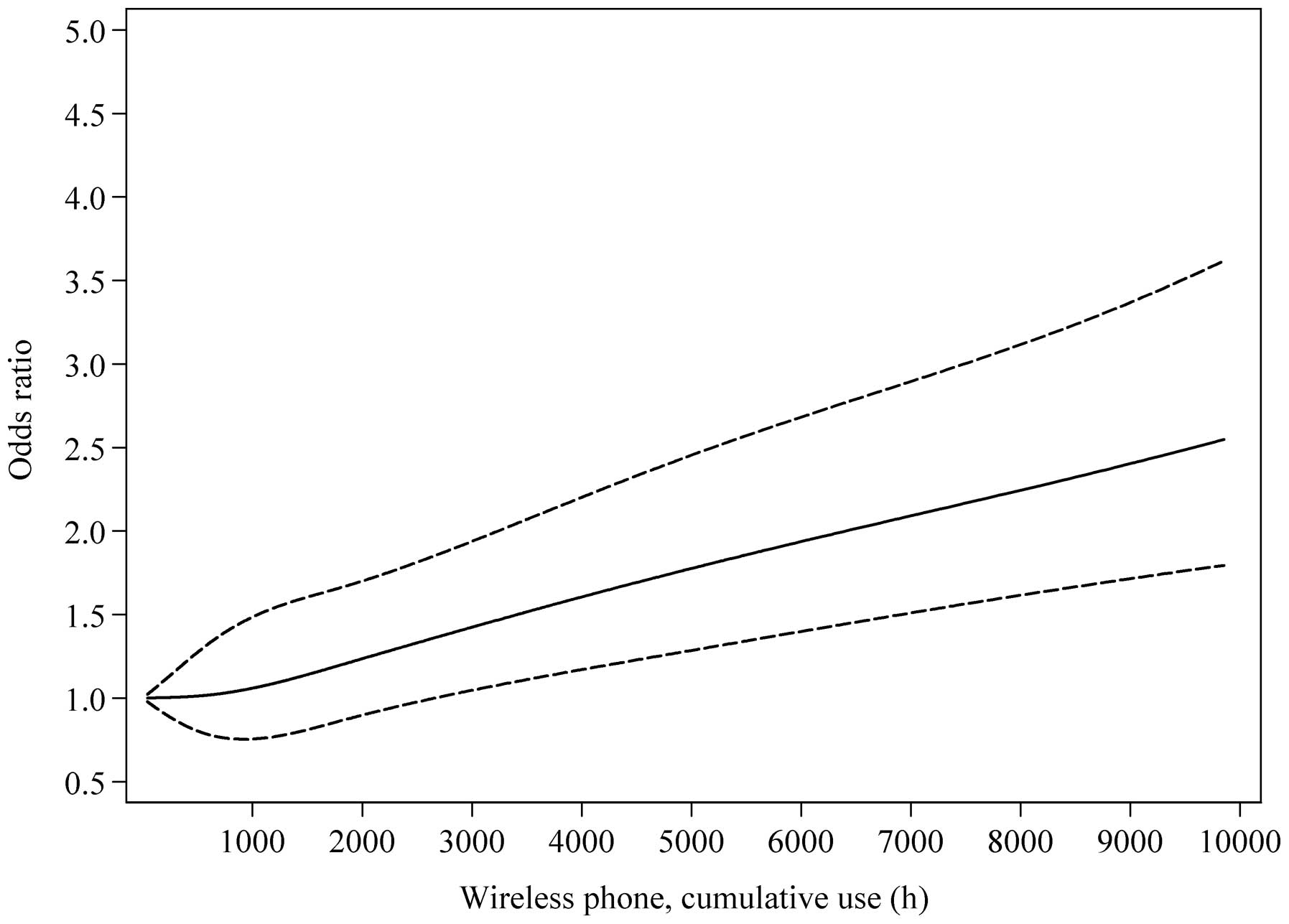
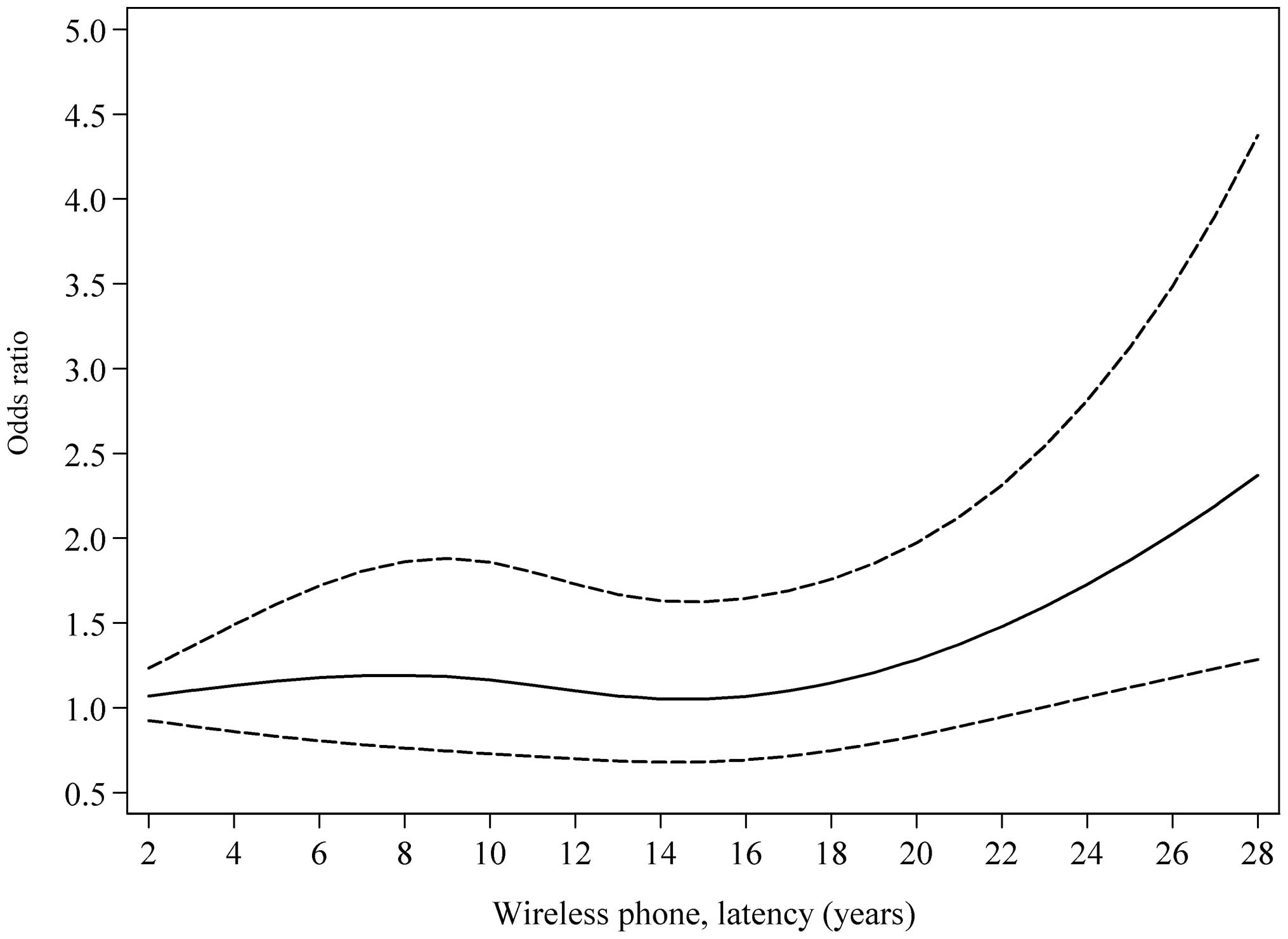
|
1.
|
Baan R, Grosse Y, Lauby-Secretan B, et al:
Carcinogenicity of radiofrequency electromagnetic fields. Lancet
Oncol. 12:624–626. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of
Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Non-ionizing radiation, Part 2:
Radiofrequency electromagnetic fields. 102:IARCPress; Lyon: 2013,
http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol102/mono102.pdf.
