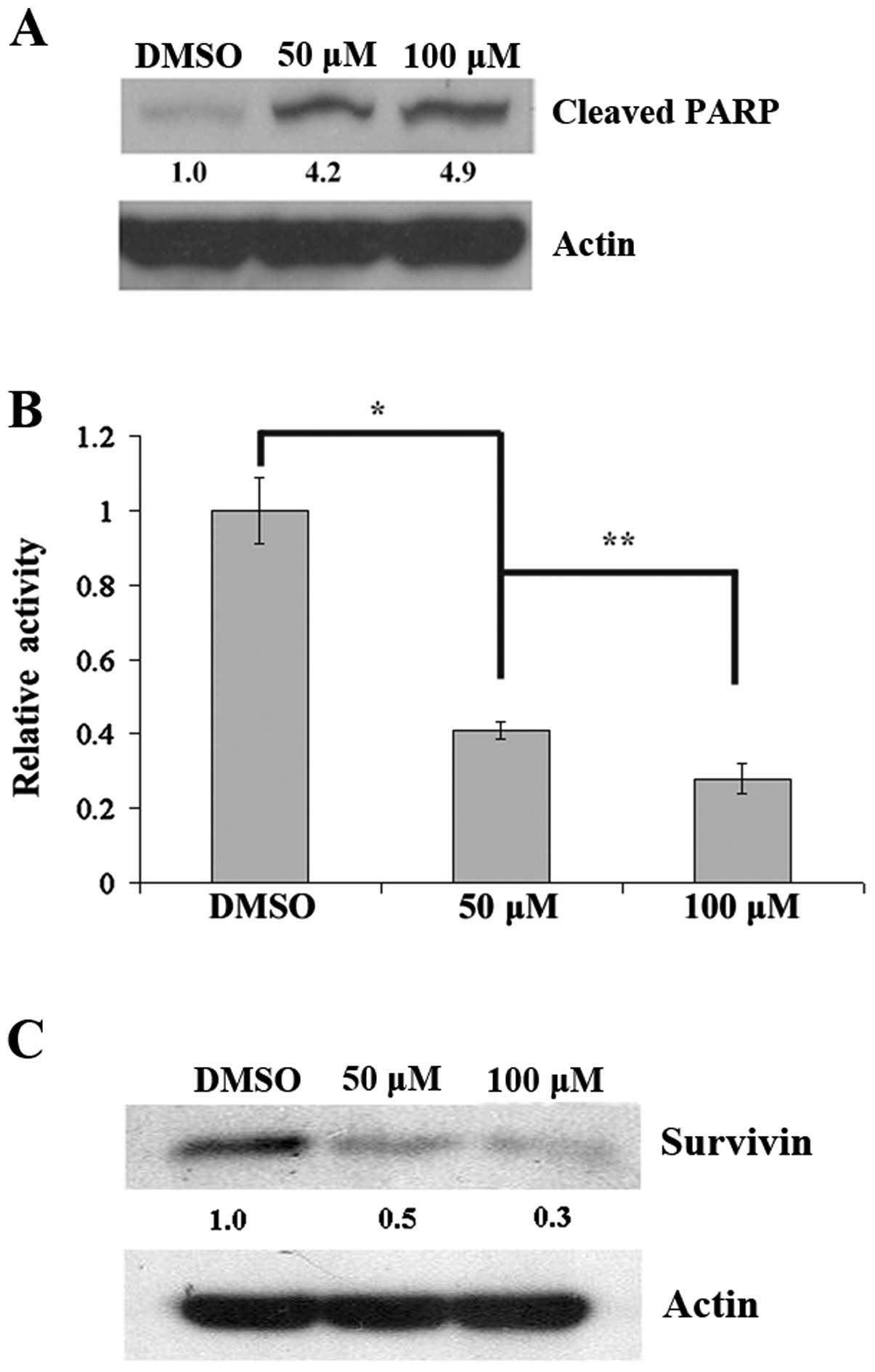
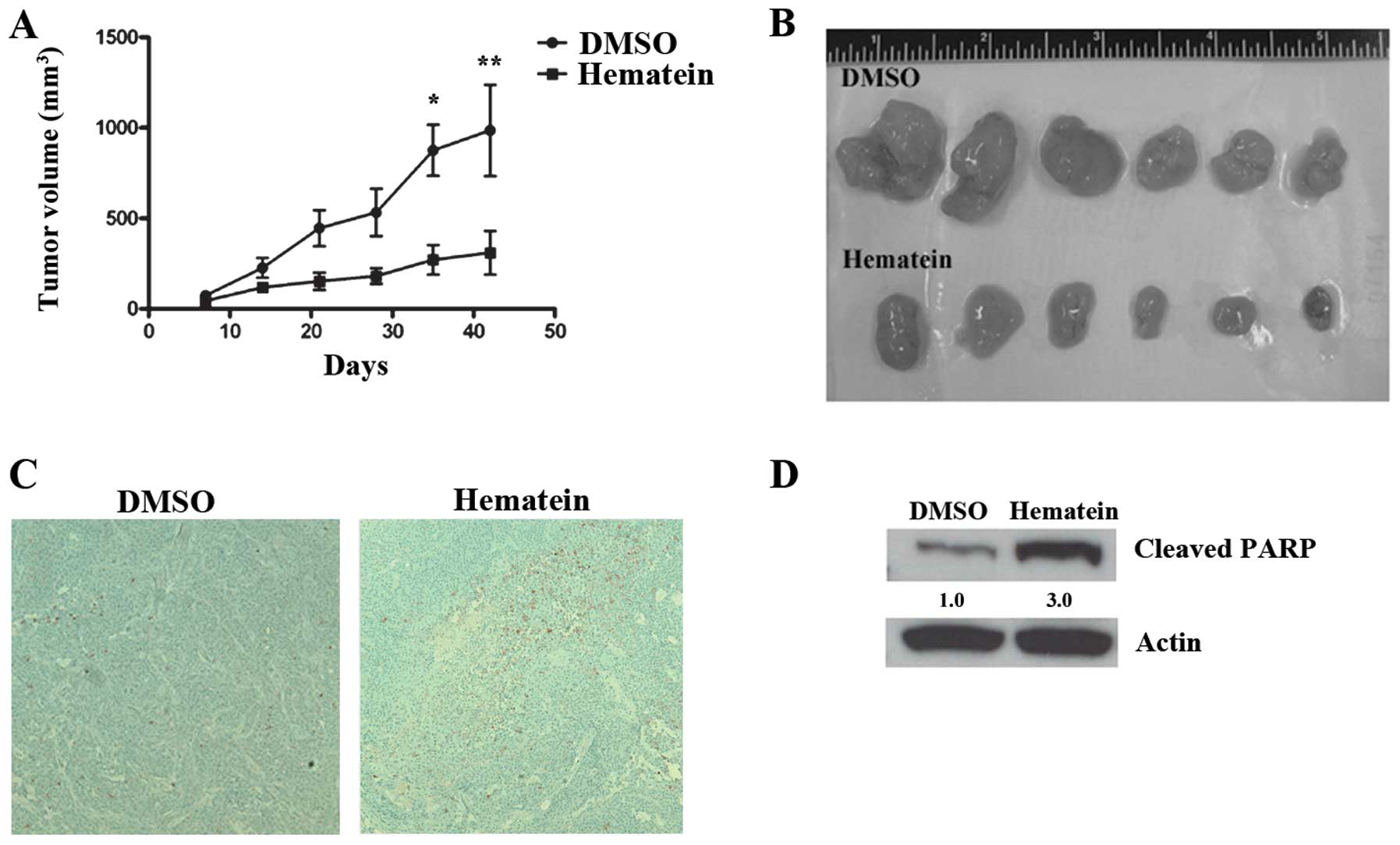
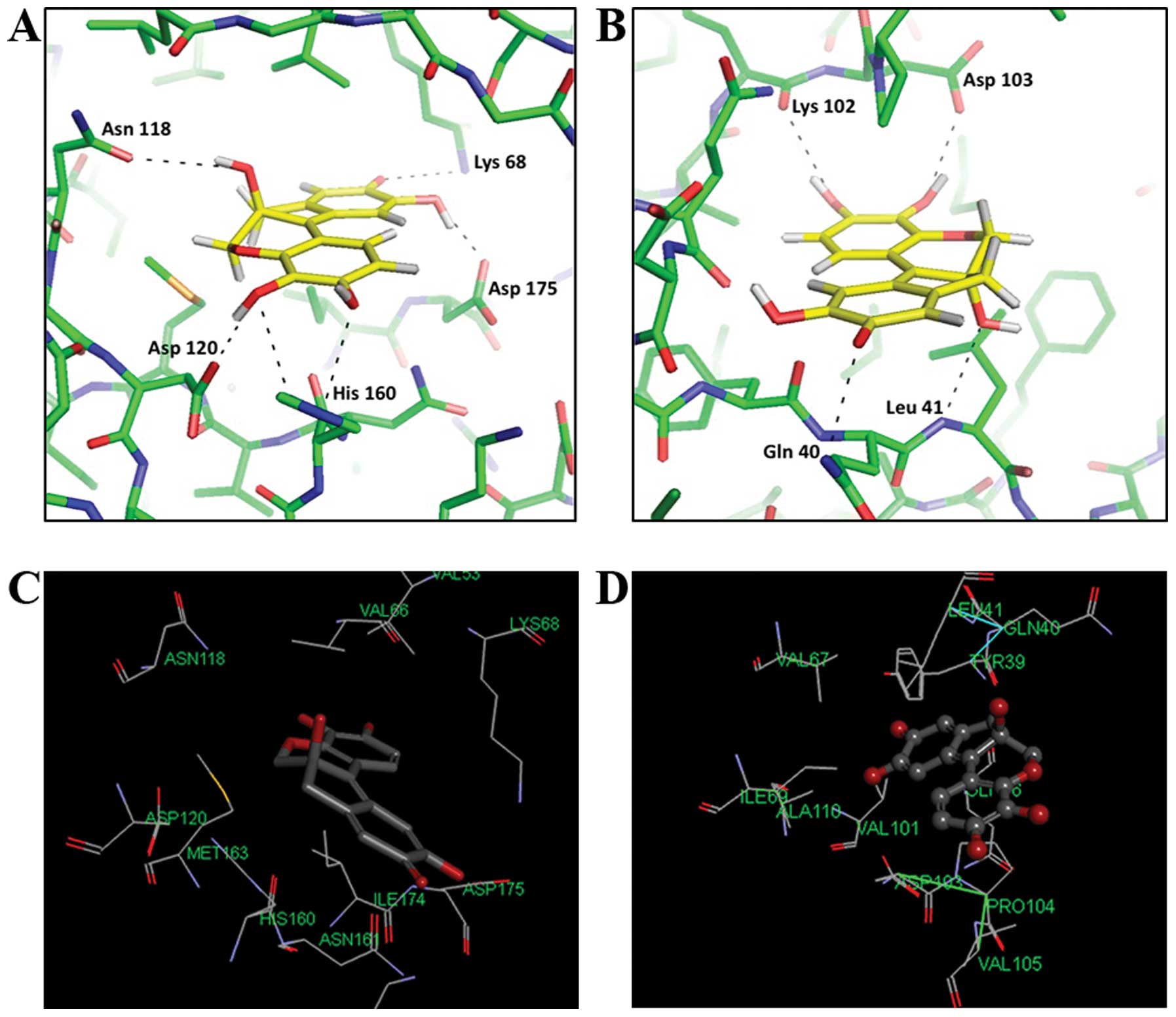
|
1.
|
Meggio F and Pinna LA:
One-thousand-and-one substrates of protein kinase CK2? FASEB J.
17:349–368. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Pinna LA: The raison d’etre of
constitutively active protein kinases: the lesson of CK2. Acc Chem
Res. 36:378–384. 2003.
|
|
3.
|
Tawfic S, Yu S, Wang H, Faust R, Davis A
and Ahmed K: Protein kinase CK2 signal in neoplasia. Histol
Histopathol. 16:573–582. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Seldin DC and Leder P: Casein kinase II
alpha transgene-induced murine lymphoma: relation to theileriosis
in cattle. Science. 267:894–897. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Landesman-Bollag E, Song DH, Romieu-Mourez
R, et al: Protein kinase CK2: signaling and tumorigenesis in the
mammary gland. Mol Cell Biochem. 227:153–165. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Kim JS, Eom JI, Cheong JW, et al: Protein
kinase CK2alpha as an unfavorable prognostic marker and novel
therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res.
