|
1.
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al: Global
cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Tajima Y, Yamazaki K, Makino R, et al:
Gastric and intestinal phenotypic marker expression in early
differentiated-type tumors of the stomach: clinicopathologic
significance and genetic background. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6469–6479.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Hartman ML and Czyz M: Anti-apoptotic
proteins on guard of melanoma cell survival. Cancer Lett.
331:24–34. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
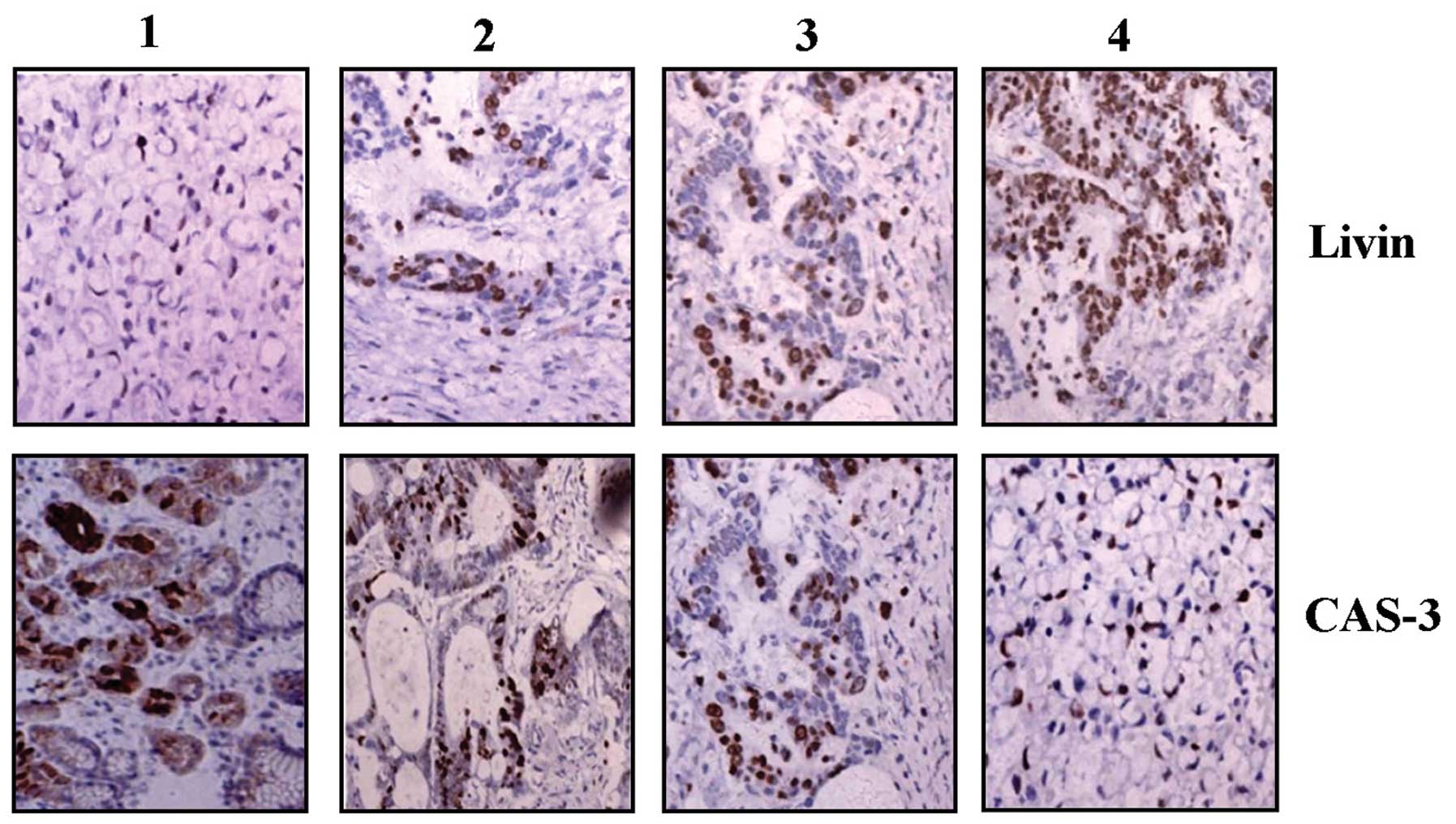
4.
