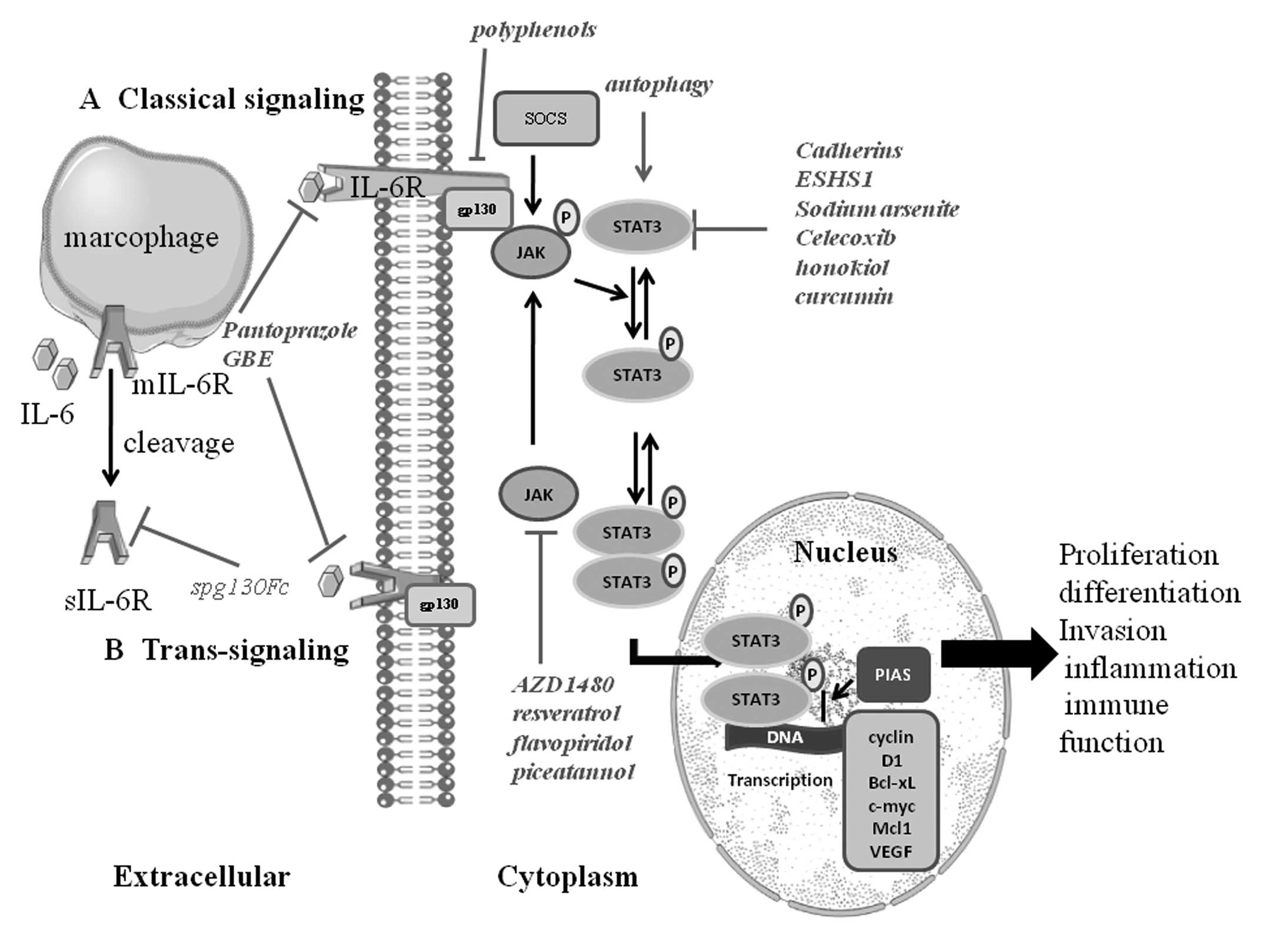
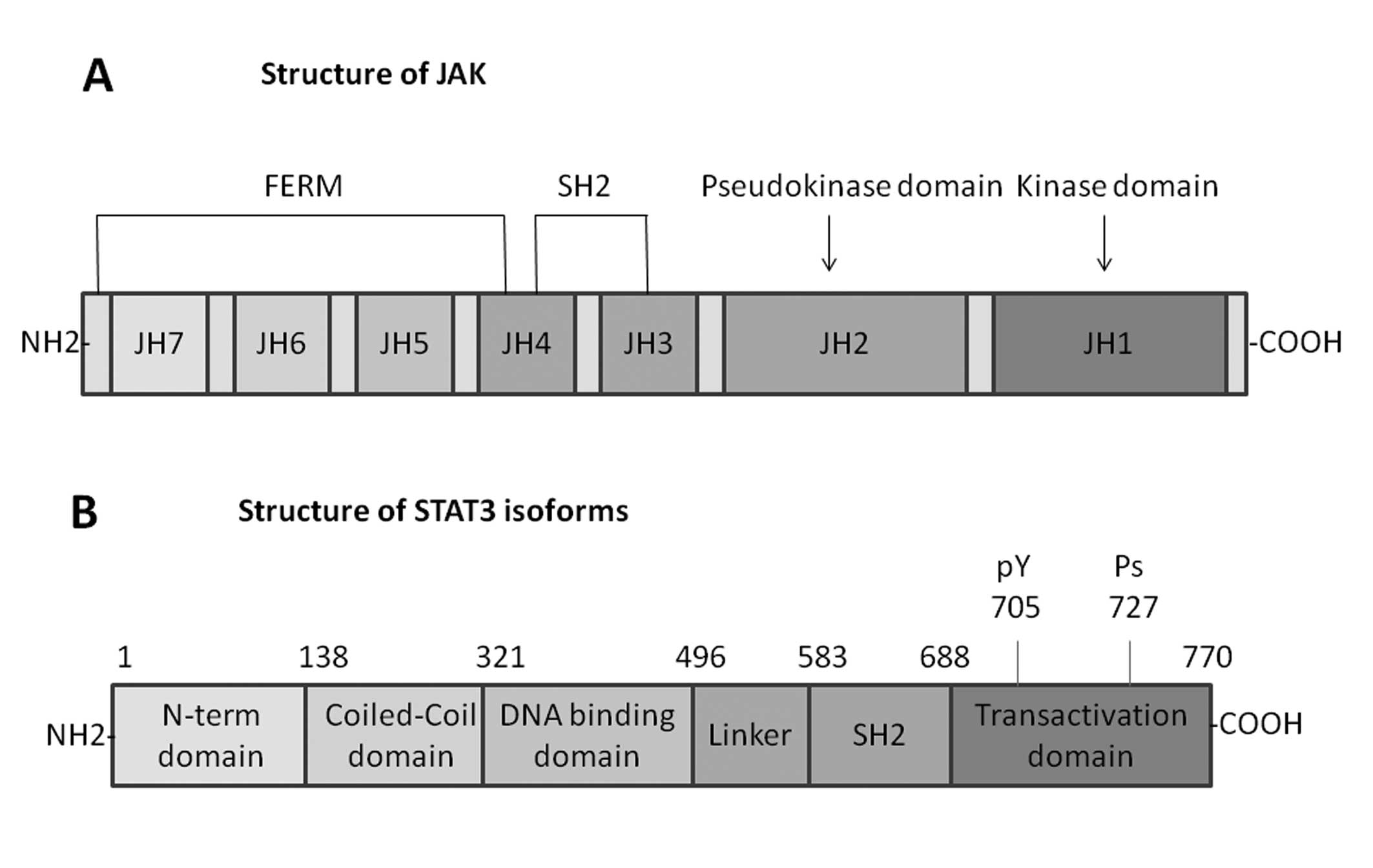
|
1.
|
Niwa Y, Kanda H, Shikauchi Y, et al:
Methylation silencing of SOCS-3 promotes cell growth and migration
by enhancing JAK/STAT and FAK signalings in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncogene. 24:6406–6417. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Lacronique V, Boureux A, Valle VD, et al:
A TEL-JAK2 fusion protein with constitutive kinase activity in
human leukemia. Science. 278:1309–1312. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Zhang F, Li C, Halfter H and Liu J:
Delineating an oncostatin M-activated STAT3 signaling pathway that
coordinates the expression of genes involved in cell cycle
regulation and extracellular matrix deposition of MCF-7 cells.