13:1019–1028. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Laramas M, Pasquier D, Filhol O, Ringeisen
F, Descotes JL and Cochet C: Nuclear localization of protein kinase
CK2 catalytic subunit (CK2alpha) is associated with poor prognostic
factors in human prostate cancer. Eur J Cancer. 43:928–934. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
O-charoenrat P, Rusch V, Talbot SG, et al:
Casein kinase II alpha subunit and C1-inhibitor are independent
predictors of outcome in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of
the lung. Clin Cancer Res. 10:5792–5803. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Gapany M, Faust RA, Tawfic S, Davis A,
Adams GL and Ahmed K: Association of elevated protein kinase CK2
activity with aggressive behavior of squamous cell carcinoma of the
head and neck. Mol Med. 1:659–666. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Stalter G, Siemer S, Becht E, Ziegler M,
Remberger K and Issinger OG: Asymmetric expression of protein
kinase CK2 subunits in human kidney tumors. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 202:141–147. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Ruzzene M, Penzo D and Pinna LA: Protein
kinase CK2 inhibitor 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzotriazole (TBB) induces
apoptosis and caspase-dependent degradation of haematopoietic
lineage cell-specific protein 1 (HS1) in Jurkat cells. Biochem J.
364:41–47. 2002.
|
|
12.
|
Pagano MA, Meggio F, Ruzzene M,
Andrzejewska M, Kazimierczuk Z and Pinna LA:
2-Dimethylamino-4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-1H-benzimidazole: a novel
powerful and selective inhibitor of protein kinase CK2. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 321:1040–1044. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Sarno S, De Moliner E, Ruzzene M, et al:
Biochemical and three-dimensional-structural study of the specific
inhibition of protein kinase CK2 by
[5-oxo-5,6-dihydroindolo-(1,2-a)quinazolin-7-yl] acetic acid (IQA).
Biochem J. 374:639–646. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Siddiqui-Jain A, Drygin D, Streiner N, et
al: CX-4945, an orally bioavailable selective inhibitor of protein
kinase CK2, inhibits prosurvival and angiogenic signaling and
exhibits antitumor efficacy. Cancer Res. 70:10288–10298. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Hung MS, Xu Z, Lin YC, et al:
Identification of hematein as a novel inhibitor of protein kinase
CK2 from a natural product library. BMC Cancer. 9:1352009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Oh SR, Kim DS, Lee IS, Jung KY, Lee JJ and
Lee HK: Anti-complementary activity of constituents from the
heartwood of Caesalpinia sappan. Planta Med. 64:456–458. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Bettinger C and Zimmermann HW: New
investigations on hematoxylin, hematein, and hematein-aluminium
complexes. II. Hematein-aluminium complexes and hemalum staining.
Histochemistry. 96:215–228. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Lorber DM and Shoichet BK: Hierarchical
docking of databases of multiple ligand conformations. Curr Top Med
Chem. 5:739–749. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Raaf J, Brunstein E, Issinger OG and
Niefind K: The CK2 alpha/ CK2 beta interface of human protein
kinase CK2 harbors a binding pocket for small molecules. Chem Biol.
15:111–117. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Meng EC, Shoichet BK and Kuntz ID:
Automated docking with grid-based energy evaluation. J Computat
Chem. 13:505–524. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21.
|
Raaf J, Issinger OG and Niefind K:
Insights from soft X-rays: the chlorine and sulfur sub-structures
of a CK2alpha/DRB complex. Mol Cell Biochem. 316:15–23. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Di Maira G, Salvi M, Arrigoni G, et al:
Protein kinase CK2 phosphorylates and upregulates Akt/PKB. Cell
Death Differ. 12:668–677. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Duncan JS and Litchfield DW: Too much of a
good thing: the role of protein kinase CK2 in tumorigenesis and
prospects for therapeutic inhibition of CK2. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1784:33–47. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Yde CW, Frogne T, Lykkesfeldt AE, Fichtner
I, Issinger OG and Stenvang J: Induction of cell death in
antiestrogen resistant human breast cancer cells by the protein
kinase CK2 inhibitor DMAT. Cancer Lett. 256:229–237. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Tapia JC, Torres VA, Rodriguez DA, Leyton
L and Quest AF: Casein kinase 2 (CK2) increases survivin expression
via enhanced beta-catenin-T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer binding
factor-dependent transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:15079–15084. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Ponce DP, Yefi R, Cabello P, et al: CK2
functionally interacts with AKT/PKB to promote the
beta-catenin-dependent expression of survivin and enhance cell
survival. Mol Cell Biochem. 356:127–132. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Moucadel V, Prudent R, Sautel CF, et al:
Antitumoral activity of allosteric inhibitors of protein kinase
CK2. Oncotarget. 2:997–1010. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|