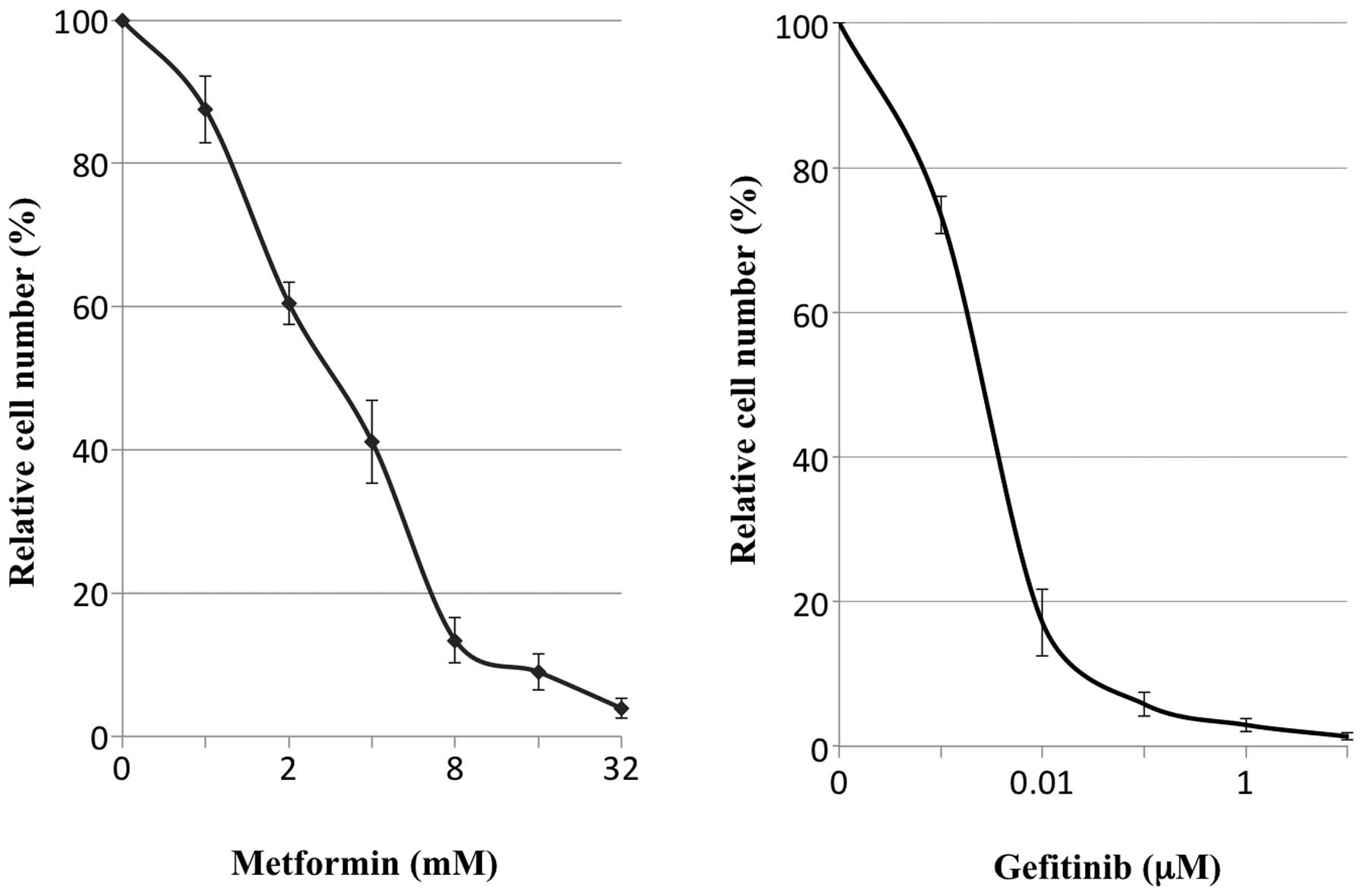
