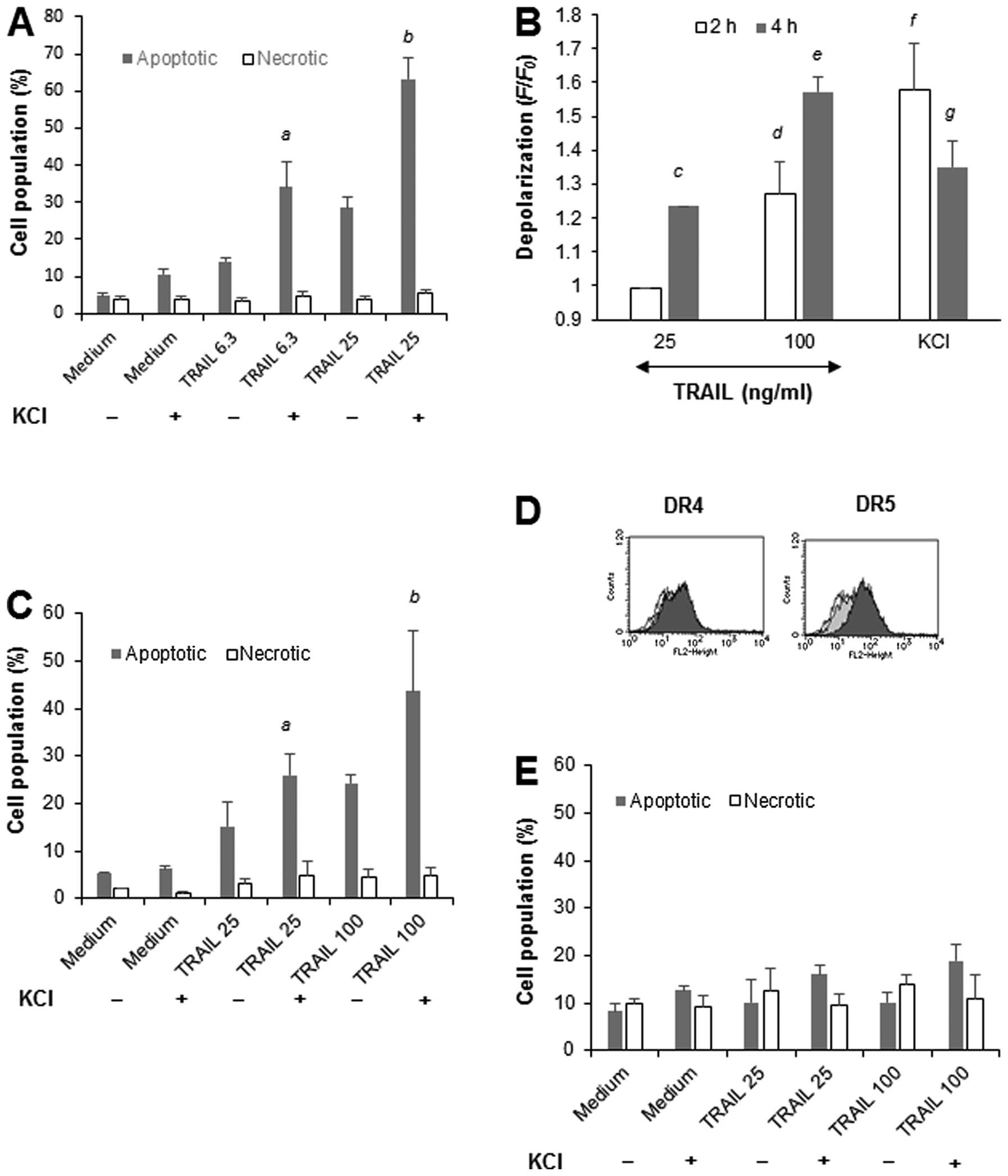
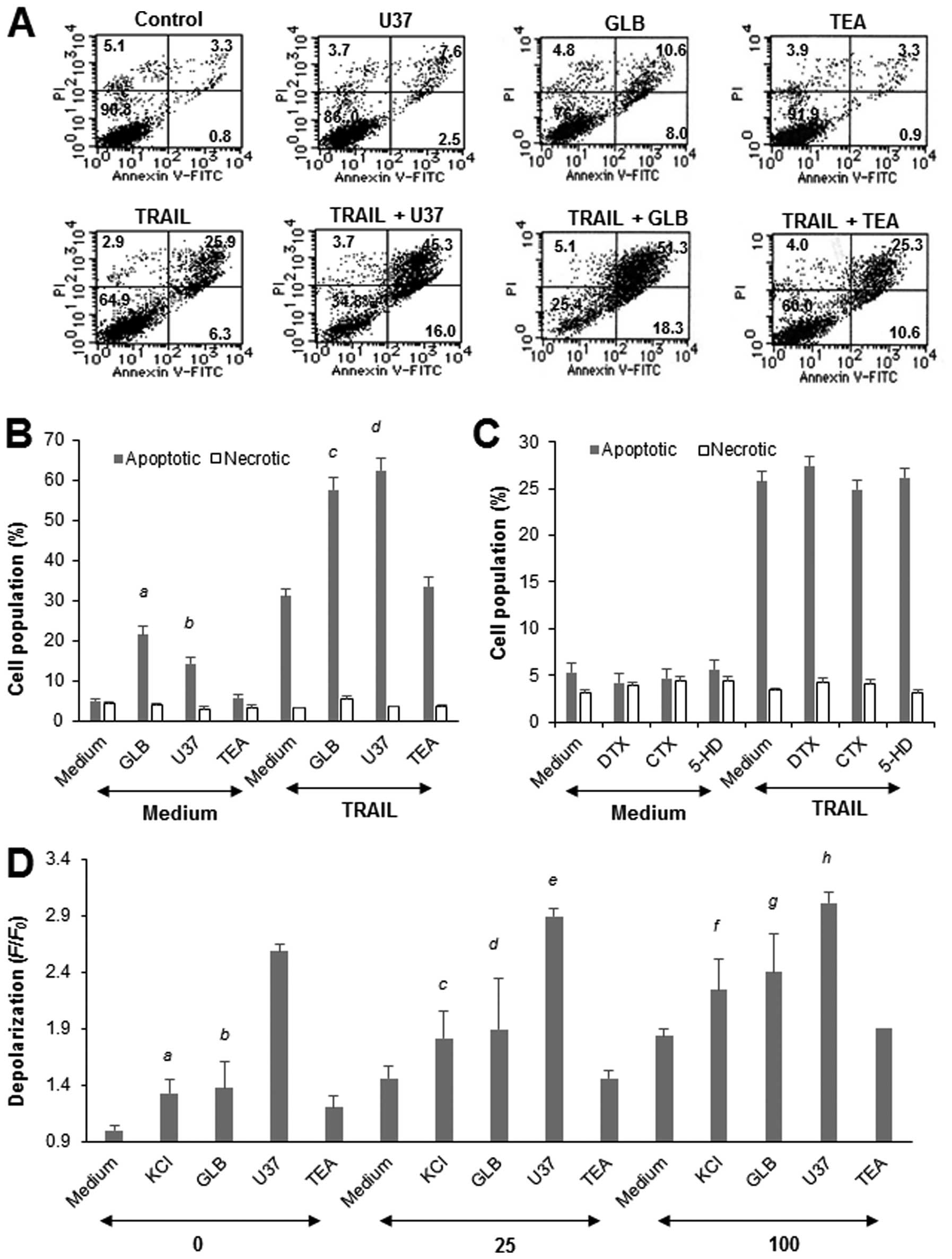
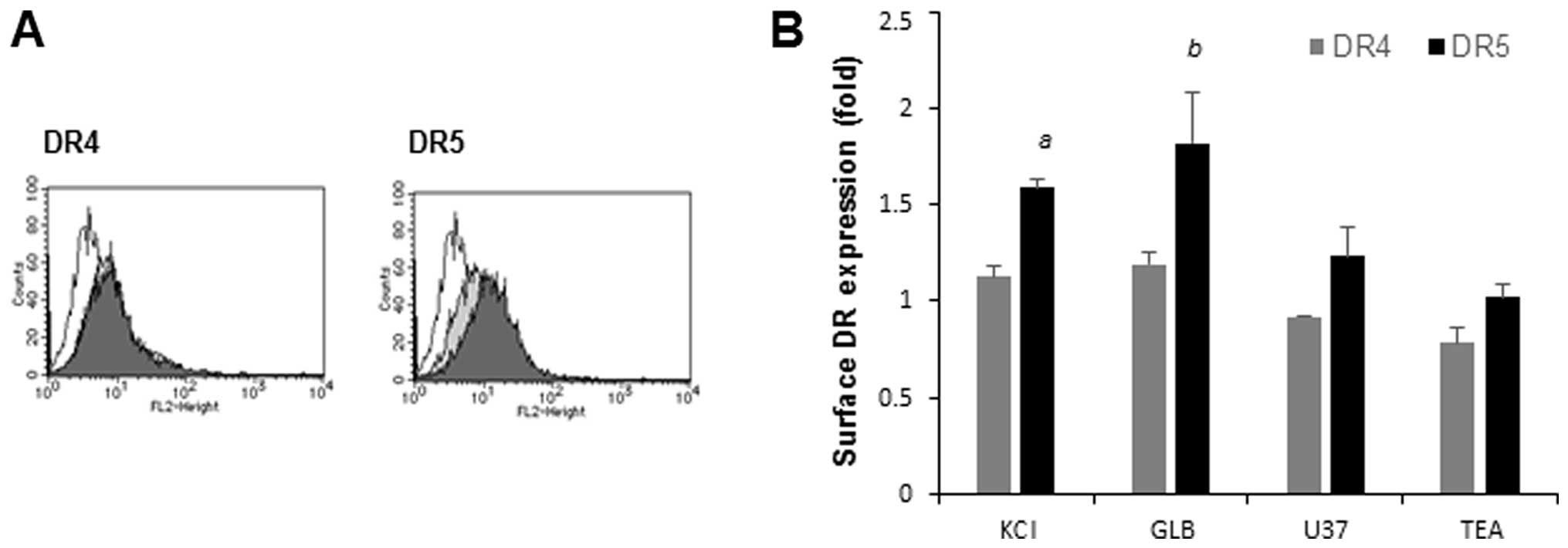
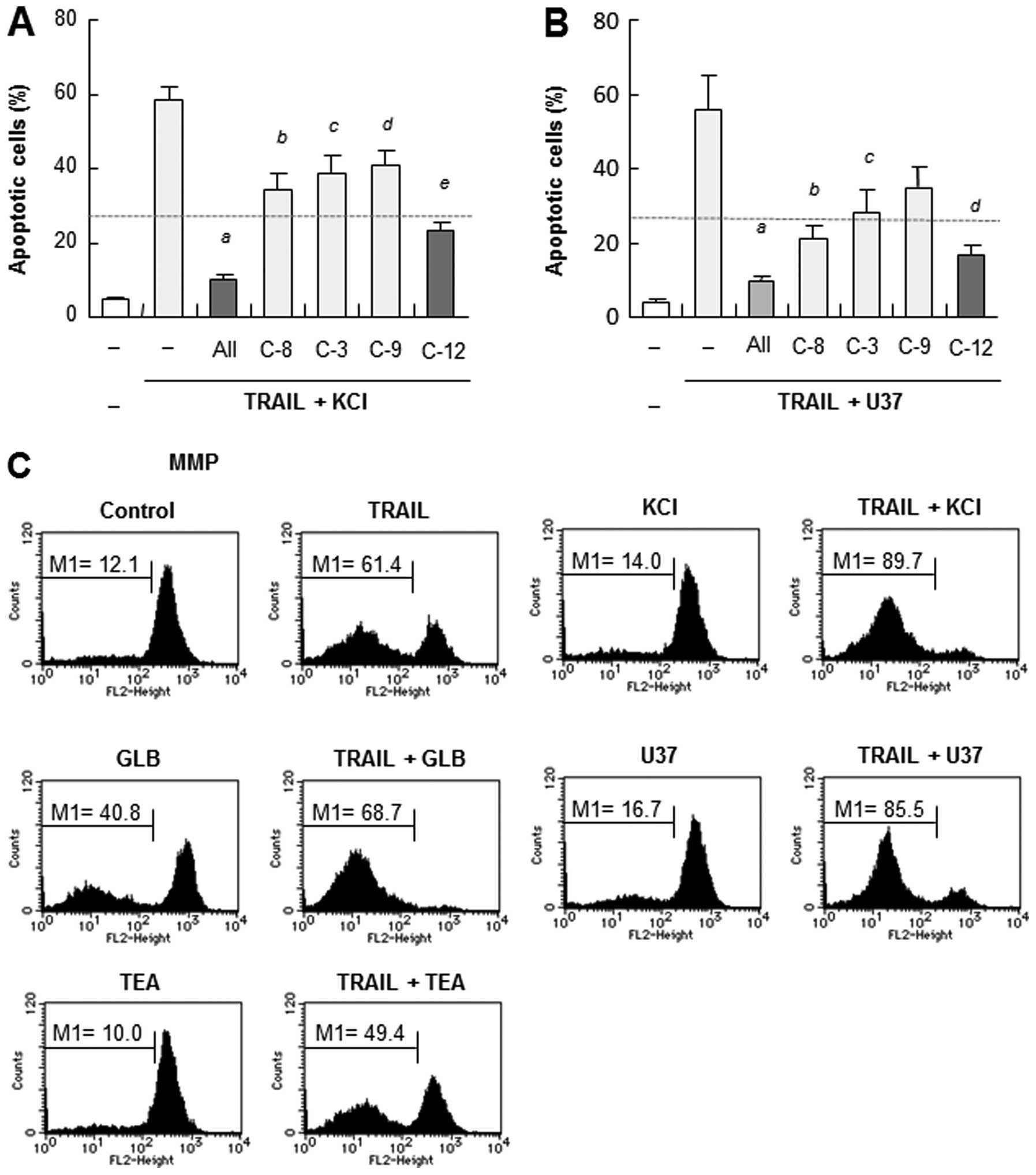
|
1.
|
LeBlanc HN and Ashkenazi A: Apo2L/TRAIL
and its death and decoy. Cell Death Differ. 10:66–75. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A,
Schow P, Kim KJ and Ashkenazi A: Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment
of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5.
Immunity. 12:612–620. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Lavrik IN, Golks A and Krammer PH:
Caspases: pharmacological manipulation of cell death. J Clin
Invest. 15:2665–2662. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Danial NN and Korsmeyer SJ: Cell death:
critical control points. Cell. 116:205–219. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Green DR: Apoptotic pathways: paper wraps
stone blunts scissors. Cell. 102:1–4. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Korsmeyer SJ, Wei MC, Saito M, Weiler S,
