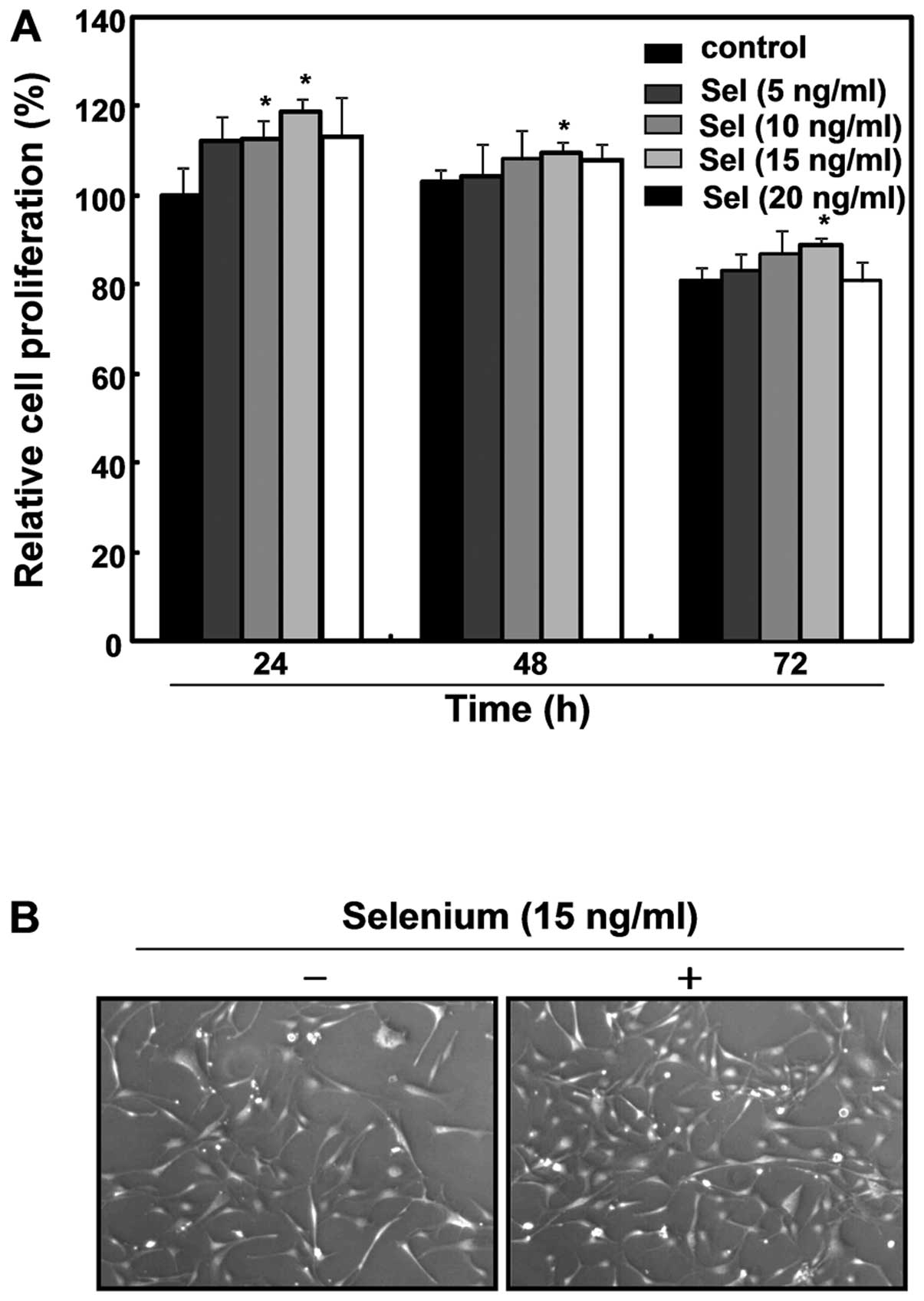
