|
1.
|
Krejs GJ: Gastric cancer: epidemiology and
risk factors. Dig Dis. 28:600–603. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
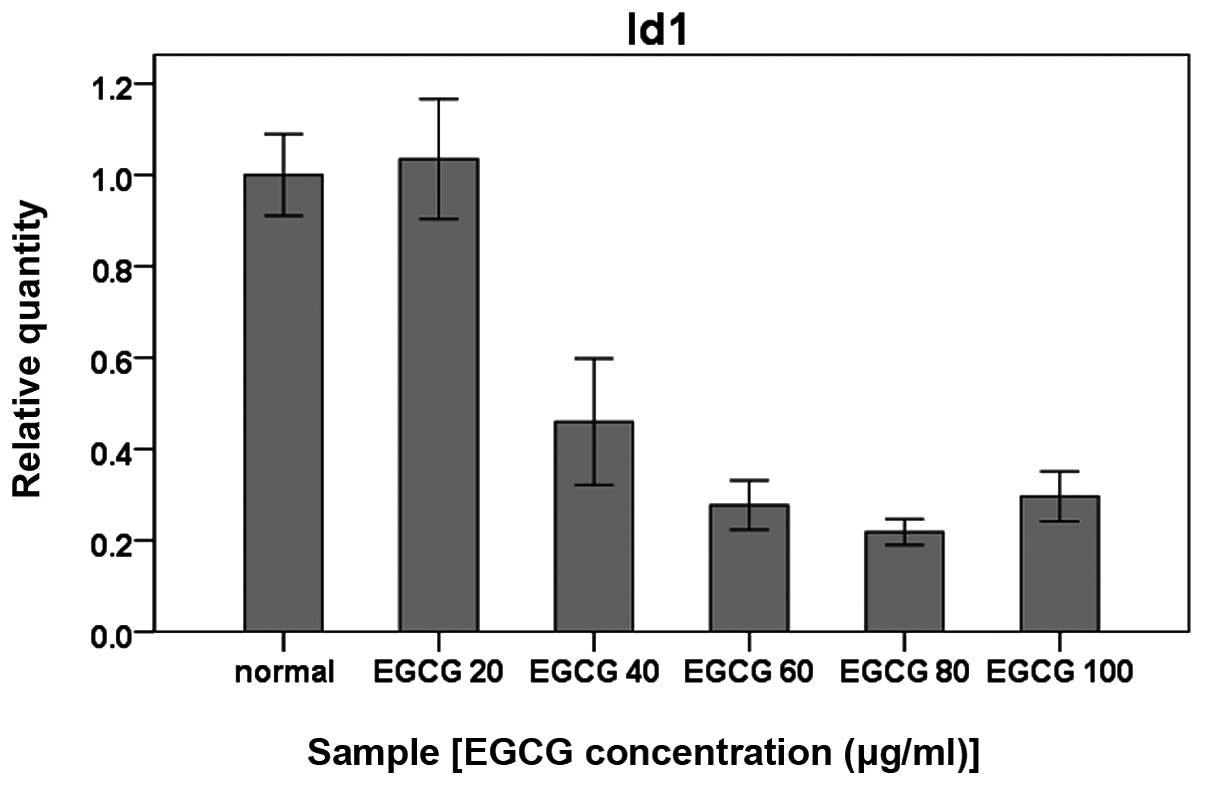
