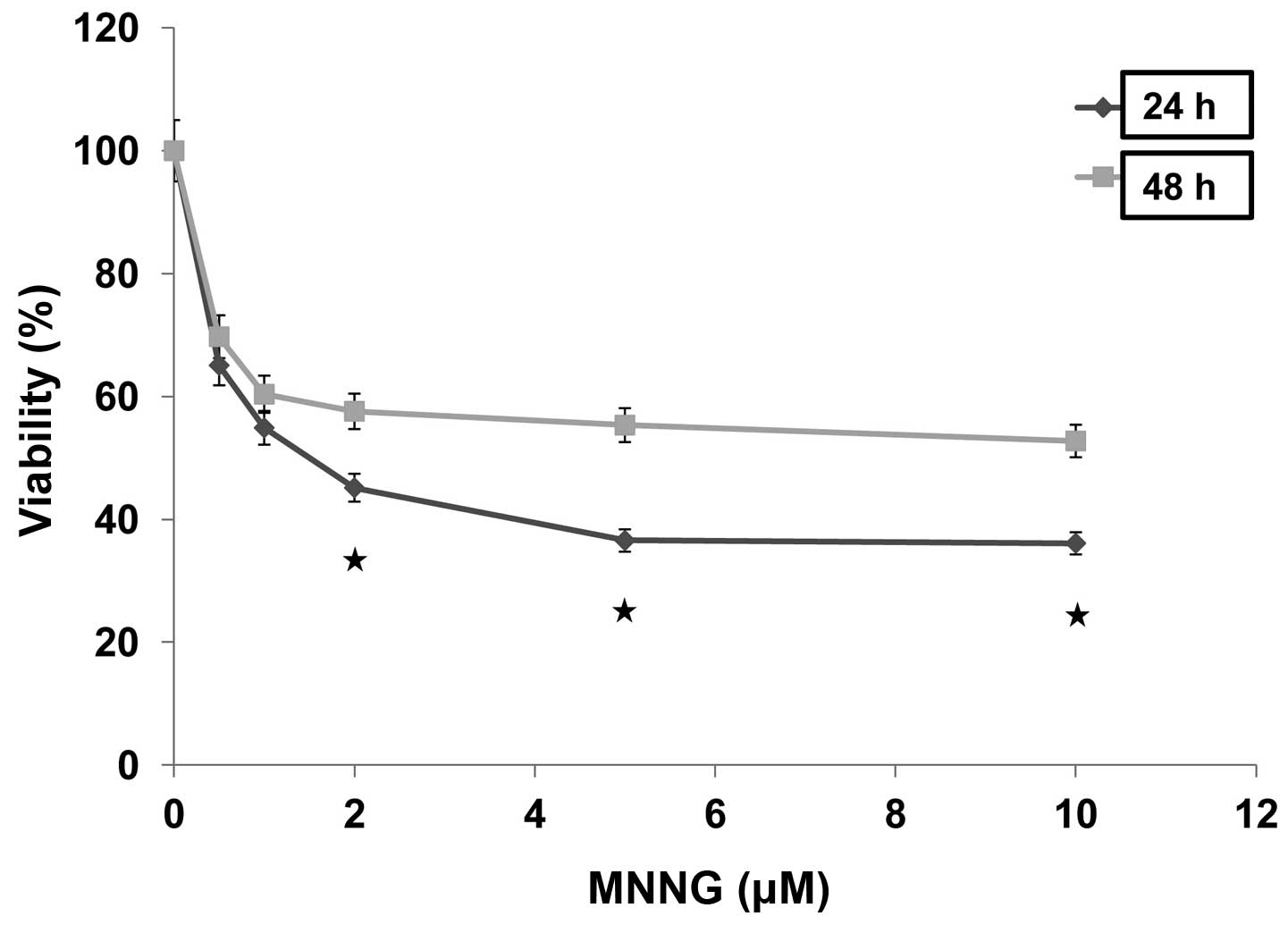
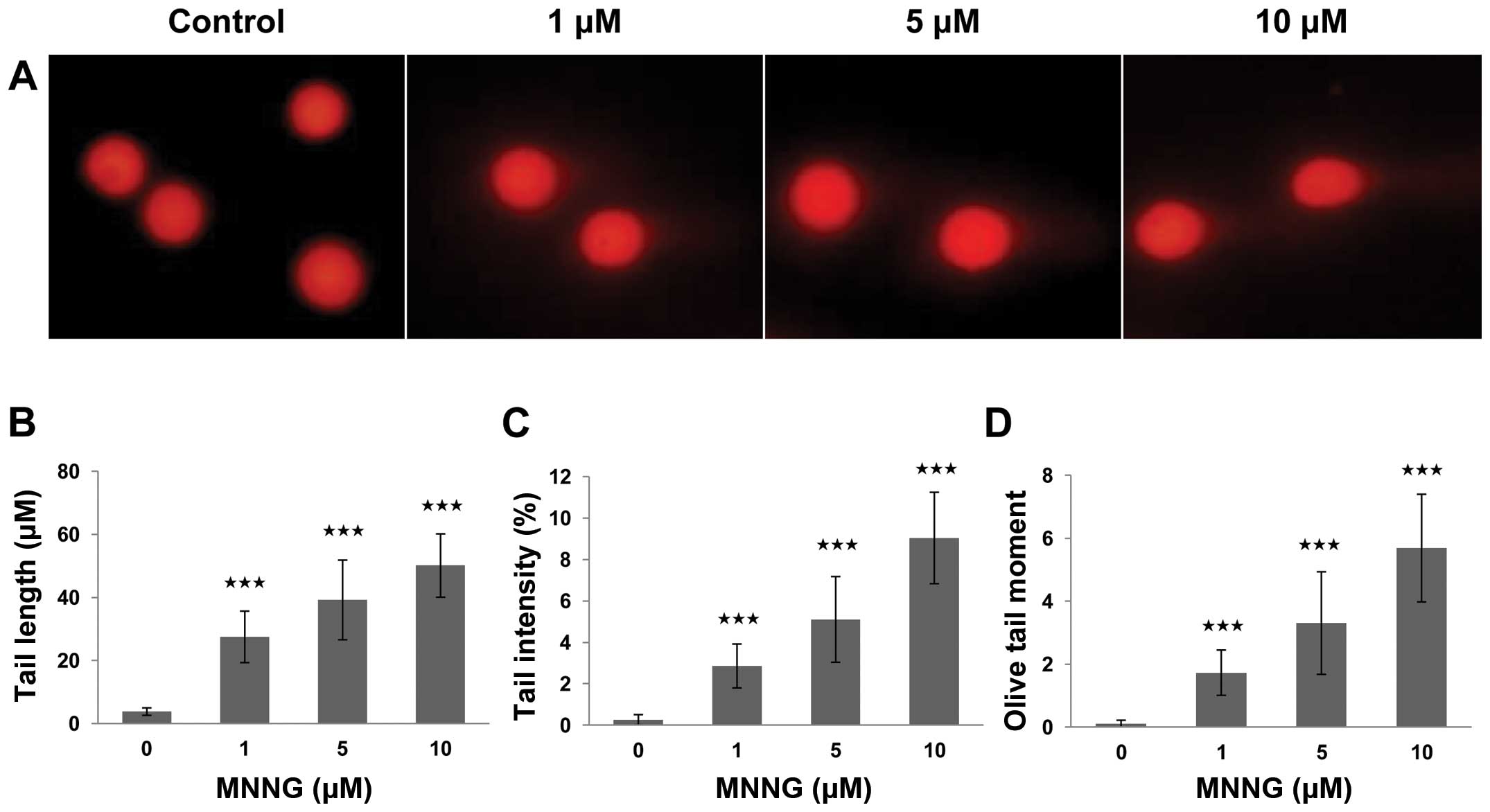
|
1.
|
Hoeijmakers JH: DNA damage, aging, and
cancer. N Engl J Med. 361:1475–1485. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Sedgwick B, Bates PA, Paik J, Jacobs SC
and Lindahl T: Repair of alkylated DNA: recent advances. DNA
Repair. 6:429–442. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Maher RL, Branagan AM and Morrical SW:
Coordination of DNA replication and recombination activities in the
maintenance of genome stability. J Cell Biochem. 112:2672–2682.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Fu D, Calvo JA and Samson LD: Balancing
repair and tolerance of DNA damage caused by alkylating agents. Nat
Rev Cancer. 12:104–120. 2012.
|
|
5.
|
Zhou BB and Elledge SJ: The DNA damage
response: putting checkpoints in perspective. Nature. 408:433–439.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Lam M, Carmichael AR and Griffiths HR: An
aqueous extract of Fagonia cretica induces DNA damage, cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in breast cancer cells via FOXO3a and
p53 expression. PLoS One. 7:e401522012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Greer EL and Brunet A: FOXO transcription
factors at the interface between longevity and tumor suppression.