Oncogene. 22:894–905. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Alvarez JV, Greulich H, Sellers WR,
Meyerson M and Frank DA: Signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 is required for the oncogenic effects of
non-small-cell lung cancer-associated mutations of the epidermal
growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 66:3162–3168. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Zamo A, Chiarle R, Piva R, et al:
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) activates Stat3 and protects
hematopoietic cells from cell death. Oncogene. 21:1038–1047. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Khong TL, Thairu N, Larsen H, Dawson PM,
Kiriakidis S and Paleolog EM: Identification of the angiogenic gene
signature induced by EGF and hypoxia in colorectal cancer. BMC
Cancer. 13:5182013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Guthrie GJ, Roxburgh CS, Horgan PG and
McMillan DC: Does interleukin-6 link explain the link between
tumour necrosis, local and systemic inflammatory responses and
outcome in patients with colorectal cancer? Cancer Treat Rev.
39:89–96. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Chung YC and Chang YF: Serum interleukin-6
levels reflect the disease status of colorectal cancer. J Surg
Oncol. 83:222–226. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Gordziel C, Bratsch J, Moriggl R, Knosel T
and Friedrich K: Both STAT1 and STAT3 are favourable prognostic
determinants in colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 109:138–146.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Dambacher J, Beigel F, Seiderer J, et al:
Interleukin 31 mediates MAP kinase and STAT1/3 activation in
intestinal epithelial cells and its expression is upregulated in
inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 56:1257–1265. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Kishimoto T: IL-6: from its discovery to
clinical applications. Int Immunol. 22:347–352. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Rose-John S: Coordination of interleukin-6
biology by membrane bound and soluble receptors. Adv Exp Med Biol.
495:145–151. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Culig Z: Cytokine disbalance in common
human cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:308–314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Haan S, Hermanns
HM, Muller-Newen G and Schaper F: Principles of interleukin
(IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem J.
374:1–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Aoki Y, Feldman GM and Tosato G:
Inhibition of STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis and decreases
survivin expression in primary effusion lymphoma. Blood.
101:1535–1542. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Leeman RJ, Lui VW and Grandis JR: STAT3 as
a therapeutic target in head and neck cancer. Expert Opin Biol
Ther. 6:231–241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Haan C, Kreis S, Margue C and Behrmann I:
Jaks and cytokine receptors - an intimate relationship. Biochem
Pharmacol. 72:1538–1546. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Rane SG and Reddy EP: JAKs, STATs and Src
kinases in hematopoiesis. Oncogene. 21:3334–3358. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Subramaniam A, Shanmugam MK, Perumal E, et
al: Potential role of signal transducer and activator of
transcription (STAT)3 signaling pathway in inflammation, survival,
proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1835:46–60. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Fan Y, Mao R and Yang J: NF-kappaB and
STAT3 signaling pathways collaboratively link inflammation to
cancer. Protein Cell. 4:176–185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Xu Q, Briggs J, Park S, et al: Targeting
Stat3 blocks both HIF-1 and VEGF expression induced by multiple
oncogenic growth signaling pathways. Oncogene. 24:5552–5560. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Ma J and Cao X: Regulation of Stat3
nuclear import by importin alpha5 and importin alpha7 via two
different functional sequence elements. Cell Signal. 18:1117–1126.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Shuai K: The STAT family of proteins in
cytokine signaling. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 71:405–422. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Candido J and Hagemann T: Cancer-related
inflammation. J Clin Immunol. 33(Suppl 1): S79–S84. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Grivennikov S and Karin M: Autocrine IL-6
signaling: a key event in tumorigenesis? Cancer Cell. 13:7–9.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Neurath MF and Finotto S: IL-6 signaling
in autoimmunity, chronic inflammation and inflammation-associated
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:83–89. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Naugler WE and Karin M: The wolf in
sheep’s clothing: the role of interleukin-6 in immunity,
inflammation and cancer. Trends Mol Med. 14:109–119. 2008.
|
|
29.