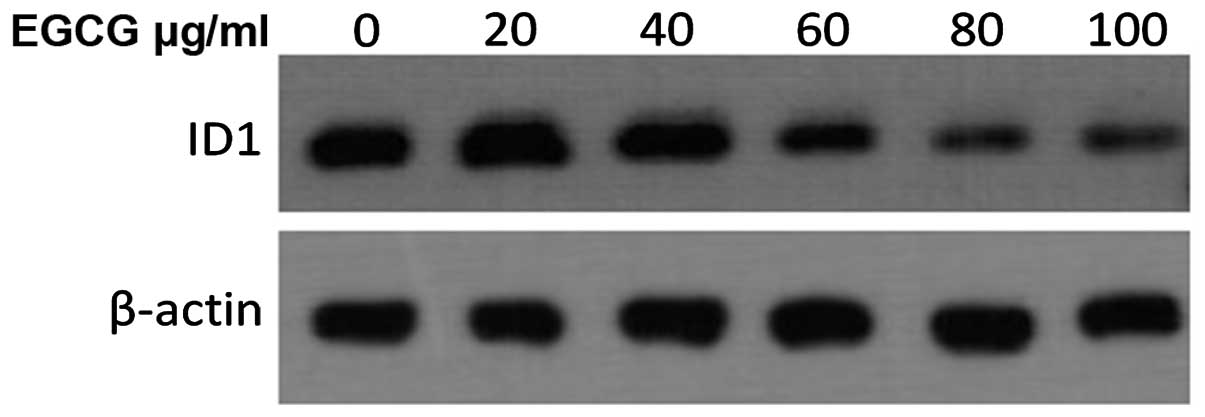
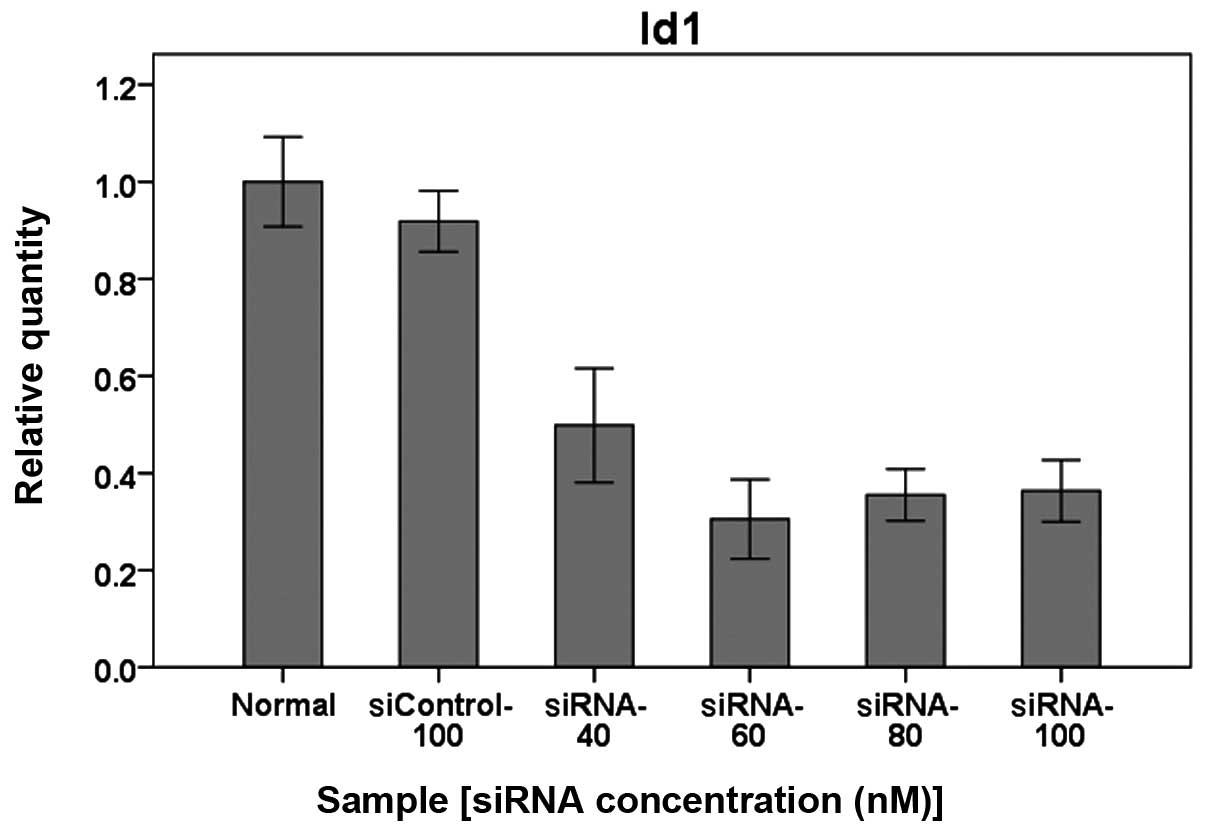
|
Yang L: Incidence and mortality of gastric
cancer in China. World J Gastroenterol. 12:17–20. 2006.
