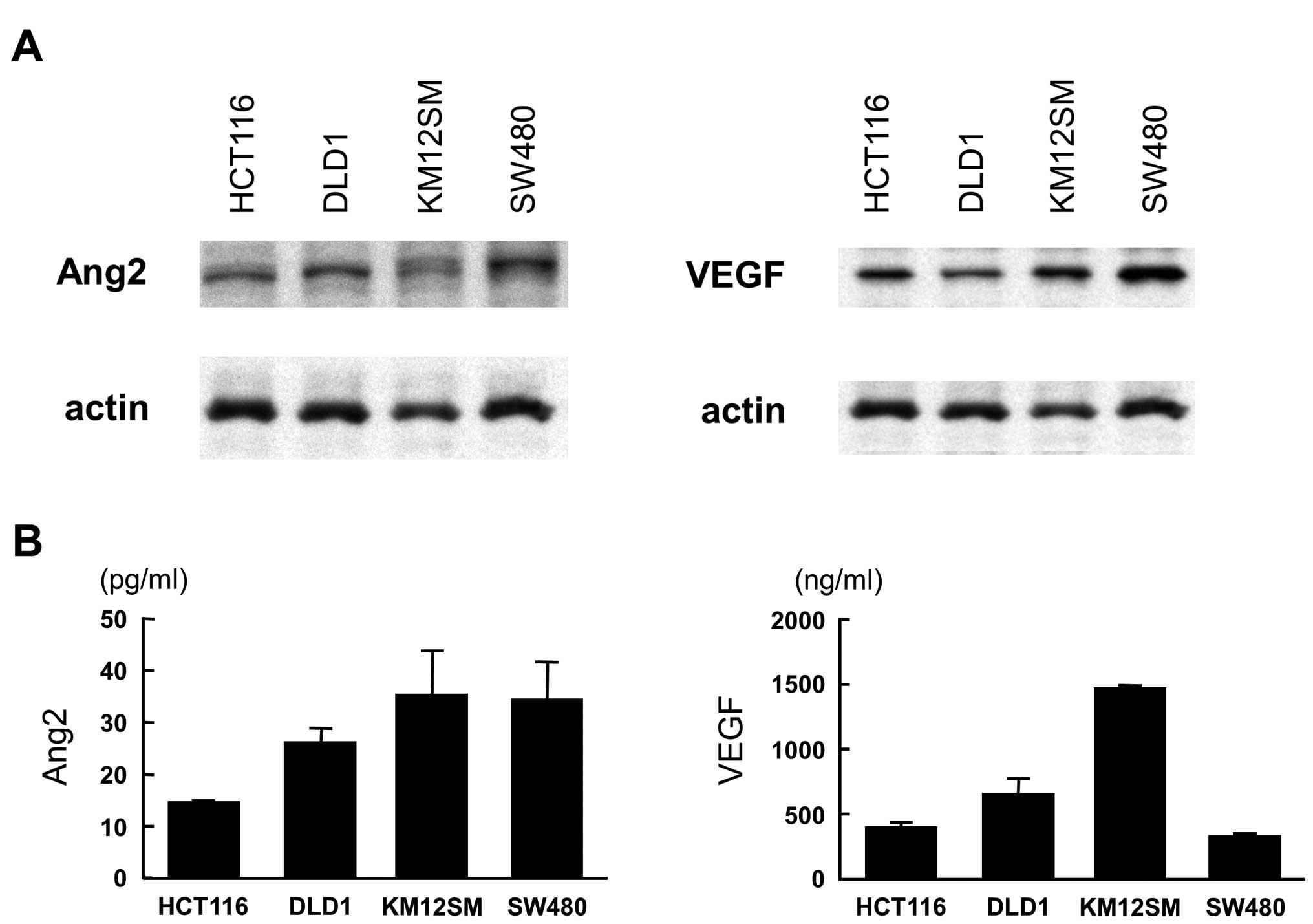
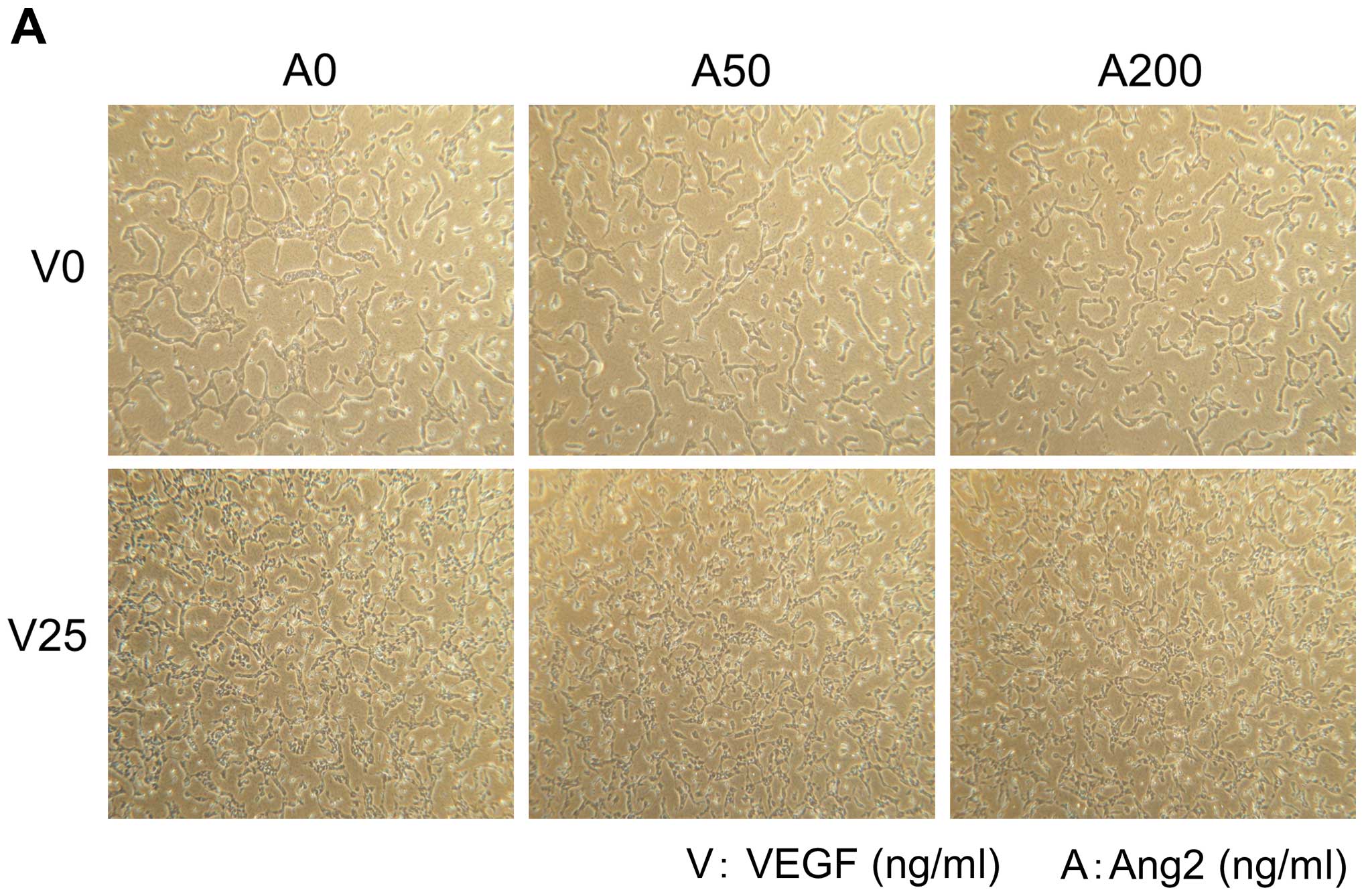
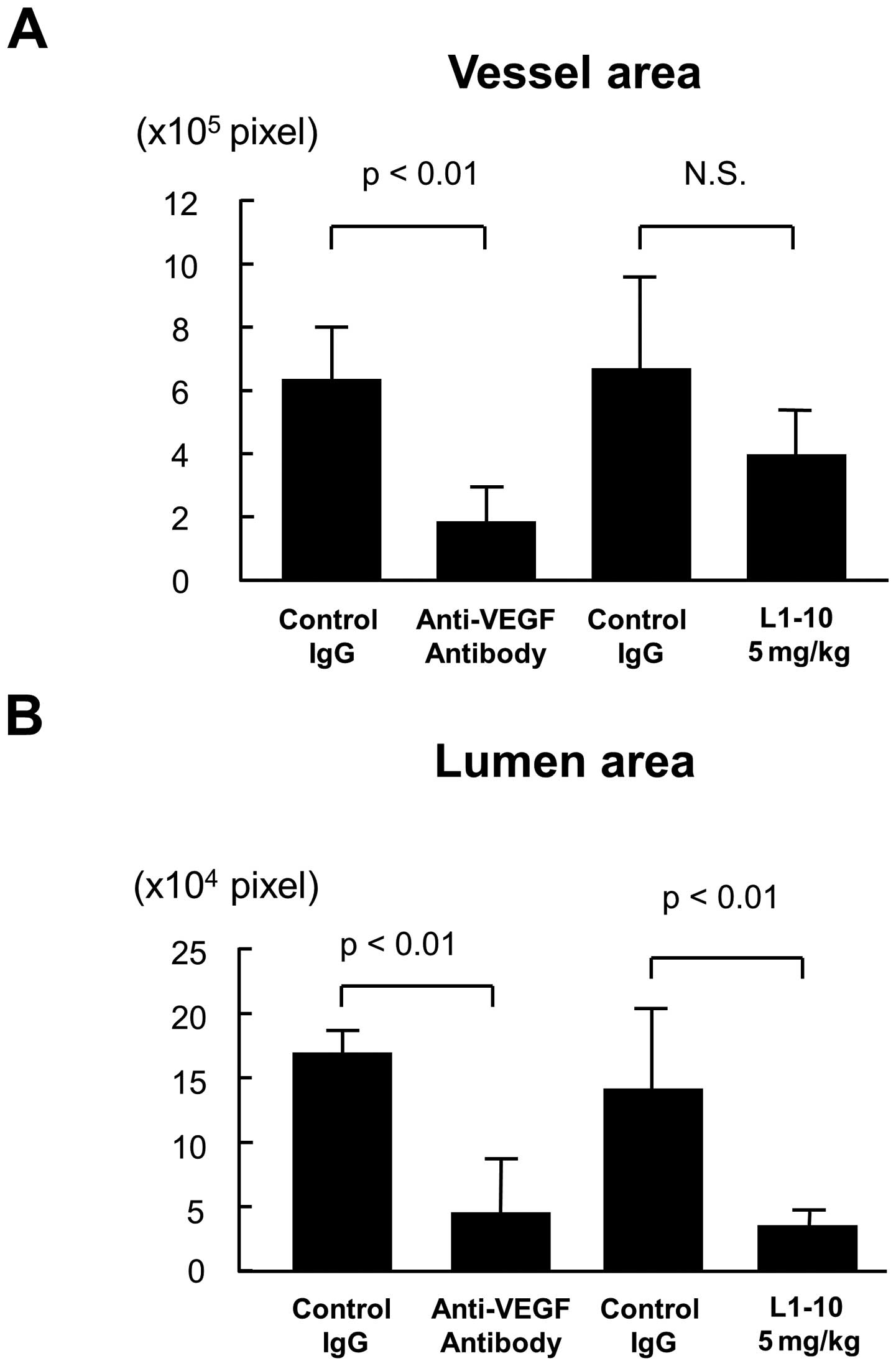
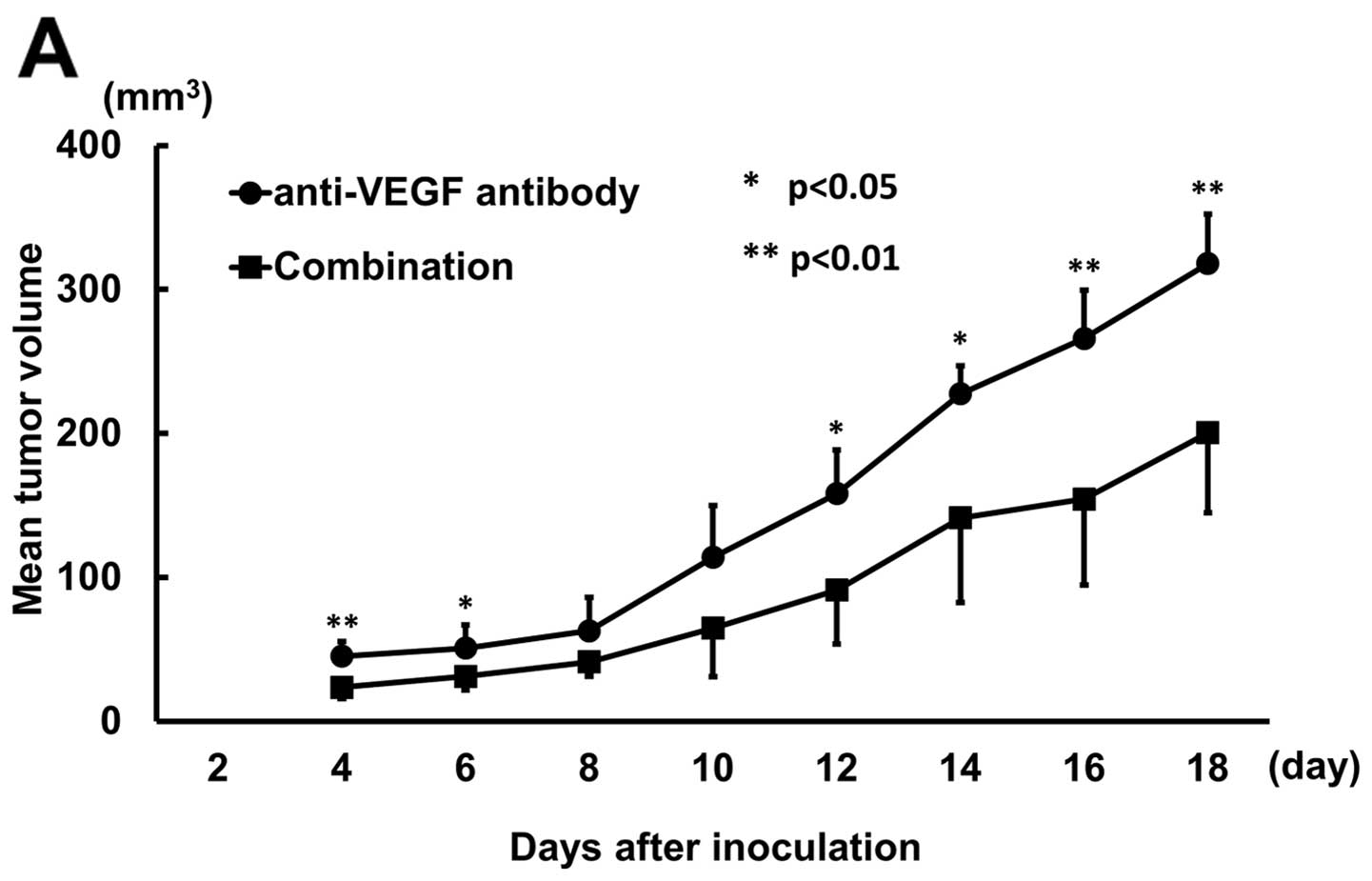
|
1.
|
Bergers G and Benjamin LE: Tumorigenesis
and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:401–410. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Kabbinavar F, Hurwitz HI, Fehrenbacher L,
et al: Phase II, randomized trial comparing bevacizumab plus
fluorouracil (FU)/leucovorin (LV) with FU/LV alone in patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 21:60–65. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Ogawa M, Yamamoto H, Nagano H, et al:
Hepatic expression of ANG2 RNA in metastatic colorectal cancer.
Hepatology. 39:528–539. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, et
al: Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for
metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 350:2335–2342. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, et al:
Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo
angiogenesis. Science. 277:55–60. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, et al:
Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor,
during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell. 87:1171–1180. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Oliner J, Min H, Leal J, et al:
Suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth by selective
inhibition of angiopoietin-2. Cancer Cell. 6:507–516. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Brown JL, Cao ZA, Pinzon-Ortiz M, et al: A
human monoclonal anti-ANG2 antibody leads to broad antitumor
activity in combination with VEGF inhibitors and chemotherapy
agents in preclinical models. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:145–156. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Coxon A, Bready J, Min H, et al:
Context-dependent role of angiopoietin-1 inhibition in the
suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth: implications for AMG
386, an angiopoietin-1/2-neutralizing peptibody. Mol Cancer Ther.
