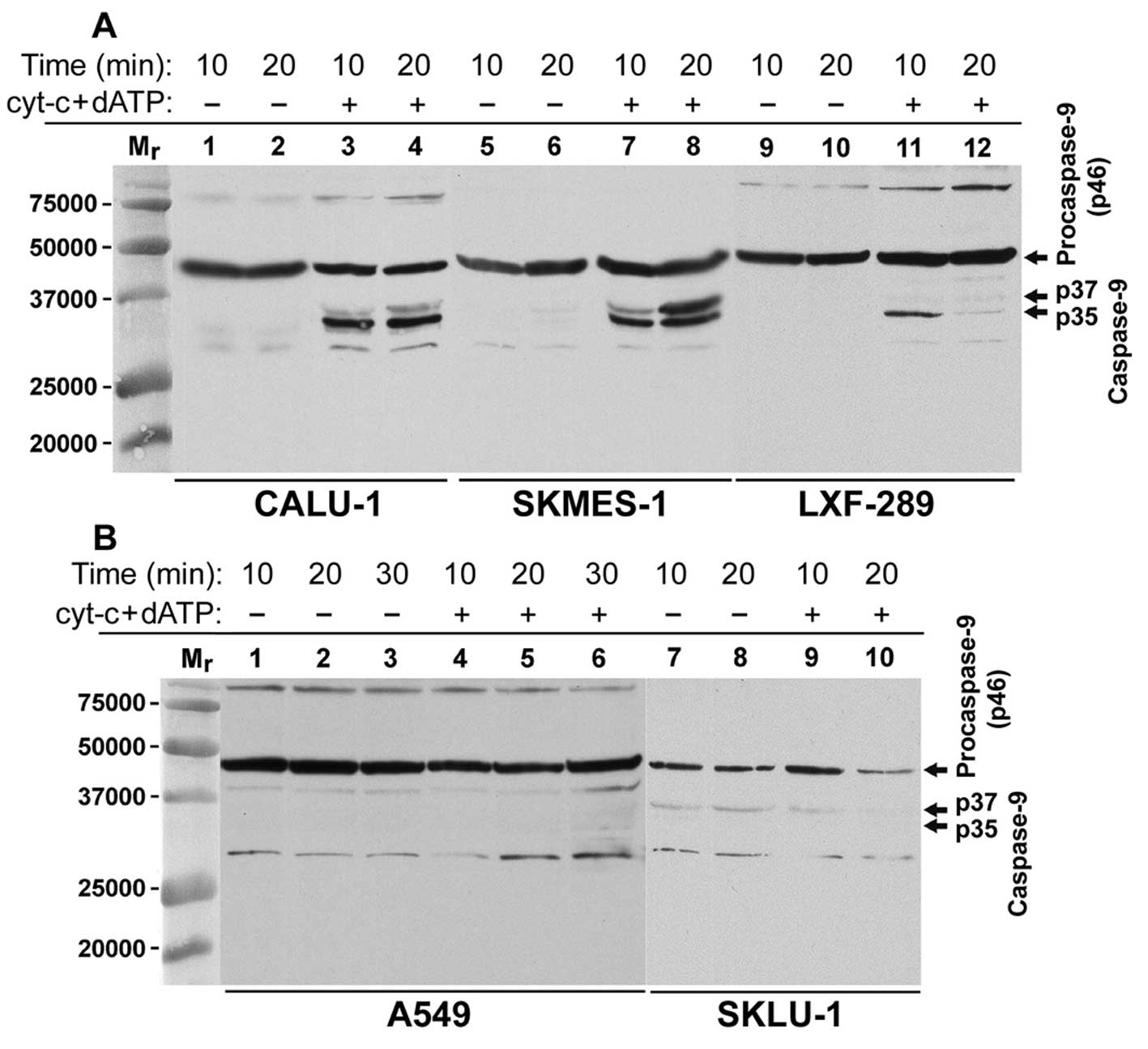
