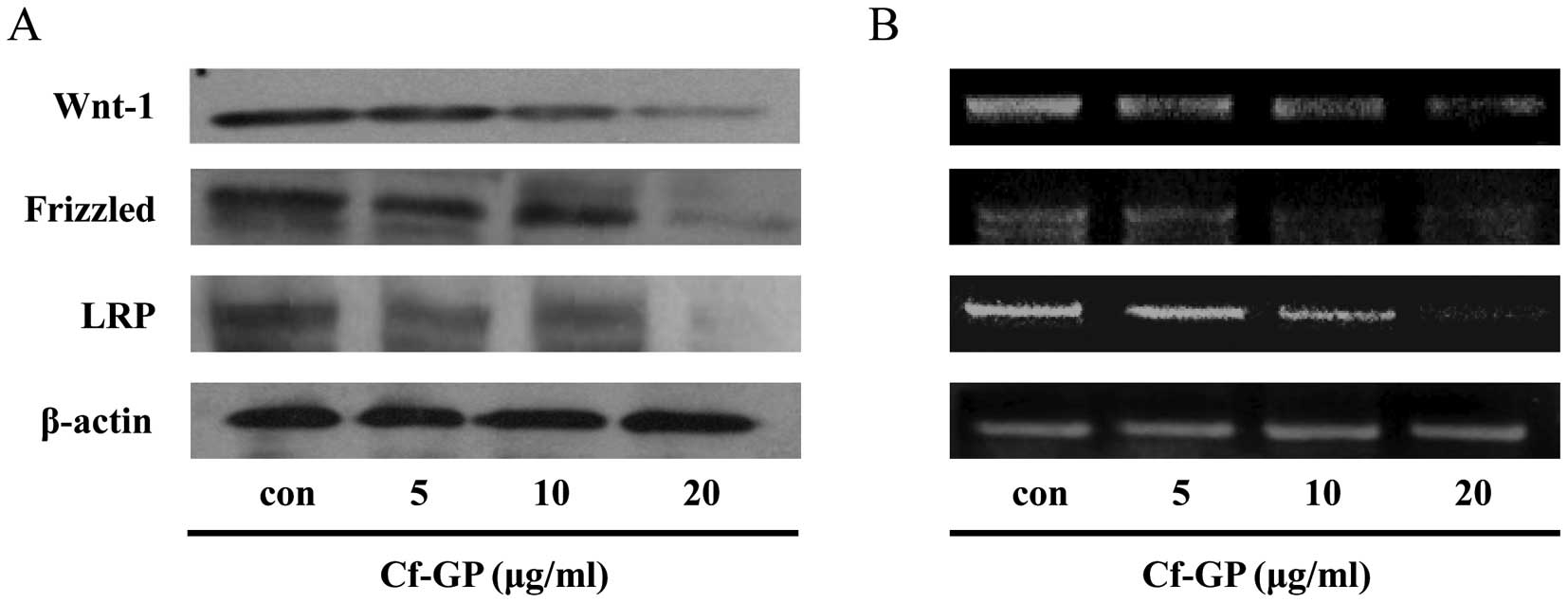
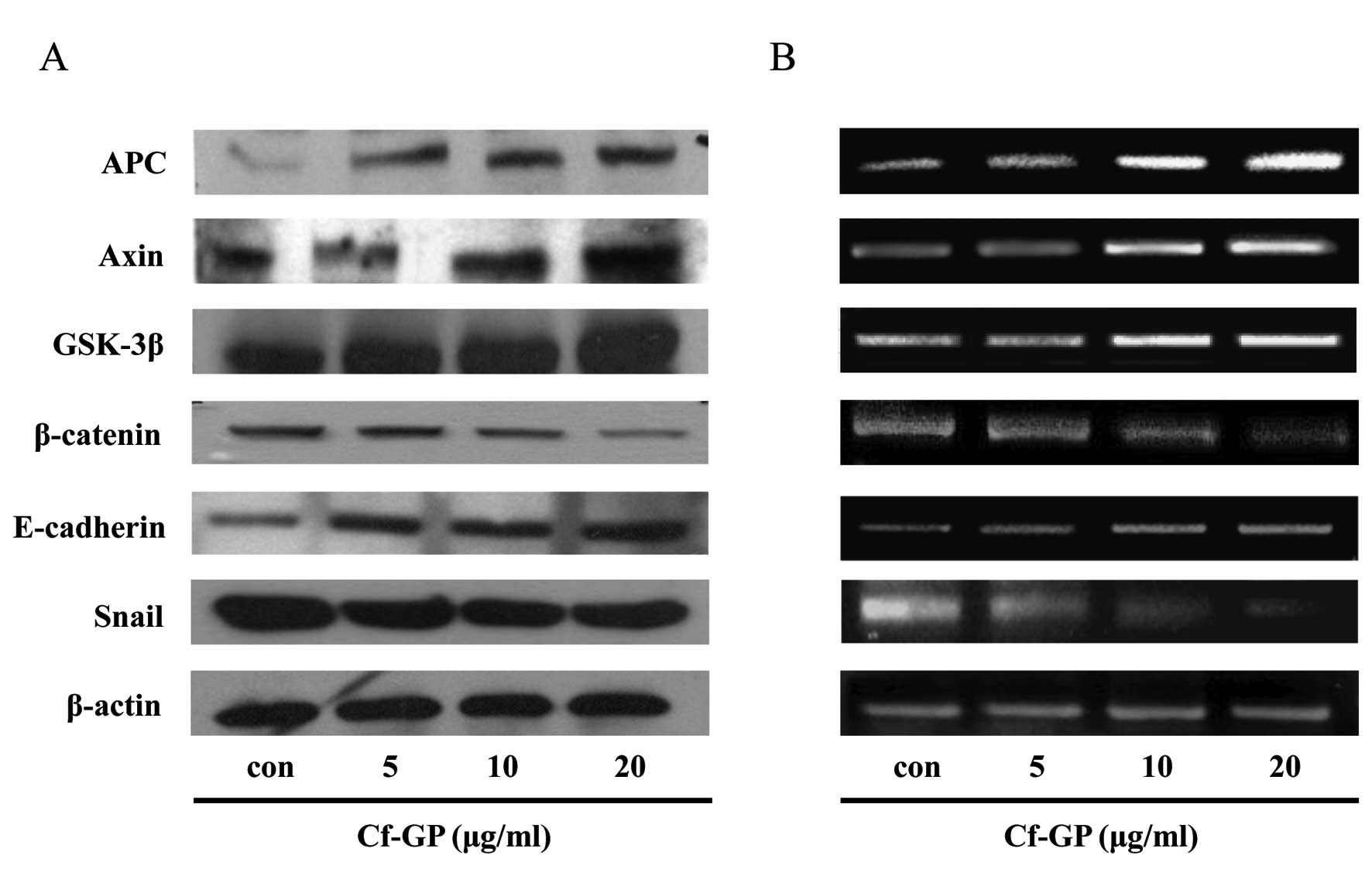
|
1.
|
Dann CE, Hsieh JC, Rattner A, Sharma D,
Nathans J and Leahy DJ: Insight into Wnt binding and signaling from
the structures of two Frizzled cysteine-rich domains. Nature.
412:86–90. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Hsieh JC, Ranttner A, Smallwood PM and
Nathans J: Biochemical characterization of Wnt-frizzled
interactions using a soluble, biologically active vertebrate Wnt
protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:3546–3551. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Cadigan KM and Nusse R: Wnt signaling: a
common theme in animal development. Genes Dev. 11:3286–3305. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV and Kaykas
A: Wnt and beta-catenin signaling: diseases and therapies. Nat Rev
Genet. 5:691–701. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Nelson WJ and Nusse R: Convergence of Wnt,
beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 303:1483–1487. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Miller JR, Hocking AM, Brown JD and Moon
RT: Mechanism and function of signal transduction by the
Wnt/beta-catenin and Wnt/Ca2+ pathways. Oncogene.
18:7860–7872. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
You L, Uematsu K, Xu Z, Mazieres J, Lee A,
McCormick F and Jablons DM: Inhibition of Wnt-1 signaling induces
apoptosis in β-catenin-deficient mesothelioma cells. Cancer Res.
64:3474–3478. 2004.
|
|
8.
|
Jho EH: Wnt signal transduction and its
involvement in human diseases. J Korean Endocr Soc. 20:306–318.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Rubinfeld B, Albert I, Porfiri E, Fiol C,
Munemitsu S and Polakis P: Binding of GSK3β to the APC-β-catenin
complex and regulation of complex assembly. Science. 272:1023–1026.
