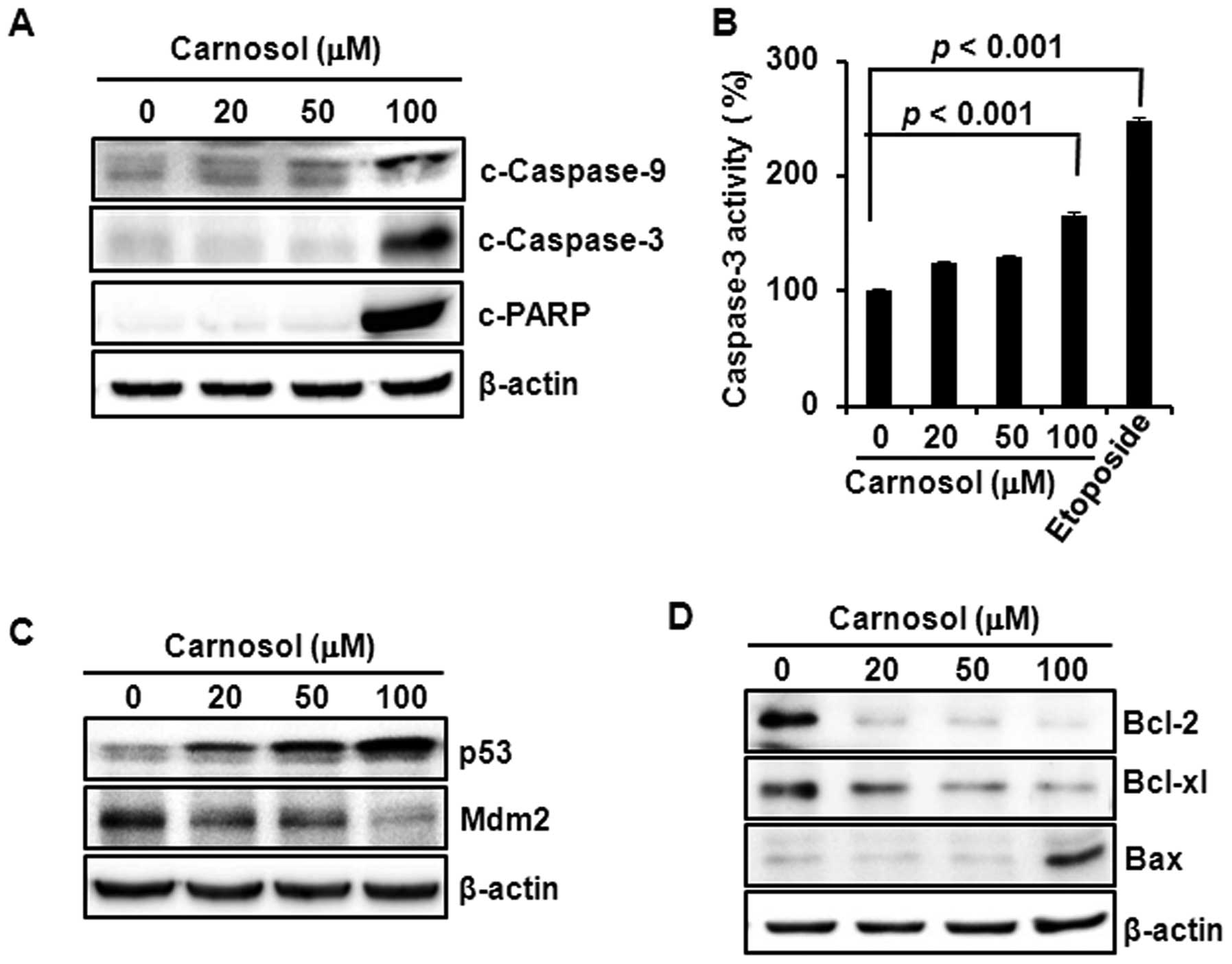
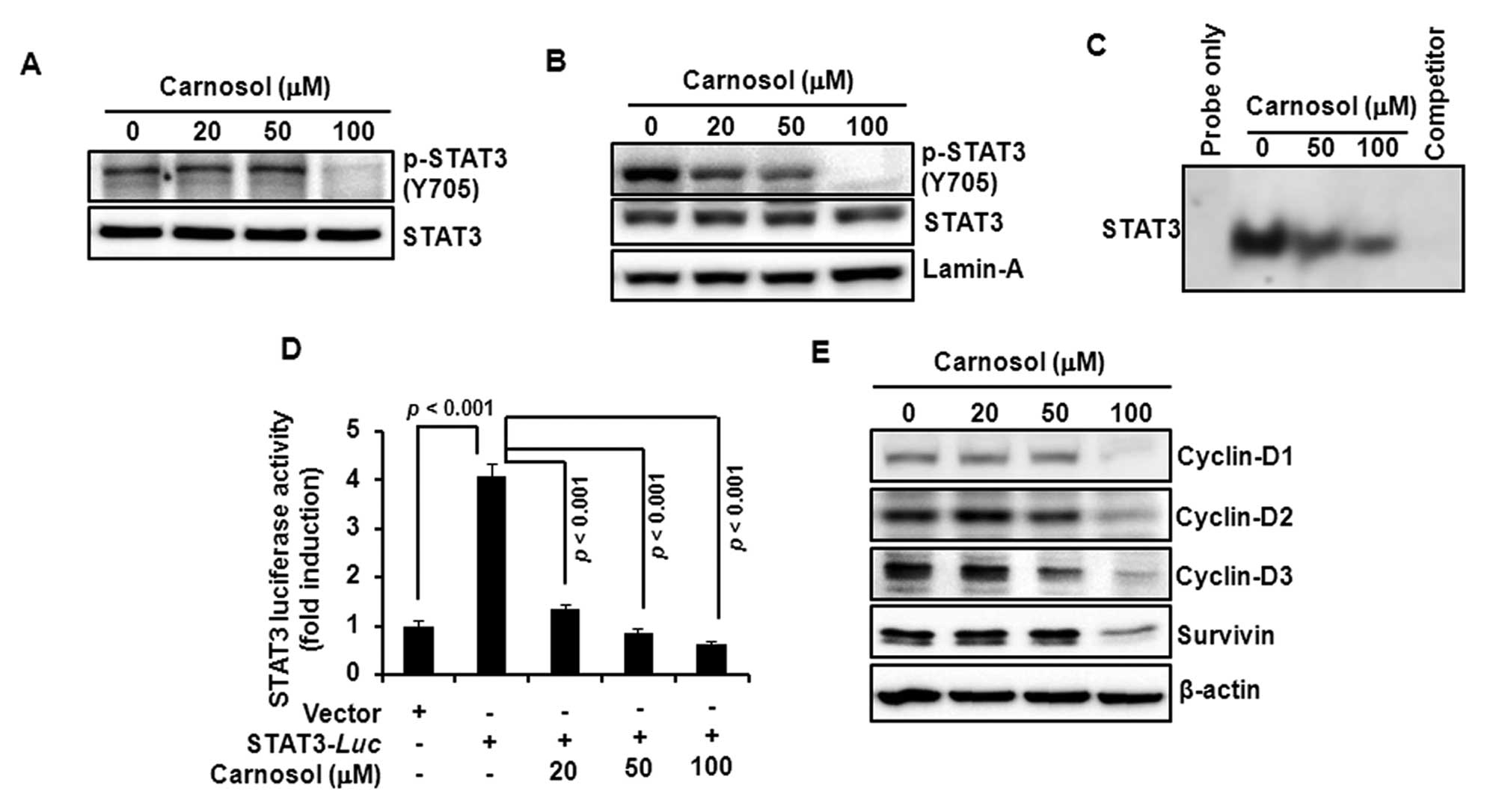
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C and Ward
EM: Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and
trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1893–1907. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Merika E, Saif MW, Katz A, Syrigos K and
Morse M: Review. Colon cancer vaccines: an update. In Vivo.
24:607–628. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Chung MY, Lim TG and Lee KW: Molecular
mechanisms of chemopreventive phytochemicals against
gastroenterological cancer development. World J Gastroenterol.
19:984–993. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Moran AE, Carothers AM, Weyant MJ, Redston
M and Bertagnolli MM: Carnosol inhibits beta-catenin tyrosine
phosphorylation and prevents adenoma formation in the C57BL/6J/
Min/+ (Min/+) mouse. Cancer Res. 65:1097–1104. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Cheng AC, Lee MF, Tsai ML, et al: Rosmanol
potently induces apoptosis through both the mitochondrial apoptotic
pathway and death receptor pathway in human colon adenocarcinoma
COLO 205 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:485–493. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Neergheen VS, Bahorun T, Taylor EW, Jen LS
and Aruoma OI: Targeting specific cell signaling transduction
pathways by dietary and medicinal phytochemicals in cancer
chemoprevention. Toxicology. 278:229–241. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Burz C, Berindan-Neagoe I, Balacescu O and
Irimie A: Apoptosis in cancer: key molecular signaling pathways and
therapy targets. Acta Oncol. 48:811–821. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Martin SJ and Green DR: Protease
activation during apoptosis: death by a thousand cuts? Cell.
82:349–352. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Aggarwal BB, Takada Y and Oommen OV: From
chemoprevention to chemotherapy: common targets and common goals.
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 13:1327–1338. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Johnston PA and Grandis JR: STAT3
signaling: anticancer strategies and challenges. Mol Interv.
