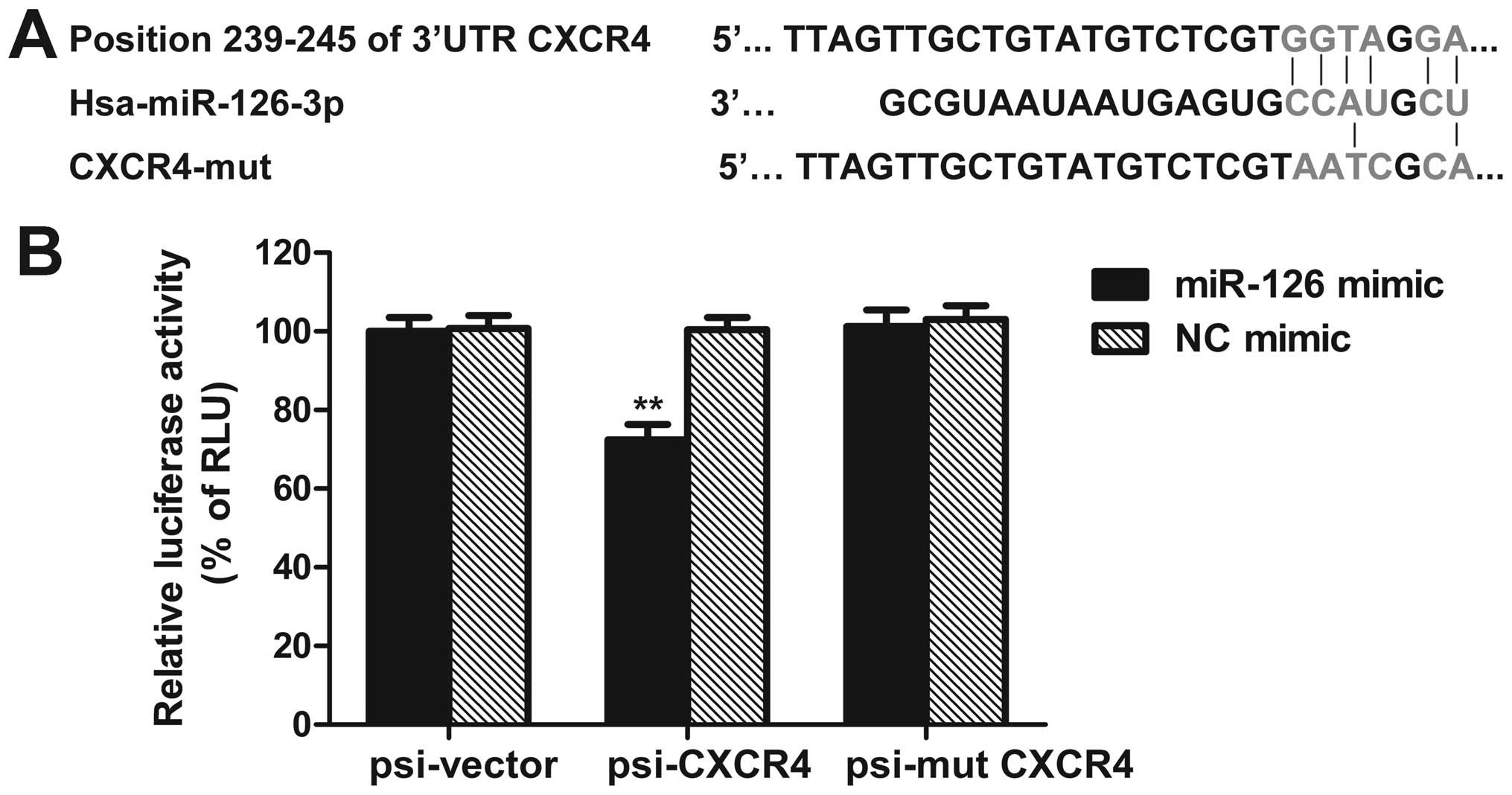
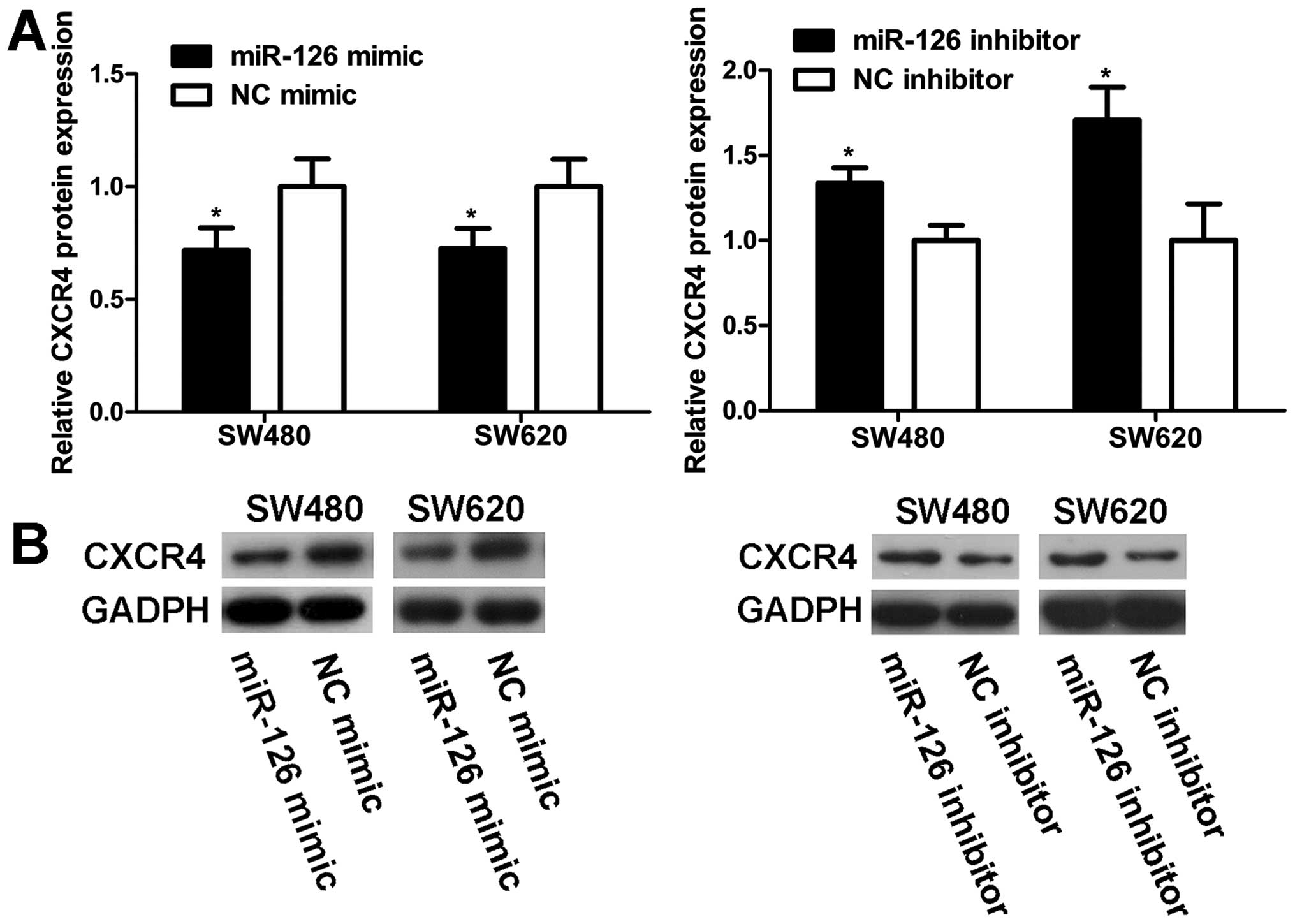
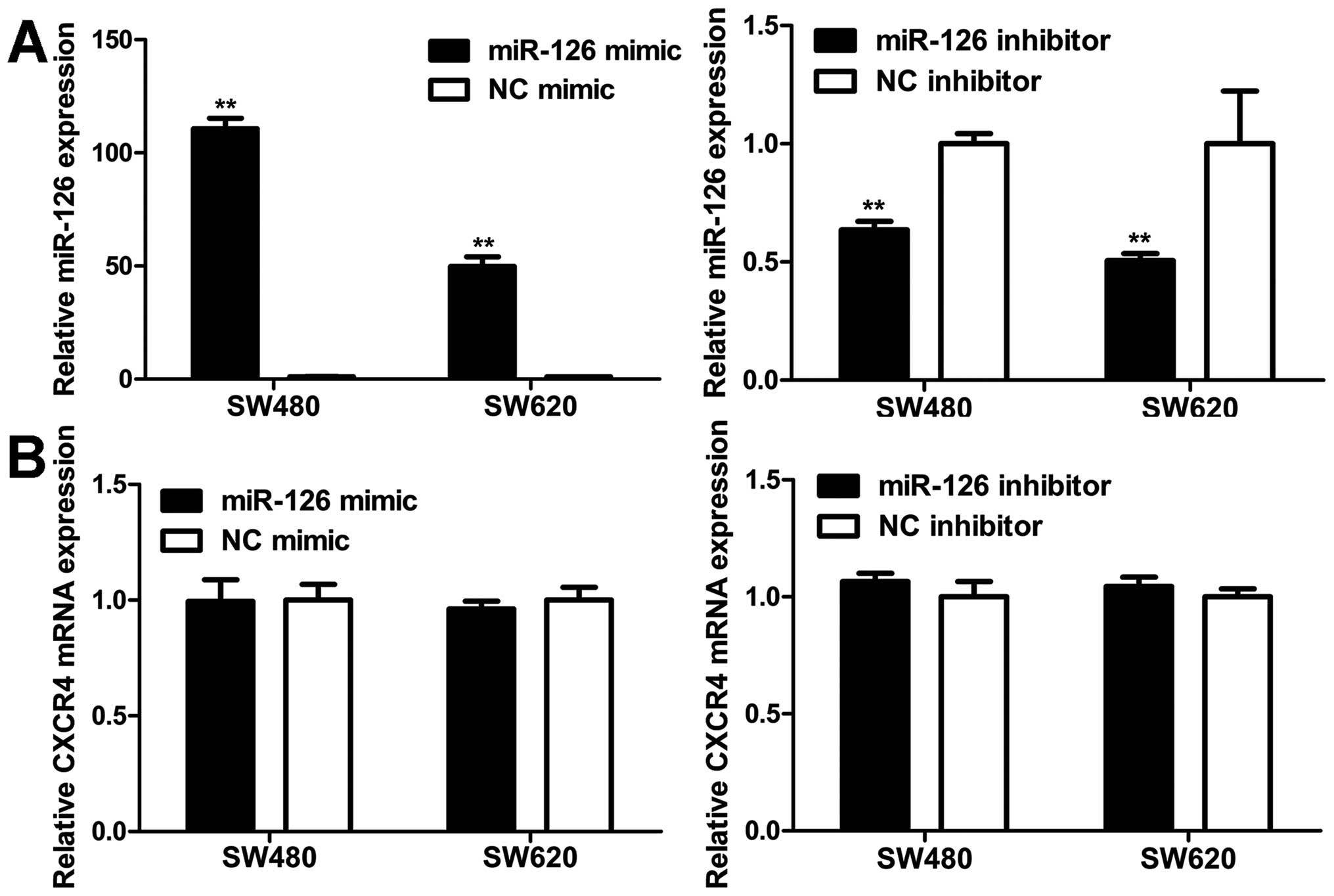
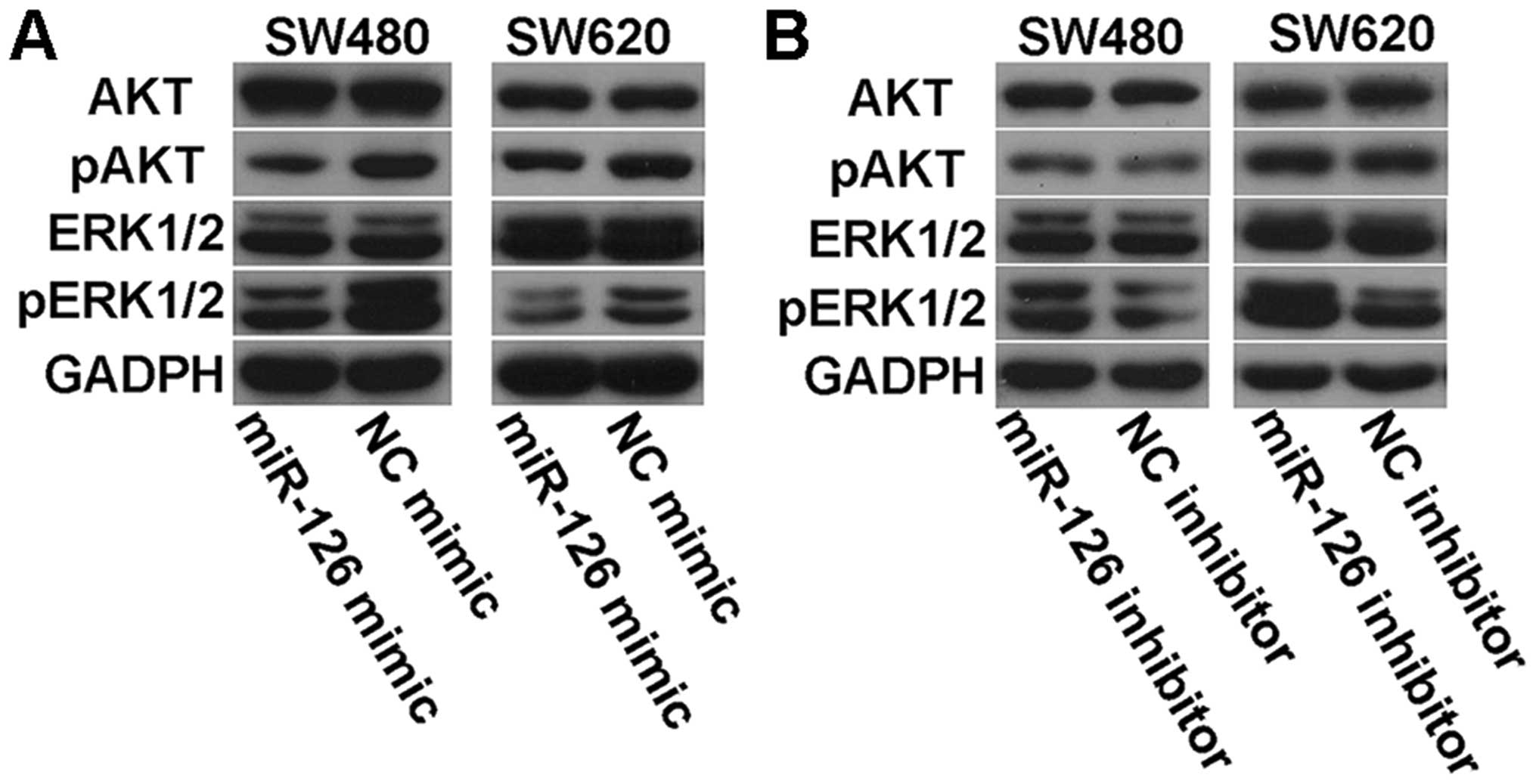
|
1.
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Lan YT, Yang SH, Chang SC, et al: Analysis
of the seventh edition of American Joint Committee on colon cancer
staging. Int J Colorectal Dis. 27:657–663. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Pasquinelli AE: MicroRNAs and their
targets: recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal
relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 13:271–282. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, et