9:2641–2651. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Falcon BL, Hashizume H, Koumoutsakos P, et
al: Contrasting actions of selective inhibitors of angiopoietin-1
and angiopoietin-2 on the normalization of tumor blood vessels. Am
J Pathol. 175:2159–2170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Morikawa K, Walker SM, Nakajima M, Pathak
S, Jessup JM and Fidler IJ: Influence of organ environment on the
growth, selection, and metastasis of human colon carcinoma cells in
nude mice. Cancer Res. 48:6863–6871. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Yamamoto H, Kondo M, Nakamori S, et al:
JTE-522, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, is an effective
chemopreventive agent against rat experimental liver fibrosis1.
Gastroenterology. 125:556–571. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Morrissey C, Dowell A, Koreckij TD, et al:
Inhibition of angiopoietin-2 in LuCaP 23.1 prostate cancer tumors
decreases tumor growth and viability. Prostate. 70:1799–1808.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Tressel SL, Kim H, Ni CW, et al:
Angiopoietin-2 stimulates blood flow recovery after femoral artery
occlusion by inducing inflammation and arteriogenesis. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:1989–1995. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Bayless KJ and Davis GE: The Cdc42 and
Rac1 GTPases are required for capillary lumen formation in
three-dimensional extracellular matrices. J Cell Sci.
115:1123–1136. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Davis GE, Bayless KJ and Mavila A:
Molecular basis of endothelial cell morphogenesis in
three-dimensional extracellular matrices. Anat Rec. 268:252–275.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Folkman J and Haudenschild C: Angiogenesis
in vitro. Nature. 288:551–556. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Bayless KJ, Salazar R and Davis GE:
RGD-dependent vacuolation and lumen formation observed during
endothelial cell morphogenesis in three-dimensional fibrin matrices
involves the alpha(v)beta(3) and alpha(5)beta(1) integrins. Am J
Pathol. 156:1673–1683. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Davis GE and Bayless KJ: An integrin and
Rho GTPase-dependent pinocytic vacuole mechanism controls capillary
lumen formation in collagen and fibrin matrices. Microcirculation.
10:27–44. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Yang S, Graham J, Kahn JW, Schwartz EA and
Gerritsen ME: Functional roles for PECAM-1 (CD31) and VE-cadherin
(CD144) in tube assembly and lumen formation in three-dimensional
collagen gels. Am J Pathol. 155:887–895. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Kamei M, Saunders WB, Bayless KJ, Dye L,
Davis GE and Weinstein BM: Endothelial tubes assemble from
intracellular vacuoles in vivo. Nature. 442:453–456. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Hashizume H, Falcon BL, Kuroda T, et al:
Complementary actions of inhibitors of angiopoietin-2 and VEGF on
tumor angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Res. 70:2213–2223. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Huang H, Lai JY, Do J, et al: Specifically
targeting angiopoietin-2 inhibits angiogenesis, Tie2-expressing
monocyte infiltration, and tumor growth. Clin Cancer Res.
17:1001–1011. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Chae SS, Kamoun WS, Farrar CT, et al:
Angiopoietin-2 interferes with anti-VEGFR2-induced vessel
normalization and survival benefit in mice bearing gliomas. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:3618–3627. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Herynk MH, Tsan R, Radinsky R and Gallick
GE: Activation of c-Met in colorectal carcinoma cells leads to
constitutive association of tyrosine-phosphorylated beta-catenin.
Clin Exp Metastasis. 20:291–300. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Kim Y, Park H, Lim Y, et al: Decreased
syndecan-2 expression correlates with trichostatin-A
induced-morphological changes and reduced tumorigenic activity in
colon carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 22:826–830. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Shim WS, Ho IA and Wong PE: Angiopoietin:
a TIE(d) balance in tumor angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 5:655–665.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Jain RK: Normalization of tumor
vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy.
Science. 307:58–62. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|