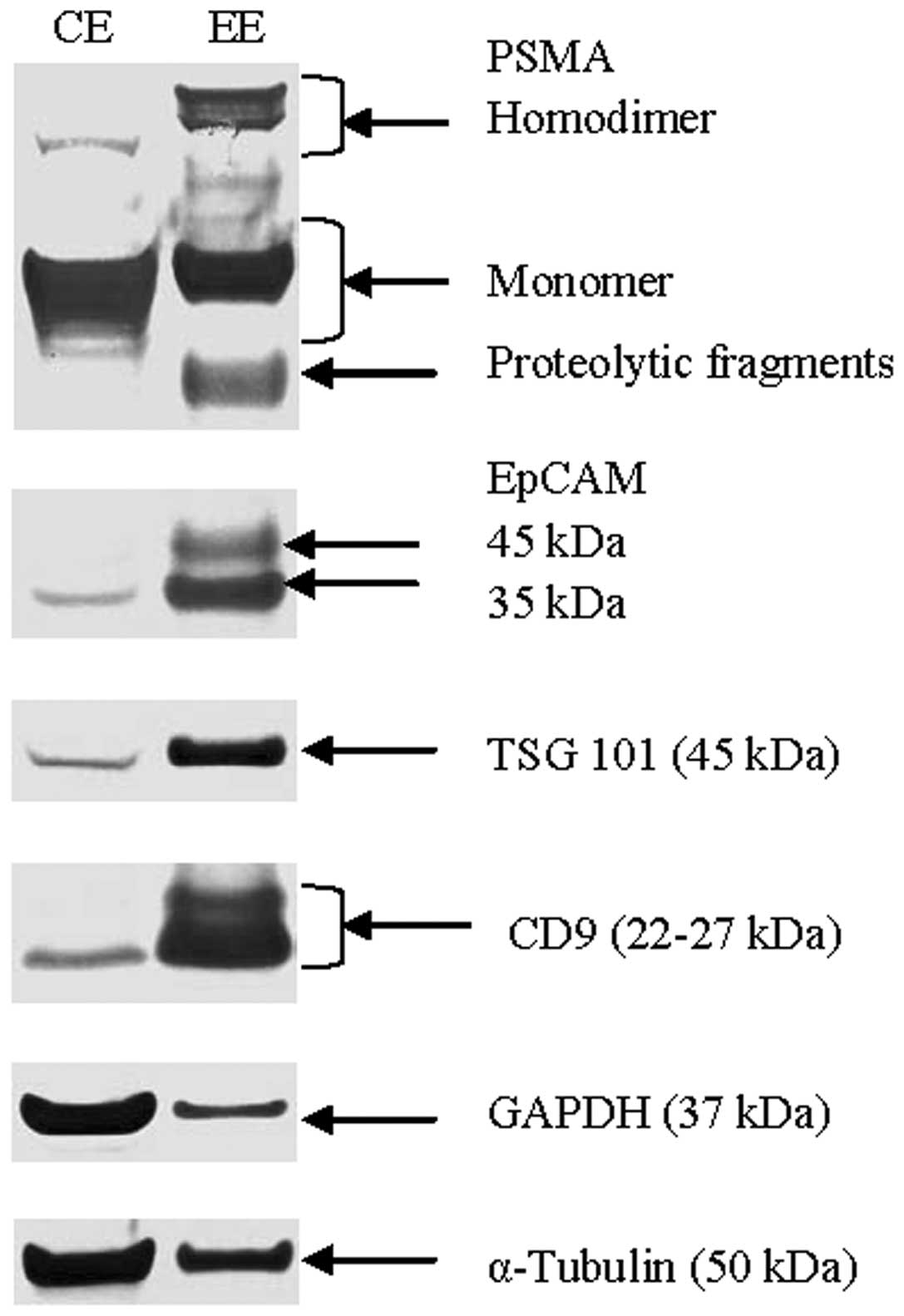
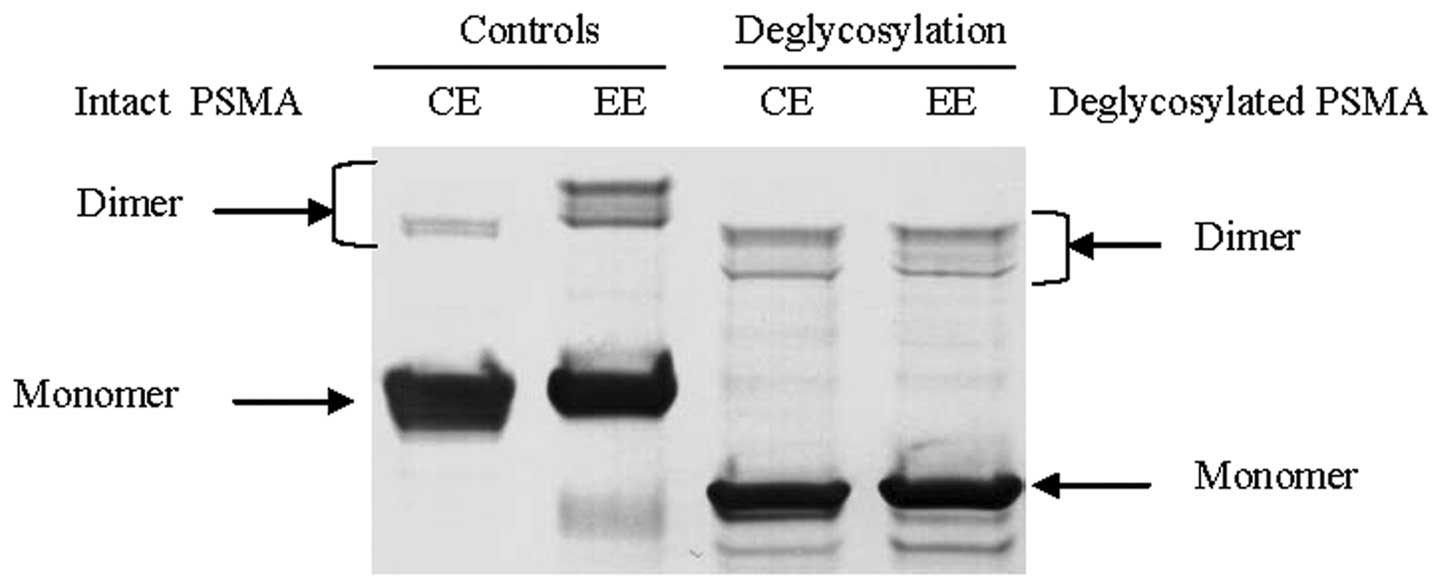
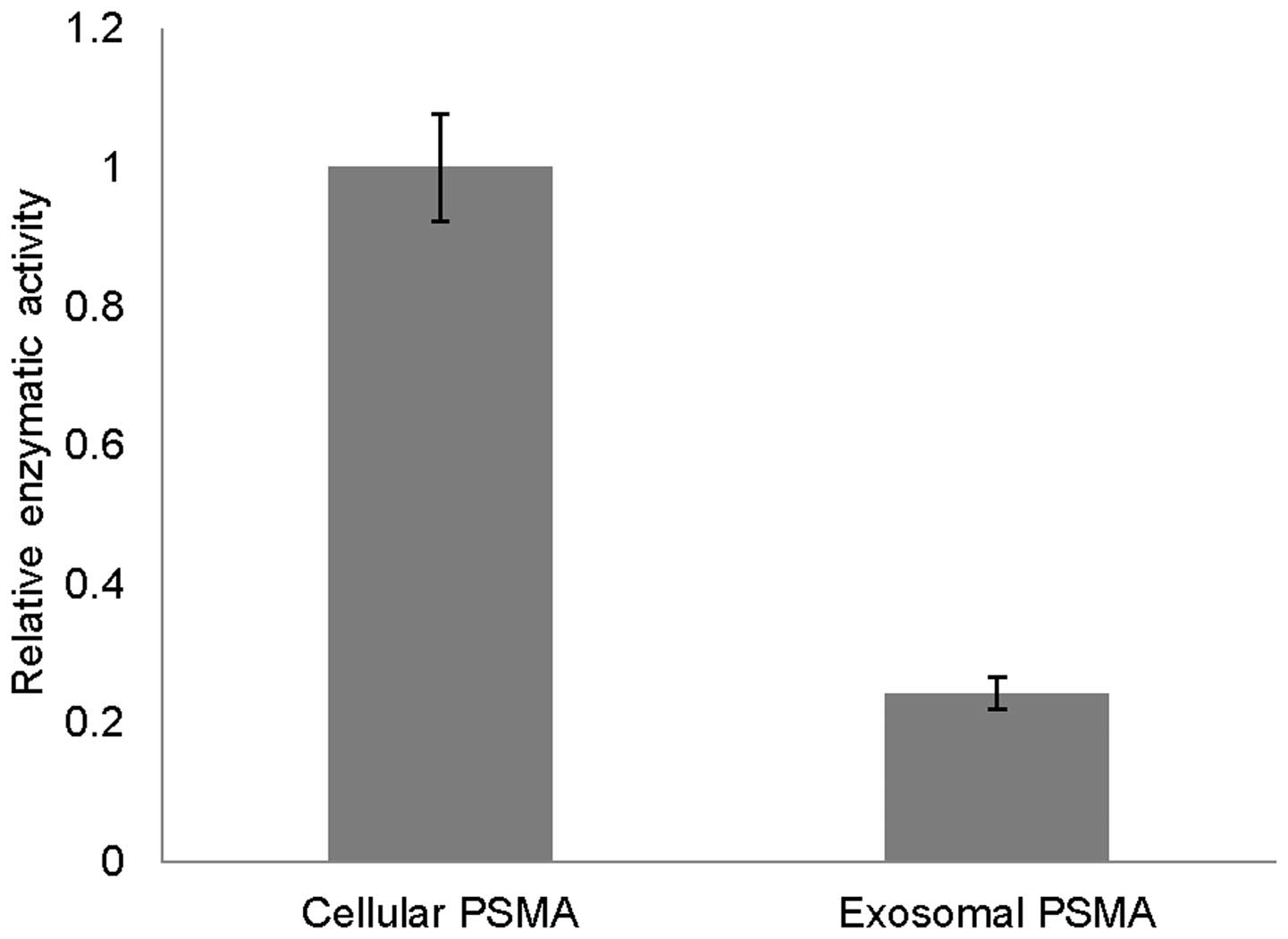
|
1.
|
Bacich DJ, Pinto JT, Tong WP and Heston
WD: Cloning, expression, genomic localization, and enzymatic
activities of the mouse homolog of prostate-specific membrane
antigen/NAALADase/folate hydrolase. Mamm Genome. 12:117–123. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Chang SS, Reuter VE, Heston WD and Gaudin
PB: Comparison of anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen
antibodies and other immunomarkers in metastatic prostate
carcinoma. Urology. 57:1179–1183. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Chang SS, O’Keefe DS, Bacich DJ, Reuter
VE, Heston WD and Gaudin PB: Prostate-specific membrane antigen is
produced in tumor-associated neovasculature. Clin Cancer Res.
5:2674–2681. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Liu H, Rajasekaran AK, Moy P, et al:
Constitutive and antibody-induced internalization of
prostate-specific membrane antigen. Cancer Res. 58:4055–4060.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Rajasekaran AK, Anilkumar G and
Christiansen JJ: Is prostate-specific membrane antigen a
multifunctional protein? Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 288:C975–C981.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Liu T, Wu LY, Kazak M and Berkman CE:
Cell-surface labeling and internalization by a fluorescent
inhibitor of prostate-specific membrane antigen. Prostate.
68:955–964. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Tagawa ST, Beltran H, Vallabhajosula S, et
al: Anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen-based
radioimmunotherapy for prostate cancer. Cancer. 116:1075–1083.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Wolf P, Freudenberg N, Buhler P, et al:
Three conformational antibodies specific for different PSMA
epitopes are promising diagnostic and therapeutic tools for
prostate cancer. Prostate. 70:562–569. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Murphy GP, Greene TG, Tino WT, Boynton AL
and Holmes EH: Isolation and characterization of monoclonal
antibodies specific for the extracellular domain of prostate
specific membrane antigen. J Urol. 160:2396–2401. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Morris MJ, Pandit-Taskar N, Divgi CR, et
al: Phase I evaluation of J591 as a vascular targeting agent in
progressive solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2707–2713. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Milowsky MI, Nanus DM, Kostakoglu L, et
al: Vascular targeted therapy with anti-prostate-specific membrane
antigen monoclonal antibody J591 in advanced solid tumors. J Clin
Oncol. 25:540–547. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Tsukamoto T, Wozniak KM and Slusher BS:
Progress in the discovery and development of glutamate
carboxypeptidase II inhibitors. Drug Discov Today. 12:767–776.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Kularatne SA, Zhou Z, Yang J, Post CB and
Low PS: Design, synthesis, and preclinical evaluation of
prostate-specific membrane antigen targeted (99m)Tc-radioimaging
agents. Mol Pharm. 6:790–800. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Lapi SE, Wahnishe H, Pham D, et al:
Assessment of an 18F-labeled phosphoramidate peptidomimetic as a
new prostate-specific membrane antigen-targeted imaging agent for
prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 50:2042–2048. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Cho SY, Gage KL, Mease RC, et al:
Biodistribution, tumor detection, and radiation dosimetry of
18F-DCFBC, a low-molecular-weight inhibitor of prostate-specific
membrane antigen, in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. J
Nucl Med. 53:1883–1891. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Azmi AS, Bao B and Sarkar FH: Exosomes in
cancer development, metastasis, and drug resistance: a
comprehensive review. Cancer Metastasis Rev. May 25–2013.(Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
17.