|
Kim DK, Alvarado CS, Abramowsky CR, et al:
Expression of inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein (IAP) livin by
neuroblastoma cells: correlation with prognostic factors and
outcome. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 8:621–629. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
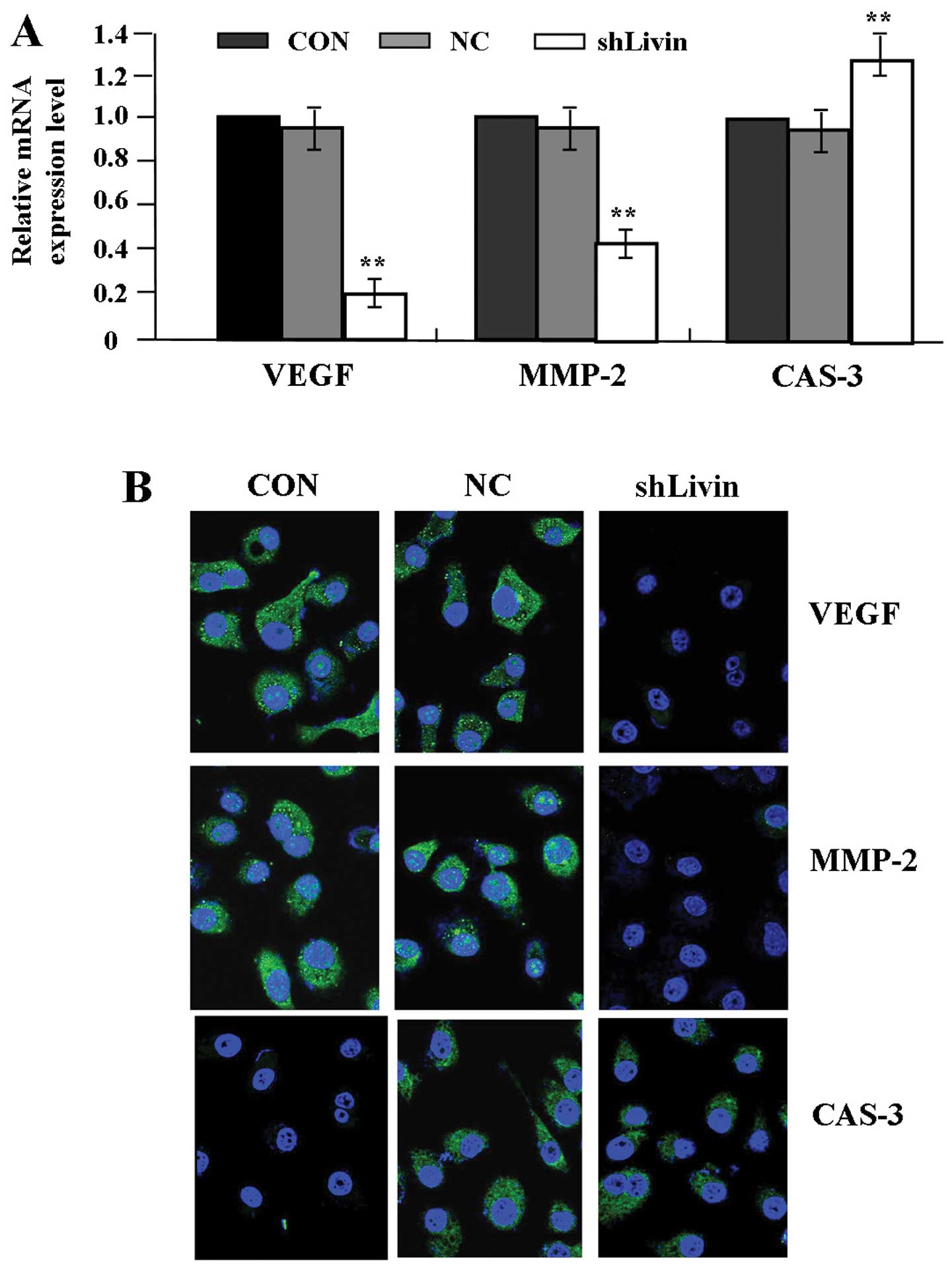
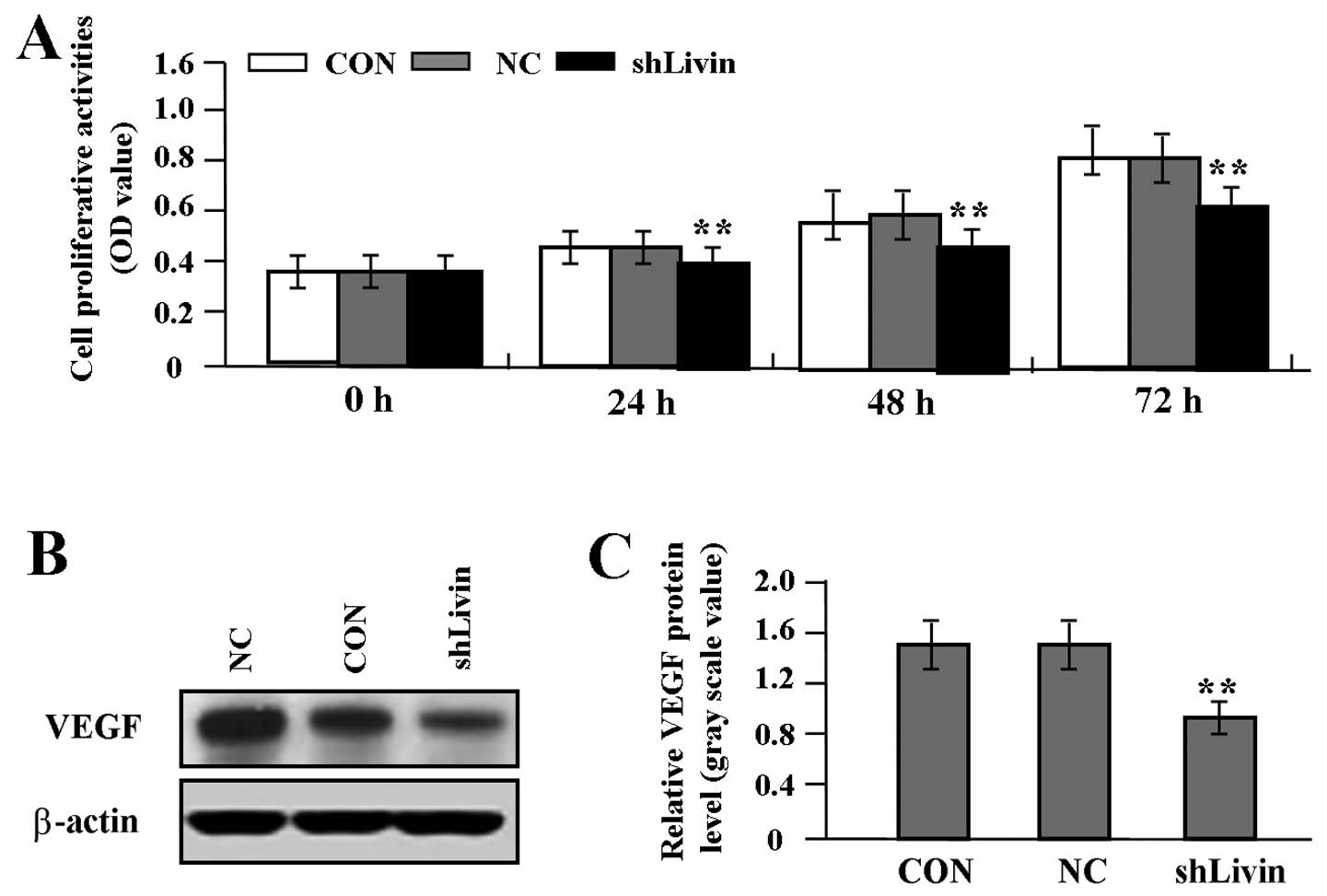
5.
