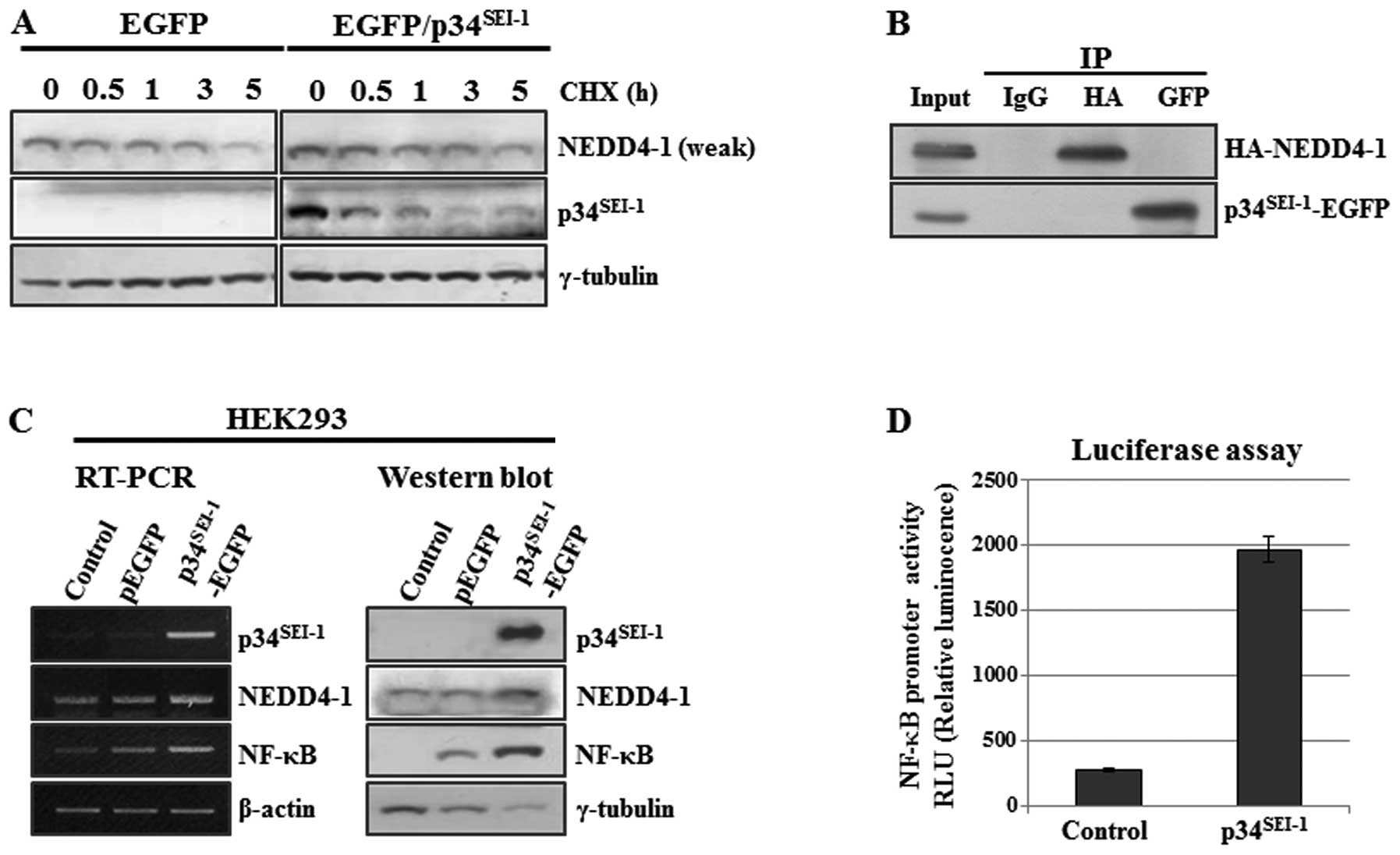
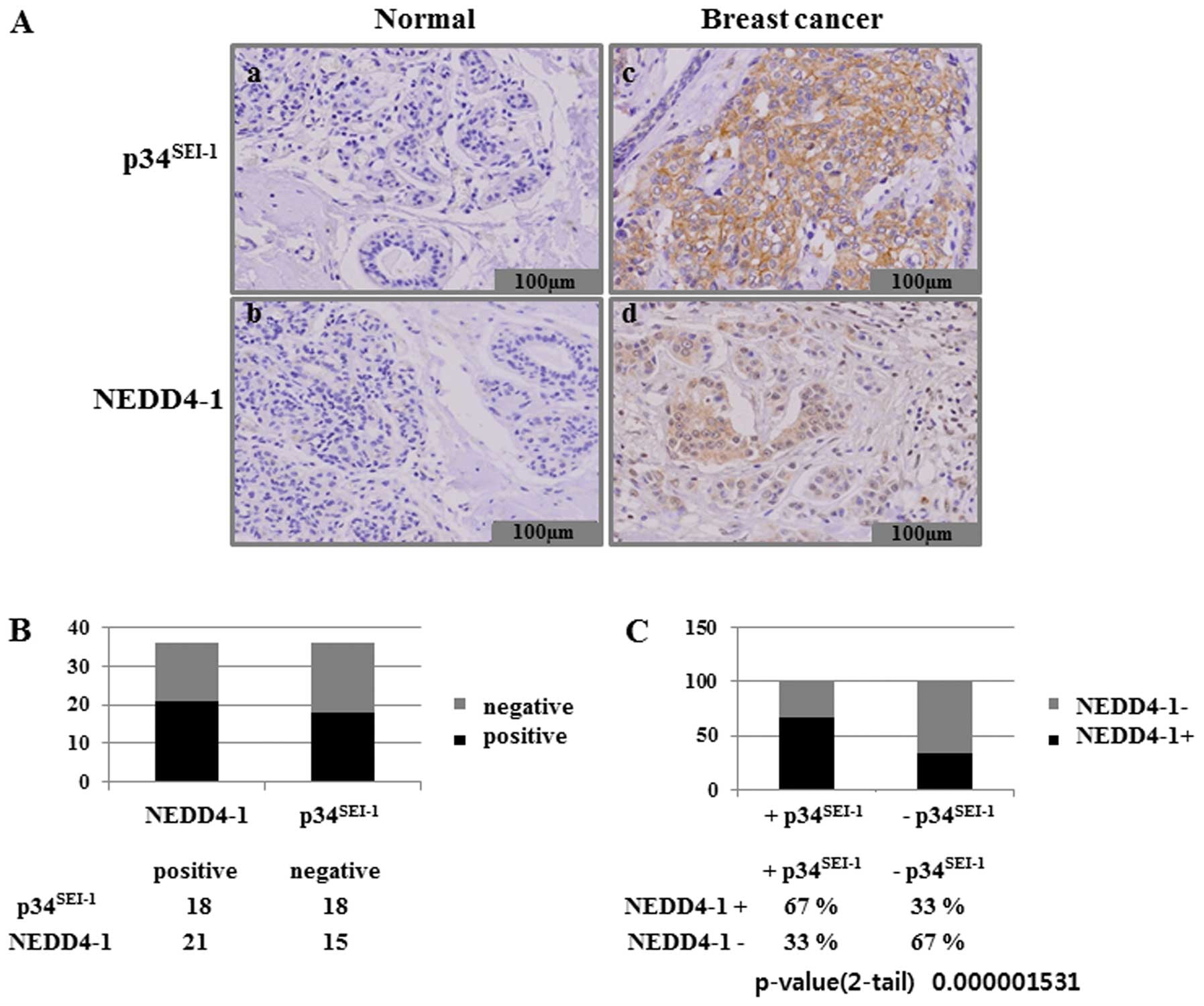
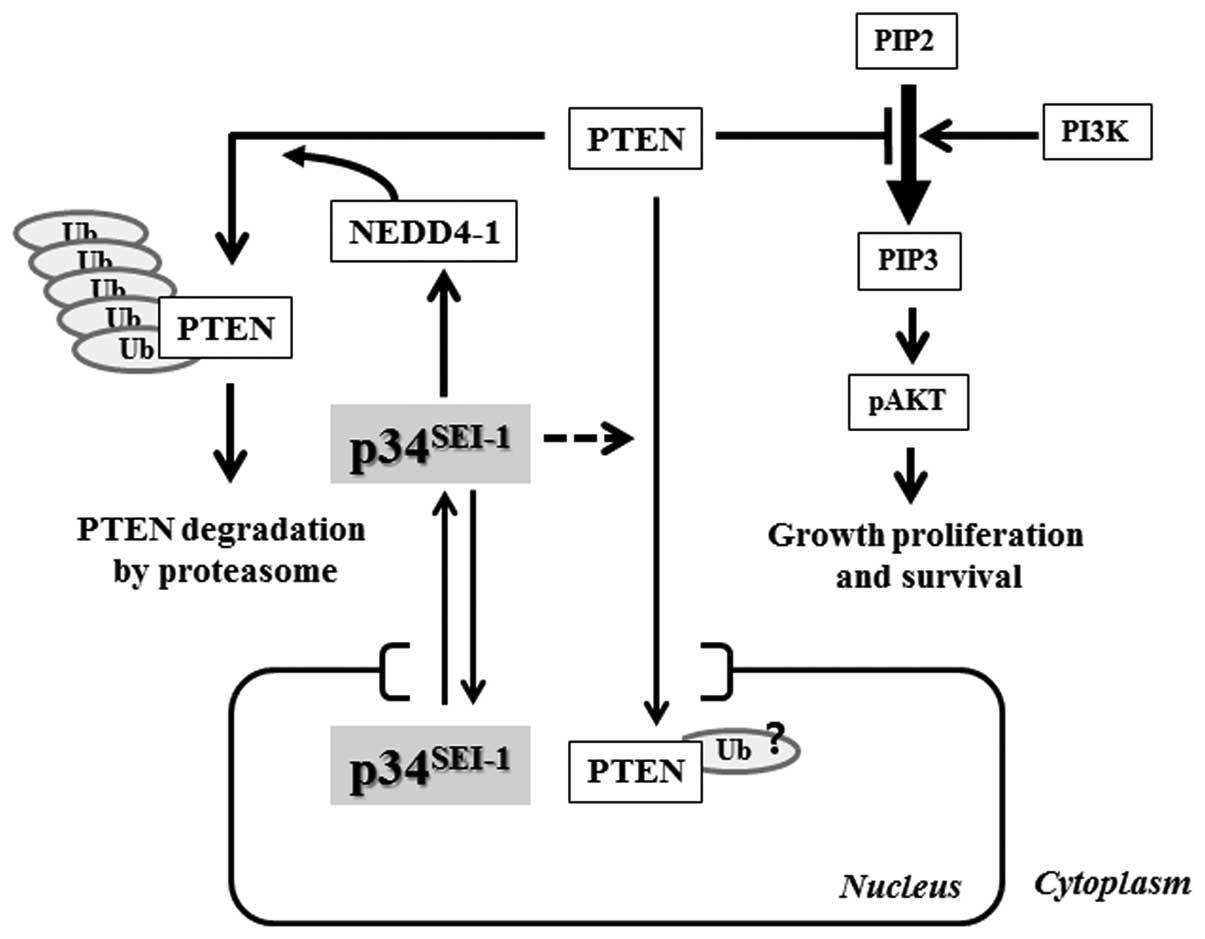
|
1.
|
Morgensztern D and McLeod HL:
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as a target for cancer therapy. Anticancer
Drugs. 16:797–803. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Cortot A, Armand JP and Soria JC:
PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway inhibitors. Bull Cancer. 93:19–26. 2006.(In
French).
|
|
3.
|
Yap TA, Garrett MD, Walton MI, Raynaud F,
de Bono JS and Workman P: Targeting the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway:
progress, pitfalls, and promises. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 8:393–412.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
LoPiccolo J, Blumenthal GM, Bernstein WB
and Dennis PA: Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: effective
combinations and clinical considerations. Drug Resist Updat.
11:32–50. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Yuan TL and Cantley LC: PI3K pathway
alterations in cancer: variations on a theme. Oncogene.
27:5497–5510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Kong D and Yamori T: Advances in
