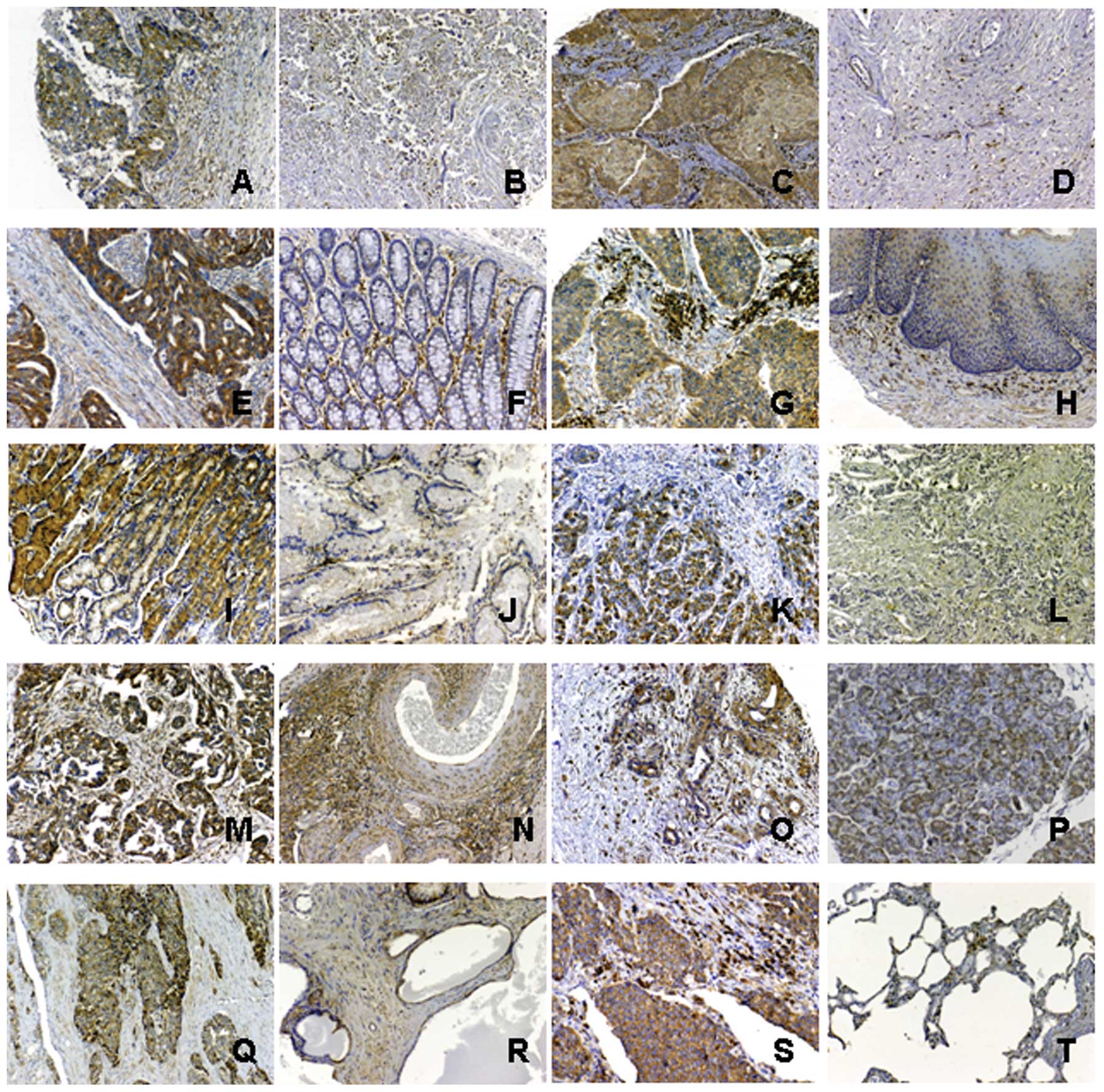
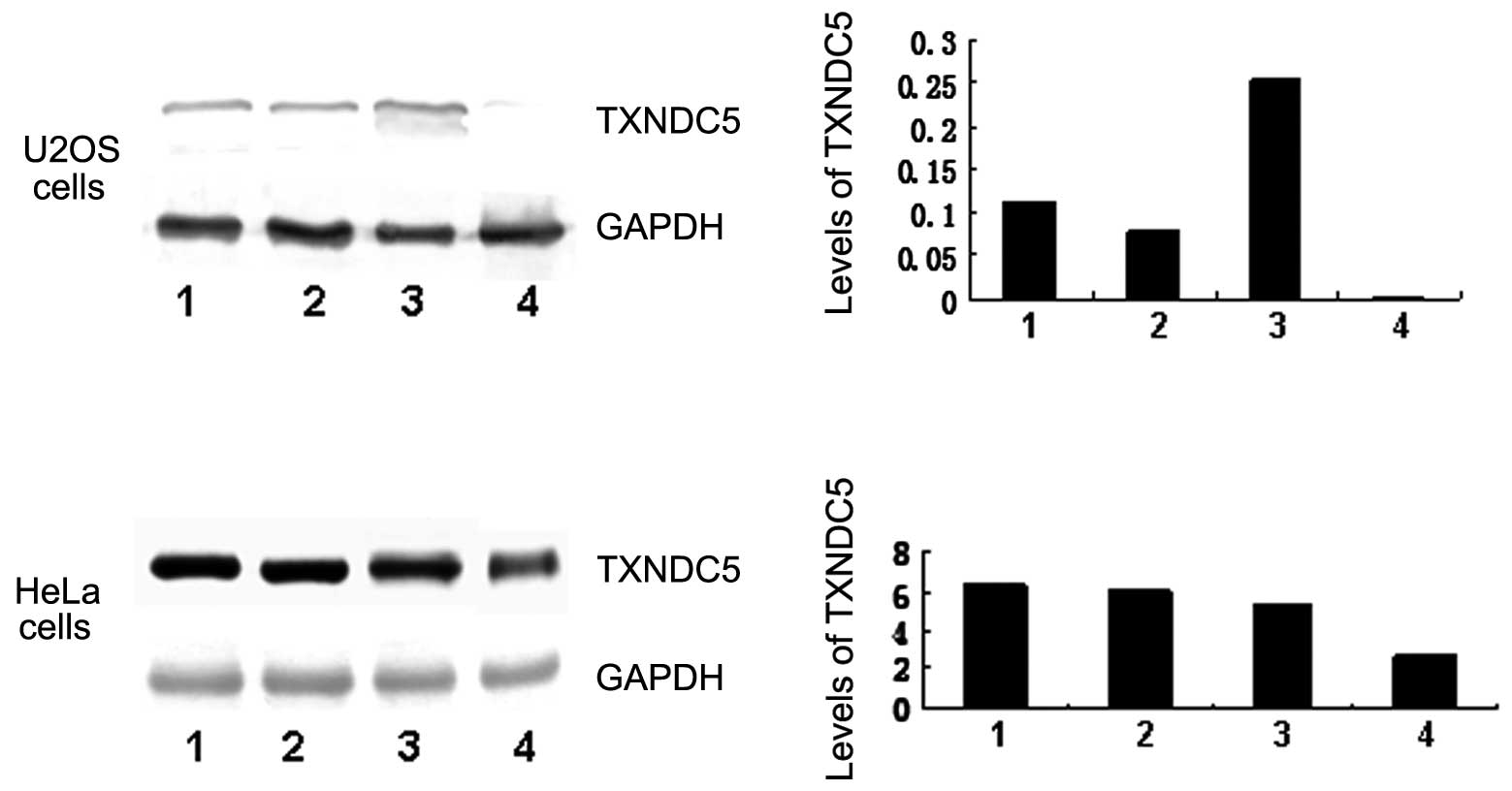
|
1.
|
Edman JC, Ellis L, Blacher RW, Roth RA and
Rutter WJ: Sequence of protein disulphide isomerase and
implications of its relationship to thioredoxin. Nature.