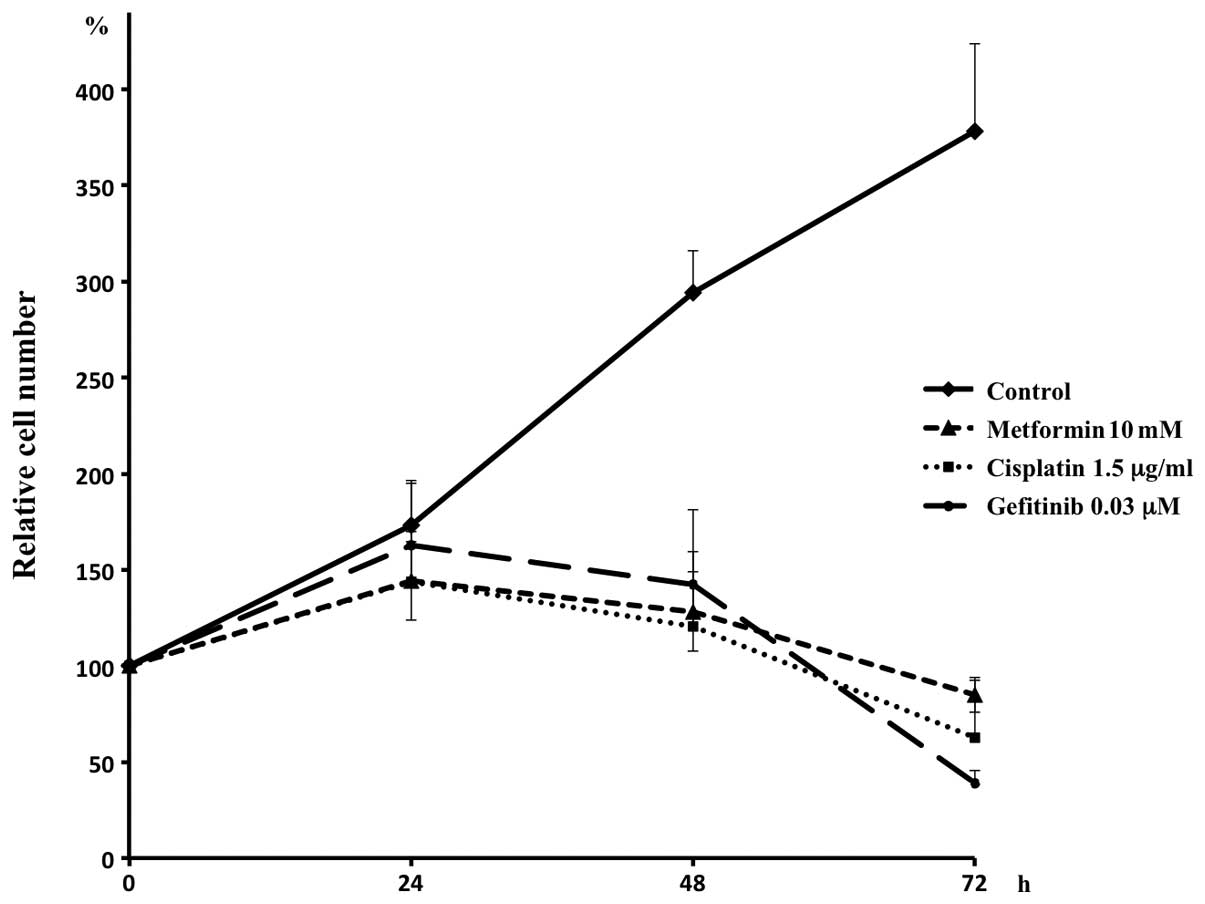