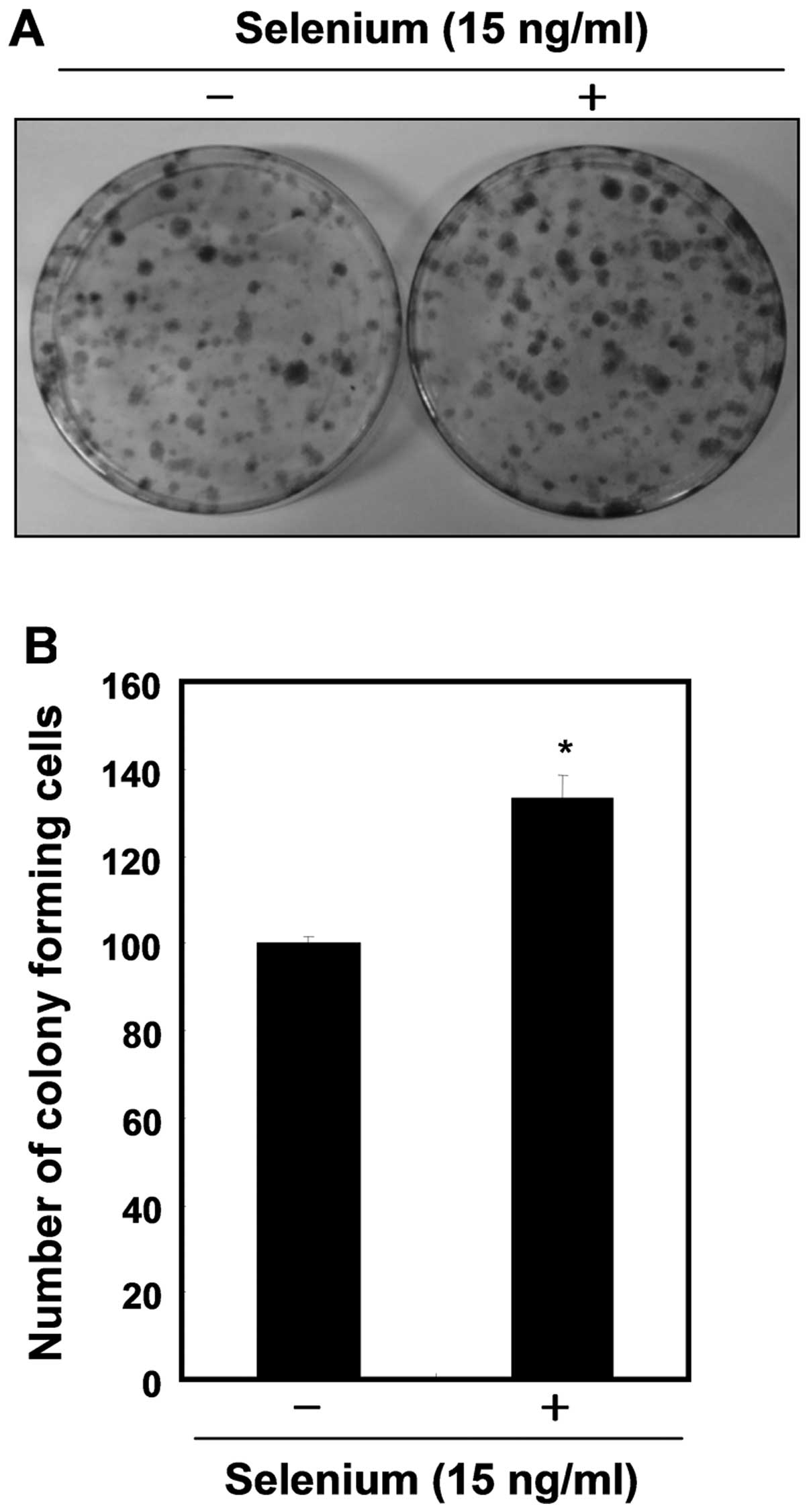
