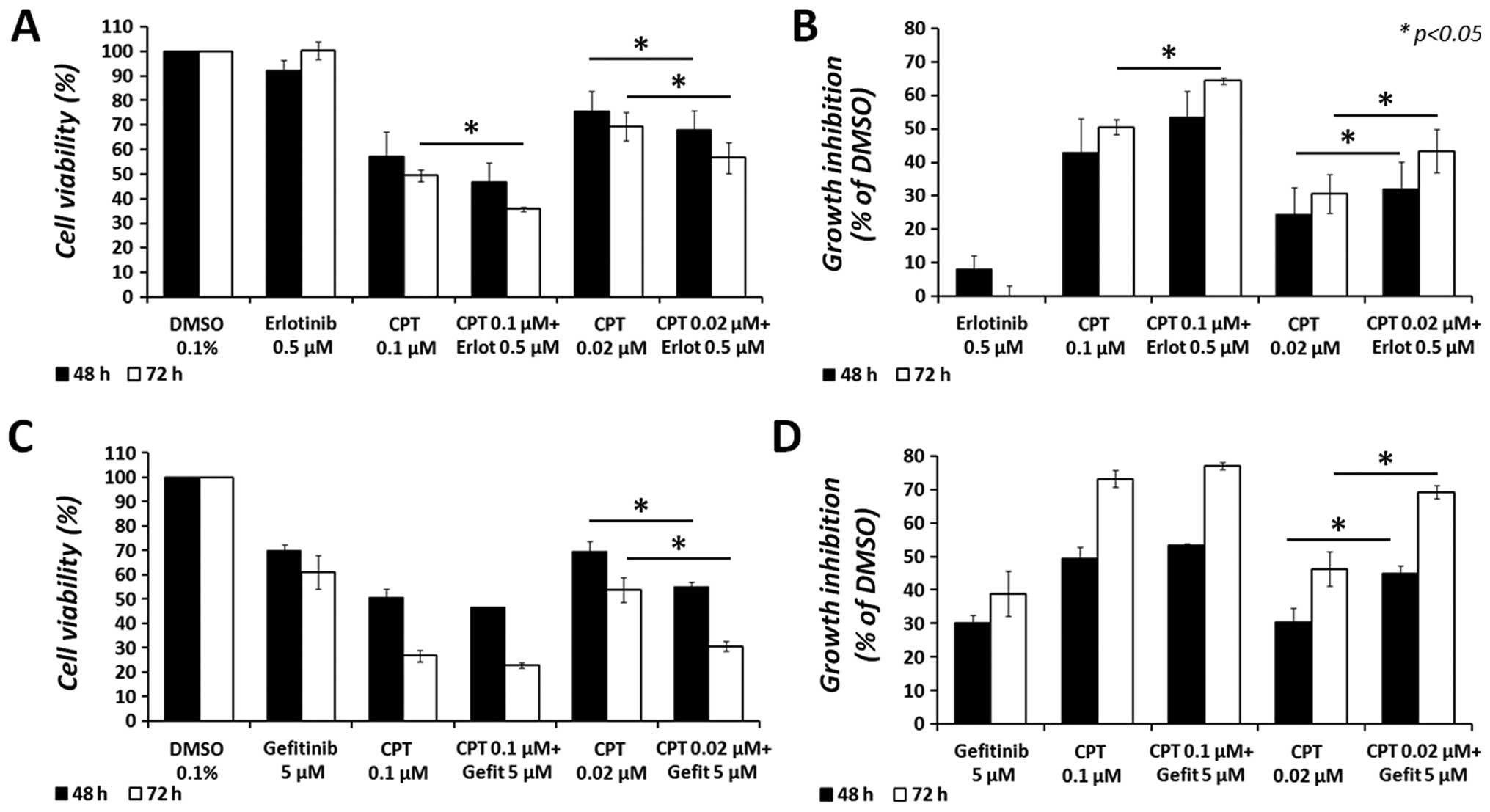
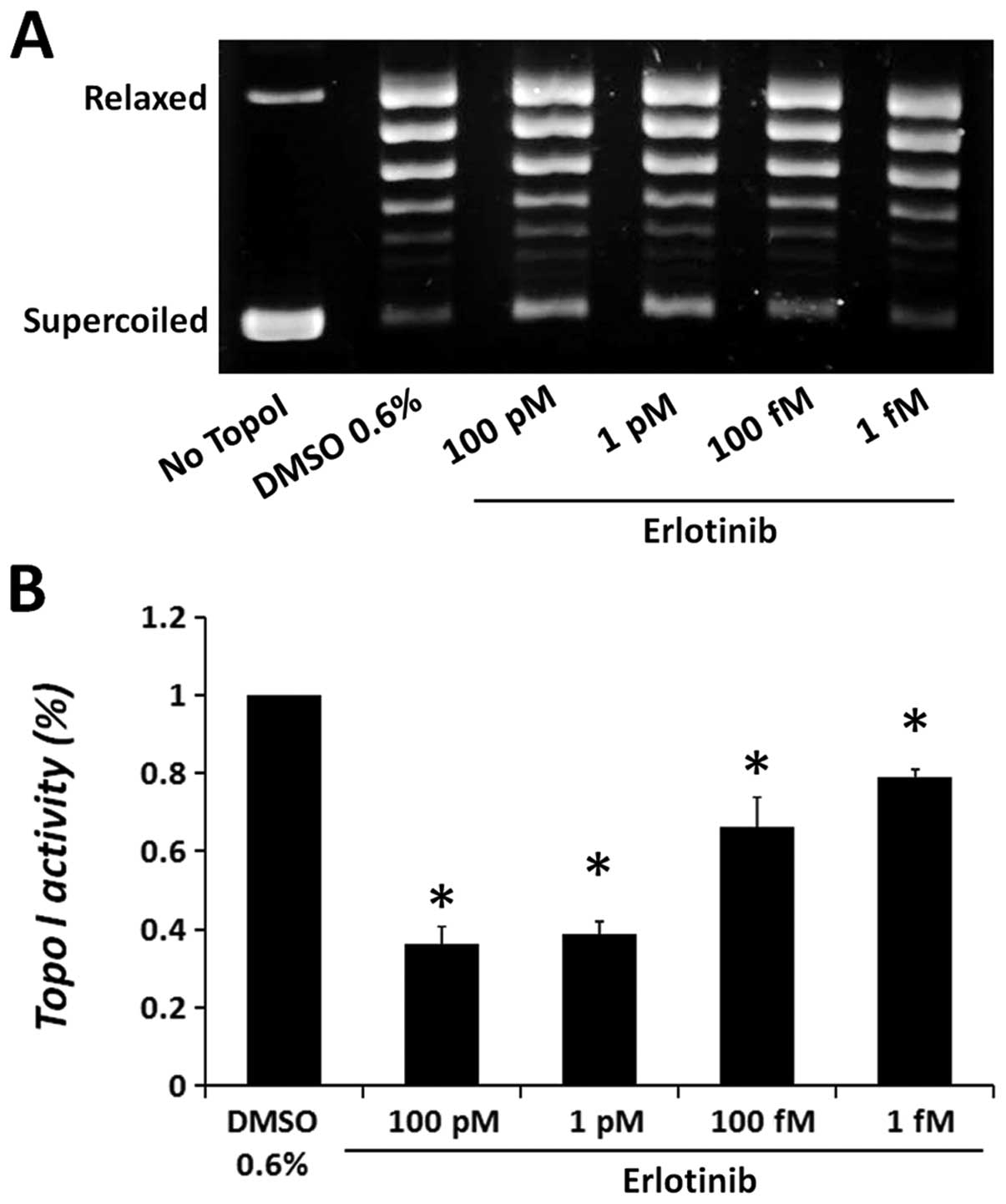
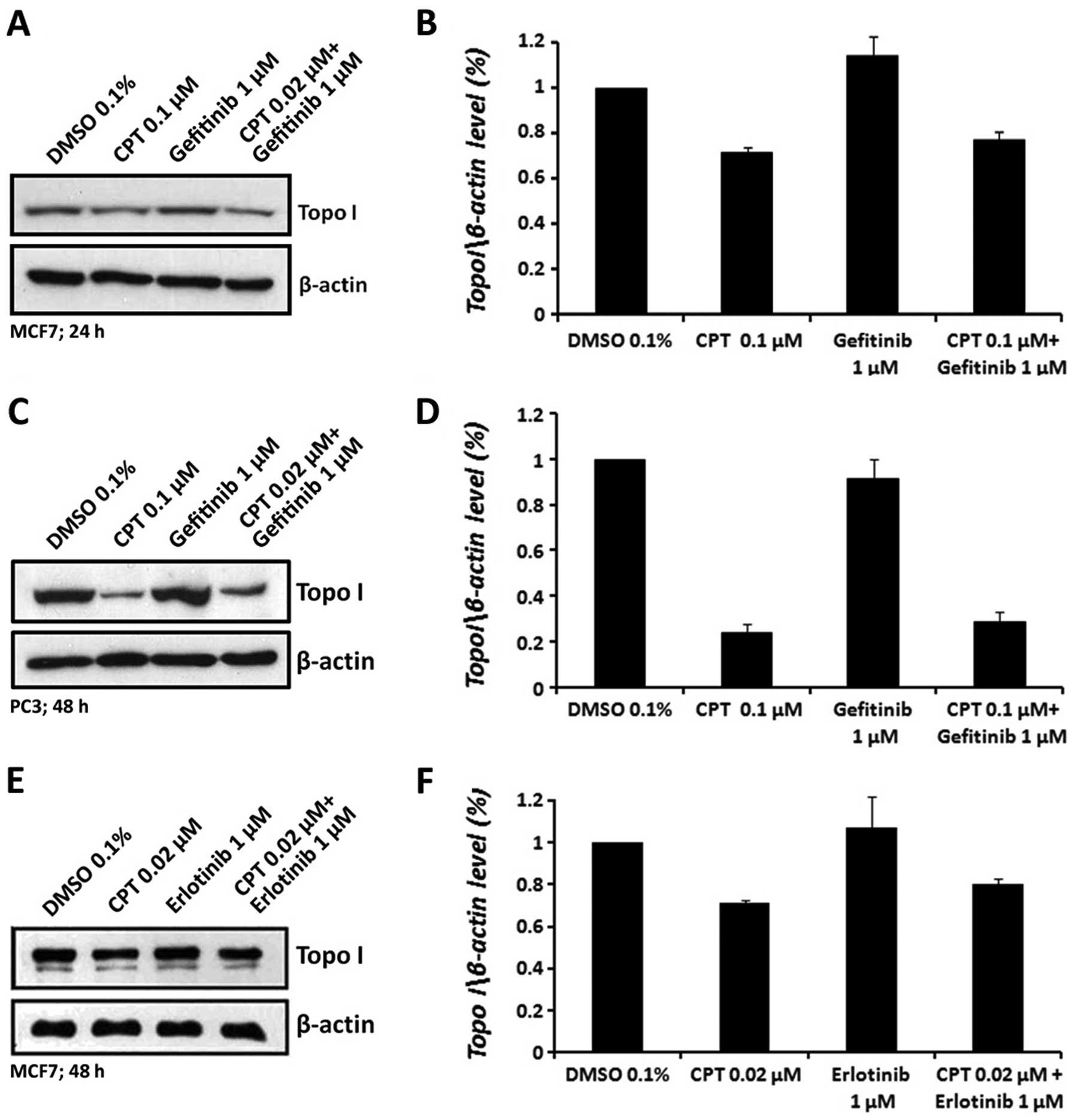
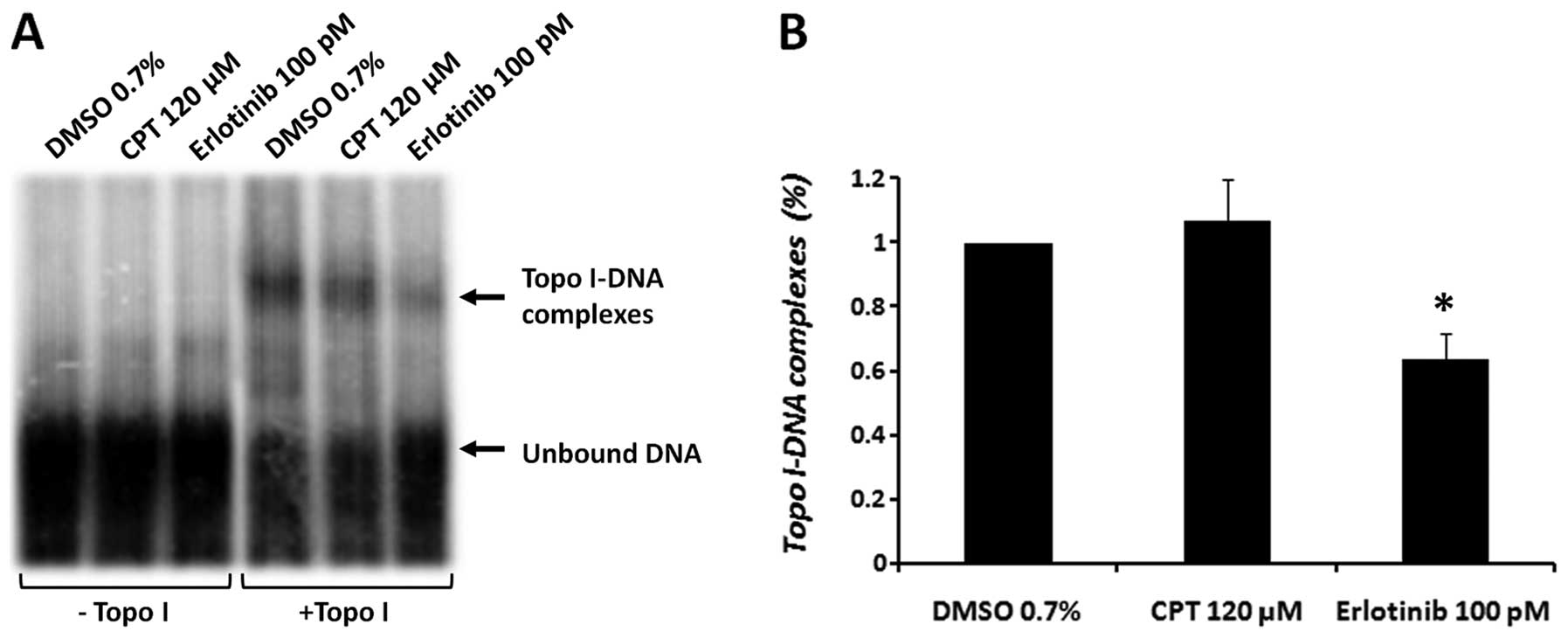
|
1.
|
Cretaio E, Pattarello L, Fontebasso Y,
Benedetti P and Losasso C: Human DNA topoisomerase IB: structure
and functions. Ital J Biochem. 56:91–102. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Forterre P, Gribaldo S, Gadelle D and
Serre M: Origin and evolution of DNA topoisomerases. Biochimie.
89:427–446. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Wang JC: DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev
Biochem. 65:635–692. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Corbett KD and Berger JM: Structure,
molecular mechanisms, and evolutionary relationships in DNA
topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 33:95–118. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Tomicic MT and Kaina B: Topoisomerase
degradation, DSB repair, p53 and IAPs in cancer cell resistance to
camptothecin-like topoisomerase I inhibitors. Biochim Biophysica
Acta. 1835:11–27. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Haglof KJ, Popa E and Hochster HS: Recent
developments in the clinical activity of topoisomerase-1
inhibitors. Cancer Ther. 1:117–145. 2006.
|
|
7.
|
Pommier Y: Topoisomerase I inhibitors:
camptothecins and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:789–802. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Ciardiello F, Caputo R, Bianco R, et al:
Antitumor effect and potentiation of cytotoxic drugs activity in
human cancer cells by ZD-1839 (Iressa), an epidermal growth factor
receptor-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res.