|
Knupfer H and Preiss R: Serum
interleukin-6 levels in colorectal cancer patients - a summary of
published results. Int J Colorectal Dis. 25:135–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Atreya R and Neurath MF: Involvement of
IL-6 in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease and colon
cancer. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 28:187–196. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Jones SA, Richards PJ, Scheller J and
Rose-John S: IL-6 transsignaling: the in vivo consequences. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 25:241–253. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Li Y, de Haar C, Chen M, et al:
Disease-related expression of the IL6/STAT3/SOCS3 signalling
pathway in ulcerative colitis and ulcerative colitis-related
carcinogenesis. Gut. 59:227–235. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Shimazaki J, Goto Y, Nishida K, Tabuchi T,
Motohashi G and Ubukata H: In patients with colorectal cancer,
preoperative serum interleukin-6 level and granulocyte/lymphocyte
ratio are clinically relevant biomarkers of long-term cancer
progression. Oncology. 84:356–361. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34.
|
Jess T, Rungoe C and Peyrin-Biroulet L:
Risk of colorectal cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis: a
meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:639–645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Canavan C, Abrams KR and Mayberry J:
Meta-analysis: colorectal and small bowel cancer risk in patients
with Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 23:1097–1104.
2006.
|
|
36.
|
Atreya R and Neurath MF: New therapeutic
strategies for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Mucosal
Immunol. 1:175–182. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Atreya R, Mudter J, Finotto S, et al:
Blockade of interleukin 6 trans signaling suppresses T-cell
resistance against apoptosis in chronic intestinal inflammation:
evidence in crohn disease and experimental colitis in vivo. Nat
Med. 6:583–588. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38.
|
Yamamoto K and Rose-John S: Therapeutic
blockade of interleukin-6 in chronic inflammatory disease. Clin
Pharmacol Ther. 91:574–576. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Xiong H, Zhang ZG, Tian XQ, et al:
Inhibition of JAK1, 2/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis, cell cycle
arrest, and reduces tumor cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells.
Neoplasia. 10:287–297. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Xiong H, Hong J, Du W, et al: Roles of
STAT3 and ZEB1 proteins in E-cadherin down-regulation and human
colorectal cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem.
287:5819–5832. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Akira S, Nishio Y, Inoue M, et al:
Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3
p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated
signaling pathway. Cell. 77:63–71. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Levy DE and Lee CK: What does Stat3 do? J
Clin Invest. 109:1143–1148. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Takeda K, Noguchi K, Shi W, et al:
Targeted disruption of the mouse Stat3 gene leads to early
embryonic lethality. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:3801–3804. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Bowman T, Garcia R, Turkson J and Jove R:
STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene. 19:2474–2488. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45.
|
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G,
et al: Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell. 98:295–303. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46.
|
Zugowski C, Lieder F, Muller A, et al:
STAT3 controls matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression in colon
carcinoma cells by both direct and AP-1-mediated interaction with
the MMP-1 promoter. Biol Chem. 392:449–459. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Pan Q, Pan H, Lou H, Xu Y and Tian L:
Inhibition of the angiogenesis and growth of Aloin in human
colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Cell Int. 13:692013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Qian WF, Guan WX, Gao Y, et al: Inhibition
of STAT3 by RNA interference suppresses angiogenesis in colorectal
carcinoma. Brazilian journal of medical and biological research =
Revista brasileira de pesquisas medicas e biologicas / Sociedade
Brasileira de Biofisica [et al]. 44:1222–1230.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Lee J, Kim JC, Lee SE, et al: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) protein
suppresses adenoma-to-carcinoma transition in Apcmin/+ mice via
regulation of Snail-1 (SNAI) protein stability. J Biol Chem.
287:18182–18189. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, et al:
IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial
cells and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell.
15:103–113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Guo Y, Xu F, Lu T, Duan Z and Zhang Z:
Interleukin-6 signaling pathway in targeted therapy for cancer.
