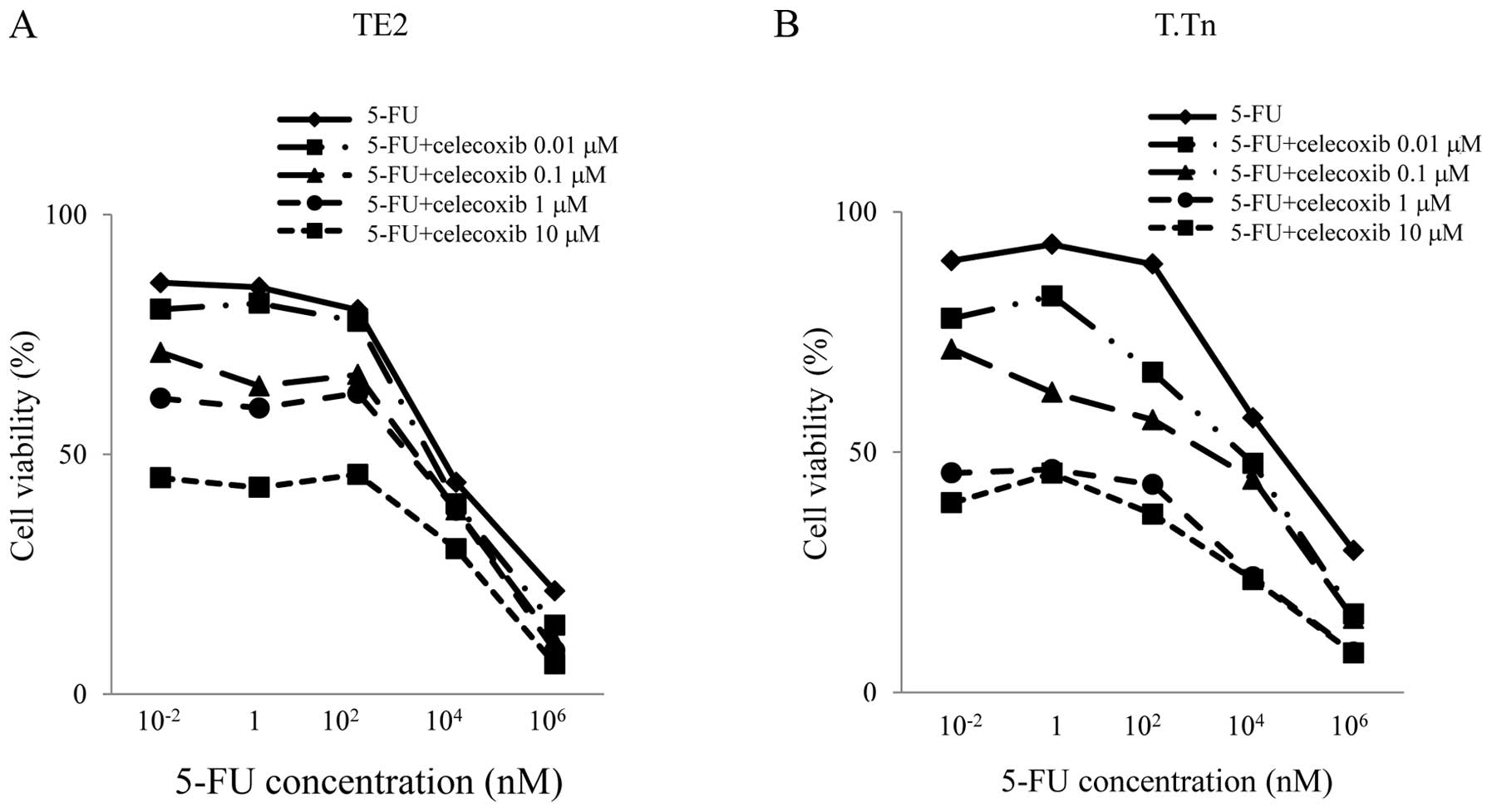
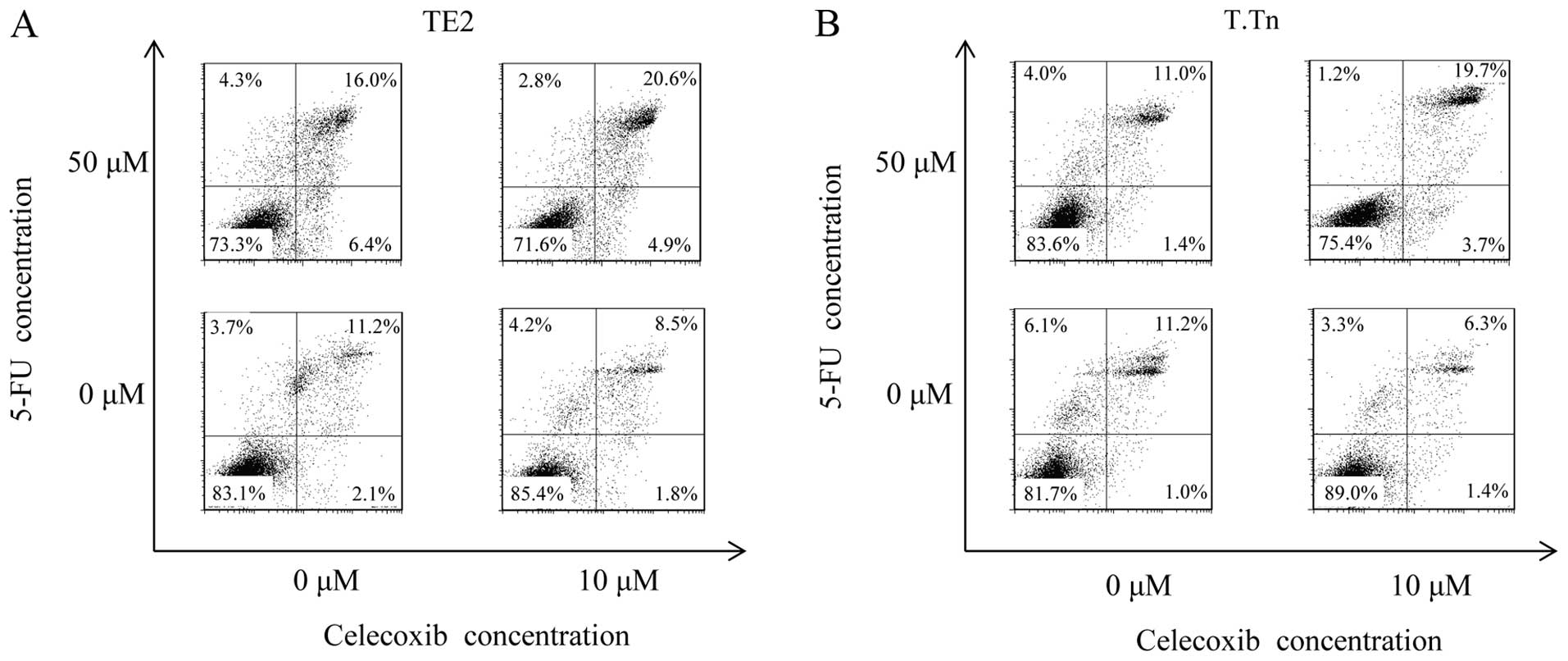
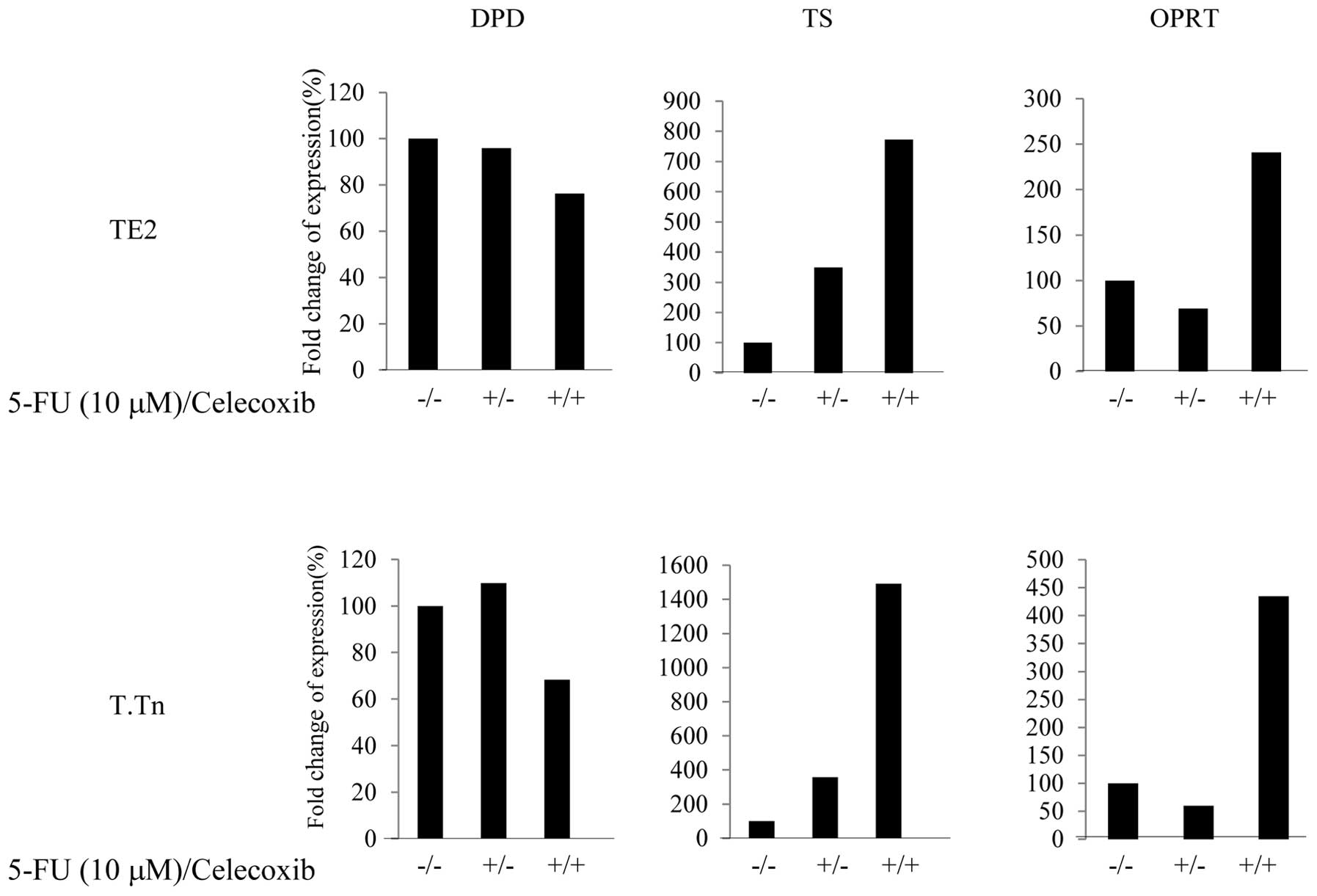
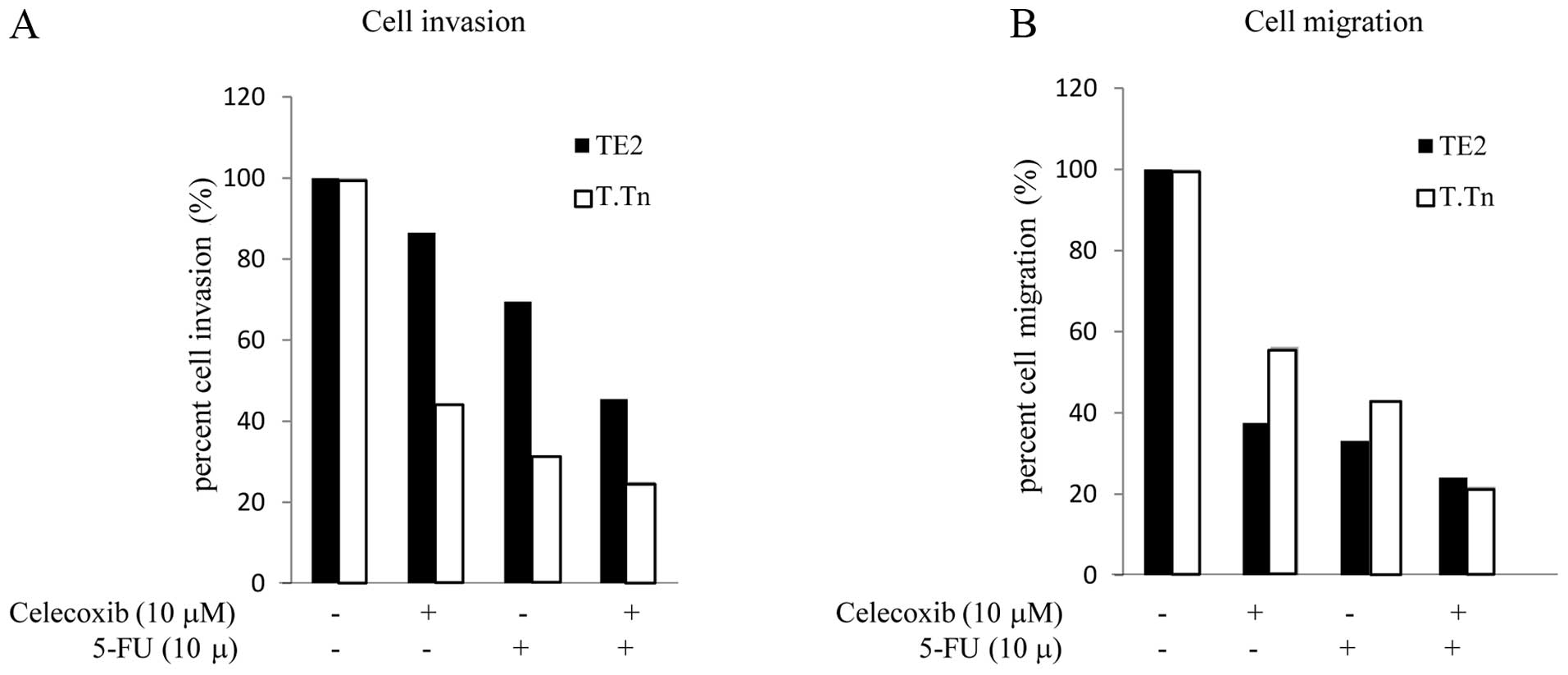
|
1.
|
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA and
Luketich JD: Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 381:400–412. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Siersema PD: Esophageal cancer.
Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 37:943–964. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Rizzo MT: Cyclooxygenase-2 in oncogenesis.
Clin Chim Acta. 412:671–687. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Smith WL, DeWitt DL and Garavito RM:
Cyclooxygenases: structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu
Rev Biochem. 69:145–182. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Dempke W, Rie C, Grothey A and Schmoll HJ:
Cyclooxygenase-2: a novel target for cancer chemotherapy? J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 127:411–417. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Shamma A, Yamamoto H, Doki Y, et al:
Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 in squamous carcinogenesis of the