al: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor
suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 27:2128–2136. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Ozen M, Creighton CJ, Ozdemir M and
Ittmann M: Widespread deregulation of microRNA expression in human
prostate cancer. Oncogene. 27:1788–1793. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Wang X, Tang S, Le SY, et al: Aberrant
expression of oncogenic and tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical
cancer is required for cancer cell growth. PLoS One. 3:e25572008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Babashah S and Soleimani M: The oncogenic
and tumour suppressive roles of microRNAs in cancer and apoptosis.
Eur J Cancer. 47:1127–1137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Li XM, Wang AM, Zhang J and Yi H:
Down-regulation of miR-126 expression in colorectal cancer and its
clinical significance. Med Oncol. 28:1054–1057. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Tavazoie SF, Alarcon C, Oskarsson T, et
al: Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer
metastasis. Nature. 451:147–152. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Feng R, Chen X, Yu Y, et al: miR-126
functions as a tumour suppressor in human gastric cancer. Cancer
Lett. 298:50–63. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Guo C, Sah JF, Beard L, Willson JK,
Markowitz SD and Guda K: The noncoding RNA, miR-126, suppresses the
growth of neoplastic cells by targeting phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase signaling and is frequently lost in colon cancers. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 47:939–946. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Liu B, Peng XC, Zheng XL, Wang J and Qin
YW: MiR-126 restoration down-regulate VEGF and inhibit the growth
of lung cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Lung Cancer.