|
Kleinberg L, Lie AK, Flørenes VA, et al:
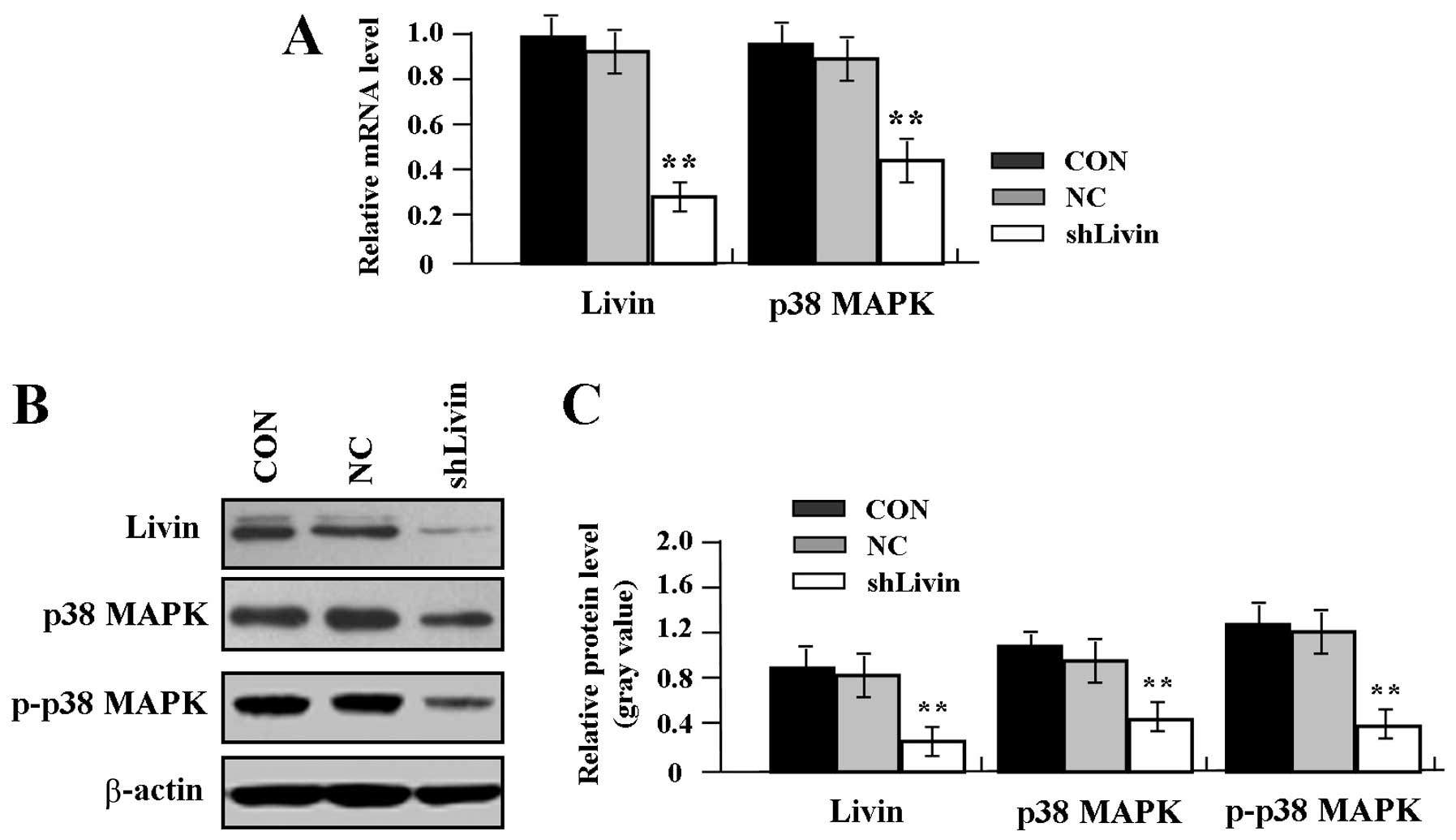
Expression of inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein family members in
malignant mesothelioma. Hum Pathol. 38:986–994. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Nedelcu T, Kubista B, Koller A, et al:
Livin and Bcl-2 expression in high-grade osteosarcoma. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 134:237–244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Lazar I, Perlman R, Lotem M, et al: The
clinical effect of the inhibitor of apopotosis protein livin in
melanoma. Oncology. 82:197–204. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Liu HB, Kong CZ, Zeng Y, et al: Livin may
serve as a marker for prognosis of bladder cancer relapse and a
target of bladder cancer treatment. Urol Oncol. 27:277–283. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Liu H, Wang S, Sun H, et al: Inhibition of
tumorigenesis and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by
siRNA-mediated silencing of the livin gene. Mol Med Rep. 3:903–907.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Crnković-Mertens I, Bulkescher J, Mensger
C, et al: Isolation of peptides blocking the function of
anti-apoptotic Livin protein. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:1895–1905.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Wang X, Xu J, Ju S, et al: Livin gene
plays a role in drug resistance of colon cancer cells. Clin
Biochem. 43:655–660. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Dasgupta A, Alvarado CS, Xu Z, et al:
Expression and functional role of inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein
livin (BIRC7) in neuroblastoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
400:53–59. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Ding ZY, Liu GH, Olsson B, et al:
Upregulation of the anti-apoptotic factor Livin contributes to
cisplatin resistance in colon cancer cells. Tumour Biol.