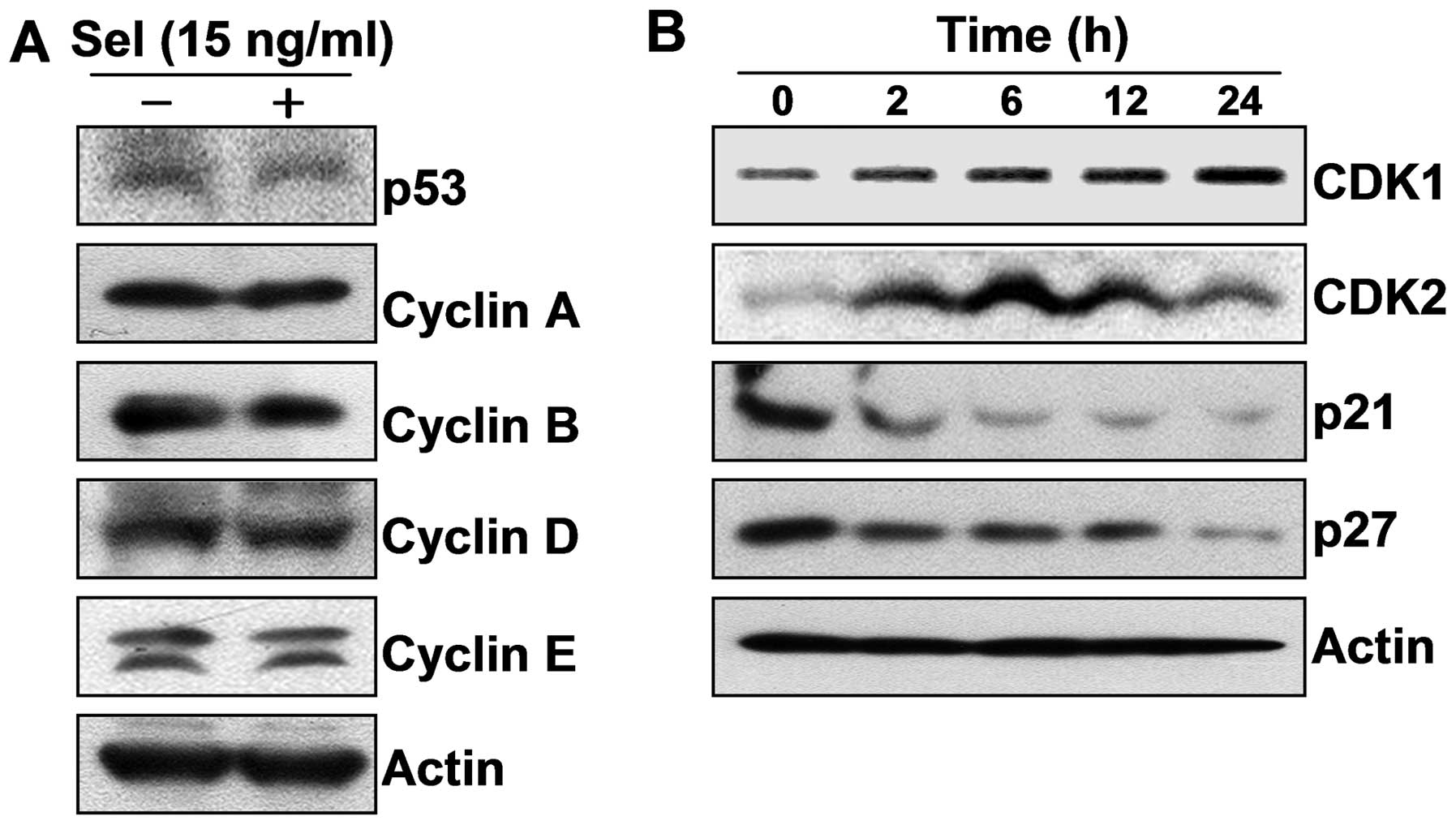