Cancer Treat Rev. 38:904–910. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Puchalski T, Prabhakar U, Jiao Q, Berns B
and Davis HM: Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of an
anti-interleukin-6 chimeric monoclonal antibody (siltuximab) in
patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
16:1652–1661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Tanaka T, Narazaki M and Kishimoto T:
Therapeutic targeting of the interleukin-6 receptor. Annu Rev
Pharmacol Toxicol. 52:199–219. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Garnero P, Thompson E, Woodworth T and
Smolen JS: Rapid and sustained improvement in bone and cartilage
turnover markers with the anti-interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor
tocilizumab plus methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients with
an inadequate response to methotrexate: results from a substudy of
the multi-center double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of
tocilizumab in inadequate responders to methotrexate alone.
Arthritis Rheum. 62:33–43. 2010.
|
|
55.
|
Yang X, Zhang F, Wang Y, et al: Oroxylin A
inhibits colitis-associated carcinogenesis through modulating the
IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 19:1990–2000.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Becker C, Fantini MC, Schramm C, et al:
TGF-beta suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition
of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity. 21:491–501. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Waetzig GH and Rose-John S: Hitting a
complex target: an update on interleukin-6 trans-signalling. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 16:225–236. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Xiong H, Su WY, Liang QC, et al:
Inhibition of STAT5 induces G1 cell cycle arrest and reduces tumor
cell invasion in human colorectal cancer cells. Lab Invest.
89:717–725. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Trengove MC and Ward AC: SOCS proteins in
development and disease. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2:1–29. 2013.
|
|
60.
|
Isomoto H: Epigenetic alterations in
cholangiocarcinoma-sustained IL-6/STAT3 signaling in
cholangio-carcinoma due to SOCS3 epigenetic silencing. Digestion.
79(Suppl 1): 2–8. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Gao SM, Chen CQ, Wang LY, et al: Histone
deacetylases inhibitor sodium butyrate inhibits JAK2/STAT signaling
through upregulation of SOCS1 and SOCS3 mediated by HDAC8
inhibition in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Exp Hematol.
41:261–270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62.
|
Liu SH, Wang KB, Lan KH, et al:
Calpain/SHP-1 interaction by honokiol dampening peritoneal
dissemination of gastric cancer in nu/nu mice. PloS One.
7:e437112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Xiong H, Du W, Zhang YJ, et al:
Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, suppresses
JAK2/STAT3 signaling via inducing the promoter-associated histone
acetylation of SOCS1 and SOCS3 in human colorectal cancer cells.
Mol Carcinog. 51:174–184. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64.
|
Shuai K and Liu B: Regulation of
gene-activation pathways by PIAS proteins in the immune system. Nat
Rev Immunol. 5:593–605. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65.
|
Chung CD, Liao J, Liu B, et al: Specific
inhibition of Stat3 signal transduction by PIAS3. Science.
278:1803–1805. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66.
|
Saydmohammed M, Joseph D and Syed V:
Curcumin suppresses constitutive activation of STAT-3 by
up-regulating protein inhibitor of activated STAT-3 (PIAS-3) in
ovarian and endometrial cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 110:447–456.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67.
|
Brantley EC, Nabors LB, Gillespie GY, et
al: Loss of protein inhibitors of activated STAT-3 expression in
glioblastoma multiforme tumors: implications for STAT-3 activation
and gene expression. Clin Cancer Res. 14:4694–4704. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68.
|
Redell MS, Ruiz MJ, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB
and Tweardy DJ: Stat3 signaling in acute myeloid leukemia:
ligand-dependent and-independent activation and induction of
apoptosis by a novel small-molecule Stat3 inhibitor. Blood.
117:5701–5709. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69.
|
Fletcher S, Drewry JA, Shahani VM, Page BD
and Gunning PT: Molecular disruption of oncogenic signal transducer
and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) protein. Biochem Cell
Biol. 87:825–833. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70.
|
Bromberg J and Wang TC: Inflammation and
cancer: IL-6 and STAT3 complete the link. Cancer Cell. 15:79–80.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71.
|
Zhuang Q, Hong F, Shen A, et al: Pien
Tze Huang inhibits tumor cell proliferation and promotes
apoptosis via suppressing the STAT3 pathway in a colorectal cancer
mouse model. Int J Oncol. 40:1569–1574. 2012.
|
|
72.
|
Cai Q, Lin J, Wei L, et al: Hedyotis
diffusa Willd inhibits colorectal cancer growth in vivo via
inhibition of STAT3 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 13:6117–6128.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73.
|
Lin W, Zheng L, Zhuang Q, et al: Spica
prunellae promotes cancer cell apoptosis, inhibits cell
proliferation and tumor angiogenesis in a mouse model of colorectal
cancer via suppression of stat3 pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med.