Oh KJ and Schlesinger PH: Pro-apoptotic cascade activates BID,
which oligomerizes BAK or BAX into pores that result in the release
of cytochrome c. Cell Death Differ. 7:1166–1173. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Yan N and Shi Y: Mechanisms of apoptosis
through structural biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 21:35–56. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Dyer MJ, MacFarlane M and Cohen GM:
Barriers to effective TRAIL-targeted therapy of malignancy. J Clin
Oncol. 25:4506–4507. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Bortner CD, Gomez-Angelats M and Cidlowski
JA: Plasma membrane depolarization without repolarization is an
early molecular event in anti-Fas-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
276:4304–4314. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Yin W, Li X, Feng S, et al: Plasma
membrane depolarization and Na,K-ATPase impairment induced by
mitochondrial toxins augment leukemia cell apoptosis via a novel
mitochondrial amplification mechanism. Biochem Pharmacol.
78:191–202. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Nolte F, Friedrich O, Rojewski M, Fink RH,
Schrezenmeier H and Körper S: Depolarisation of the plasma membrane
in the arsenic trioxide (As2O3)-and
anti-CD95-induced apoptosis in myeloid cells. FEBS Lett. 578:85–89.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Ghoumari AM, Piochon C, Tomkiewicz C, et
al: Neuroprotective effect of mifepristone involves neuron
depolarization. FASEB J. 20:1377–1386. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Suzuki Y, Inoue T, Murai M,
Suzuki-Karasaki M, Ochiai T and Ra C: Depolarization potentiates
TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells: role for
ATP-sensitive K+ channels and endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Int J Oncol. 41:465–475. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Inoue T and Suzuki-Karasaki Y:
Mitochondrial superoxide mediates mitochondrial and endoplasmic
reticulum dysfunctions in TRAIL-induced apoptosis in Jurkat cells.
Free Radic Biol Med. 61:273–284. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Chen LH, Jiang CC, Kiejda KA, et al:
Thapsigargin sensitizes human melanoma cells to TRAIL-induced
apoptosis by up-regulation of TRAIL-R2 through the unfolded protein
response. Carcinogenesis. 28:2328–2336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Jiang CC, Chen LH, Gillespie S, et al:
Tunicamycin sensitizes human melanoma cells to tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by
up-regulation of TRAIL-R2 via the unfolded protein response. Cancer
Res. 67:5880–5888. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Liu H, Jiang CC, Lavis CJ, et al:
2-Deoxy-D-glucose enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human
melanoma cells through XBP-1-mediated up-regulation of TRAIL-R2.
