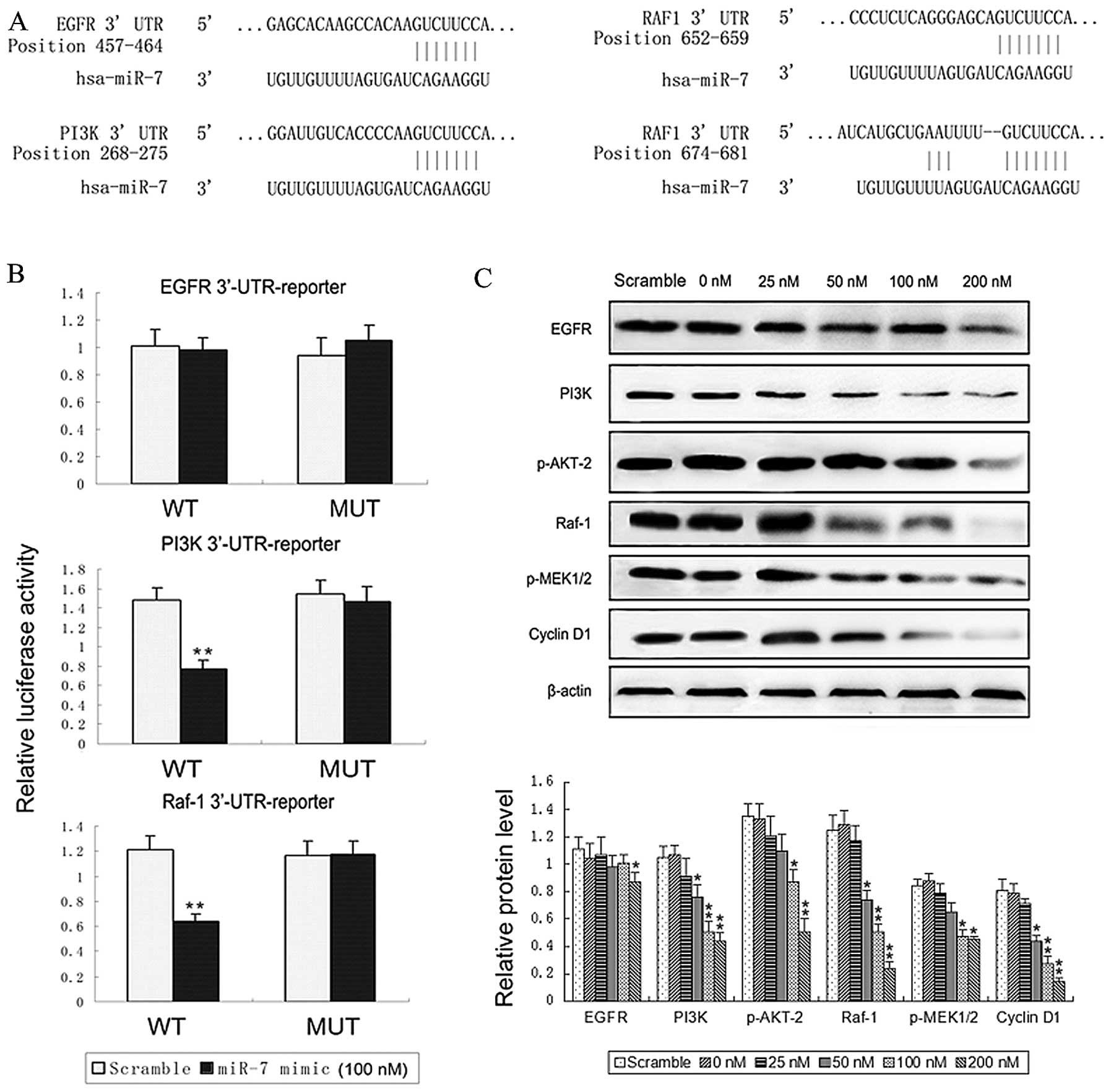
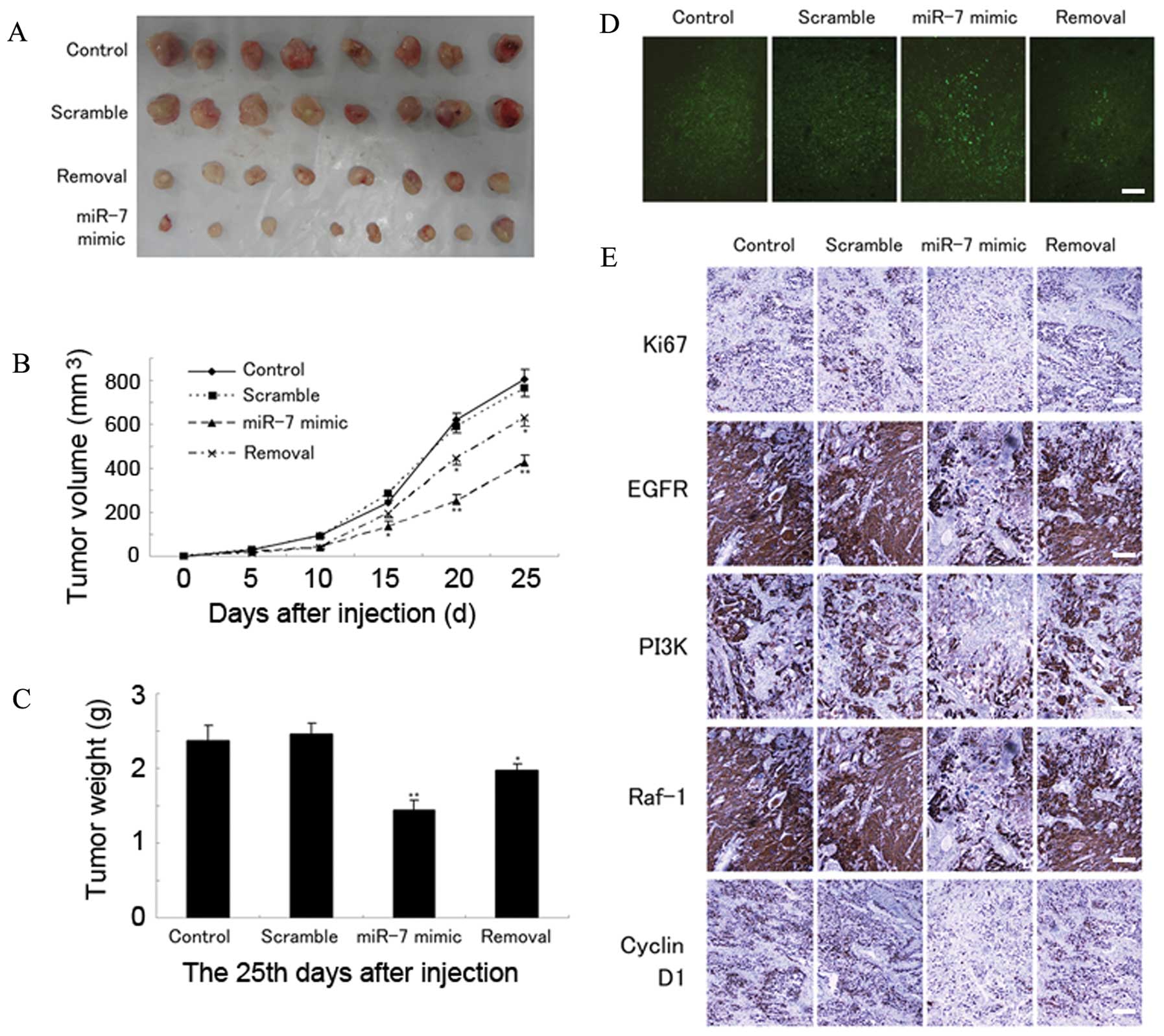
|
1.
|
Raizer JJ, Grimm S, Chamberlain MC, et al:
A phase 2 trial of single-agent bevacizumab given in an
every-3-week schedule for patients with recurrent high-grade
gliomas. Cancer. 116:5297–5305. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Bonavia R, Inda MM, Cavenee WK and Furnari
FB: Heterogeneity maintenance in glioblastoma: a social network.