234:683–693. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Sun JG, Liao RX, Zhang SX, et al: Role of
inhibitor of apoptosis protein Livin in radiation resistance in
nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 26:585–592.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Abd-Elrahman I, Hershko K, Neuman T, et
al: The inhibitor of apoptosis protein Livin (ML-IAP) plays a dual
role in tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 69:5475–5480. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Kempkensteffen C, Hinz S, Christoph F, et
al: Expression of the apoptosis inhibitor livin in renal cell
carcinomas: correlations with pathology and outcome. Tumour Biol.
28:132–138. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Dai CH, Li J, Shi SB, et al: Survivin and
Smac gene expressions but not livin are predictors of prognosis in
non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with adjuvant
chemotherapy following surgery. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 40:327–335. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Yan B: Research progress on Livin protein:
an inhibitor of apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 357:39–45. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Xi RC, Biao WS and Gang ZZ: Significant
elevation of survivin and livin expression in human colorectal
cancer: inverse correlation between expression and overall
survival. Onkologie. 34:428–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Li J, Chen P, Li XQ, et al: Elevated
levels of survivin and livin mRNA in bronchial aspirates as markers
to support the diagnosis of lung cancer. Int J Cancer.
132:1098–1104. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Xi RC, Sheng YR, Chen WH, et al:
Expression of survivin and livin predicts early recurrence in
non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. J Surg Oncol. 107:550–554.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Chang H and Schimmer AD: Livin/melanoma
inhibitor of apoptosis protein as a potential therapeutic target
for the treatment of malignancy. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:24–30. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Li H, Chen Y, Chen G, et al: Expression of
livin in lung cancer tissue and its relationship with the
expression of caspase-3. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 10:486–490.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Wang TS, Ding QQ, Guo RH, et al:
Expression of livin in gastric cancer and induction of apoptosis in
SGC-7901 cells by shRNA-mediated silencing of livin gene. Biomed
Pharmacother. 64:333–338. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Liang YZ, Fang TY, Xu HG, et al:
Expression of CD44v6 and Livin in gastric cancer tissue. Chin Med
J. 125:3161–3165. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Ye L, Song X, Li S, et al: Livin-α
promotes cell proliferation by regulating G1-S cell cycle
transition in prostate cancer. Prostate. 71:42–51. 2011.
|
|
27.
|
Chen F, Yang D, Che X, et al: Livin
mediates tumor cell invasion in the DU-145 cell line via NF-κB.
Oncol Rep. 27:2010–2016. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Wang H, Tan SS, Wang XY, et al: Silencing
livin gene by siRNA leads to apoptosis induction, cell cycle
arrest, and proliferation inhibition in malignant melanoma LiBr
cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:1968–1974. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Yang D, Song X, Zhang J, et al:
Suppression of livin gene expression by siRNA leads to growth
inhibition and apoptosis induction in human bladder cancer T24
cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 74:1039–1044. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Yuan B, Ran B, Wang S, et al: siRNA
directed against Livin inhibits tumor growth and induces apoptosis
in human glioma cells. J Neurooncol. 107:81–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Kajdaniuk D, Marek B, Fołtyn W, et al:
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in endocrinology and
oncology. Endokrynol Pol. 62:14–22. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Li X, Fan S, Li L, et al: RNA
interference-mediated knockdown of Livin suppresses cell
proliferation and invasion and enhances the chemosensitivity to
cisplatin in human osteosarcoma cells. Int J Oncol. 43:159–168.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Liu C, Wu X, Luo C, et al: Antisense
oligonucleotide targeting Livin induces apoptosis of human bladder
cancer cell via a mechanism involving caspase 3. Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 29:632010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Shin I, Kim S, Song H, et al:
H-Ras-specific activation of Rac-MKK3/6-p38 pathway: its critical
role in invasion and migration of breast epithelial cells. Biol
Chem. 280:14675–14683. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Hideshima T, Akiyama M, Hayashi T, et al:
Targeting p38 MAPK inhibits multiple myeloma cell growth in the
bone marrow milieu. Blood. 101:703–705. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Noguchi K, Yamana H, Kitanaka C, et al:
Differential role of the JNK and p38 MAPK pathway in c-Myc- and
s-Myc-mediated apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 267:221–227.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|