esophagus. Clin Cancer Res. 6:1229–1238. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Hida T, Yatabe Y, Achiwa H, et al:
Increased expression of cyclooxygenase 2 occurs frequently in human
lung cancers, specifically in adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res.
58:3761–3764. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Dannenberg AJ and Subbaramaiah K:
Targeting cyclooxygenase-2 in human neoplasia: rationale and
promise. Cancer Cell. 4:431–436. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Okamura H, Fujiwara H, Umehara S, et al:
COX-2 overexpression Induced by gene transfer reduces sensitivity
of TE13 esophageal carcinoma cells to 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin.
Anticancer Res. 33:537–542. 2013.
|
|
10.
|
Higashi Y, Kanekura T and Kanzaki T:
Enhanced expression of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 in human skin
epidermal cancer cells: evidence for growth suppression by
inhibiting COX-2 expression. Int J Cancer. 86:667–671. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Lucci A, Krishnamurthy S, Singh B, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in primary breast cancers predicts
dissemination of cancer cells to the bone marrow. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 117:61–68. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Van Nes JG, de Kruijf EM, Faratian D, et
al: COX2 expression in prognosis and in prediction to endocrine
therapy in early breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
125:671–685. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Hashimoto N, Inayama M, Fujishima M and
Shiozaki H: Clinicopathologic significance of expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Hepatogastroenterology. 54:758–760. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Akutsu Y, Hanari N, Yusup G, et al: COX2
expression predicts resistance to chemoradiotherapy in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:2946–2951. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Jendrossek V: Targeting apoptosis pathways
by Celecoxib in cancer. Cancer Lett. 332:313–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Boolbol SK, Dannenberg AJ, Chadburn A, et
al: Cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression and tumor formation are blocked
by sulindac in a murine model of familial adenomatous polyposis.
Cancer Res. 56:2556–2560. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Tsujii M, Kawano S and DuBois RN:
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human colon cancer cells increases
metastatic potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:3336–3340. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Kwak YE, Jeon NK, Kim J and Lee EJ: The
cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitor celecoxib suppresses
proliferation and invasiveness in the human oral squamous
carcinoma. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1095:99–112. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Dai ZJ, Ma XB, Kang HF, et al: Antitumor
activity of the selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, celecoxib, on
breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Cell Int. 12:532012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Soslow RA, Dannenberg AJ, Rush D, et al:
COX-2 is expressed in human pulmonary, colonic, and mammary tumors.