6:2053–2063. 2000.
|
|
9.
|
Koizumi F, Kanzawa F, Ueda Y, et al:
Synergistic interaction between the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor
gefitinib (‘Iressa’) and the DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor CPT-11
(irinotecan) in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
108:464–472. 2004.
|
|
10.
|
Chen J, Smith M, Kolinsky K, et al:
Antitumor activity of HER1/EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor
erlotinib, alone and in combination with CPT-11 (irinotecan) in
human colorectal cancer xenograft models. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 59:651–659. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Friedmann B, Caplin M, Hartley JA and
Hochhauser D: Modulation of DNA repair in vitro after treatment
with chemo-therapeutic agents by the epidermal growth factor
receptor inhibitor gefitinib (ZD1839). Clin Cancer Res.
10:6476–6486. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Normanno N, Bianco C, De Luca A, Maiello
MR and Salomon DS: Target-based agents against ErbB receptors and
their ligands: a novel approach to cancer treatment. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 10:1–21. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Uberall I, Kolár Z, Trojanec R, Berkovcová
J and Hajdúch M: The status and role of ErbB receptors in human
cancer. Exp Mol Pathol. 84:79–89. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Oda K, Matsuoka Y, Funahashi A and Kitano
H: A comprehensive pathway map of epidermal growth factor receptor
signaling. Mol Syst Biol. 1:2005.0010,. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Harari PM: Epidermal growth factor
receptor inhibition strategies in oncology. Endocr Relat Cancer.
11:689–708. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Smith J: Erlotinib: small-molecule
targeted therapy in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer.
Clin Ther. 27:1513–1534. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Aflalo E, Seri I, Segal S, Gazit A and
Priel E: Inhibition of topoisomerase I activity by tyrphostin
derivatives, protein tyrosine kinase blockers: mechanism of action.
Cancer Res. 54:5138–5142. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Bendetz-Nezer S, Gazit A and Priel E: DNA
topoisomerase I as one of the cellular targets of certain
tyrphostin derivatives. Mol Pharmacol. 66:627–634. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Ciardiello F, Bianco R, Damiano V, et al:
Antitumor activity of sequential treatment with topotecan and
anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody C225.
Clin Cancer Res. 5:909–916. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Ueno NT and Zhang D: Targeting EGFR in
triple negative breast cancer. J Cancer. 2:324–328. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Azzariti A, Xu J, Porcelli L and Paradiso
A: The schedule-dependent enhanced cytotoxic activity of
7-ethyl-10-hydroxy-camptothecin (SN-38) in combination with
Gefitinib (Iressa, ZD1839). Biochem Pharmacol. 68:135–144. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Johnston MD, Finter NB and Young PA: Dye
uptake method for assay of interferon activity. Methods Enzymol.
78:394–399. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Auer B, Vosberg HP, Buhre U, Klocker H,
Hirsch-Kauffmann M and Schweiger M: Intracellular distribution of
DNA topoisomerase I in fibroblasts from patients with Fanconi’s
anaemia. Hum Genet. 61:369–371. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF and Maniatis T:
Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor
Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 1989
|
|
25.
|
Kaufmann SH and Svingen PA: Immunoblot
analysis and band depletion assays. Methods in Molecular Biology,
DNA topoisomerase protocols: DNA Topoisomerase Protocols. Bjornsti
MA and Osheroff N: 94. Humana Press Inc; Totowa, NJ: pp. 253–268.
1999, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Stevnsner T, Mortensen UH, Westergaard O
and Bonven BJ: Interaction between eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I
and a specific binding sequence. J Biol Chem. 264:10110–10113.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Desai SD, Li TK, Rodriguez-Bauman A, Rubin
EH and Liu LF: Ubiquitin/26S proteasome-mediated degradation of
topoisomerase I as a resistance mechanism to camptothecin in tumor
cells. Cancer Res. 61:5926–5932. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Desai SD, Liu LF, Vazquez-Abad D and
D’Arpa P: Ubiquitin-dependent destruction of topoisomerase I is
stimulated by the antitumor drug camptothecin. J Biol Chem.