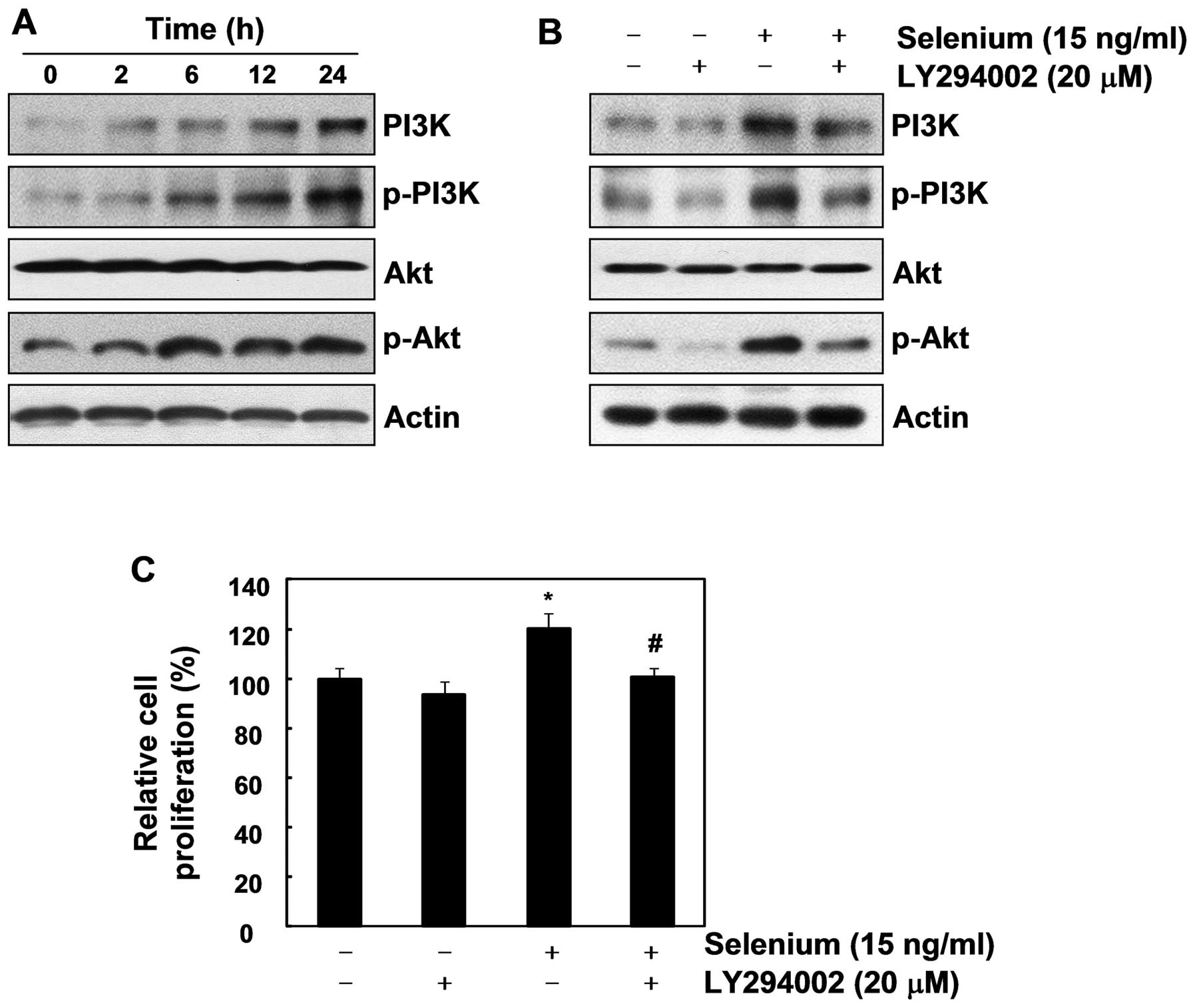
|
1.