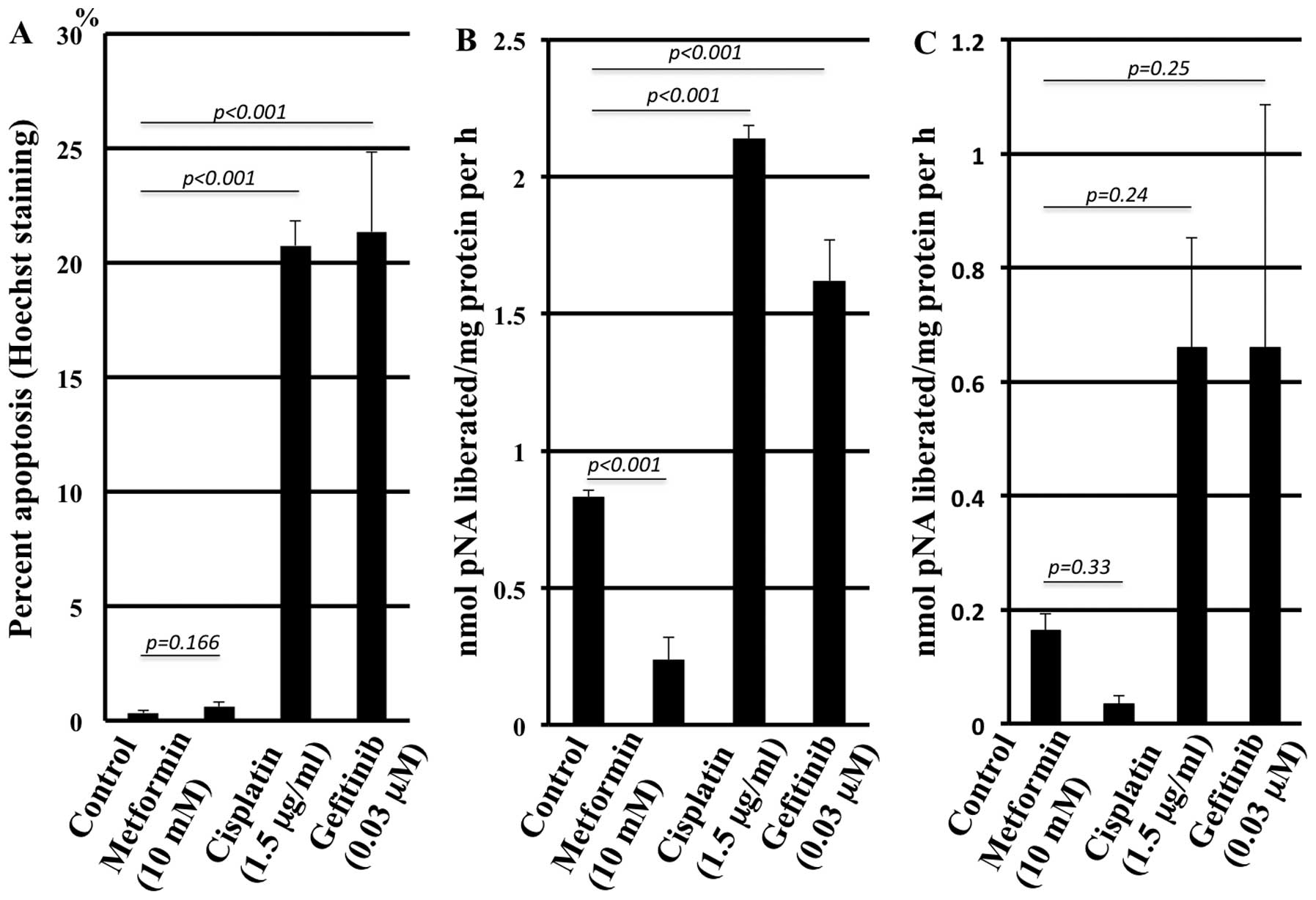
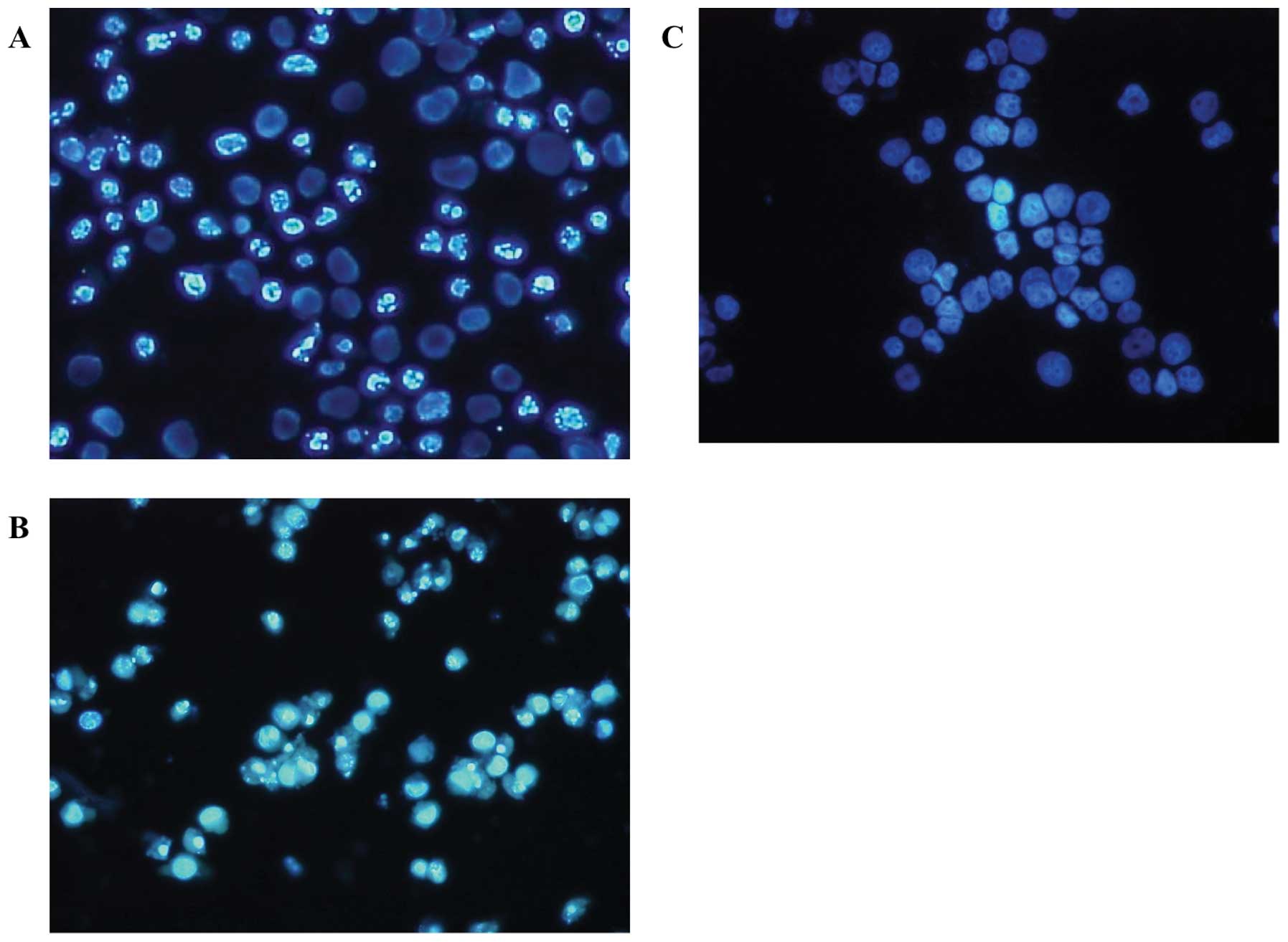