Oncogene. 24:7410–7425. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Shang YC and Hou J:
Clever cancer strategies with FoxO transcription factors. Cell
Cycle. 7:3829–3839. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Tran H, Brunet A, Grenier JM, Datta SR,
Fornace AJ Jr, DiStefano PS, Chiang LW and Greenberg ME: DNA repair
pathway stimulated by the Forkhead transcription factor FOXO3a
through the Gadd45 protein. Science. 296:530–534. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Lei H and Quelle FW: FOXO transcription
factors enforce cell cycle checkpoints and promote survival of
hematopoietic cells after DNA damage. Mol Cancer Res. 7:1294–1303.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
de Keizer PL, Packer LM, Szypowska AA,
Riedl-Polderman PE, van den Broek NJ, de Bruin A, Dansen TB, Marais
R, Brenkman AB and Burgering BM: Activation of forkhead box O
transcription factors by oncogenic BRAF promotes p21cip1-dependent
senescence. Cancer Res. 70:8526–8536. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Huang H and Tindall DJ: Dynamic FoxO
transcription factors. J Cell Sci. 120:2479–2487. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Yang JY and Hung MC: A new fork for
clinical application: targeting forkhead transcription factors in
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 15:752–757. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Vogt PK, Jiang H and Aoki M: Triple layer
control: phosphorylation, acetylation and ubiquitination of FOXO
proteins. Cell Cycle. 4:908–913. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Rena G, Prescott AR, Guo S, Cohen P and
Unterman TG: Roles of the forkhead in rhabdomyosarcoma (FKHR)
phosphorylation sites in regulating 14-3-3 binding, transactivation
and nuclear targeting. Biochem J. 354:605–612. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Essers MA, Weijzen S, Vries-Smits AM,
Saarloos I, de Ruiter ND, Bos JL and Burgering BM: FOXO
transcription factor activation by oxidative stress mediated by the
small GTPase Ral and JNK. EMBO J. 23:4802–4812. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Fu Z and Tindall DJ: FOXOs, cancer and
regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene. 27:2312–2319. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson
B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu JC and Sasaki
YF: Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in
vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen. 35:206–221.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Dhawan A, Bajpayee M and Parmar D: Comet
assay: a reliable tool for the assessment of DNA damage in
different models. Cell Biol Toxicol. 25:5–32. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Drabløs F, Feyzi E, Aas PA, Vaagbø CB,
Kavli B, Bratlie MS, Peña-Diaz J, Otterlei M, Slupphaug G and
Krokan HE: Alkylation damage in DNA and RNA - repair mechanisms and
medical significance. DNA Repair. 3:1389–1407. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Cok I, Ulutaş OK, Okuşluk O, Durmaz E and
Demir N: Evaluation of DNA damage in common carp (Cyprinus
carpio L.) by comet assay for determination of possible
pollution in Lake Mogan (Ankara). Sci World J. 11:1455–1461.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Schroering AG and Williams KJ: Rapid
induction of chromatin-associated DNA mismatch repair proteins
after MNNG treatment. DNA Repair. 7:951–969. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Jasin M: Homologous repair of DNA damage
and tumori genesis: the BRCA connection. Oncogene. 21:8981–8993.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Abraham RT: Cell cycle checkpoint
signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev. 15:2177–2196.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Matsuoka S, Ballif BA, Smogorzewska A,
McDonald ER III, Hurov KE, Luo J, Bakalarski CE, Zhao Z, Solimini
N, Lerenthal Y, Shiloh Y, Gygi SP and Elledge SJ: ATM and ATR
substrate analysis reveals extensive protein networks responsive to
DNA damage. Science. 316:1160–1166. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Hirano M, Hirano K, Nishimura J and
Kanaide H: Transcriptional up-regulation of p27 (Kip1) during
contact-induced growth arrest in vascular endothelial cells. Exp
Cell Res. 271:356–367. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Hildesheim J and Fornace AJ Jr: Gadd45a:
an elusive yet attractive candidate gene in pancreatic cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 8:2475–2479. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Stahl M, Dijkers PF, Kops GJ, Lens SM,
Coffer PJ, Burgering BM and Medema RH: The forkhead transcription
factor FoxO regulates transcription of p27Kip1 and Bim
in response to IL-2. J Immunol. 168:5024–5031. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Nakamura T and Sakamoto K: Forkhead
transcription factor FOXO subfamily is essential for reactive
oxygen species-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 281:47–55.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Hou J and Shang YC:
The ‘O’ class: crafting clinical care with FoxO transcription
factors. Adv Exp Med Biol. 665:242–260. 2009.
|
|
31.
|
Matsuzaki H, Daitoku H, Hatta M, Tanaka K
and Fukamizu A: Insulin-induced phosphorylation of FKHR (Foxo1)
targets to proteasomal degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:11285–11290. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Davis RJ: Signal transduction by the JNK
group of MAP kinases. Cell. 103:239–252. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Lüpertz R, Chovolou Y, Unfried K,
Kampkötter A, Wätjen W and Kahl R: The forkhead transcription
factor FOXO4 sensitizes cancer cells to doxorubicin-mediated
cytotoxicity. Carcinogenesis. 29:2045–2052. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Wang MC, Bohmann D and Jasper H: JNK
extends life span and limits growth by antagonizing cellular and
organism-wide responses to insulin signaling. Cell. 121:115–125.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Hong YK, Lee S, Park SH, Lee JH, Han SY,
Kim ST, Kim YK, Jeon S, Koo BS and Cho KS: Inhibition of JNK/dFOXO
pathway and caspases rescues neurological impairments in Drosophila
Alzheimer’s disease model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 419:49–53.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|