272:24159–24164. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Desai SD, Zhang H, Rodriguez-Bauman A, et
al: Transcription-dependent degradation of topoisomerase I-DNA
covalent complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 23:2341–2350. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Wang HK, Morris-Natschke SL and Lee KH:
Recent advances in discovery and development of topoisomerase
inhibitors as antitumor agents. Med Res Rev. 17:367–425. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Pommier Y, Pourquier P, Fan Y and
Strumberg D: Mechanism of action of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I
and drugs targeted to the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1400:83–105. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Wang JC: Cellular roles of DNA
topoisomerases: a molecular perspective. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
3:430–440. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Wang JC: DNA topoisomerases as targets of
therapeutics: an overview. Adv Pharmacol. 29A:1–19. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Baselga J, Gomez P, Awada A, et al: The
addition of cetuximab to cisplatin increases overall response rate
(ORR) and progression-free survival (PFS) in metastatic
triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC): results of a randomized phase
II study (BALI-1). Ann Oncol. 21(Suppl 8): 27402010.
|
|
35.
|
Wu X, Yalowich JC and Hasinoff BB:
Cisplatin inhibits the catalytic activity of DNA topoisomerase II
by binding to critical protein thiol groups and by binding to DNA.
AACR Meeting: Experimental and Molecular Therapeutics 31:
Topoisomerase, Telomerase, and Nucleosides/Nucleotides. Abst.
3079,. 2004
|
|
36.
|
Aoe K, Kiura K, Ueoka H, et al: Cisplatin
down-regulates topoisomerase I activity in lung cancer cell lines.
Anticancer Res. 24:3893–3897. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Camp ER, Summy J, Bauer TW, Liu W, Gallick
GE and Ellis LM: Molecular mechanisms of resistance to therapies
targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Clin Cancer Res.
11:397–405. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Chen YJ: Mechanisms underlying resistance
to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in non-small cell
lung cancer. Biol Biomed Rep. 2:141–148. 2012.
|
|
39.
|
Chen YJ, Huang WC, Wei YL, et al: Elevated
BCRP/ABCG2 expression confers acquired resistance to gefitinib in
wild-type EGFR-expressing cells. PLoS One. 6:e214282011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Jorissen RN, Walker F, Pouliot N, Garrett
TP, Ward CW and Burgess AW: Epidermal growth factor receptor:
mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp Cell Res. 284:31–53.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Kim H, Kim SH, Kim MJ, et al: EGFR
inhibitors enhanced the susceptibility to NK cell-mediated lysis of
lung cancer cells. J Immunother. 34:372–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Ling YH, Li T, Yuan Z, Haigentz M Jr,
Weber TK and Perez-Soler R: Erlotinib, an effective epidermal
growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces
p27KIP1 up-regulation and nuclear translocation in
association with cell growth inhibition and G1/S phase arrest in
human non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Mol Pharmacol.
72:248–258. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Li Z, Xu M, Xing S, et al: Erlotinib
effectively inhibits JAK2V617F activity and polycythemia
vera cell growth. J Biol Chem. 282:3428–3432. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Shi Z, Peng XX, Kim IW, et al: Erlotinib
(Tarceva, OSI-774) antagonizes ATP-binding cassette subfamily B
member 1 and ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2-mediated
drug resistance. Cancer Res. 67:11012–11020. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Yang CH, Huang CJ, Yang CS, et al:
Gefitinib reverses chemotherapy resistance in gefitinib-insensitive
multidrug resistant cancer cells expressing ATP-binding cassette
family protein. Cancer Res. 65:6943–6949. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46.
|
Yanase K, Tsukahara S, Asada S, Ishikawa
E, Imai Y and Sugimoto Y: Gefitinib reverses breast cancer
resistance protein-mediated drug resistance. Mol Cancer Ther.
3:1119–1125. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Marchetti S, de Vries NA, Buckle T, et al:
Effect of the ATP-binding cassette drug transporters ABCB1, ABCG2,
and ABCC2 on erlotinib hydrochloride (Tarceva) disposition in in
vitro and in vivo pharmacokinetic studies employing
Bcrp1−/−/Mdr1a/1b−/− (triple-knockout) and
wild-type mice. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:2280–2287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Normanno N, Maiello MR and De Luca A:
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
(EGFR-TKIs): simple drugs with a complex mechanism of action? J
Cell Physiol. 194:13–19. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|