|
Thery C: Exosomes: secreted vesicles and
intercellular communications. F1000 Biol Rep. 3:152011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Thompson CA, Purushothaman A, Ramani VC,
Vlodavsky I and Sanderson RD: Heparanase regulates secretion,
composition, and function of tumor cell-derived exosomes. J Biol
Chem. 288:10093–10099. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Kharaziha P, Ceder S, Li Q and Panaretakis
T: Tumor cell-derived exosomes: a message in a bottle. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1826:103–111. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Liu T, Mendes DE and Berkman CE: From AR
to c-Met: Androgen deprivation leads to a signaling pathway switch
in prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 43:1125–1130.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Liu T, Wu LY, Fulton MD, Johnson JM and
Berkman CE: Prolonged androgen deprivation leads to downregulation
of androgen receptor and prostate-specific membrane antigen in
prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 41:2087–2092. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Liu T, Wu LY and Berkman CE:
Prostate-specific membrane antigen-targeted photodynamic therapy
induces rapid cytoskeletal disruption. Cancer Lett. 296:106–112.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Liu T, Toriyabe Y and Berkman CE:
Purification of prostate-specific membrane antigen using
conformational epitope-specific antibody-affinity chromatography.
Protein Expr Purif. 49:251–255. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Wu LY, Anderson MO, Toriyabe Y, et al: The
molecular pruning of a phosphoramidate peptidomimetic inhibitor of
prostate-specific membrane antigen. Bioorg Med Chem. 15:7434–7443.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Anderson MO, Wu LY, Santiago NM, et al:
Substrate specificity of prostate-specific membrane antigen. Bioorg
Med Chem. 15:6678–6686. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Maung J, Mallari JP, Girtsman TA, et al:
Probing for a hydrophobic a binding register in prostate-specific
membrane antigen with phenylalkylphosphonamidates. Bioorg Med Chem.
12:4969–4979. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Lehmann BD, Paine MS, Brooks AM, et al:
Senescence-associated exosome release from human prostate cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 68:7864–7871. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Hosseini-Beheshti E, Pham S, Adomat H, Li
N and Tomlinson Guns ES: Exosomes as biomarker enriched
microvesicles: characterization of exosomal proteins derived from a
panel of prostate cell lines with distinct AR phenotypes. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 11:863–885. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Mitchell PJ, Welton J, Staffurth J, et al:
Can urinary exosomes act as treatment response markers in prostate
cancer? J Transl Med. 7:42009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Rajasekaran SA, Anilkumar G, Oshima E, et
al: A novel cytoplasmic tail MXXXL motif mediates the
internalization of prostate-specific membrane antigen. Mol Biol
Cell. 14:4835–4845. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R and
Conrad R: Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition,
biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1820:940–948. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Tauro BJ, Greening DW, Mathias RA, et al:
Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and
immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer
cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods. 56:293–304. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33.
|
Trzpis M, McLaughlin PM, de Leij LM and
Harmsen MC: Epithelial cell adhesion molecule: more than a
carcinoma marker and adhesion molecule. Am J Pathol. 171:386–395.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Ghosh A and Heston WD: Tumor target
prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and its regulation in
prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem. 91:528–539. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35.
|
Wu LY, Liu T, Hopkins MR, Davis WC and
Berkman CE: Chemoaffinity capture of pre-targeted prostate cancer
cells with magnetic beads. Prostate. 72:1532–1541. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|