development of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors. Curr Med
Chem. 16:2839–2854. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Qiao M, Sheng S and Pardee AB: Metastasis
and AKT activation. Cell Cycle. 7:2991–2996. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Xue G, Restuccia DF, Lan Q, et al:
Akt/PKB-mediated phosphorylation of Twist1 promotes tumor
metastasis via mediating cross-talk between PI3K/Akt and TGF-beta
signaling axes. Cancer Discov. 2:248–259. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Brader S and Eccles SA: Phosphoinositide
3-kinase signalling pathways in tumor progression, invasion and
angiogenesis. Tumori. 90:2–8. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Grille SJ, Bellacosa A, Upson J, et al:
The protein kinase Akt induces epithelial mesenchymal transition
and promotes enhanced motility and invasiveness of squamous cell
carcinoma lines. Cancer Res. 63:2172–2178. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Toker A and Yoeli-Lerner M: Akt signaling
and cancer: surviving but not moving on. Cancer Res. 66:3963–3966.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Yoeli-Lerner M and Toker A: Akt/PKB
signaling in cancer: a function in cell motility and invasion. Cell
Cycle. 5:603–605. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Gagnon V, St-Germain ME, Parent S and
Asselin E: Akt activity in endometrial cancer cells: regulation of
cell survival through cIAP-1. Int J Oncol. 23:803–810.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Maehama T and Dixon JE: The tumor
suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second
messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem.
273:13375–13378. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Stambolic V, Suzuki A, de la Pompa JL, et
al: Negative regulation of PKB/Akt-dependent cell survival by the
tumor suppressor PTEN. Cell. 95:29–39. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Akca H, Demiray A, Tokgun O and Yokota J:
Invasiveness and anchorage independent growth ability augmented by
PTEN inactivation through the PI3K/AKT/NFκB pathway in lung cancer
cells. Lung Cancer. 73:302–309. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Carver BS, Chapinski C, Wongvipat J, et
al: Reciprocal feedback regulation of PI3K and androgen receptor
signaling in PTEN-deficient prostate cancer. Cancer Cell.