317:267–270. 1985. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Freedman RB, Hirst TR and Tuite MF:
Protein disulphide isomerase: building bridges in protein folding.
Trends Biochem Sci. 19:331–336. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Knoblach B, Keller BO, Groenendyk J,
Aldred S, Zheng J, Lemire BD, Li L and Michalak M: ERp19 and ERp46,
new members of the thioredoxin family of endoplasmic reticulum
proteins. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2:1104–1109. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Charlton HK, Webster J, Kruger S, Simpson
F, Richards AA and Whitehead JP: ERp46 binds to AdipoR1, but not
AdipoR2, and modulates adiponectin signaling. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 392:234–239. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Sullivan DC, Huminiecki L, Moore JW, Boyle
JJ, Poulsom R, Creamer D, Barker J and Bicknell R: EndoPDI, a novel
protein-disulfide isomerase-like protein that is preferentially
expressed in endothelial cells acts as a stress survival factor. J
Biol Chem. 47:47079–47088. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Wang Y, Ma Y, Lü B, Xu E, Huang Q and Lai
M: Differential expression of mimecan and thioredoxin
domain-containing protein 5 in colorectal adenoma and cancer: a
proteomic study. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 232:1152–1159. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Vincent EE, Elder DJ, Phillips L, Heesom
KJ, Pawade J, Luckett M, Sohail M, May MT, Hetzel MR and Tavaré
JML: Overexpression of the TXNDC5 protein in non-small cell lung
carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 31:1577–1582. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Zhang L, Hou Y, Li N, Wu K and Zhai J: The
influence of TXNDC5 gene on gastric cancer cell. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 136:1497–1505. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
The International HapMap Consortium:
Integrating ethics and science in the International HapMap Project.
Nat Rev Genet. 5:467–475. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J and Daly MJ:
Haploview analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps.
Bioinformatics. 21:263–265. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Li Z, Zhang Z, He Z, Tang W, Li T, Zeng Z,
He L and Shi Y: A partition-ligation-combination-subdivision EM
algorithm for haplotype inference with multiallelic markers: update
of the SHEsis. Cell Res. 19:519–523. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Policastro LL, Ibañez IL, Notcovich C,
Durán HA and Podhajcer OL: The tumor microenvironment:
characterization, redox considerations and novel approaches for
ROS-targeted gene therapy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 19:854–895. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Dang CV: Links between metabolism and
cancer. Genes Dev. 26:877–890. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Wang L, Zheng Y, Xu H, Yan X and Chang X:
Investigate pathogenic mechanism of TXNDC5 in rheumatoid arthritis.
PLoS One. 8:e533012013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Jeong KH, Shin MK, Uhm YK, Kim HJ, Chung
JH and Lee MH: Association of TXNDC5 gene polymorphisms and
susceptibility to nonsegmental vitiligo in the Korean population.
Br J Dermatol. 162:759–764. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Lin SH, Liu CM, Liu YL, Shen-Jang Fann C,
Hsiao PC, Wu JY, Hung SI, Chen CH, Wu HM, Jou YS, Liu SK, Hwang TJ,
Hsieh MH, Chang CC, Yang WC, Lin JJ, Chou FH, Faraone SV, Tsuang
MT, Hwu HG and Chen WJ: Clustering by neurocognition for fine
mapping of the schizophrenia susceptibility loci on chromosome 6p.
Genes Brain Behav. 8:785–794. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Chang X, Zhao Y, Yan X, Pan J, Fang K and
Wang L: Investigating a pathogenic role for TXNDC5 in rheumatoid
arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 13:R122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|