I.
Oncogene. 20:2055–2067. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Zahradka P, Werner JP, Buhay S, Litchie B,
Helwer G and Thomas S: NF-κB activation is essential for
angiotensin II-dependent proliferation and migration of vascular
smooth muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 34:1609–1621. 2002.
|
|
18.
|
Zhu L, Fukuda S, Cordis G, Das DK and
Maulik N: Anti-apoptotic protein survivin plays a significant role
in tubular morphogenesis of human coronary arteriolar endothelial
cells by hypoxic preconditioning. FEBS Lett. 508:369–374. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Stehlik C, de Martin R, Kumabashiri I,
Schmid JA, Binder BR and Lipp J: Nuclear factor (NF)-κB-regulated
X-chromosome-linked iap gene expression protects endothelial cells
from tumor necrosis factor α-induced apoptosis. J Exp Med.
188:211–216. 1998.
|
|
20.
|
Pahl HL: Activators and target genes of
Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Oncogene. 18:6853–6866. 1999.
|
|
21.
|
Grossmann M, O’Reilly LA, Gugasyan R,
Strasser A, Adams JM and Gerondakis S: The anti-apoptotic
activities of Rel and RelA required during B-cell maturation
involve the regulation of Bcl-2 expression. EMBO J. 19:6351–6360.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Nicot C, Mahieux R, Takemoto S and
Franchini G: Bcl-XL is up-regulated by HTLV-I and
HTLV-II in vitro and in ex vivo ATLL samples. Blood. 96:275–281.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Jin S, Pang R-P, Shen J-N, Huang G, Wang J
and Zhou J-G: Grifolin induces apoptosis via inhibition of PI3K/AKT
signalling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells. Apoptosis.
12:1317–1326. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Manning BD and Cantley LC: AKT/PKB
signaling: navigating downstream. Cell. 129:1261–1274. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Perissinotto E, Cavalloni G, Leone F,
Fonsato V, Mitola S, Grignani G, Surrenti N, Sangiolo D, Bussolino
F, Piacibello W and Aglietta M: Involvement of chemokine receptor
4/stromal cell-derived factor 1 system during osteosarcoma tumor
progression. Clin Cancer Res. 11:490–497. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Kimura R, Ishikawa C, Rokkaku T, Janknecht
R and Mori N: Phosphorylated c-Jun and Fra-1 induce matrix
metalloproteinase-1 and thereby regulate invasion activity of 143B
osteosarcoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:1543–1553. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Asai T, Ueda T, Itoh K, Yoshioka K, Aoki
Y, Mori S and Yoshikawa H: Establishment and characterization of a
murine osteosarcoma cell line (LM8) with high metastatic potential
to the lung. Int J Cancer. 76:418–422. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR,
Pfeffer LM and Donner DB: NF-κB activation by tumour necrosis
factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature. 401:82–85.
1999.
|
|
29.
|
Ali NN, Gilston V and Winyard PG:
Activation of NF-κB in human osteoblasts by stimulators of bone
resorption. FEBS Lett. 460:315–320. 1999.
|
|
30.
|
Dan HC, Sun M, Kaneko S, Feldman RI,
Nicosia SV, Wang H-G, Tsang BK and Cheng JQ: Akt phosphorylation
and stabilization of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein
(XIAP). J Biol Chem. 279:5405–5412. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Liang Y-L, Wang L-Y, Wu H, Ma D-Z, Xu Z
and Zha X-L: PKB phosphorylation and survivin expression are
cooperatively regulated by disruption of microfilament
cytoskeleton. Mol Cell Biochem. 254:257–263. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Pugazhenthi S, Nesterova A, Sable C,
Heidenreich KA, Boxer LM, Heasley LE and Reusch JE-B: Akt/protein
kinase B up-regulates Bcl-2 expression through cAMP-response
element-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 275:10761–10766. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Longhi A, Errani C, De Paolis M, Mercuri M
and Bacci G: Primary bone osteosarcoma in the pediatric age: state
of the art. Cancer Treat Rev. 32:423–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Gialeli G, Theocharis AD and Karamanos NK:
Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their
pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 278:16–27. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Jawad MU, Garamszegi N, Garamszegi SP,
Correa-Medina M, Diez JA, Wen R and Scully SP: Matrix
metalloproteinase 1: role in sarcoma biology. PLoS One.
5:e142502010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|