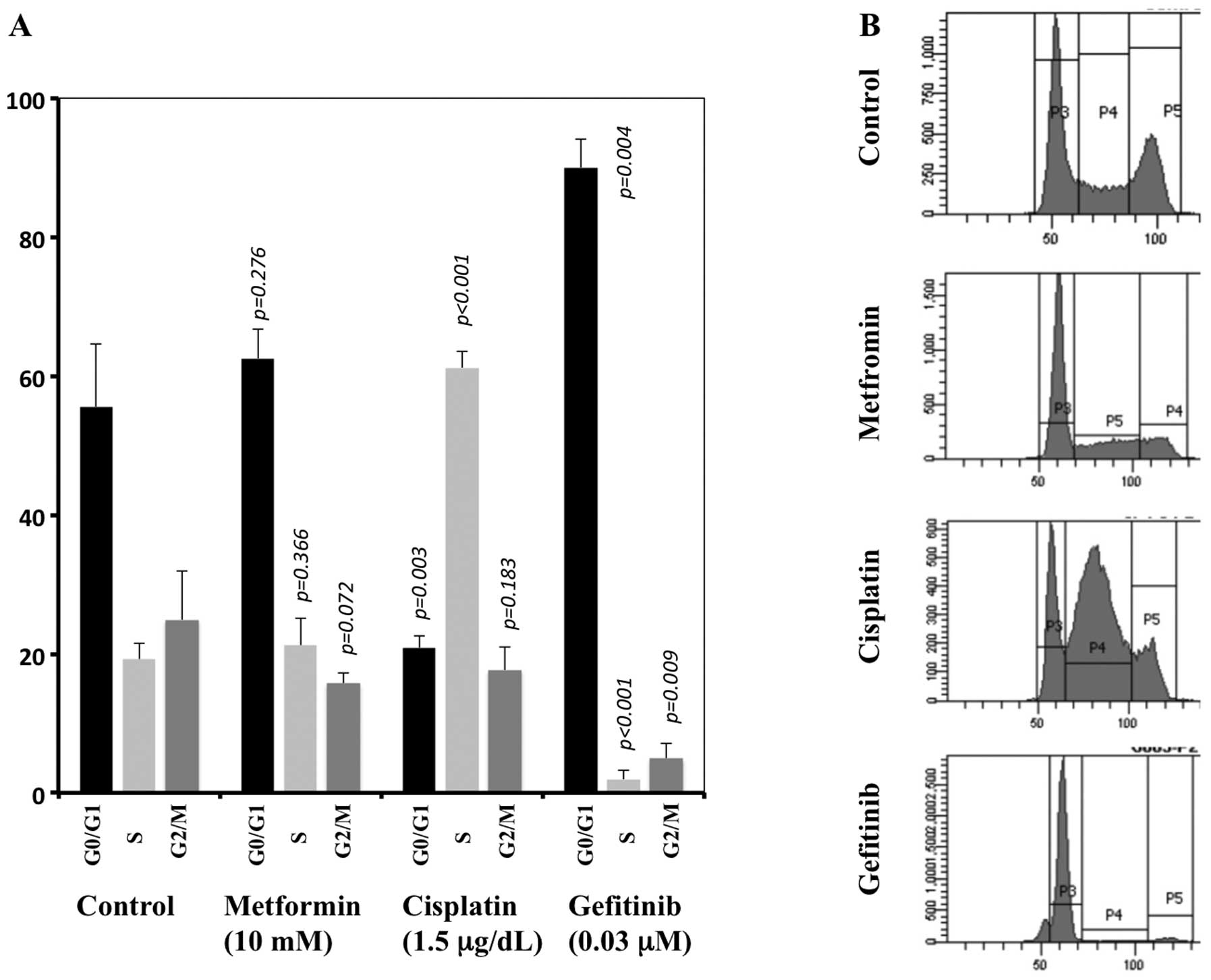