|
|
4.
|
Hemalswarya S and Doble M: Potential
synergism of natural products in the treatment of cancer. Phytother
Res. 20:239–249. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Cao G, Chen M, Song Q, et al: EGCG
protects against UVB-induced apoptosis via oxidative stress and the
JNK1/c-Jun pathway in ARPE19 cells. Mol Med Rep. 5:54–59.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Ziaedini A, Jafari A and Zakeri A:
Extraction of antioxidants and caffeine from green tea (Camelia
sinensis) leaves: kinetics and modeling. Food Sci Technol.
16:505–510. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Chen D, Wan SB, Yang H, Yuan J, Chan TH
and Dou QP: EGCG, green tea polyphenols and their synthetic analogs
and prodrugs for human cancer prevention and treatment. Adv Clin
Chem. 53:155–177. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Rao SD and Pagidas K:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a natural polyphenol, inhibits cell
proliferation and induces apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells.
Anticancer Res. 30:2519–2523. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Patra SK, Rizzi F, Silva A, Rugina DO and
Bettuzzi S: Molecular targets of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate
(EGCG): specificity and interaction with membrane lipid rafts. J
Physiol Pharmacol. 59(Suppl 9): 217–235. 2008.
|
|
10.
|
Johnson JJ, Bailey HH and Mukhtar H: Green
tea polyphenols for prostate cancer chemoprevention: a
translational perspective. Phytomedicine. 17:3–13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Mandel SA, Amit T, Kalfon L, Reznichenko
L, Weinreb O and Youdim MB: Cell signaling pathways and iron
chelation in the neurorestorative activity of green tea
polyphenols: special reference to epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG).
J Alzheimers Dis. 15:211–222. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Yang H, Zonder JA and Dou QP: Clinical
development of novel proteasome inhibitors for cancer treatment.
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 18:957–971. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Khan N and Mukhtar H: Multitargeted
therapy of cancer by green tea polyphenols. Cancer Lett.
269:269–280. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Lin RW, Chen CH, Wang YH, et al:
(−)-Epigallocatechin gallate inhibition of osteoclastic
differentiation via NF-kappaB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
379:1033–1037. 2009.
|
|
15.
|
Han S, Gou C, Hong L, et al: Expression
and significances of Id1 helix-loop-helix protein overexpression in
gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 216:63–71. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Tsuchiya T, Okaji Y, Tsuno NH, et al:
Targeting Id1 and Id3 inhibits peritoneal metastasis of gastric
cancer. Cancer Sci. 96:784–790. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Aranha MM, Sola S, Low WC, Steer CJ and
Rodrigues CM: Caspases and p53 modulate FOXO3A/Id1 signaling during
mouse neural stem cell differentiation. J Cell Biochem.
107:748–758. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Benezra R, Davis RL, Lockshon D, Turner DL
and Weintraub H: The protein Id: a negative regulator of
helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 61:49–59. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Evan G and Littlewood T: A matter of life
and cell death. Science. 281:1317–1322. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Barone MV, Pepperkok R, Peverali FA and
Philipson L: Id proteins control growth induction in mammalian
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:4985–4988. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Hara E, Yamaguchi T, Nojima H, et al:
Id-related genes encoding helix-loop-helix proteins are required
for G1 progression and are repressed in senescent human
fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 269:2139–2145. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Peverali FA, Ramqvist T, Saffrich R,
Pepperkok R, Barone MV and Philipson L: Regulation of G1
progression by E2A and Id helix-loop-helix proteins. EMBO J.