11:18–26. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Masuda M, Suzui M, Yasumatu R, et al:
Constitutive activation of signal transducers and activators of
transcription 3 correlates with cyclin D1 overexpression and may
provide a novel prognostic marker in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 62:3351–3355. 2002.
|
|
14.
|
Lau GK and Ye D: STAT3 implicated in the
development of colon cancer: a step closer for targeted therapy?
Gastroenterology. 139:353–355. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Lin L, Liu A, Peng Z, et al: STAT3 is
necessary for proliferation and survival in colon cancer-initiating
cells. Cancer Res. 71:7226–7237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Slattery ML, Lundgreen A, Kadlubar SA,
Bondurant KL and Wolff RK: JAK/STAT/SOCS-signaling pathway and
colon and rectal cancer. Mol Carcinog. 52:155–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Laird AD, Li G, Moss KG, et al: Src family
kinase activity is required for signal tranducer and activator of
transcription 3 and focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation and
vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in vivo and for
anchorage-dependent and -independent growth of human tumor cells.
Mol Cancer Ther. 2:461–469. 2003.
|
|
18.
|
Kundu J, Wahab SM, Kundu JK, et al: Tob1
induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, migration and
invasion of gastric cancer cells by activating Smad4 and inhibiting
beta-catenin signaling. Int J Oncol. 41:839–848. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Kundu JK, Shin YK, Kim SH and Surh YJ:
Resveratrol inhibits phorbol ester-induced expression of COX-2 and
activation of NF-kappaB in mouse skin by blocking IkappaB kinase
activity. Carcinogenesis. 27:1465–1474. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Johnson JJ: Carnosol: a promising
anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory agent. Cancer Lett. 305:1–7.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Dorrie J, Sapala K and Zunino SJ:
Carnosol-induced apoptosis and downregulation of Bcl-2 in B-lineage
leukemia cells. Cancer Lett. 170:33–39. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Johnson JJ, Syed DN, Heren CR, Suh Y,
Adhami VM and Mukhtar H: Carnosol, a dietary diterpene, displays
growth inhibitory effects in human prostate cancer PC3 cells
leading to G2-phase cell cycle arrest and targets the
5′-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway. Pharm Res.
25:2125–2134. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Cherbonnel-Lasserre C and Dosanjh MK:
Suppression of apoptosis by overexpression of Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL
promotes survival and mutagenesis after oxidative damage.
Biochimie. 79:613–617. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Zhu S, Li T, Tan J, et al: Bax is
essential for death receptor-mediated apoptosis in human colon
cancer cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 27:577–581. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Valassiadou KE, Stefanaki K, Tzardi M, et
al: Immunohistochemical expression of p53, bcl-2, mdm2 and waf1/p21
proteins in colorectal adenocarcinomas. Anticancer Res.
17:2571–2576. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Bonnotte B, Favre N, Moutet M, et al:
Bcl-2-mediated inhibition of apoptosis prevents immunogenicity and
restores tumorigenicity of spontaneously regressive tumors. J
Immunol. 161:1433–1438. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Shaw P, Bovey R, Tardy S, Sahli R, Sordat
B and Costa J: Induction of apoptosis by wild-type p53 in a human
colon tumor-derived cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
89:4495–4499. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Kim DH, Kundu JK and Surh YJ: Redox
modulation of p53: mechanisms and functional significance. Mol
Carcinog. 50:222–234. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Rigatti MJ, Verma R, Belinsky GS,
Rosenberg DW and Giardina C: Pharmacological inhibition of Mdm2
triggers growth arrest and promotes DNA breakage in mouse colon
tumors and human colon cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 51:363–378.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Miyashita T and Reed JC: Tumor suppressor
p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene.
Cell. 80:293–299. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Miyashita T, Krajewski S, Krajewska M, et
al: Tumor suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene
expression in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 9:1799–1805.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Lotem J, Peled-Kamar M, Groner Y and Sachs
L: Cellular oxidative stress and the control of apoptosis by
wild-type p53, cytotoxic compounds, and cytokines. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 93:9166–9171. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Corvinus FM, Orth C, Moriggl R, et al:
Persistent STAT3 activation in colon cancer is associated with
enhanced cell proliferation and tumor growth. Neoplasia. 7:545–555.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Lin Q, Lai R, Chirieac LR, et al:
Constitutive activation of JAK3/ STAT3 in colon carcinoma tumors
and cell lines: inhibition of JAK3/STAT3 signaling induces
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of colon carcinoma cells. Am J
Pathol. 167:969–980. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Kanda N, Seno H, Konda Y, et al: STAT3 is
constitutively activated and supports cell survival in association
with survivin expression in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene.
23:4921–4929. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Asanuma K, Tsuji N, Endoh T, Yagihashi A
and Watanabe N: Survivin enhances Fas ligand expression via
up-regulation of specificity protein 1-mediated gene transcription
in colon cancer cells. J Immunol. 172:3922–3929. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|