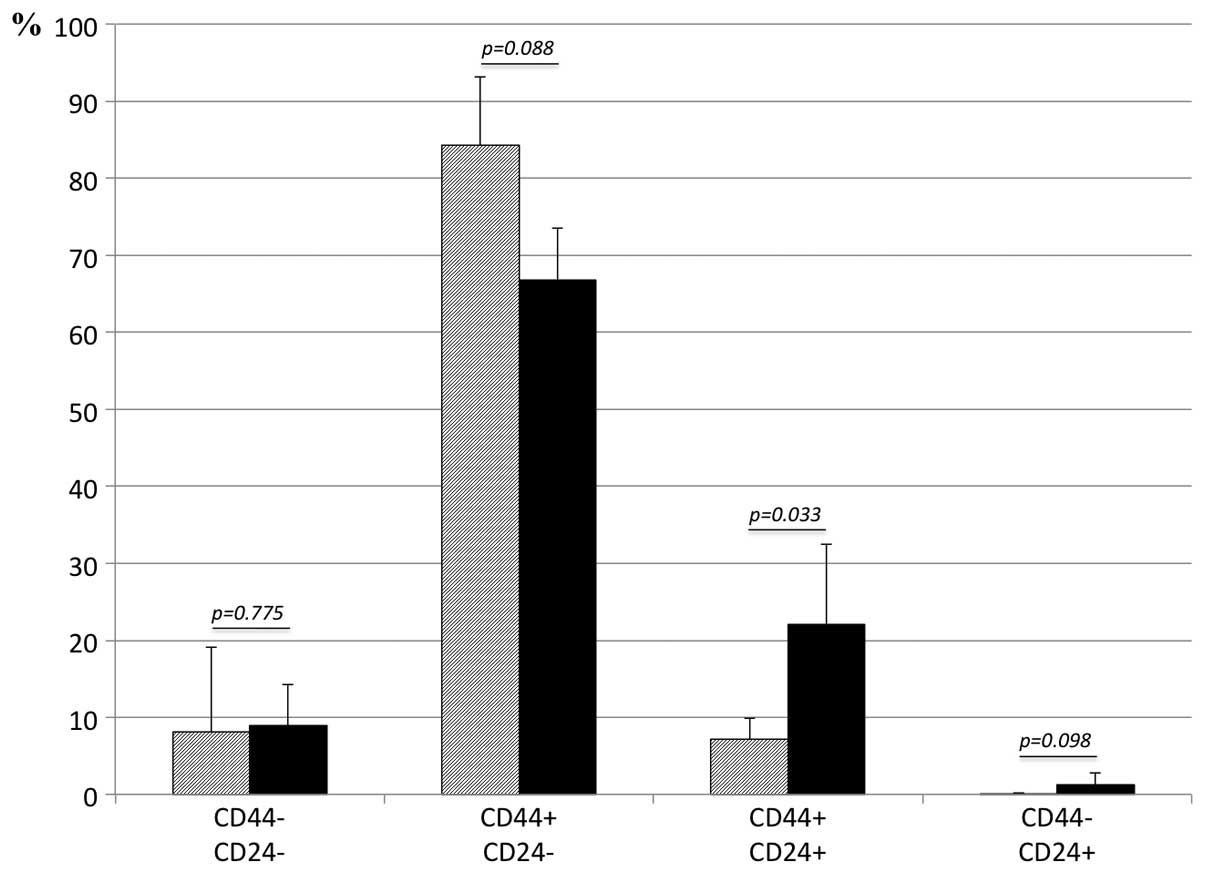