13:4291–4301. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Alani RM, Young AZ and Shifflett CB: Id1
regulation of cellular senescence through transcriptional
repression of p16/Ink4a. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:7812–7816.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Lee TK, Man K, Ling MT, et al:
Over-expression of Id-1 induces cell proliferation in
hepatocellular carcinoma through inactivation of p16INK4a/RB
pathway. Carcinogenesis. 24:1729–1736. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Ohtani N, Zebedee Z, Huot TJ, et al:
Opposing effects of Ets and Id proteins on p16INK4a expression
during cellular senescence. Nature. 409:1067–1070. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Ling MT, Wang X, Ouyang XS, et al:
Activation of MAPK signaling pathway is essential for Id-1 induced
serum independent prostate cancer cell growth. Oncogene.
21:8498–8505. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Cheung HW, Ling MT, Tsao SW, Wong YC and
Wang X: Id-1-induced Raf/MEK pathway activation is essential for
its protective role against taxol-induced apoptosis in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 25:881–887. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Ling MT, Wang X, Ouyang XS, Xu K, Tsao SW
and Wong YC: Id-1 expression promotes cell survival through
activation of NF-kappaB signalling pathway in prostate cancer
cells. Oncogene. 22:4498–4508. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Kim H, Chung H, Kim HJ, et al: Id-1
regulates Bcl-2 and Bax expression through p53 and NF-kappaB in
MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 112:287–296.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Chen C, Shen G, Hebbar V, Hu R, Owuor ED
and Kong AN: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced stress signals in
HT-29 human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis.
24:1369–1378. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Qanungo S, Das M, Haldar S and Basu A:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces mitochondrial membrane
depolarization and caspase-dependent apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
cells. Carcinogenesis. 26:958–967. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Gupta S, Ahmad N, Nieminen AL and Mukhtar
H: Growth inhibition, cell-cycle dysregulation, and induction of
apoptosis by green tea constituent (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate
in androgen-sensitive and androgen-insensitive human prostate
carcinoma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 164:82–90. 2000.
|
|
33.
|
Hofmann CS and Sonenshein GE: Green tea
polyphenol epigallocatechin-3 gallate induces apoptosis of
proliferating vascular smooth muscle cells via activation of p53.
FASEB J. 17:702–704. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Roy AM, Baliga MS and Katiyar SK:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces apoptosis in estrogen
receptor-negative human breast carcinoma cells via modulation in
protein expression of p53 and Bax and caspase-3 activation. Mol
Cancer Ther. 4:81–90. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Nihal M, Ahmad N, Mukhtar H and Wood GS:
Anti-proliferative and proapoptotic effects of
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on human melanoma: possible
implications for the chemoprevention of melanoma. Int J Cancer.
114:513–521. 2005.
|
|
36.
|
Ahmad N, Gupta S and Mukhtar H: Green tea
polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate differentially modulates
nuclear factor kappaB in cancer cells versus normal cells. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 376:338–346. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37.
|
Gupta S, Hastak K, Afaq F, Ahmad N and
Mukhtar H: Essential role of caspases in
epigallocatechin-3-gallate-mediated inhibition of nuclear factor
kappa B and induction of apoptosis. Oncogene. 23:2507–2522. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Vittal R, Selvanayagam ZE, Sun Y, et al:
Gene expression changes induced by green tea polyphenol
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in human bronchial epithelial 21BES
cells analyzed by DNA microarray. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:1091–1099.
2004.
|
|
39.
|
Naasani I, Seimiya H and Tsuruo T:
Telomerase inhibition, telomere shortening, and senescence of
cancer cells by tea catechins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
249:391–396. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|