Cancer Res. 71:4055–4060. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Masica DL and Karchin R: Correlation of
somatic mutation and expression identifies genes important in human
glioblastoma progression and survival. Cancer Res. 71:4550–4561.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Yang RY, Yang KS, Pike LJ and Marshall GR:
Targeting the dimerization of epidermal growth factor receptors
with small-molecule inhibitors. Chem Biol Drug Des. 76:1–9. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Tabunoki H, Saito N, Suwanborirux K, et
al: Molecular network profiling of U373MG human glioblastoma cells
following induction of apoptosis by novel marine-derived
anti-cancer 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids. Cancer Cell
Int. 12:142012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Ivliev AE, ‘t Hoen PA and Sergeeva MG:
Coexpression network analysis identifies transcriptional modules
related to proastro cytic differentiation and sprouty signaling in
glioma. Cancer Res. 70:10060–10070. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Rong Y, Belozerov VE, Tucker-Burden C, et
al: Epidermal growth factor receptor and PTEN modulate tissue
factor expression in glioblastoma through JunD/activator protein-1
transcriptional activity. Cancer Res. 69:2540–2549. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Mazzoleni S, Politi LS, Pala M, et al:
Epidermal growth factor receptor expression identifies functionally
and molecularly distinct tumor-initiating cells in human
glioblastoma multiforme and is required for gliomagenesis. Cancer
Res. 70:7500–7513. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Martinez I and Dimaio D: B-Myb, cancer,
senescence, and microRNAs. Cancer Res. 71:5370–5373. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Ibrahim AF, Weirauch U, Thomas M, et al:
MicroRNA replacement therapy for miR-145 and miR-33a is efficacious
in a model of colon carcinoma. Cancer Res. 71:5214–5224. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Farazi TA, Horlings HM, Ten Hoeve JJ, et
al: MicroRNA sequence and expression analysis in breast tumors by
deep sequencing. Cancer Res. 71:4443–4453. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Liu N, Landreh M, Cao K, et al: The
microRNA miR-34 modulates ageing and neurodegeneration in
Drosophila. Nature. 482:519–523. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Wu DG, Wang YY, Fan LG, et al: MicroRNA-7
regulates glioblastoma cell invasion via targeting focal adhesion
kinase expression. Chin Med J. 124:2616–2621. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Nguyen HT, Dalmasso G, Yan Y, et al:
MicroRNA-7 modulates CD98 expression during intestinal epithelial
cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 285:1479–1489. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Reddy SD, Ohshiro K, Rayala SK and Kumar
R: MicroRNA-7, a homeobox D10 target, inhibits p21-activated kinase
1 and regulates its functions. Cancer Res. 68:8195–8200. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Webster RJ, Giles KM, Price KJ, et al:
Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in human
cancer cells by microRNA-7. J Biol Chem. 284:5731–5741. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Xiong S, Zheng Y, Jiang P, et al:
MicroRNA-7 inhibits the growth of human non-small cell lung cancer
A549 cells through targeting BCL-2. Int J Biol Sci. 7:805–814.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 435:834–838.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Hu BS, Tan JW, Zhu GH, et al: WWOX induces
apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of human hepatoma cell line
SMMC-7721. World J Gastroenterol. 18:3020–3026. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Yoo AS, Sun AX, Li L, et al:
MicroRNA-mediated conversion of human fibroblasts to neurons.