19:575–586. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Taylor CJ, Qiao J, Colon NC, Schlegel C,
Josifi E and Chung DH: Integrin-linked kinase regulates phosphatase
and tensin homologue activity to promote tumorigenesis in
neuroblastoma cells. Surgery. 150:162–168. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Tian XX, Pang JC, To SS and Ng HK:
Restoration of wild-type PTEN expression leads to apoptosis,
induces differentiation, and reduces telomerase activity in human
glioma cells. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 58:472–479. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
McMenamin ME, Soung P, Perera S, Kaplan I,
Loda M and Sellers WR: Loss of PTEN expression in paraffin-embedded
primary prostate cancer correlates with high Gleason score and
advanced stage. Cancer Res. 59:4291–4296. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Chang JG, Chen YJ, Perng LI, et al:
Mutation analysis of the PTEN/MMAC1 gene in cancers of the
digestive tract. Eur J Cancer. 35:647–651. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Wang X, Trotman LC, Koppie T, et al:
NEDD4-1 is a protooncogenic ubiquitin ligase for PTEN. Cell.
128:129–139. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Amodio N, Scrima M, Palaia L, et al:
Oncogenic role of the E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4-1, a PTEN negative
regulator, in non-small-cell lung carcinomas. Am J Pathol.
177:2622–2634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Hayashi R, Goto Y, Ikeda R, Yokoyama KK
and Yoshida K: CDCA4 is an E2F transcription factor family-induced
nuclear factor that regulates E2F-dependent transcriptional
activation and cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 281:35633–35648.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Hsu SI, Yang CM, Sim KG, Hentschel DM,
O’Leary E and Bonventre JV: TRIP-Br: a novel family of PHD zinc
finger-and bromodomain-interacting proteins that regulate the
transcriptional activity of E2F-1/DP-1. EMBO J. 20:2273–2285. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Hong SW, Kim CJ, Park WS, et al: p34SEI-1
inhibits apoptosis through the stabilization of the X-linked
inhibitor of apoptosis protein: p34SEI-1 as a novel target for
anti-breast cancer strategies. Cancer Res. 69:741–746. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Li Y, Nie CJ, Hu L, et al:
Characterization of a novel mechanism of genomic instability
involving the SEI1/SET/NM23H1 pathway in esophageal cancers. Cancer
Res. 70:5695–5705. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Tang DJ, Hu L, Xie D, et al: Oncogenic
transformation by SEI-1 is associated with chromosomal instability.
Cancer Res. 65:6504–6508. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Lee SL, Hong SW, Shin JS, et al: p34SEI-1
inhibits doxorubicin-induced senescence through a pathway mediated
by protein kinase C-delta and c-Jun-NH2-kinase 1 activation in
human breast cancer MCF7 cells. Mol Cancer Res. 7:1845–1853. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Lin Q, Wang J, Childress C, Sudol M, Carey
DJ and Yang W: HECT E3 ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-1 ubiquitinates ACK
and regulates epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced degradation of
EGF receptor and ACK. Mol Cell Biol. 30:1541–1554. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Trotman LC, Wang X, Alimonti A, et al:
Ubiquitination regulates PTEN nuclear import and tumor suppression.
Cell. 128:141–156. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Fouladkou F, Landry T, Kawabe H, et al:
The ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-1 is dispensable for the regulation of
PTEN stability and localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:8585–8590. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Burow ME, Weldon CB, Melnik LI, et al:
PI3-K/AKT regulation of NF-kappaB signaling events in suppression
of TNF-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 271:342–345.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Holmes KM, Annala M, Chua CY, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2-driven glioma
progression is prevented by blocking a clinically significant
integrin, integrin-linked kinase, and NF-kappaB network. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 109:3475–3480. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35.
|
Judge AR, Koncarevic A, Hunter RB, Liou
HC, Jackman RW and Kandarian SC: Role for IkappaBalpha, but not
c-Rel, in skeletal muscle atrophy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
292:C372–C382. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Van Themsche C, Leblanc V, Parent S and
Asselin E: X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) regulates
PTEN ubiquitination, content, and compartmentalization. J Biol
Chem. 284:20462–20466. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Sarma SN, Kim YJ and Ryu JC: Gene
expression profiles of human promyelocytic leukemia cell lines
exposed to volatile organic compounds. Toxicology. 271:122–130.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Du F and Galan JE: Selective inhibition of
type III secretion activated signaling by the Salmonella
effector AvrA. PLoS Pathog. 5:e10005952009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|