1996.
|
|
10.
|
Rubinfeld B, Robbins P, El-Gamil M, Albert
I, Porfiri E and Polakis P: Stabilization of β-catenin by genetic
defects in melanoma cell lines. Science. 275:1790–1792. 1997.
|
|
11.
|
Liu C, Li Y, Semenov M, Han C, Baeg GH,
Tan Y, Zhang Z, Lin X and He X: Control of β-catenin
phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism. Cell.
108:837–847. 2002.
|
|
12.
|
Moon RT, Boweman B, Boutros M and Perrimon
N: The promise and perils of Wnt signaling through β-catenin.
Science. 296:1644–1646. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Lee SY, Jeon HM, Ju MK, Kim CH, Jeong EK,
Park HG and Kang HS: Snail switches 5-FU-induced apoptosis to
necrosis through Akt/PKB activation and p53 down-regulation. J Life
Sci. 22:1018–1023. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Wodarz A and Nusse R: Mechanisms of Wnt
signaling in development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 14:59–88. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Uthoff SM, Eichenberger MR, McAuliffe TL,
Hamilton CJ and Galandiuk S: Wingless type frizzled protein
receptor signaling and its putative role in human colon cancer. Mol
Carcinog. 31:56–62. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H,
Zawel L, da Costa LT, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW:
Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science.
281:1509–1512. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: β-catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999.
|
|
18.
|
Pongracz JE and Stockley RA: Wnt signaling
in lung development and diseases. Respir Res. 26:7–15. 2006.
|
|
19.
|
Di Stefano A, Maestrelli P, Roggeri A,
Turato G, Calabro S, Potena A, Mapp CE, Ciaccia A, Covacev L,
Fabbri LM and Saetta M: Upregulation of adhesion molecules in the
bronchial mucosa of subjects with chronic obstructive bronchitis.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 149:803–810. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Kim YM, Kim IH and Nam TJ: Induction of
apoptosis signaling by a glycoprotein of Capsosiphon
fulvescens in AGS cell. Kor J Fish Aquat Sci. 44:216–224.
2011.
|
|
21.
|
Kim YM, Kim IH and Nam TJ: Capsosiphon
fulvescens glycoprotein reduces AGS gastric cancer cell
migration by downregulating transforming growth factor-β1 and
integrin expression. Int J Oncol. 43:1059–1065. 2013.
|
|
22.
|
Chea SC: Inhibitory effect of naringenin
on MMP-2, −9 activity and expression in HT-1080 cells. J Environ
Toxicol. 24:63–70. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Rezai KA, Farrokh-Siar L, Gasyna EM and
Ernest JT: Trypan blue induces apoptosis in human retinal pigment
epithelial cells. Am J Ophthalmol. 138:492–495. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
He B, You L, Uematsu K, Xu Z, Lee AY,
Matsangou M, McCormick F and Jablons DM: A monoclonal antibody
against Wnt-1 induces apoptosis in human cancer cells. Neoplasia.
6:7–14. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Miller JR: The Wnts. Genome Biol.
3:Reviews3001. 2002.
|
|
26.
|
Van Gijn ME, Daemen MJ, Smits JF and
Blankestejin WM: The Wnt-frizzled cascade in cardiovascular
disease. Cardiovasc Res. 55:16–24. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Green JL, Kuntz SG and Sternberg PW: Ror
receptor tyrosine kinases: orphans no more. Trends Cell Biol.
18:536–544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Angers S and Moon RT: Proximal events in
Wnt signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:468–477.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Clevers H: Wnt/β-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006.
|
|
30.
|
MacDonal BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling: components, mechanism, and diseases. Dev
Cell. 17:9–26. 2009.
|
|
31.
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Diagaradjane P, Anand P,
Harikumar KB, Deorukhkar A, Gelovani J, Guha S, Krishnan S and
Aggarwal BB: Curcumin sensitizes human colorectal cancer to
capecitabine by modulation of cyclin D1, COX-2, MMP-9, VEGF and
CXCR4 expression in an orthotopic mouse model. Int J Cancer.
125:2187–2197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Tharakan ST, Inamoto T, Sung B, Aggarwal
BB and Kamat AM: Curcumin potentiates the antitumor effects of
gemcitabine in an orthtopic model of human bladder cancer through
suppression of proliferative and angiogenic biomarkers. Biochem
Pharmacol. 79:218–228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Kim YM, Kim IH and Nam TJ: Induction of
apoptosis signaling by glycoprotein of Capsosiphon
fulvescens in human gastric cancer (AGS) cells. Nutr Cancer.
64:761–769. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|