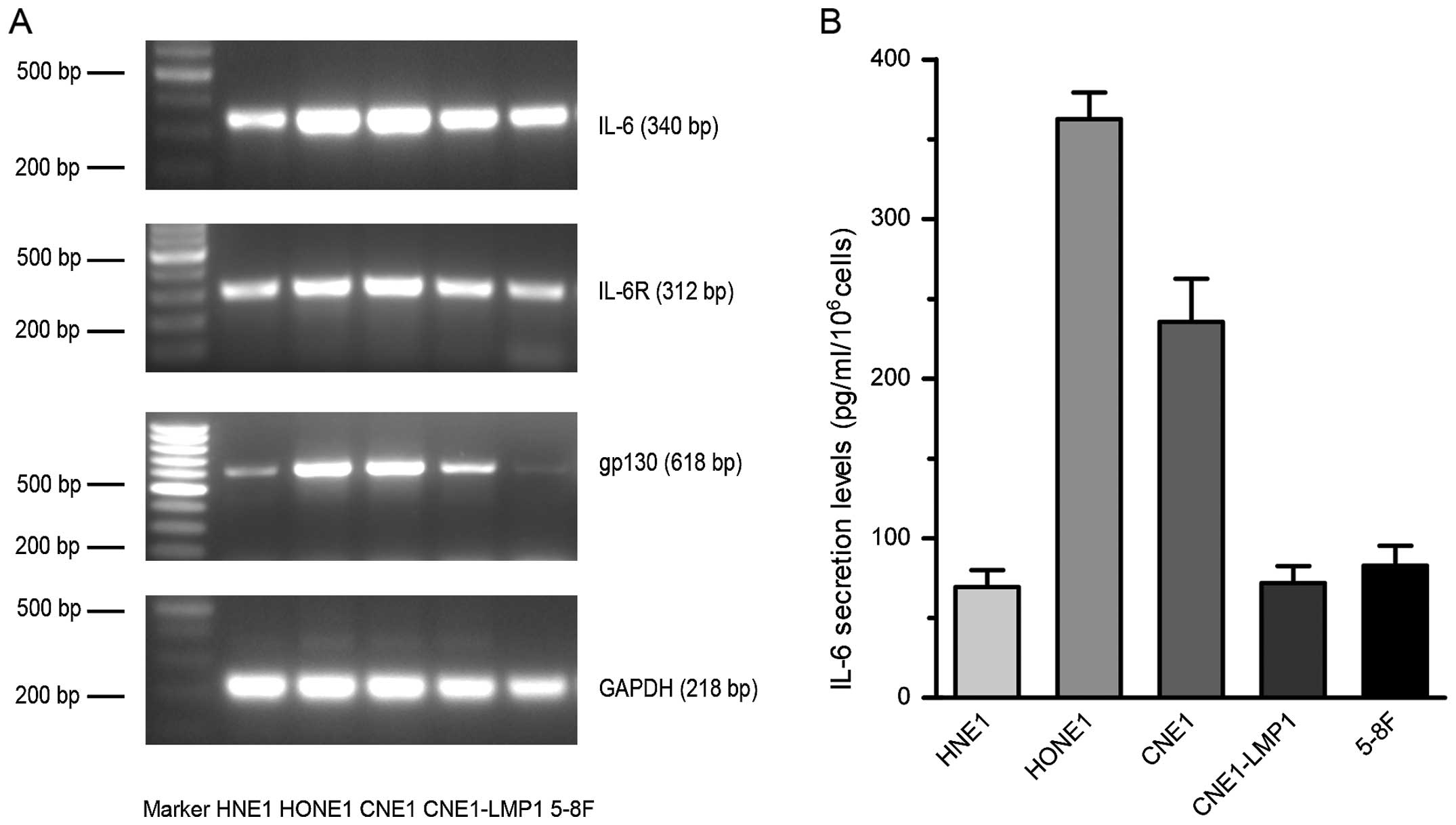
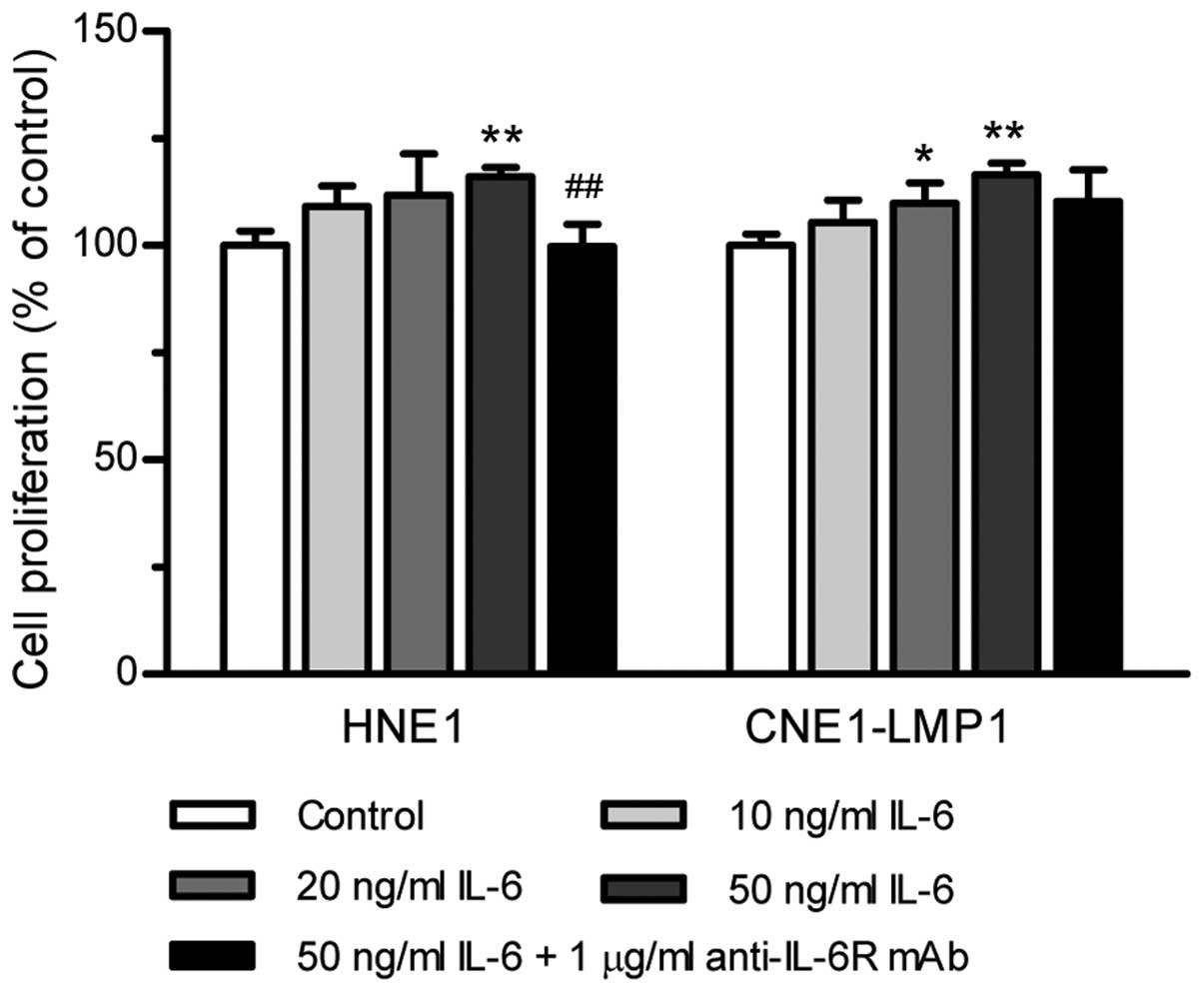
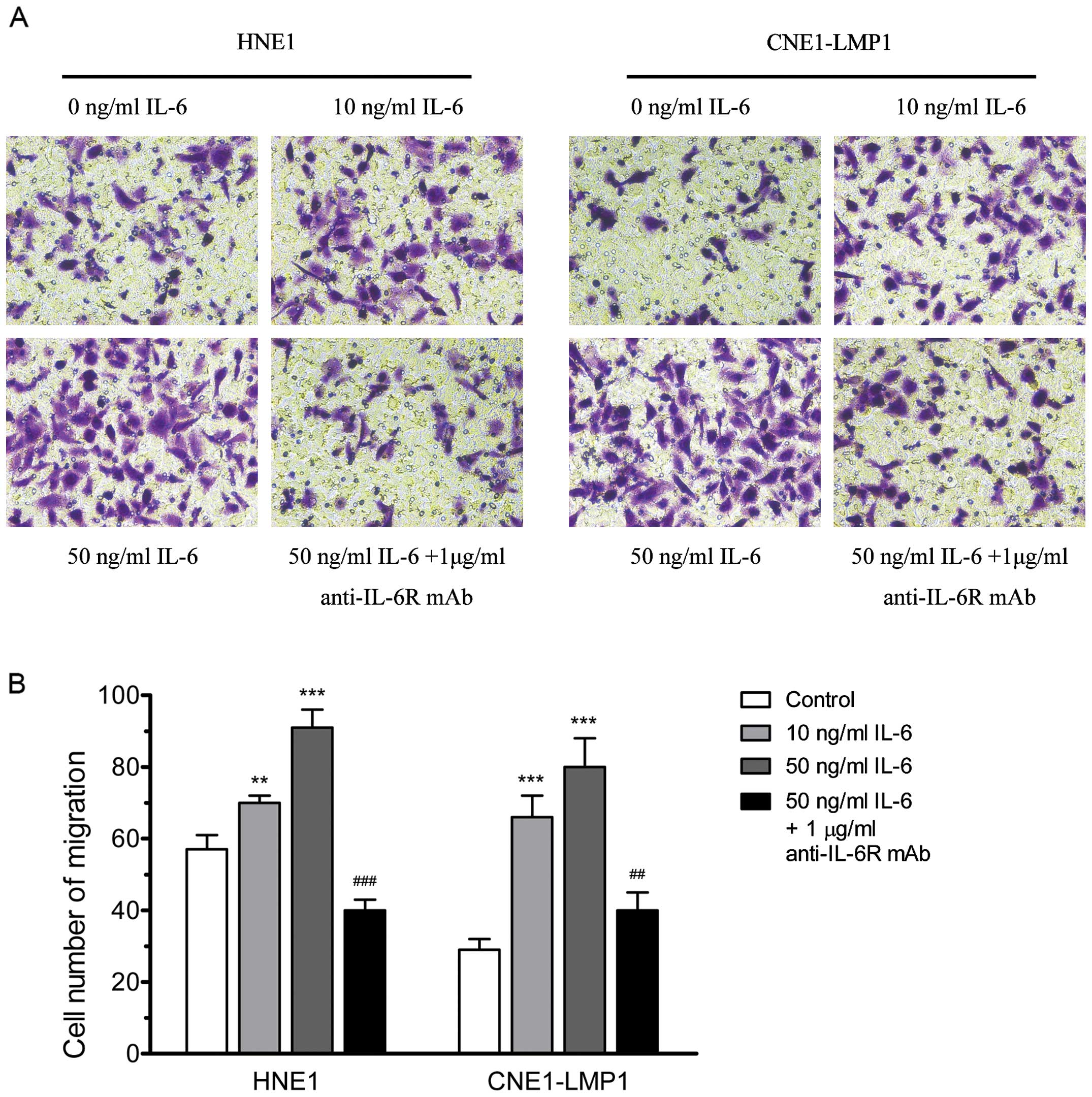
|
1.
|
Chan AT: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann
Oncol. 21(Suppl 7): vii308–vii312. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Wei WI and Mok VW: The management of neck
metastases in nasopharyngeal cancer. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head
Neck Surg. 15:99–102. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Huang CJ, Leung SW, Lian SL, Wang CJ, Fang
FM and Ho YH: Patterns of distant metastases in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 12:229–234. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Lee AW, Lin JC and Ng WT: Current
management of nasopharyngeal cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol.
22:233–244. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Wang J, Shi M, Hsia Y, et al: Failure
patterns and survival in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma
treated with intensity modulated radiation in Northwest China: a
pilot study. Radiat Oncol. 7:22012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Chang CH, Hsiao CF, Yeh YM, et al:
Circulating interleukin-6 level is a prognostic marker for survival
in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer patients treated with
chemotherapy. Int J Cancer. 132:1977–1985. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Ravishankaran P and Karunanithi R:
Clinical significance of preoperative serum interleukin-6 and
C-reactive protein level in breast cancer patients. World J Surg
Oncol. 9:182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Schafer ZT and Brugge JS: IL-6 involvement
in epithelial cancers. J Clin Invest. 117:3660–3663. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Yanaihara N, Anglesio MS, Ochiai K, et al:
Cytokine gene expression signature in ovarian clear cell carcinoma.
Int J Oncol. 41:1094–1100. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Haan S, Hermanns
HM, Muller-Newen G and Schaper F: Principles of interleukin
(IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem J.