Cancer. 89:2637–2645. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Gupta S, Srivastava M, Ahmad N, Bostwick
DG and Mukhtar H: Over-expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human
prostate adenocarcinoma. Prostate. 42:73–78. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Sano H, Kawahito Y, Wilder RL, et al:
Expression of cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in human colorectal cancer.
Cancer Res. 55:3785–3789. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Hwang D, Scollard D, Byrne J and Levine E:
Expression of cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 in human breast
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 90:455–460. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
De Groot DJ, de Vries EG, Groen HJ and de
Jong S: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to potentiate
chemotherapy effects: from lab to clinic. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
61:52–69. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Takemura M, Morimura K, Yoshida K and
Fujiwara Y: Four resected cases with basaloid carcinoma of
esophagus - comparison of 5-FU-related enzymes (thymidylate
synthase (TS), dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), orotate
phosphoribosyl transferase (OPRT)) between basaloid carcinoma and
squamous cell carcinoma. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 37:2143–2146. 2010.In
Japanese.
|
|
26.
|
Ofverholm A, Arkblad E, Skrtic S,
Albertsson P, Shubbar E and Enerback C: Two cases of 5-fluorouracil
toxicity linked with gene variants in the DPYD gene. Clin Biochem.
43:331–334. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Ostapowicz A and Dolegowska B: Review of
methods for determination of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase and
possible application in screening previous chemotheraphy with
5-fluorouracil. Przegl Lek. 69:694–697. 2012.In Polish.
|
|
28.
|
Li WZ, Huo QJ, Wang XY and Xu F:
Inhibitive effect of celecoxib on the adhesion and invasion of
human tongue squamous carcinoma cells to extracellular matrix via
down regulation of MMP-2 expression. Prostaglandins Other Lipid
Mediat. 93:113–119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Sheng H, Shao J, Morrow JD, Beauchamp RD
and DuBois RN: Modulation of apoptosis and Bcl-2 expression by
prostaglandin E2 in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res.
58:362–366. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Oshima H and Oshima M: The role of
PGE2-associated inflammatory responses in gastric cancer
development. Semin Immunopathol. 35:139–150. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Cianchi F, Cortesini C, Bechi P, et al:
Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase 2 gene expression correlates with
tumor angiogenesis in human colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology.
121:1339–1347. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Elder DJ, Halton DE, Crew TE and Paraskeva
C: Apoptosis induction and cyclooxygenase-2 regulation in human
colorectal adenoma and carcinoma cell lines by the
cyclooxygenase-2-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
NS-398. Int J Cancer. 86:553–560. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Irie T, Tsujii M, Tsuji S, et al:
Synergistic antitumor effects of celecoxib with 5-fluorouracil
depend on IFN-gamma. Int J Cancer. 121:878–883. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Kuipers GK, Slotman BJ, Wedekind LE, et
al: Radiosensitization of human glioma cells by cyclooxygenase-2
(COX-2) inhibition: independent on COX-2 expression and dependent
on the COX-2 inhibitor and sequence of administration. Int J Radiat
Biol. 83:677–685. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35.
|
Shin YK, Park JS, Kim HS, et al:
Radiosensitivity enhancement by celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase (COX)-2
selective inhibitor, via COX-2-dependent cell cycle regulation on
human cancer cells expressing differential COX-2 levels. Cancer
Res. 65:9501–9509. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Jun HJ, Kim YM, Park SY, et al: Modulation
of ionizing radiation-induced G2 arrest by cyclooxygenase-2 and its
inhibitor celecoxib. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 75:225–234.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Davis TW, O’Neal JM, Pagel MD, et al:
Synergy between celecoxib and radiotherapy results from inhibition
of cyclooxygenase-2-derived prostaglandin E2, a survival factor for
tumor and associated vasculature. Cancer Res. 64:279–285. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38.
|
Kim BM, Won J, Maeng KA, Han YS, Yun YS
and Hong SH: Nimesulide, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, acts
synergistically with ionizing radiation against A549 human lung
cancer cells through the activation of caspase-8 and caspase-3. Int
J Oncol. 34:1467–1473. 2009.
|
|
39.
|
Raju U, Ariga H, Dittmann K, Nakata E, Ang
KK and Milas L: Inhibition of DNA repair as a mechanism of enhanced
radio-response of head and neck carcinoma cells by a selective
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, celecoxib. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 63:520–528. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|