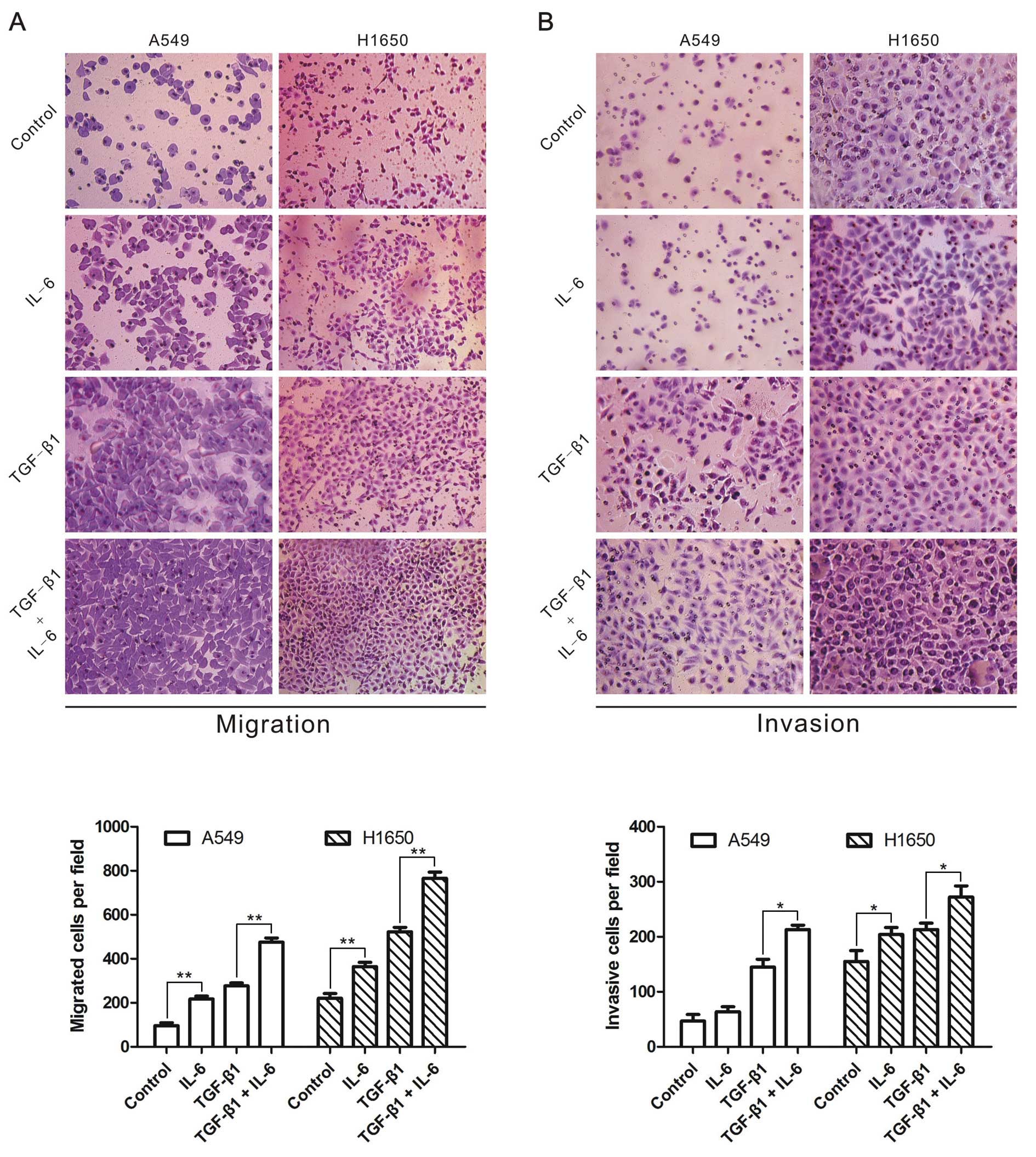
|
1.
|
Gupta GP and Massague J: Cancer
metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 127:679–695. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Kang Y and Massague J:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: twist in development and
metastasis. Cell. 118:277–279. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R and Thompson
EW: The epithelialmesenchymal transition: new insights in
signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 172:973–981.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelialmesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Vincent T, Neve EP, Johnson JR, et al: A
SNAIL1-SMAD3/4 transcriptional repressor complex promotes TGF-beta
mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol.
11:943–950. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Horiguchi K, Sakamoto K, Koinuma D, et al:
TGF-beta drives epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
deltaEF1-mediated downregulation of ESRP. Oncogene. 31:3190–3201.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Pirozzi G, Tirino V, Camerlingo R, et al:
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition by TGFbeta-1 induction
increases stemness characteristics in primary non small cell lung
cancer cell line. PLoS One. 6:e215482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Massague J and Chen YG: Controlling
TGF-beta signaling. Genes Dev. 14:627–644. 2000.
|
|
13.
|
Roberts AB, Tian F, Byfield SD, et al:
Smad3 is key to TGF-beta-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition, fibrosis, tumor suppression and metastasis. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 17:19–27. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Smith AP, Verrecchia A, Faga G, et al: A
positive role for Myc in TGFbeta-induced Snail transcription and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene. 28:422–430. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Reka AK, Kurapati H, Narala VR, et al:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation
inhibits tumor metastasis by antagonizing Smad3-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:3221–3232.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Sullivan NJ, Sasser AK, Axel AE, et al:
Interleukin-6 induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition
phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 28:2940–2947.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Rojas A, Liu G, Coleman I, et al: IL-6
promotes prostate tumori-genesis and progression through autocrine
cross-activation of IGF-IR. Oncogene. 30:2345–2355. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Xiong H, Hong J, Du W, et al: Roles of
STAT3 and ZEB1 proteins in E-cadherin down-regulation and human
colorectal cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem.