374:1–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Grivennikov S and Karin M: Autocrine IL-6
signaling: a key event in tumorigenesis? Cancer Cell. 13:7–9. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Yi H, Cho HJ, Cho SM, et al: Blockade of
interleukin-6 receptor suppresses the proliferation of H460 lung
cancer stem cells. Int J Oncol. 41:310–316. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Xie G, Yao Q, Liu Y, et al: IL-6-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotes the generation of breast
cancer stem-like cells analogous to mammosphere cultures. Int J
Oncol. 40:1171–1179. 2012.
|
|
16.
|
Ara T and Declerck YA: Interleukin-6 in
bone metastasis and cancer progression. Eur J Cancer. 46:1223–1231.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Kleiner DE and Stetler-Stevenson WG:
Matrix metalloproteinases and metastasis. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 43(Suppl): S42–S51. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Kallakury BV, Karikehalli S, Haholu A,
Sheehan CE, Azumi N and Ross JS: Increased expression of matrix
metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinases 1 and 2 correlate with poor prognostic variables
in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 7:3113–3119.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Libra M, Scalisi A, Vella N, et al:
Uterine cervical carcinoma: role of matrix metalloproteinases
(review). Int J Oncol. 34:897–903. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Kurahara S, Shinohara M, Ikebe T, et al:
Expression of MMPs, MT-MMP, and TIMPs in squamous cell carcinoma of
the oral cavity: correlations with tumor invasion and metastasis.
Head Neck. 21:627–638. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Kataoka M, Yamagata S, Takagi H, et al:
Matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 in esophageal cancer. Int J Oncol.
8:773–779. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Roomi MW, Monterrey JC, Kalinovsky T, Rath
M and Niedzwiecki A: Patterns of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in
human cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep. 21:1323–1333. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Roomi MW, Monterrey JC, Kalinovsky T, Rath
M and Niedzwiecki A: In vitro modulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9
in human cervical and ovarian cancer cell lines by cytokines,
inducers and inhibitors. Oncol Rep. 23:605–614. 2010.
|
|
24.
|
Roomi MW, Monterrey JC, Kalinovsky T,
Niedzwiecki A and Rath M: Modulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 by
cytokines, mitogens and inhibitors in lung cancer and malignant
mesothelioma cell lines. Oncol Rep. 22:1283–1291. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Roomi MW, Kalinovsky T, Monterrey J, Rath
M and Niedzwiecki A: In vitro modulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9
in adult human sarcoma cell lines by cytokines, inducers and
inhibitors. Int J Oncol. 43:1787–1798. 2013.
|
|
26.
|
Kossakowska AE, Edwards DR, Prusinkiewicz
C, et al: Interleukin-6 regulation of matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP-2 and MMP-9) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase
(TIMP-1) expression in malignant non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Blood.
94:2080–2089. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Wang Y, Li L, Guo X, et al: Interleukin-6
signaling regulates anchorage-independent growth, proliferation,
adhesion and invasion in human ovarian cancer cells. Cytokine.
59:228–236. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Wang X, Lee SO, Xia S, et al: Endothelial
cells enhance prostate cancer metastasis via IL-6→androgen
receptor→TGF-β→MMP-9 signals. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:1026–1037.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Chow KC, Chiou SH, Ho SP, et al: The
elevated serum interleukin-6 correlates with the increased serum
butyrate level in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol
Rep. 10:813–819. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Tan EL, Selvaratnam G, Kananathan R and
Sam CK: Quantification of Epstein-Barr virus DNA load,
interleukin-6, interleukin-10, transforming growth factor-beta1 and
stem cell factor in plasma of patients with nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 6:2272006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Horikawa T, Yoshizaki T, Sheen TS, Lee SY
and Furukawa M: Association of latent membrane protein 1 and matrix
metalloproteinase 9 with metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Cancer. 89:715–723. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Wong TS, Kwong DL, Sham JS, Wei WI, Kwong
YL and Yuen AP: Clinicopathologic significance of plasma matrix
metalloproteinase-2 and -9 levels in patients with undifferentiated
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 30:560–564. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33.
|
Liu Z, Li L, Yang Z, et al: Increased
expression of MMP9 is correlated with poor prognosis of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 10:2702010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Glaser R, Zhang HY, Yao KT, et al: Two
epithelial tumor cell lines (HNE-1 and HONE-1) latently infected
with Epstein-Barr virus that were derived from nasopharyngeal
carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 86:9524–9528. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Du CW, Wen BG, Li DR, et al: Latent
membrane protein-1 of Epstein-Barr virus increases sensitivity to
arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cell. Exp Oncol. 27:267–272. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Yan Z, Yong-Guang T, Fei-Jun L, Fa-Qing T,
Min T and Ya C: Interference effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate
on targets of nuclear factor kappaB signal transduction pathways
activated by EB virus encoded latent membrane protein 1. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 36:1473–1481. 2004.