|
Aasen T, Raya A, Barrero MJ, Garreta E,
Consiglio A, Gonzalez F, Vassena R, Bilić J, Pekarik V, Tiscornia
G, Edel M, Boué S and Izpisúa Belmonte JC: Efficient and rapid
generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human
keratinocytes. Nat Biotechnol. 26:1276–1284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Im JE, Song SH, Kim JY, Kim KL, Baek SH,
Lee DR and Suh W: Vascular differentiation of multipotent
spermatogonial stem cells derived from neonatal mouse testis. Exp
Mol Med. 44:303–309. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Taura D, Sone M, Homma K, Oyamada N,
Takahashi K, Tamura N, Yamanaka S and Nakao K: Induction and
isolation of vascular cells from human induced pluripotent stem
cells - brief report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:1100–1103.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Welham MJ, Kingham E, Sanchez-Ripoll Y,
Kumpfmueller B, Storm M and Bone H: Controlling embryonic stem cell
proliferation and pluripotency: the role of PI3K- and
GSK-3-dependent signalling. Biochem Soc Trans. 39:674–678. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Lee MY, Lim HW, Lee SH and Han HJ: Smad,
PI3K/Akt, and Wnt-dependent signaling pathways are involved in
BMP-4-induced ESC self-renewal. Stem Cells. 27:1858–1868. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Chen L and Khillan JS: A novel signaling
by vitamin A/retinol promotes self renewal of mouse embryonic stem
cells by activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway via insulin-like
growth factor-1 receptor. Stem Cells. 28:57–63. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Kimura T and Nakano T: Induction of
pluripotency in primordial germ cells. Histol Histopathol.
26:643–650. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Lee SR, Bar-Noy S, Kwon J, Levine RL,
Stadtman TC and Rhee SG: Mammalian thioredoxin reductase: oxidation
of the C terminal cysteine/selenocysteine active site forms a
thioselenide, and replacement of selenium with sulfur markedly
reduces catalytic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:2521–2526.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Rayman MP: The importance of selenium to
human health. Lancet. 356:233–241. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Combs GF and Gray WP Jr: Chemopreventive
agents: selenium. Pharmacol Ther. 79:179–192. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Ganther HE: Selenium metabolism,
selenoproteins and mechanisms of cancer prevention: complexities
with thioredoxin reductase. Carcinogenesis. 20:1657–1666. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Kim JH, Hue JJ, Kang BS, Park H, Nam SY,
Yun YW, Kim JS and Lee BJ: Effects of selenium on colon
carcinogenesis induced by azoxymethane and dextran sodium sulfate
in mouse model with high-iron diet. Lab Anim Res. 27:9–18. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Ferby I, Blazquez M, Palmer A, Eritja R
and Nebreda AR: A novel p34cdc2-binding and activating protein that
is necessary and sufficient to trigger G2/M progression in
Xenopus oocytes. Genes Dev. 13:2177–2189. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Kim JH, Lee MR, Kim JH, Jee MK and Kang
SK: IFATS collection: selenium induces improvement of stem cell
behaviors in human adipose-tissue stromal cells via SAPK/JNK and
stemness acting signals. Stem Cells. 26:2724–2734. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
O’Connor PM, Ferris DK, Pagano M, Draetta
G, Pines J, Hunter T, Longo DL and Kohn KW: G2 delay induced by
nitrogen mustard in human cells affects cyclin A/cdk2 and cyclin
B1/cdc2-kinase complexes differently. J Biol Chem. 268:8298–8308.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Nurse P: A long twentieth century of the
cell cycle and beyond. Cell. 100:71–78. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Yuan TL and Cantley LC: PI3K pathway
alterations in cancer: variations on a theme. Oncogene.
27:5497–5510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Steelman LS, Pohnert SC, Shelton JG,
Franklin RA, Bertrand FE and McCubrey JA: JAK/STAT, Raf/MEK/ERK,
PI3K/Akt and BCR-ABL in cell cycle progression and leukemogenesis.
Leukemia. 18:189–218. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Chatani Y, Tanimura S, Miyoshi N, Hattori
A, Sato M and Kohno M: Cell type-specific modulation of cell growth
by transforming growth factor beta 1 does not correlate with
mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem.