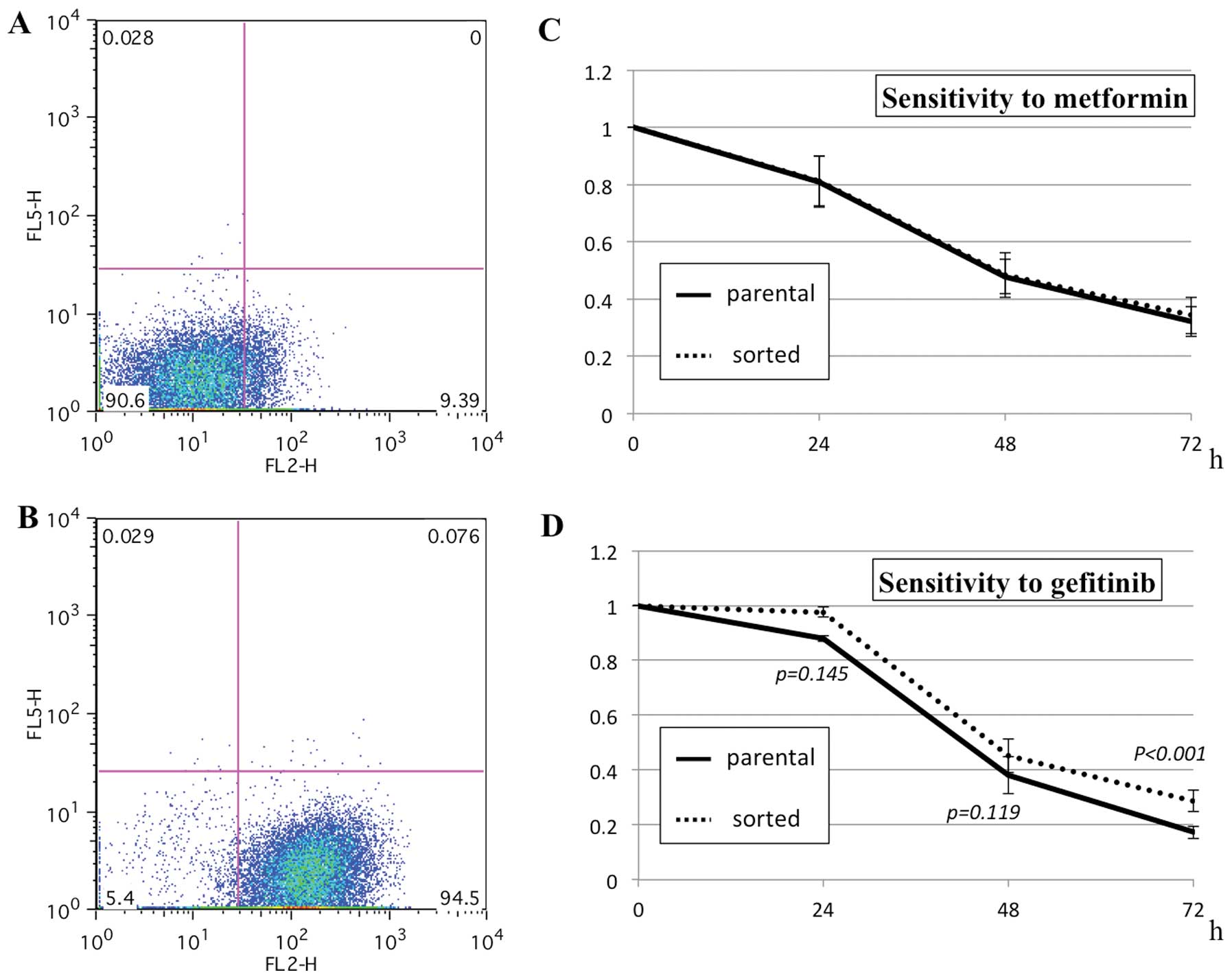
|
1.