66:169–175. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Zhang J, Du YY, Lin YF, et al: The cell
growth suppressor, mir-126, targets IRS-1. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 377:136–140. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Hamada S, Satoh K, Fujibuchi W, et al:
MiR-126 acts as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer cells via
the regulation of ADAM9. Mol Cancer Res. 10:3–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Zhang Y, Yang P, Sun T, et al: miR-126 and
miR-126* repress recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells
and inflammatory monocytes to inhibit breast cancer metastasis. Nat
Cell Biol. 15:284–294. 2013.
|
|
19.
|
Zhang Y, Wang X, Xu B, et al: Epigenetic
silencing of miR-126 contributes to tumor invasion and angiogenesis
in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 30:1976–1984. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Miko E, Margitai Z, Czimmerer Z, et al:
miR-126 inhibits proliferation of small cell lung cancer cells by
targeting SLC7A5. FEBS Lett. 585:1191–1196. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Li N, Tang A, Huang S, et al: MiR-126
suppresses colon cancer cell proliferation and invasion via
inhibiting RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem.
380:107–119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Li Z, Lu J, Sun M, et al: Distinct
microRNA expression profiles in acute myeloid leukemia with common
translocations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:15535–15540. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Fish JE, Santoro MM, Morton SU, et al:
miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev
Cell. 15:272–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Wang S, Aurora AB, Johnson BA, et al: The
endothelial-specific microRNA miR-126 governs vascular integrity
and angiogenesis. Dev Cell. 15:261–271. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Otsubo T, Akiyama Y, Hashimoto Y, Shimada
S, Goto K and Yuasa Y: MicroRNA-126 inhibits SOX2 expression and
contributes to gastric carcinogenesis. PLoS One. 6:e166172011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Oberlin E, Amara A, Bachelerie F, et al:
The CXC chemokine SDF-1 is the ligand for LESTR/fusin and prevents
infection by T-cell-line-adapted HIV-1. Nature. 382:833–835. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Kim J, Takeuchi H, Lam ST, et al:
Chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in colorectal cancer patients
increases the risk for recurrence and for poor survival. J Clin
Oncol. 23:2744–2753. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Murakami T, Kawada K, Iwamoto M, et al:
The role of CXCR3 and CXCR4 in colorectal cancer metastasis. Int J
Cancer. 132:276–287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Punj V, Matta H, Schamus S, Tamewitz A,
Anyang B and Chaudhary PM: Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated
herpesvirus-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein (vFLIP) K13
suppresses CXCR4 expression by upregulating miR-146a. Oncogene.
29:1835–1844. 2010.
|
|
30.
|
Tano N, Kim HW and Ashraf M: microRNA-150
regulates mobilization and migration of bone marrow-derived
mononuclear cells by targeting Cxcr4. PLoS One. 6:e231142011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Labbaye C, Spinello I, Quaranta MT, et al:
A three-step pathway comprising PLZF/miR-146a/CXCR4 controls
megakaryopoiesis. Nat Cell Biol. 10:788–801. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Yasumoto K, Koizumi K, Kawashima A, et al:
Role of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in peritoneal carcinomatosis of
gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 66:2181–2187. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Wendt MK, Drury LJ, Vongsa RA and Dwinell
MB: Constitutive CXCL12 expression induces anoikis in colorectal
carcinoma cells. Gastroenterology. 135:508–517. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Shen X, Artinyan A, Jackson D, Thomas RM,
Lowy AM and Kim J: Chemokine receptor CXCR4 enhances proliferation
in pancreatic cancer cells through AKT and ERK dependent pathways.
Pancreas. 39:81–87. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Brand S, Dambacher J, Beigel F, et al:
CXCR4 and CXCL12 are inversely expressed in colorectal cancer cells
and modulate cancer cell migration, invasion and MMP-9 activation.
Exp Cell Res. 310:117–130. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|