13:1442013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74.
|
Kim SW, Park KC, Jeon SM, et al:
Abrogation of galectin-4 expression promotes tumorigenesis in
colorectal cancer. Cell Oncol. 36:169–178. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75.
|
Kuno T, Hatano Y, Tomita H, et al:
Organo-magnesium suppresses inflammation-associated colon
carcinogenesis in male Crj: CD-1 mice. Carcinogenesis. 34:361–369.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76.
|
Uddin S, Hussain AR, Khan OS and Al-Kuraya
KS: Role of dysregulated expression of leptin and leptin receptors
in colorectal carcinogenesis. Tumour Biol. Sep 7–2013.Epub ahead of
print.
|
|
77.
|
Ganji PN, Park W, Wen J, et al:
Antiangiogenic effects of ganetespib in colorectal cancer mediated
through inhibition of HIF-1alpha and STAT-3. Angiogenesis.
16:903–917. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78.
|
Zhu Z, Li E, Liu Y, et al: Inhibition of
Jak-STAT3 pathway enhances bufalin-induced apoptosis in colon
cancer SW620 cells. World J Surg Oncol. 10:2282012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79.
|
Huang S, Chen M, Ding X and Zou X: Proton
pump inhibitor selectively suppresses proliferation and restores
the chemosensitivity of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting STAT3
signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 17:585–592. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80.
|
Lamy S, Akla N, Ouanouki A, Lord-Dufour S
and Beliveau R: Diet-derived polyphenols inhibit angiogenesis by
modulating the interleukin-6/STAT3 pathway. Exp Cell Res.
318:1586–1596. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81.
|
Chen JS, Chen YH, Huang PH, et al: Ginkgo
biloba extract reduces high-glucose-induced endothelial adhesion by
inhibiting the redox-dependent interleukin-6 pathways. Cardiovas
Diabetol. 11:492012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82.
|
Hedvat M, Huszar D, Herrmann A, et al: The
JAK2 inhibitor AZD1480 potently blocks Stat3 signaling and
oncogenesis in solid tumors. Cancer Cell. 16:487–497. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83.
|
Geletu M, Arulanandam R, Chevalier S, et
al: Classical cadherins control survival through the gp130/Stat3
axis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:1947–1959. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84.
|
Chang Y, Wang SX, Wang YB, et al: ECHS1
interacts with STAT3 and negatively regulates STAT3 signaling. FEBS
Lett. 587:607–613. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85.
|
Ivanov VN, Wen G and Hei TK: Sodium
arsenite exposure inhibits AKT and Stat3 activation, suppresses
self-renewal and induces apoptotic death of embryonic stem cells.
Apoptosis. 18:188–200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86.
|
Liu DB, Hu GY, Long GX, Qiu H, Mei Q and
Hu GQ: Celecoxib induces apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines via inhibition of STAT3
phosphorylation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 33:682–690. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87.
|
Kang R, Tang D, Lotze MT and Zeh HJ III:
AGER/RAGE-mediated autophagy promotes pancreatic tumorigenesis and
bioenergetics through the IL6-pSTAT3 pathway. Autophagy. 8:989–991.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88.
|
Wu CT, Chen MF, Chen WC and Hsieh CC: The
role of IL-6 in the radiation response of prostate cancer. Radiat
Oncol. 8:1592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89.
|
Yao X, Li G, Xu H and Lu C: Inhibition of
the JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway by ganoderic acid A enhances
chemosensitivity of HepG2 cells to cisplatin. Planta Med.
78:1740–1748. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90.
|
Putoczki TL, Thiem S, Loving A, et al:
Interleukin-11 is the dominant IL-6 family cytokine during
gastrointestinal tumorigenesis and can be targeted therapeutically.
Cancer Cell. 24:257–271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|