270:30686–30692. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Martin P and Pognonec P: ERK and cell
death: cadmium toxicity, sustained ERK activation and cell death.
FEBS J. 277:39–46. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Downward J: Targeting Ras signaling
pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:11–22. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Kempf
RC, Long J, Laidler P, Mijatovic S, Maksimovic-Ivanic D, Stivala F,
Mazzarino MC, Donia M, Fagone P, Malaponte G, Nicoletti F, Libra M,
Milella M, Tafuri A, Bonati A, Bäsecke J, Cocco L, Evangelisti C,
Martelli AM, Montalto G, Cervello M and McCubrey JA: Roles of the
Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathways in controlling growth
and sensitivity to therapy-implications for cancer and aging. Aging
(Albany, NY). 3:192–222. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Zhong WD, Han ZD, He HC, Bi XC, Dai QS,
Zhu G, Ye YK, Liang YX, Qin WJ, Zhang Z, Zeng GH and Chen ZN:
CD147, MMP-1, MMP-2 and MMP-9 protein expression as significant
prognostic factors in human prostate cancer. Oncology. 75:230–236.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Jezierska A and Motyl T: Matrix
metalloproteinase-2 involvement in breast cancer progression: a
mini-review. Med Sci Monit. 15:RA32–RA40. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Dinarina A, Perez LH, Davila A, Schwab M,
Hunt T and Nebreda AR: Characterization of a new family of
cyclin-dependent kinase activators. Biochem J. 386:349–355. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Lenormand JL, Dellinger RW, Knudsen KE,
Subramani S and Donoghue DJ: Speedy: a novel cell cycle regulator
of the G2/M transition. EMBO J. 18:1869–1877. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Porter LA, Kong-Beltran M and Donoghue DJ:
Spy1 interacts with p27Kip1 to allow G1/S progression.
Mol Cell Biol. 14:3664–3674. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Paling NR, Wheadon H, Bone HK and Welham
MJ: Regulation of embryonic stem cell self-renewal by
phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent signaling. J Biol Chem.
279:48063–48070. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Watanabe S, Umehara H, Murayama K, Okabe
M, Kimura T and Nakano T: Activation of Akt signaling is sufficient
to maintain pluripotency in mouse and primate embryonic stem cells.
Oncogene. 25:2697–2707. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Kimura T, Tomooka M, Yamano N, Murayama K,
Matoba S, Umehara H, Kanai Y and Nakano T: AKT signaling promotes
derivation of embryonic germ cells from primordial germ cells.
Development. 135:869–879. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Liu N, Lu M, Feng XM, Ma FX, Fang ZH, Tian
XM, Ren Q, Zhang L, Liu B, Huang PP, Liu L and Han ZC: Exogenous
Nanog alleviates but is insufficient to reverse embryonic stem
cells differentiation induced by PI3K signaling inhibition. J Cell
Biochem. 106:1041–1047. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Heissig B, Hattori K, Dias S, Friedrich M,
Ferris B, Hackett NR, Crystal RG, Besmer P, Lyden D, Moore MA, Werb
Z and Rafii S: Recruitment of stem and progenitor cells from the
bone marrow niche requires MMP-9 mediated release of kit-ligand.
Cell. 109:625–637. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Yu Q, Chen L, You Y, Zou C, Zhang Y, Liu Q
and Cheng F: Erythropoietin combined with granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor enhances MMP-2 expression in mesenchymal
stem cells and promotes cell migration. Mol Med Rep. 4:31–36.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Klemke RL, Cai S, Giannini AL, Gallagher
PJ, deLanerolle P and Cheresh DA: Regulation of cell motility by
mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Cell Biol. 137:481–492. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Jo M, Thomas KS, Somlyo AV, Somlyo AP and
Gonias SL: Cooperativity between the Ras-ERK and Rho-Rho kinase
pathways in urokinase-type plasminogen activator-stimulated cell
migration. J Biol Chem. 277:12479–12485. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|