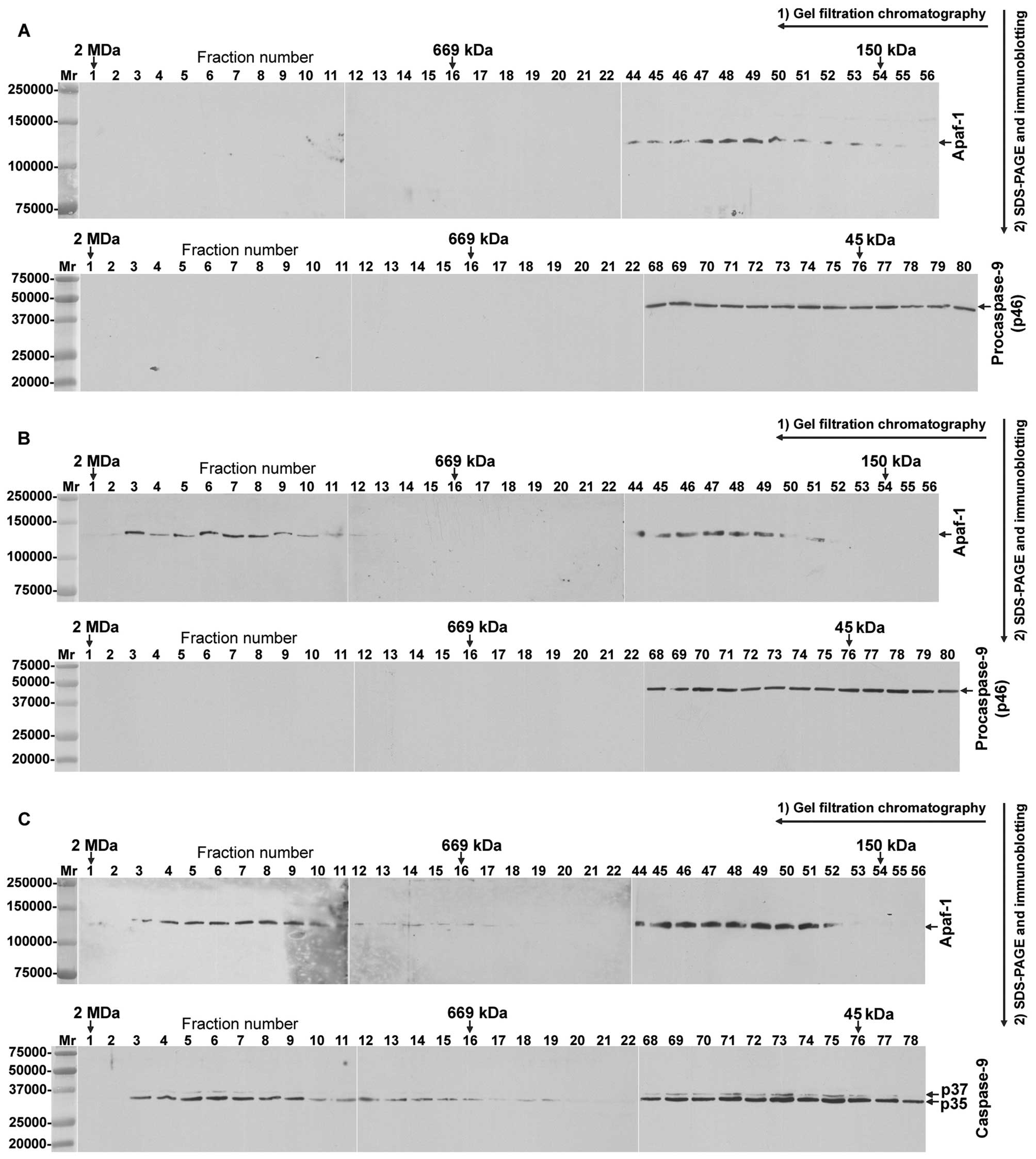
|
1.
