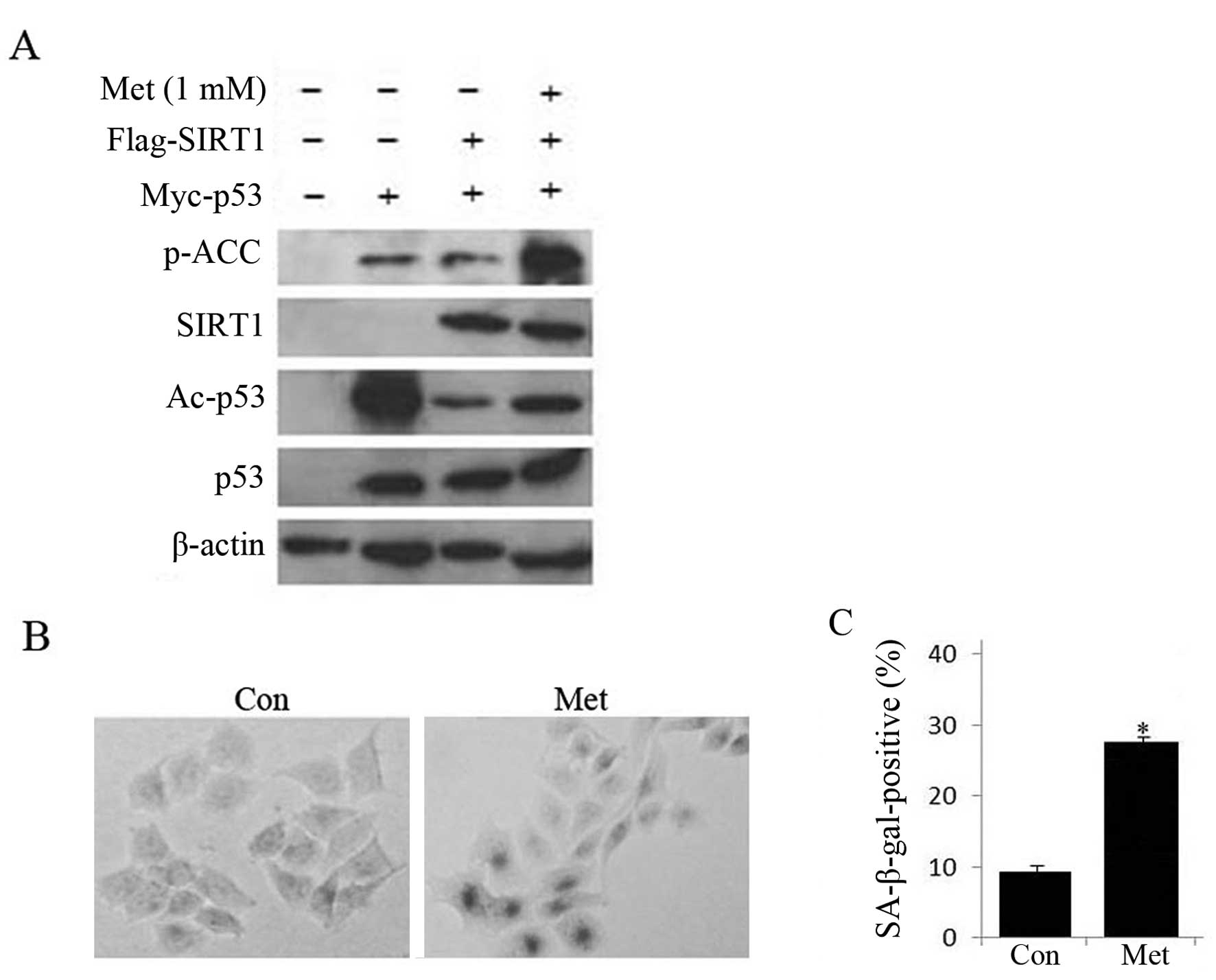
|
1.
|
Collado M, Blasco MA and Serrano M:
Cellular senescence in cancer and aging. Cell. 130:223–233. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Collado M and Serrano M: Senescence in
tumors: evidence from mice and humans. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:51–57.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Kang TW, Yevsa T, Woller N, et al:
Senescence surveillance of pre-malignant hepatocytes limits live
cancer development. Nature. 479:547–551. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Kuilman T, Michaloglou C, Mooi WJ and
Peeper DS: The essence of senescence. Genes Dev. 24:2463–2479.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, et al: A
biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in
aging skin in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:9363–9367. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Debacq-Chainiaux F, Erusalimsky JD,
Campisi J and Toussaint O: Protocols to detect
senescence-associated beta-galactosidase (SA-βgal) activity, a
biomarker of senescent cells in culture and in vivo. Nat Protoc.
