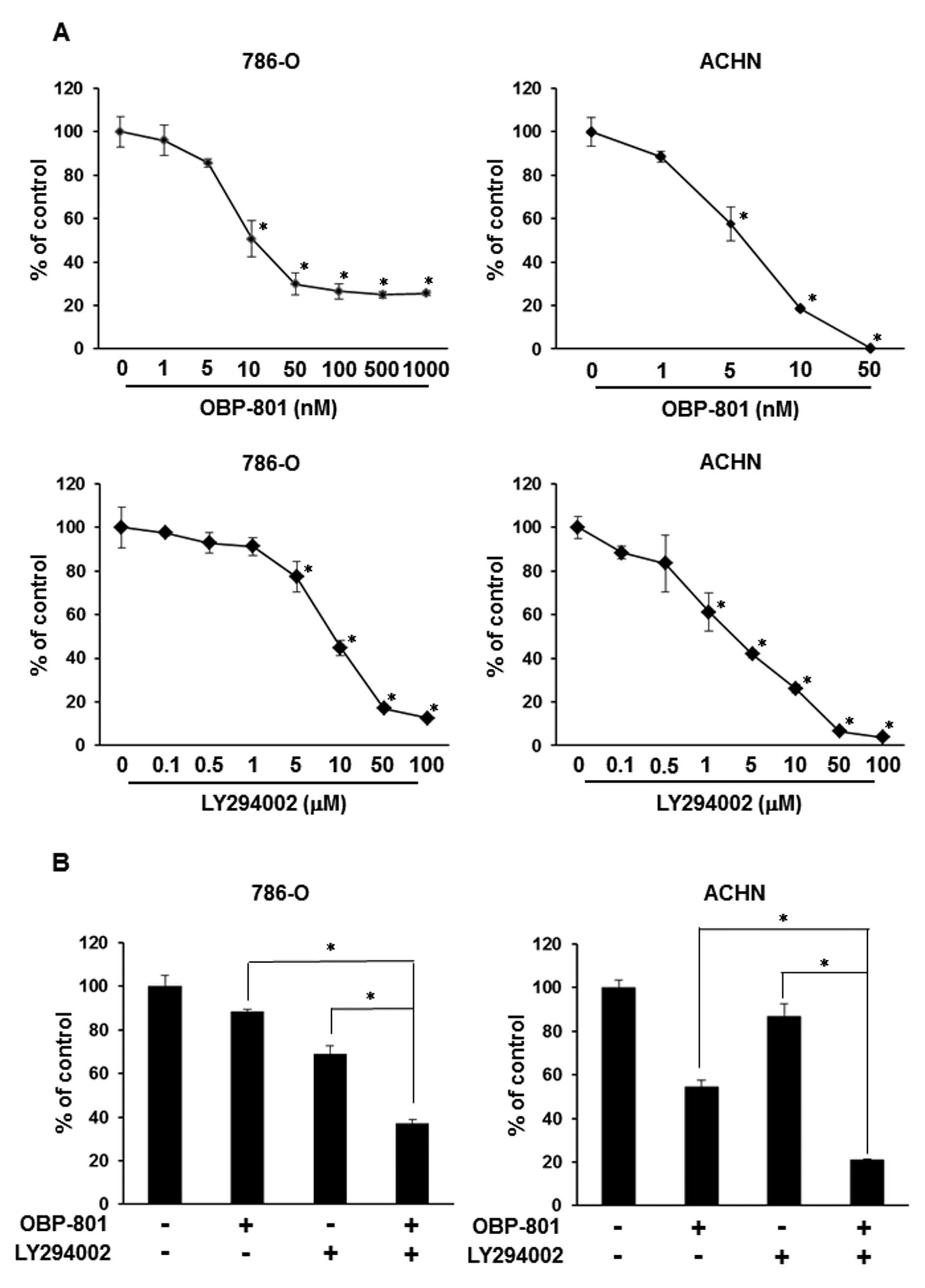
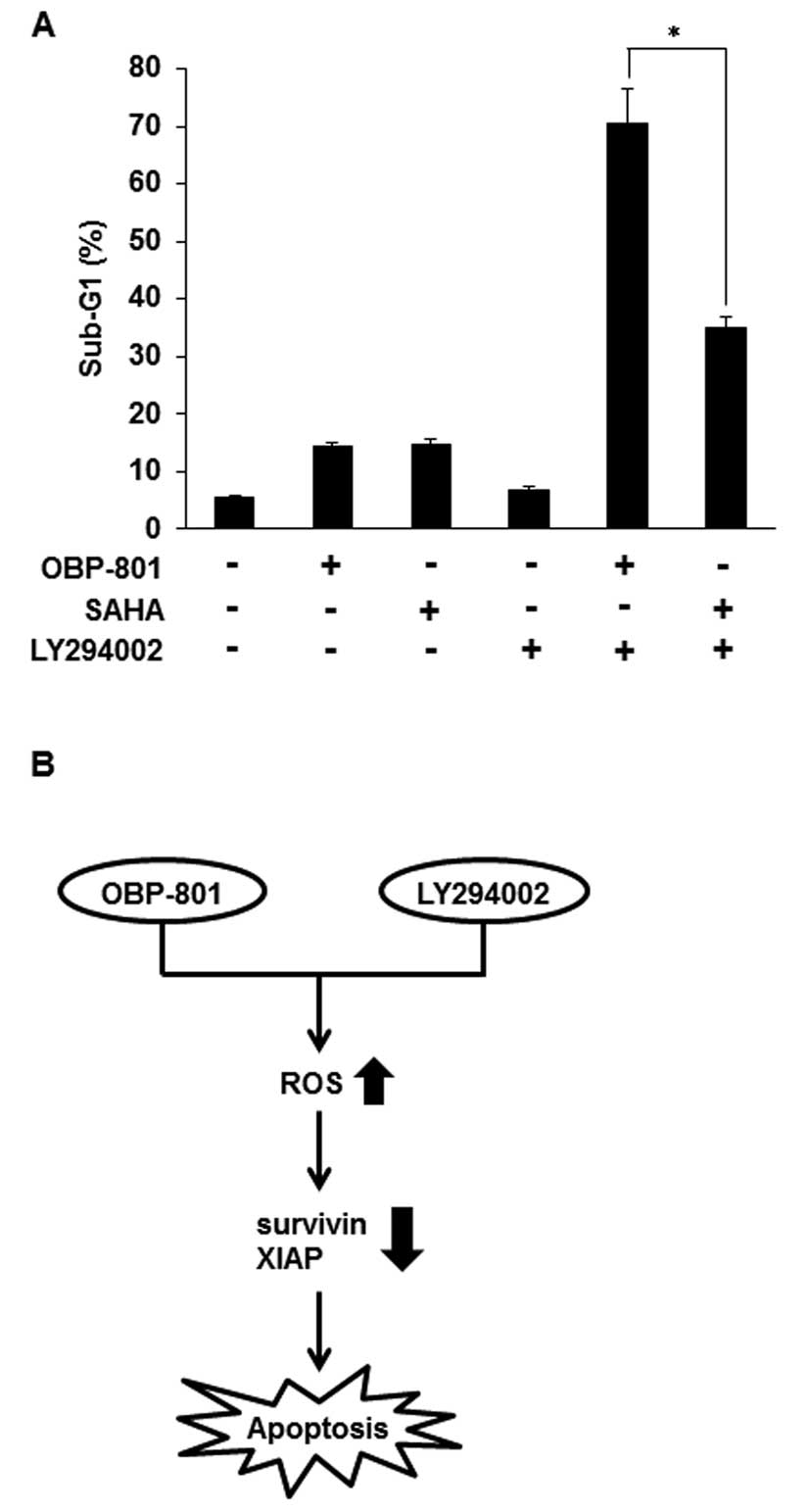
|
1.
|
Rini BI, Campbell SC and Escudier B: Renal
cell carcinoma. Lancet. 373:1119–1132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Gupta K, Miller JD, Li JZ, Russell MW and
Charbonneau C: Epidemiologic and socioeconomic burden of metastatic
renal cell carcinoma (mRCC): a literature review. Cancer Treat Rev.
34:193–205. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Kanno T, Kamba T, Yamasaki T, et al: JunB
promotes cell invasion and angiogenesis in VHL-defective renal cell
carcinoma. Oncogene. 31:3098–3110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Mahalingam D, Medina EC, Esquivel JA II,
et al: Vorinostat enhances the activity of temsirolimus in renal
cell carcinoma through suppression of survivin levels. Clin Cancer
Res. 16:141–153. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Carew JS, Esquivel JA II, Espitia CM, et
al: ELR510444 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis by abrogating
HIF activity and disrupting microtubules in renal cell carcinoma.
PloS One. 7:e311202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Sosman JA, Puzanov I and Atkins MB:
Opportunities and obstacles to combination targeted therapy in
renal cell cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:S764–S769. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Marks PA, Richon VM and Rifkind RA:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: inducers of differentiation or
apoptosis of transformed cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:1210–1216.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Koyama M, Izutani Y, Goda AE, et al:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors and
15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 synergistically induce
apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2320–2332. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Shindoh N, Mori M, Terada Y, et al: YM753,
a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, exhibits antitumor activity
with selective, sustained accumulation of acetylated histones in
tumors in the WiDr xenograft model. Int J Oncol. 32:545–555.
2008.
|
|
10.
|
Luo J, Manning BD and Cantley LC:
Targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer: rationale and
promise. Cancer Cell. 4:257–262. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Sourbier C, Lindner V, Lang H, et al: The
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway: a new target in human renal
cell carcinoma therapy. Cancer Res. 66:5130–5142. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Brognard J, Clark AS, Ni Y and Dennis PA:
Akt/protein kinase B is constitutively active in non-small cell
lung cancer cells and promotes cellular survival and resistance to
chemotherapy and radiation. Cancer Res. 61:3986–3997.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Kulik G, Carson JP, Vomastek T, et al:
Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces BID cleavage and bypasses
antiapoptotic signals in prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Cancer Res.