Accessed July 11, 2013.
|
|
3.
|
Interphone Study Group: Brain tumour risk
in relation to mobile telephone use: results of the INTERPHONE
international case-control study. Int J Epidemiol. 39:675–694.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Hansson Mild K:
Methodological aspects of epidemiological studies on the use of
mobile phones and their association with brain tumors. Open Env
Sciences. 2:54–61. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Hansson Mild K:
Use of mobile phones and cordless phones is associated with
increased risk for glioma and acoustic neuroma. Pathophysiology.
20:85–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Cardis E and Sadetzki S: Indications of
possible brain tumour risk in mobile phone studies: should we be
concerned? Occup Environ Med. 68:169–171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Wilén J, Sandström M and Hansson Mild K:
Subjective symptoms among mobile phone users - a consequence of
absorption of radiofrequency fields? Bioelectromagnetics.
24:152–159. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Hardell L, Hansson Mild K, Påhlson A and
Hallquist A: Ionizing radiation, cellular telephones and the risk
for brain tumours. Eur J Cancer Prev. 10:523–529. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Cardis E, Deltour I, Mann S, et al:
Distribution of RF energy emitted by mobile phones in anatomical
structures of the brain. Phys Med Biol. 53:2771–2783. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Hardell L, Näsman Å, Påhlson A, Hallquist
A and Hansson Mild K: Use of cellular telephones and the risk for
brain tumours: A case-control study. Int J Oncol. 15:113–116.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Hardell L, Hallquist A, Hansson Mild K,
Carlberg M, Påhlson A and Lilja A: Cellular and cordless telephones
and the risk for brain tumours. Eur J Cancer Prev. 11:377–386.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Hansson Mild K:
Case-control study of the association between the use of cellular
and cordless telephones and malignant brain tumors diagnosed during
2000–2003. Environ Res. 100:232–241. 2006.
|
|
13.
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Hansson Mild K:
Pooled analysis of two case-control studies on use of cellular and
cordless telephones and the risk for malignant brain tumours
diagnosed in 1997–2003. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 79:630–639.
2006.
|
|
14.
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Hansson Mild K:
Epidemiological evidence for an association between use of wireless
phones and tumor diseases. Pathophysiology. 16:113–122. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Hansson Mild K:
Pooled analysis of case-control studies on malignant brain tumours
and the use of mobile and cordless phones including living and
deceased subjects. Int J Oncol. 38:1465–1474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Carlberg M and Hardell L: On the
association between glioma, wireless phones, heredity and ionising
radiation. Pathophysiology. 19:243–252. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Interphone Study Group: Acoustic neuroma
risk in relation to mobile telephone use: results of the INTERPHONE
international case-control study. Cancer Epidemiol. 35:453–464.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Post-och Telestyrelsen: Svensk Telemarknad
2010. http://www.statistik.pts.se/pts2011/FILES/RAPPORTER/2010/Telemarknad_2010.pdf.
Accessed July 11, 2013.
|
|
19.
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Gee D: Mobile
phone use and brain tumour risk: early warnings, early actions?
Late Lessons from Early Warnings, Part 2. European Environment
Agency; Copenhagen: 2013, http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/late-lessons-2/late-lessons-chapters/late-lessons-ii-chapter-21/at_download/file.
Accessed July 11, 2013.
|
|
20.
|
Harrell FE Jr: Regression Modeling
Strategies With Application to Linear Models, Logistic Regression
and Survival Analysis. Springer; New York, NY: pp. 20–26. 2001
|
|
21.
|
Hardell L: Relation of soft tissue
sarcoma, malignant lymphoma, and colon cancer to phenoxy acids,
chlorophenols and other agents. Scand J Work Environ Health.
7:119–130. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Carlberg M, Söderqvist F, Hansson Mild K
and Hardell L: Meningioma patients diagnosed 2007–2009 and the
association with use of mobile and cordless phones: a case-control
study. Environ Health. 12:602013.
|
|
23.