287:5819–5832. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Bromberg J and Wang TC: Inflammation and
cancer: IL-6 and STAT3 complete the link. Cancer Cell. 15:79–80.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Looyenga BD, Hutchings D, Cherni I,
Kingsley C, Weiss GJ and Mackeigan JP: STAT3 is activated by JAK2
independent of key oncogenic driver mutations in non-small cell
lung carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e308202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Huang C, Yang G, Jiang T, Zhu G, Li H and
Qiu Z: The effects and mechanisms of blockage of STAT3 signaling
pathway on IL-6 inducing EMT in human pancreatic cancer cells in
vitro. Neoplasma. 58:396–405. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Xie TX, Huang FJ, Aldape KD, et al:
Activation of stat3 in human melanoma promotes brain metastasis.
Cancer Res. 66:3188–3196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Abdulghani J, Gu L, Dagvadorj A, et al:
Stat3 promotes meta-static progression of prostate cancer. Am J
Pathol. 172:1717–1728. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Enewold L, Mechanic LE, Bowman ED, et al:
Serum concentrations of cytokines and lung cancer survival in
African Americans and Caucasians. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
18:215–222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Pine SR, Mechanic LE, Enewold L, et al:
Increased levels of circulating interleukin 6, interleukin 8,
C-reactive protein, and risk of lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
103:1112–1122. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Calon A, Espinet E, Palomo-Ponce S, et al:
Dependency of colorectal cancer on a TGF-beta-driven program in
stromal cells for metastasis initiation. Cancer Cell. 22:571–584.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Liu XL, Xiao K, Xue B, et al: Dual role of
TGFBR3 in bladder cancer. Oncol Rep. 30:1301–1308. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Jinnin M, Ihn H and Tamaki K:
Characterization of SIS3, a novel specific inhibitor of Smad3, and
its effect on transforming growth factor-beta1-induced
extracellular matrix expression. Mol Pharmacol. 69:597–607. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Massague J: TGFbeta in cancer. Cell.
134:215–230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30.
|
Sansone P and Bromberg J: Targeting the
interleukin-6/Jak/stat pathway in human malignancies. J Clin Oncol.
30:1005–1014. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
De Craene B and Berx G: Regulatory
networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:97–110. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Lo HW, Hsu SC, Xia W, et al: Epidermal
growth factor receptor cooperates with signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cancer cells via up-regulation of TWIST gene
expression. Cancer Res. 67:9066–9076. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33.
|
Colomiere M, Ward AC, Riley C, et al:
Cross talk of signals between EGFR and IL-6R through JAK2/STAT3
mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian carcinomas. Br
J Cancer. 100:134–144. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Yamashita S, Miyagi C, Fukada T, Kagara N,
Che YS and Hirano T: Zinc transporter LIVI controls
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in zebrafish gastrula organizer.
Nature. 429:298–302. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: at the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Prunier C and Howe PH: Disabled-2 (Dab2)
is required for transforming growth factor beta-induced epithelial
to mesenchymal transition (EMT). J Biol Chem. 280:17540–17548.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Cho HJ, Baek KE, Saika S, Jeong MJ and Yoo
J: Snail is required for transforming growth factor-beta-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by activating PI3 kinase/Akt
signal pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 353:337–343. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Shintani Y, Maeda M, Chaika N, Johnson KR
and Wheelock MJ: Collagen I promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in lung cancer cells via transforming growth factor-beta
signaling. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 38:95–104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Horiguchi K, Shirakihara T, Nakano A,
Imamura T, Miyazono K and Saitoh M: Role of Ras signaling in the
induction of snail by transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem.
284:245–253. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Peinado H, Quintanilla M and Cano A:
Transforming growth factor beta-1 induces snail transcription
factor in epithelial cell lines: mechanisms for epithelial
mesenchymal transitions. J Biol Chem. 278:21113–21123. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41.
|
Li H, Wang H, Wang F, Gu Q and Xu X: Snail
involves in the transforming growth factor beta1-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of retinal pigment epithelial
cells. PLoS One. 6:e233222011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Thuault S, Tan EJ, Peinado H, Cano A,
Heldin CH and Moustakas A: HMGA2 and Smads co-regulate SNAIL1
expression during induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. J Biol Chem. 283:33437–33446. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43.
|
Shih JY and Yang PC: The EMT regulator
slug and lung carcino-genesis. Carcinogenesis. 32:1299–1304. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Dauer DJ, Ferraro B, Song L, et al: Stat3
regulates genes common to both wound healing and cancer. Oncogene.
24:3397–3408. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Kiuchi N, Nakajima K, Ichiba M, et al:
STAT3 is required for the gp130-mediated full activation of the
c-myc gene. J Exp Med. 189:63–73. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Luwor RB, Baradaran B, Taylor LE, et al:
Targeting Stat3 and Smad7 to restore TGF-beta cytostatic regulation
of tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 32:2433–2441. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Zhang XL, Topley N, Ito T and Phillips A:
Interleukin-6 regulation of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta
receptor compartmentalization and turnover enhances TGF-beta1
signaling. J Biol Chem. 280:12239–12245. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|