|
|
37.
|
Song LB, Yan J, Jian SW, et al: Molecular
mechanisms of tumorgenesis and metastasis in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cell sublines. Ai Zheng. 21:158–162. 2002.(In
Chinese).
|
|
38.
|
Li J, Fan Y, Chen J, Yao KT and Huang ZX:
Microarray analysis of differentially expressed genes between
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines 5-8F and 6-10B. Cancer Genet
Cytogenet. 196:23–30. 2010.
|
|
39.
|
Chan AT: Current treatment of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 47(Suppl 3): S302–S303.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Gourzones C, Barjon C and Busson P:
Host-tumor interactions in nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Semin Cancer
Biol. 22:127–136. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Liao Q, Guo X, Li X, et al: Analysis of
the contribution of nasopharyngeal epithelial cancer cells to the
induction of a local inflammatory response. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 138:57–64. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Chang KP, Chang YT, Wu CC, et al:
Multiplexed immuno-bead-based profiling of cytokine markers for
detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and prognosis of patient
survival. Head Neck. 33:886–897. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Eliopoulos AG, Stack M, Dawson CW, et al:
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP1 and CD40 mediate IL-6 production in
epithelial cells via an NF-kappaB pathway involving TNF
receptor-associated factors. Oncogene. 14:2899–2916. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44.
|
Lo AK, Lo KW, Tsao SW, et al: Epstein-Barr
virus infection alters cellular signal cascades in human
nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Neoplasia. 8:173–180. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Chen H, Hutt-Fletcher L, Cao L and Hayward
SD: A positive autoregulatory loop of LMP1 expression and STAT
activation in epithelial cells latently infected with Epstein-Barr
virus. J Virol. 77:4139–4148. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Ataie-Kachoie P, Pourgholami MH and Morris
DL: Inhibition of the IL-6 signaling pathway: a strategy to combat
chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 24:163–173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Weidle UH, Klostermann S, Eggle D and
Kruger A: Interleukin 6/interleukin 6 receptor interaction and its
role as a therapeutic target for treatment of cachexia and cancer.
Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 7:287–302. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Hsu CP and Chung YC: Influence of
interleukin-6 on the invasiveness of human colorectal carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 26:4607–4614. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Sansone P and Bromberg J: Targeting the
interleukin-6/Jak/Stat pathway in human malignancies. J Clin Oncol.
30:1005–1014. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Hudes G, Tagawa ST, Whang YE, et al: A
phase 1 study of a chimeric monoclonal antibody against
interleukin-6, siltuximab, combined with docetaxel in patients with
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Invest New Drugs.
31:669–676. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51.
|
Guo Y, Nemeth J, O’Brien C, et al: Effects
of siltuximab on the IL-6-induced signaling pathway in ovarian
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:5759–5769. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Rossi JF, Negrier S, James ND, et al: A
phase I/II study of siltuximab (CNTO 328), an anti-interleukin-6
monoclonal antibody, in metastatic renal cell cancer. Br J Cancer.
103:1154–1162. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53.
|
Hunsucker SA, Magarotto V, Kuhn DJ, et al:
Blockade of interleukin-6 signalling with siltuximab enhances
melphalan cytotoxicity in preclinical models of multiple myeloma.
Br J Haematol. 152:579–592. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Voorhees PM, Chen Q, Small GW, et al:
Targeted inhibition of interleukin-6 with CNTO 328 sensitizes
pre-clinical models of multiple myeloma to dexamethasone-mediated
cell death. Br J Haematol. 145:481–490. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Voorhees PM, Manges RF, Sonneveld P, et
al: A phase 2 multicentre study of siltuximab, an
anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody, in patients with relapsed
or refractory multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 161:357–366. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Shinriki S, Jono H, Ota K, et al:
Humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody suppresses tumor
angiogenesis and in vivo growth of human oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5426–5434. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Kudo M, Jono H, Shinriki S, et al:
Antitumor effect of humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody
(tocilizumab) on glioma cell proliferation. Laboratory
investigation. J Neurosurg. 111:219–225. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Yoshio-Hoshino N, Adachi Y, Aoki C,
Pereboev A, Curiel DT and Nishimoto N: Establishment of a new
interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor inhibitor applicable to the gene
therapy for IL-6-dependent tumor. Cancer Res. 67:871–875. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Hsu CP, Chen YL, Huang CC, et al:
Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody inhibits the progression in
human colon carcinoma cells. Eur J Clin Invest. 41:277–284. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|