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M, Söderqvist F and
Hansson Mild K: Pooled analysis of case-control studies on acoustic
neuroma diagnosed 1997–2003 and 2007–2009 and use of mobile and
cordless phones. Int J Oncol. 43:1036–1044. 2013.
|
|
24.
|
Muscat JE, Malkin MG, Thompson S, et al:
Handheld cellular telephone use and risk of brain cancer. JAMA.
284:3001–3007. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Inskip PD, Tarone RE, Hatch EE, et al:
Cellular-telephone use and brain tumors. N Engl J Med. 344:79–86.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Auvinen A, Hietanen M, Luukkonen R and
Koskela RS: Brain tumors and salivary gland cancers among cellular
telephone users. Epidemiology. 13:356–359. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Söderqvist F, Carlberg M and Hardell L:
Review of four publications on the Danish cohort study on mobile
phone subscribers and risk of brain tumours. Rev Environ Health.
27:51–58. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Kundi M: Essential problems in the
interpretation of epidemiologic evidence for an association between
mobile phone use and brain tumours. C R Physique. 11:556–563. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Ohgaki H, Dessen P, Jourde B, et al:
Genetic pathways of glioblastoma: a population-based study. Cancer
Res. 64:6892–6899. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Hardell L: Soft-tissue sarcoma and
exposure to phenoxy acids - A clinical observation. Läkartidningen.
74:2853–2854. 1977.(In Swedish).
|
|
31.
|
Hardell L: Malignant lymphoma of
histiocytic type and exposure to phenoxyacetic acids or
chlorophenols. Lancet. 1:55–56. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Hardell L and Sandström A: Case-control
study: soft-tissue sarcomas and exposure to phenoxyacetic acids or
chlorophenols. Br J Cancer. 39:711–717. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Hardell L, Eriksson M, Lenner P and
Lundgren E: Malignant lymphoma and exposure to chemicals,
especially organic solvents, chlorophenols and phenoxy acids: a
case-control study. Br J Cancer. 43:169–176. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Hansson Mild K:
Mobile phone use and the risk for malignant brain tumors: a
case-control study on deceased cases and controls.
Neuroepidemiology. 35:109–114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Bergenheim T, Malmström A, Bolander H, et
al: Registration on regional basis of patients with primary brain
tumors. Regional differences disclosed. Läkartidningen.
104:332–341. 2007.(In Swedish).
|
|
36.
|
Barlow L, Westergren K, Holmberg L and
Talbäck M: The completeness of the Swedish Cancer Register: a
sample survey for year 1998. Acta Oncol. 48:27–33. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Hardell L and Carlberg M: Use of mobile
and cordless phones and survival of patients with glioma.
Neuroepidemiology. 40:101–108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Ohgaki H and Kleihues P: Population-based
studies on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations in
astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
64:479–489. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Vrijheid M, Cardis E, Armstrong BK, et al:
Validation of short term recall of mobile phone use for the
Interphone study. Occup Environ Med. 63:237–243. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Vrijheid M, Deltour I, Krewski D, Sanchez
M and Cardis E: The effects of recall errors and of selection bias
in epidemiologic studies of mobile phone use and cancer risk. J
Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 16:371–384. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Preston-Martin S and Mack W: Neoplasms of
the nervous system. Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention.
Schottenfeld D and Fraumeni JF Jr: Oxford University Press; New
York, NY: pp. 1231–1281. 1996
|
|
42.
|
Lai H and Singh NP: Melatonin and a
spin-trap compound block radiofrequency electromagnetic
radiation-induced DNA strand breaks in rat brain cells.
Bioelectromagnetics. 18:446–454. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Phillips JL, Singh NP and Lai H:
Electromagnetic fields and DNA damage. Pathophysiology. 16:79–88.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Liu C, Duan W, Xu S, et al: Exposure to
1800 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation induces oxidative
DNA base damage in a mouse spermatocyte-derived cell line. Toxicol
Lett. 218:2–9. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Collins VP: Gliomas. Cancer Surv.
32:37–51. 1998.
|