61:2713–2719. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Izuishi K, Kato K, Ogura T, Kinoshita T
and Esumi H: Remarkable tolerance of tumor cells to nutrient
deprivation: possible new biochemical target for cancer therapy.
Cancer Res. 60:6201–6207. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Lee CM, Fuhrman CB, Planelles V, et al:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition by LY294002
radiosensitizes human cervical cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res.
12:250–256. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Zhou C, Qiu L, Sun Y, et al: Inhibition of
EGFR/PI3K/AKT cell survival pathway promotes TSA’s effect on cell
death and migration in human ovarian cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
29:269–278. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Wang Q, Li N, Wang X, Kim MM and Evers BM:
Augmentation of sodium butyrate-induced apoptosis by
phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase inhibition in the KM20 human colon
cancer cell line. Clin Cancer Res. 8:1940–1947. 2002.
|
|
18.
|
Park JK, Cho CH, Ramachandran S, et al:
Augmentation of sodium butyrate-induced apoptosis by
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition in the human cervical
cancer cell-line. Cancer Res Treat. 38:112–117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Ozaki K, Kosugi M, Baba N, et al: Blockade
of the ERK or PI3K-Akt signaling pathway enhances the cytotoxicity
of histone deacetylase inhibitors in tumor cells resistant to
gefitinib or imatinib. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 391:1610–1615.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Wozniak MB, Villuendas R, Bischoff JR, et
al: Vorinostat interferes with the signaling transduction pathway
of T-cell receptor and synergizes with phosphoinositide-3 kinase
inhibitors in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Haematologica. 95:613–621.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Rahmani M, Yu C, Reese E, et al:
Inhibition of PI-3 kinase sensitizes human leukemic cells to
histone deacetylase inhibitor-mediated apoptosis through p44/42 MAP
kinase inactivation and abrogation of p21(CIP1/WAF1) induction
rather than AKT inhibition. Oncogene. 22:6231–6242. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22.
|
Nakata S, Yoshida T, Horinaka M, Shiraishi
T, Wakada M and Sakai T: Histone deacetylase inhibitors upregulate
death receptor 5/TRAIL-R2 and sensitize apoptosis induced by
TRAIL/APO2-L in human malignant tumor cells. Oncogene.
23:6261–6271. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Carew JS, Giles FJ and Nawrocki ST:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: mechanisms of cell death and
promise in combination cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 269:7–17. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Bots M and Johnstone RW: Rational
combinations using HDAC inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 15:3970–3977.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Ramaswamy B, Fiskus W, Cohen B, et al:
Phase I–II study of vorinostat plus paclitaxel and bevacizumab in
metastatic breast cancer: evidence for vorinostat-induced tubulin
acetylation and Hsp90 inhibition in vivo. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
132:1063–1072. 2012.
|
|
26.
|
Rathkopf D, Wong BY, Ross RW, et al: A
phase I study of oral panobinostat alone and in combination with
docetaxel in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 66:181–189. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Chinnaiyan P, Chowdhary S, Potthast L, et
al: Phase I trial of vorinostat combined with bevacizumab and
CPT-11 in recurrent glioblastoma. Neurooncology. 14:93–100.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Fritzsche FR, Weichert W, Roske A, et al:
Class I histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 are highly expressed in
renal cell cancer. BMC Cancer. 8:3812008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Hudes GR: Targeting mTOR in renal cell
carcinoma. Cancer. 115:2313–2320. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Altieri DC: Survivin, cancer networks and
pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat Revi Cancer. 8:61–70. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST and Giles
FJ: Survivin: key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel
target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5000–5005.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Krambeck AE, Dong H, Thompson RH, et al:
Survivin and b7-h1 are collaborative predictors of survival and
represent potential therapeutic targets for patients with renal
cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1749–1756. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Taniguchi H, Horinaka M, Yoshida T, et al:
Targeting the Glyoxalase pathway enhances TRAIL efficacy in cancer
cells by downregulating the expression of antiapoptotic molecules.
Mol Cancer Ther. 11:2294–2300. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Zhu L, Fukuda S, Cordis G, Das DK and
Maulik N: Anti-apoptotic protein survivin plays a significant role
in tubular morphogenesis of human coronary arteriolar endothelial
cells by hypoxic preconditioning. FEBS Lett. 508:369–374. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35.
|
Stehlik C, de Martin R, Kumabashiri I,
Schmid JA, Binder BR and Lipp J: Nuclear factor
(NF)-kappaB-regulated X-chromosome-linked iap gene expression
protects endothelial cells from tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced
apoptosis. J Exp Med. 188:211–216. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Qu Y, Wang J, Ray PS, et al:
Thioredoxin-like 2 regulates human cancer cell growth and
metastasis via redox homeostasis and NF-kappaB signaling. J Clin
Invest. 121:212–225. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Yoshioka T, Yogosawa S, Yamada T, Kitawaki
J and Sakai T: Combination of a novel HDAC inhibitor OBP-801/YM753
and a PI3K inhibitor LY294002 synergistically induces apoptosis in
human endometrial carcinoma cells due to increase of Bim with
accumulation of ROS. Gynecol Oncol. 129:425–432. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|