Nature. 476:228–231. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Xiong F, Wu C, Chang J, et al: Genetic
variation in an miRNA-1827 binding site in MYCL1 alters
susceptibility to small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 71:5175–5181.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Zhou X, Ren Y, Moore L, et al:
Downregulation of miR-21 inhibits EGFR pathway and suppresses the
growth of human glioblastoma cells independent of PTEN status. Lab
Invest. 90:144–155. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Dong H, Luo L, Hong S, et al: Integrated
analysis of mutations, miRNA and mRNA expression in glioblastoma.
BMC Syst Biol. 4:1632010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Huang PH, Miraldi ER, Xu AM, et al:
Phosphotyrosine signaling analysis of site-specific mutations on
EGFRvIII identifies determinants governing glioblastoma cell
growth. Mol Biosyst. 6:1227–1237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Lal B, Goodwin CR, Sang Y, et al: EGFRvIII
and c-Met pathway inhibitors synergize against PTEN-null/EGFRvIII+
glioblastoma xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:1751–1760.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Reznik TE, Sang Y, Ma Y, et al:
Transcription-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor activation
by hepatocyte growth factor. Mol Cancer Res. 6:139–150. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Huang PH, Cavenee WK, Furnari FB and White
FM: Uncovering therapeutic targets for glioblastoma: a systems
biology approach. Cell Cycle. 6:2750–2754. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Chou YT, Lin HH, Lien YC, et al: EGFR
promotes lung tumorigenesis by activating miR-7 through a
Ras/ERK/Myc pathway that targets the Ets2 transcriptional repressor
ERF. Cancer Res. 70:8822–8831. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Kirubakaran P, Kothapalli R, Singh KhD, et
al: In silico studies on marine actinomycetes as potential
inhibitors for Glioblastoma multiforme. Bioinformation. 6:100–106.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Kakkar A, Suri V, Jha P, et al: Loss of
heterozygosity on chromosome 10q in glioblastomas, and its
association with other genetic alterations and survival in Indian
patients. Neurol India. 59:254–261. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Halatsch ME, Löw S, Hielscher T, et al:
Epidermal growth factor receptor pathway gene expressions and
biological response of glioblastoma multiforme cell lines to
erlotinib. Anticancer Res. 28:3725–3728. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Motomura K, Natsume A, Kishida Y, et al:
Benefits of interferon-β and temozolomide combination therapy for
newly diagnosed primary glioblastoma with the unmethylated MGMT
promoter: a multicenter study. Cancer. 117:1721–1730. 2011.
|
|
33.
|
Griffero F, Daga A, Marubbi D, et al:
Different response of human glioma tumor-initiating cells to
epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors. J Biol Chem.
284:7138–7148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I, et
al: A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by
functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell. 147:358–369. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Patterson EE, Holloway AK, Weng J, et al:
MicroRNA profiling of adrenocortical tumors reveals miR-483 as a
marker of malignancy. Cancer. 117:1630–1639. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Paroo Z, Ye X, Chen S and Liu Q:
Phosphorylation of the human microRNA-generating complex mediates
MAPK/Erk signaling. Cell. 139:112–122. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Hide T, Takezaki T, Nakatani Y, et al:
Combination of a ptgs2 inhibitor and an epidermal growth factor
receptor-signaling inhibitor prevents tumorigenesis of
oligodendrocyte lineage-derived glioma-initiating cells. Stem
Cells. 29:590–599. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38.
|
Fu S and Kurzrock R: Development of
curcumin as an epigenetic agent. Cancer. 116:4670–4676. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Zhu H, Acquaviva J, Ramachandran P, et al:
Oncogenic EGFR signaling cooperates with loss of tumor suppressor
gene functions in gliomagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:2712–2716. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Löw S, Vougioukas VI, Hielscher T, et al:
Pathogenetic pathways leading to glioblastoma multiforme:
association between gene expressions and resistance to erlotinib.
Anticancer Res. 28:3729–3732. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Kefas B, Godlewski J, Comeau L, et al:
microRNA-7 inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor and the
Akt pathway and is down-regulated in glioblastoma. Cancer Res.
68:3566–3572. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|