4:1798–1806. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Xue W, Zender L, Miething C, et al:
Senescence and tumour clearance is triggered by p53 restoration in
murine liver carcinomas. Nature. 445:656–660. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Pollak M and Gonzalez-Angulo AM: Metformin
and hepatic carcinogenesis. Cancer Prev Res. 5:500–502. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Qu Z, Zhang Y, Liao M, Chen Y, Zhao J and
Pan Y: In vitro and in vivo antitumoral action of metformin on
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 42:922–933. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Chen HP, Shieh JJ, Chang CC, et al:
Metformin decreases hepatocellular carcinoma risk in a
dose-dependent manner: population-based and in vitro studies. Gut.
62:606–615. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Liu J, Hou M, Yuan T, et al: Enhanced
cytotoxic effect of low doses of metformin combined with ionizing
radiation on hepatoma cells via ATP deprivation and inhibition of
DNA repair. Oncol Rep. 28:1406–1412. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, et al: Role
of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J
Clin Invest. 108:1167–1174. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Ben Sahra I, Regazzetti C, Robert G, et
al: Metformin, independent of AMPK, induces mTOR inhibition and
cell-cycle arrest through REDD1. Cancer Res. 71:4366–4372.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Del Barco S, Vazquez-Martin A, Cufí S, et
al: Metformin: multi-faceted protection against cancer. Oncotarget.
2:896–917. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Wang W, Yang X, López de Silanes I,
Carling D and Gorospe M: Increased AMP:ATP ratio and AMP-activated
protein kinase activity during cellular senescence linked to
reduced HuR function. J Biol Chem. 278:27016–2723. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Cairney CJ, Bilsland AE, Evans T, et al:
Cancer cell senescence: a new frontier in drug development. Drug
Discov Today. 17:269–276. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Qian Y, Zhang J, Yan B and Chen X: DEC1, a
basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor and a novel target gene
of the p53 family, mediates p53-dependent premature senescence. J
Biol Chem. 283:2896–2905. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Mallette FA, Goumard S, Gaumont-Leclerc
MF, Moiseeva O and Ferbeyre G: Human fibroblasts require the Rb
family of tumor suppressors, but not p53, for PML-induced
senescence. Oncogene. 23:91–99. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Guarente L: Sir2 links chromatin
silencing, metabolism and aging. Genes Dev. 14:1021–1026.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Nardella C, Clohessy JG, Alimonti A and
Pandolfi PP: Pro-senescence therapy for cancer treatment. Nat Rev
Cancer. 11:503–511. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Acosta JC and Gil J: Senescence: a new
weapon for cancer therapy. Trends Cell Biol. 22:211–219. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Ewald JA, Desotelle JA, Wilding G and
Jarrard DF: Therapy-induced senescence in cancer. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 102:1536–1546. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Aljada A and Mousa SA: Metformin and
neoplasia: implications and indications. Pharmacol Ther.
133:108–115. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Lee MS, Hsu CC, Wahlqvist ML, Tsai HN,
Chang YH and Huang YC: Type 2 diabetes increases and metformin
reduces total, colorectal, liver and pancreatic cancer incidence in
taiwanese a representative population prospective cohort study of
800,000 individuals. BMC Cancer. 11:202011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Zhang ZJ, Zheng ZJ, Shi R, Su Q, Jiang Q
and Kip KE: Metformin for liver cancer prevention in patients with
type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 97:2347–2353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Zwerschke W, Mazurek S, Stöckl P, Hütter
E, Eigenbrodt E and Jansen-Dürr P: Metabolic analysis of senescent
human fibroblasts reveals a role for AMP in cellular senescence.
Biochem J. 376:403–411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Mariño G, Ugalde AP, Salvador-Montoliu N,
et al: Premature aging in mice activates a systemic metabolic
response involving autophagy induction. Hum Mol Genet.
17:2196–2211. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Sung JY, Woo CH, Kang YJ, Lee KY and Choi
HC: AMPK induces vascular smooth muscle cell senescence via LKB1
dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 413:143–148. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Imamura K, Ogura T, Kishimoto A, Kaminishi
M and Esumi H: Cell cycle regulation via p53 phosphorylation by a
5′-AMP activated protein kinase activator,
5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside, in a human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
287:562–567. 2001.
|
|
31.
|
Jones RG, Plas DR, Kubek S, et al:
AMP-activated protein kinase induces a p53-dependent metabolic
checkpoint. Mol Cell. 18:283–293. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Luo J, Nikolaev AY, Imai S, et al:
Negative control of p53 by Sir2alpha promotes cell survival under
stress. Cell. 107:137–148. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Langley E, Pearson M, Faretta M, et al:
Human SIR2 deacetylates p53 and antagonizes PML/p53-induced
cellular senescence. EMBO J. 21:2383–2396. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Wang Y, Liang Y and Vanhoutte PM: SIRT1
and AMPK in regulating mammalian senescence: a critical review and
a working model. FEBS Lett. 585:986–994. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Zu Y, Liu L, Lee MY, et al: SIRT1 promotes
proliferation and prevents senescence through targeting LKB1 in
primary porcine aortic endothelial cells. Circ Res. 106:1384–1393.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|