|
Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Maemondo M, et al:
Updated overall survival results from a randomized phase III trial
comparing gefitinib with carboplatin-paclitaxel for chemo-naive
non-small cell lung cancer with sensitive EGFR gene mutations
(NEJ002). Ann Oncol. 24:54–59. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Wakeling AE, Guy SP, Woodburn JR, et al:
ZD1839 (Iressa): an orally active inhibitor of epidermal growth
factor signaling with potential for cancer therapy. Cancer Res.
62:5749–5754. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H, et al:
Analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutation in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer and acquired resistance to
gefitinib. Clin Cancer Res. 12:5764–5769. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, et
al: MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer
by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 316:1039–1043. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Sharma SV, Lee DY, Li B, et al: A
chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell
subpopulations. Cell. 141:69–80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Towler MC and Hardie DG: AMP-activated
protein kinase in metabolic control and insulin signaling. Circ
Res. 100:328–341. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Pollak MN: Investigating metformin for
cancer prevention and treatment: the end of the beginning. Cancer
Discov. 2:778–790. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Evans JM, Donnelly LA, Emslie-Smith AM,
Alessi DR and Morris AD: Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in
diabetic patients. BMJ. 330:1304–1305. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Bowker SL, Majumdar SR, Veugelers P and
Johnson JA: Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with
type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulin. Diabetes Care.
29:254–258. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Jiralerspong S, Palla SL, Giordano SH, et
al: Metformin and pathologic complete responses to neoadjuvant
chemotherapy in diabetic patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
27:3297–3302. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Mazzone PJ, Rai H, Beukemann M, Xu M, Jain
A and Sasidhar M: The effect of metformin and thiazolidinedione use
on lung cancer in diabetics. BMC Cancer. 12:4102012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Alimova IN, Liu B, Fan Z, et al: Metformin
inhibits breast cancer cell growth, colony formation and induces
cell cycle arrest in vitro. Cell Cycle. 8:909–915. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, et al:
Metformin induces unique biological and molecular responses in
triple negative breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 8:2031–2040. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG,
Sonenberg N and Pollak M: Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent
growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
66:10269–10273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Rocha GZ, Dias MM, Ropelle ER, et al:
Metformin amplifies chemotherapy-induced AMPK activation and
antitumoral growth. Clin Cancer Res. 17:3993–4005. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Loubat A, et al:
The antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in
vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene.
27:3576–3586. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Wang LW, Li ZS, Zou DW, Jin ZD, Gao J and
Xu GM: Metformin induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells.
World J Gastroenterol. 14:7192–7198. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Gotlieb WH, Saumet J, Beauchamp MC, et al:
In vitro metformin anti-neoplastic activity in epithelial ovarian
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 110:246–250. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Rattan R, Giri S, Hartmann LC and Shridhar
V: Metformin attenuates ovarian cancer cell growth in an AMP-kinase
dispensable manner. J Cell Mol Med. 15:166–178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Rattan R, Graham RP, Maguire JL, Giri S
and Shridhar V: Metformin suppresses ovarian cancer growth and
metastasis with enhancement of cisplatin cytotoxicity in vivo.