Mol Cancer. 8:1222009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Boyce M and Yuan J: Cellular response to
endoplasmic reticulum stress: a matter of life or death. Cell Death
Differ. 13:363–373. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Breckenridge DG, Germain M, Mathai JP,
Nguyen M and Shore GC: Regulation of apoptosis by endoplasmic
reticulum pathways. Oncogene. 22:8608–8618. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Groenendyk J and Michalak M: Endoplasmic
reticulum quality control and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Pol.
52:381–395. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Robinson KM, Janes MS, Pehar M, et al:
Selective fluorescencet imaging of superoxide in vivo using
ethidium-based probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:15038–15043.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Mukhopadhyay P, Rajesh M, Kashiwaya Y,
Haskó G and Pacher P: Simple quantitative detection of
mitochondrial superoxide production in live cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 358:203–208. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Petit JM, Maftah A, Ratinaud MH and Julien
R: 10N-nonyl acridine orange interacts with cardiolipin and allows
the quantification of this phospholipid in isolated mitochondria.
Eur J Biochem. 209:267–273. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Griffith TS, Rauch CT, Smolak PJ, et al:
Functional analysis of TRAIL receptors using monoclonal antibodies.
J Immunol. 162:2597–2605. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Pukac L, Kanakaraj P, Humphreys R, et al:
HGS-ETR1, a fully human TRAIL-receptor 1 monoclonal antibody,
induces cell death in multiple tumour types in vitro and in vivo.
Br J Cancer. 92:1430–1441. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Georgakis GV, Li Y, Humphreys R, et al:
Activity of selective fully human agonistic antibodies to the TRAIL
death receptors TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 in primary and cultured
lymphoma cells: induction of apoptosis and enhancement of
doxorubicin- and bortezomib-induced cell death. Br J Haematol.
130:501–510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Tochigi M, Inoue T, Suzuki-Karasaki M,
Ochiai T, Ra C and Suzuki-Karasaki Y: Hydrogen peroxide induces
cell death in human TRAIL-resistant melanoma through intracellular
superoxide generation. Int J Oncol. 42:863–872. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu
J, Yankner BA and Yuan J: Caspase-12 mediates
endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by
amyloid beta. Nature. 403:98–103. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Szegezdi E, Fitzgerald U and Samali A:
Caspase-12 and ER-stress-mediated apoptosis: the story so far. Ann
NY Acad Sci. 1010:186–194. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Rutkowski DT and Kaufman RJ: A trip to the
ER: coping with stress. Trends Cell Biol. 14:20–28. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Jiang CC, Mao ZG, Avery-Kiejda KA, Wade M,
Hersey P and Zhang XD: Glucose-regulated protein 78 antagonizes
cisplatin and adriamycin in human melanoma cells. Carcinogenesis.
30:197–204. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Mao ZG, Jiang CC, Yang F, Thorne RF,
Hersey P and Zhang XD: TRAIL-induced apoptosis of human melanoma
cells involves activation of caspase-4. Apoptosis. 15:1211–1222.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Fas SC, Baumann S, Zhu JY, et al: Wogonin
sensitizes resistant malignant cells to TNFalpha- and TRAIL-induced
apoptosis. Blood. 108:3700–3706. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Baumann S, Fas SC, Giaisi M, et al:
Wogonin preferentially kills malignant lymphocytes and suppresses
T-cell tumor growth by inducing PLCgamma1- and
Ca2+-dependent apoptosis. Blood. 111:2354–2363. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Powlny AA and Singh SV: Multitargeted
prevention and therapy of cancer by diallyl trisulfide and related
Allium vegetable-derived organosulfur compounds. Cancer
Lett. 269:305–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Murai M, Inoue T, Suzuki-Karasaki M,
Ochiai T, Ra C, Nishida S, et al: Diallyl trisulfide sensitizes
human melanoma cells to TRAIL-induced cell death by promoting
endoplasmic reticulum-mediated apoptosis. Int J Oncol.
41:2029–2037. 2012.
|