Neoplasia. 13:483–491. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Hawley SA, Boudeau J, Reid JL, et al:
Complexes between the LKB1 tumor suppressor, STRAD alpha/beta and
MO25 alpha/beta are upstream kinases in the AMP-activated protein
kinase cascade. J Biol. 2:282003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Lizcano JM, Goransson O, Toth R, et al:
LKB1 is a master kinase that activates 13 kinases of the AMPK
subfamily, including MARK/PAR-1. EMBO J. 23:833–843. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, Pollak
M and Sonenberg N: Metformin inhibits mammalian target of
rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 67:10804–10812. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Bolster DR, Crozier SJ, Kimball SR and
Jefferson LS: AMP-activated protein kinase suppresses protein
synthesis in rat skeletal muscle through down-regulated mammalian
target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling. J Biol Chem. 277:23977–23980.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Kimura N, Tokunaga C, Dalal S, et al: A
possible linkage between AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and
mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling pathway. Genes
Cells. 8:65–79. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Inoki K, Zhu T and Guan KL: TSC2 mediates
cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival. Cell.
115:577–590. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA and Struhl K:
Metformin decreases the dose of chemotherapy for prolonging tumor
remission in mouse xenografts involving multiple cancer cell types.
Cancer Res. 71:3196–3201. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Janjetovic K, Vucicevic L, Misirkic M, et
al: Metformin reduces cisplatin-mediated apoptotic death of cancer
cells through AMPK-independent activation of Akt. Eur J Pharmacol.
651:41–50. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Harhaji-Trajkovic L, Vilimanovich U,
Kravic-Stevovic T, Bumbasirevic V and Trajkovic V: AMPK-mediated
autophagy inhibits apoptosis in cisplatin-treated tumour cells. J
Cell Mol Med. 13:3644–3654. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Costa DB, Halmos B, Kumar A, et al: BIM
mediates EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in lung
cancers with oncogenic EGFR mutations. PLoS Med. 4:1669–1679. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Memmott RM, Mercado JR, Maier CR, Kawabata
S, Fox SD and Dennis PA: Metformin prevents tobacco
carcinogen-induced lung tumorigenesis. Cancer Prev Res.
3:1066–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Sirotnak FM, Zakowski MF, Miller VA, Scher
HI and Kris MG: Efficacy of cytotoxic agents against human tumor
xenografts is markedly enhanced by coadministration of ZD1839
(Iressa), an inhibitor of EGFR tyrosine kinase. Clin Cancer Res.
6:4885–4892. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Blazquez C, Geelen MJ, Velasco G and
Guzman M: The AMP-activated protein kinase prevents ceramide
synthesis de novo and apoptosis in astrocytes. FEBS Lett.
489:149–153. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Shaw RJ, Kosmatka M, Bardeesy N, et al:
The tumor suppressor LKB1 kinase directly activates AMP-activated
kinase and regulates apoptosis in response to energy stress. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:3329–3335. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Ormerod MG, Orr RM and Peacock JH: The
role of apoptosis in cell killing by cisplatin: a flow cytometric
study. Br J Cancer. 69:93–100. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Janmaat ML, Kruyt FA, Rodriguez JA and
Giaccone G: Response to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors
in non-small cell lung cancer cells: limited antiproliferative
effects and absence of apoptosis associated with persistent
activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase or Akt kinase
pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 9:2316–2326. 2003.
|
|
37.
|
Tracy S, Mukohara T, Hansen M, Meyerson M,
Johnson BE and Janne PA: Gefitinib induces apoptosis in the
EGFRL858R non-small-cell lung cancer cell line H3255. Cancer Res.
64:7241–7244. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Cantrell LA, Zhou C, Mendivil A, Malloy
KM, Gehrig PA and Bae-Jump VL: Metformin is a potent inhibitor of
endometrial cancer cell proliferation - implications for a novel
treatment strategy. Gynecol Oncol. 116:92–98. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Kato K, Gong J, Iwama H, et al: The
antidiabetic drug metformin inhibits gastric cancer cell
proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:549–560.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Ashinuma H, Takiguchi Y, Kitazono S, et
al: Antiproliferative action of metformin in human lung cancer cell
lines. Oncol Rep. 28:8–14. 2012.
|
|
41.
|
Matsui W, Wang Q, Barber JP, et al:
Clonogenic multiple myeloma progenitors, stem cell properties, and
drug resistance. Cancer Res. 68:190–197. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Hemmati HD, Nakano I, Lazareff JA, et al:
Cancerous stem cells can arise from pediatric brain tumors. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:15178–15183. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Vermeulen L, Todaro M, de Sousa Mello F,
et al: Single-cell cloning of colon cancer stem cells reveals a
multi-lineage differentiation capacity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:13427–13432. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|