|
Cecconi F, Alvarez-Bolado G, Meyer BI,
Roth KA and Gruss P: Apaf1 (CED-4 homolog) regulates programmed
cell death in mammalian development. Cell. 94:727–737. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Hao Z, Duncan GS, Chang CC, Elia A, Fang
M, Wakeham A, Okada H, Calzascia T, Jang Y, You-Ten A, Yeh WC,
Ohashi P, Wang X and Mak TW: Specific ablation of the apoptotic
functions of cytochrome C reveals a differential requirement for
cytochrome C and Apaf-1 in apoptosis. Cell. 121:579–591. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Soengas MS, Capodieci P, Polsky D, Mora J,
Esteller M, Opitz-Araya X, McCombie R, Herman JG, Gerald WL,
Lazebnik YA, Cordon-Cardo C and Lowe SW: Inactivation of the
apoptosis effector Apaf-1 in malignant melanoma. Nature.
409:207–211. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Nguyen JT and Wells JA: Direct activation
of the apoptosis machinery as a mechanism to target cancer cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:7533–7538. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Jiang X and Wang X: Cytochrome C-mediated
apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 73:87–106. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Hausmann G, O’Reilly LA, van Driel R,
Beaumont JG, Strasser A, Adams JM and Huang DC: Pro-apoptotic
apoptosis protease-activating factor 1 (Apaf-1) has a cytoplasmic
localization distinct from Bcl-2 or Bcl-x(L). J Cell Biol.
149:623–634. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Benedict MA, Hu Y, Inohara N and Nunez G:
Expression and functional analysis of Apaf-1 isoforms. Extra Wd-40
repeat is required for cytochrome c binding and regulated
activation of procaspase-9. J Biol Chem. 275:8461–8468. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Yuan S and Akey CW: Apoptosome structure,
assembly, and procaspase activation. Structure. 21:501–515. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Yuan S, Topf M, Reubold TF, Eschenburg S
and Akey CW: Changes in Apaf-1 conformation that drive apoptosome
assembly. Biochemistry. 52:2319–2327. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Malladi S, Challa-Malladi M, Fearnhead HO
and Bratton SB: The Apaf-1•procaspase-9 apoptosome complex
functions as a proteolytic-based molecular timer. EMBO J.
28:1916–1925. 2009.
|
|
11.
|
Yuan S, Yu X, Asara JM, Heuser JE, Ludtke
SJ and Akey CW: The holo-apoptosome: activation of procaspase-9 and
interactions with caspase-3. Structure. 19:1084–1096. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Hu Q, Wu D, Chen W, Yan Z and Shi Y:
Proteolytic processing of caspase-9 zymogen is required for
apoptosome-mediated activation of caspase-9. J Biol Chem.
288:15142–15147. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Twiddy D, Brown DG, Adrain C, Jukes R,
Martin SJ, Cohen GM, Macfarlane M and Cain K: Pro-apoptotic
proteins released from the mitochondria regulate the protein
composition and caspase-processing activity of the native
Apaf-1/caspase-9 apoptosome complex. J Biol Chem. 279:19665–19682.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Twiddy D, Cohen GM, Macfarlane M and Cain
K: Caspase-7 is directly activated by the approximately 700-kDa
apoptosome complex and is released as a stable XIAP-caspase-7
approximately 200-kDa complex. J Biol Chem. 281:3876–3888. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Schafer ZT and Kornbluth S: The
apoptosome: physiological, developmental, and pathological modes of
regulation. Dev Cell. 10:549–561. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Bratton SB and Salvesen GS: Regulation of
the Apaf-1-caspase-9 apoptosome. J Cell Sci. 123:3209–3214. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Liu JR, Opipari AW, Tan L, Jiang Y, Zhang
Y, Tang H and Nunez G: Dysfunctional apoptosome activation in
ovarian cancer: implications for chemoresistance. Cancer Res.
62:924–931. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Corvaro M, Fuoco C, Wagner M and Cecconi
F: Analysis of apoptosome dysregulation in pancreatic cancer and of
its role in chemoresistance. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:209–217. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Christoph F, Hinz S, Weikert S,
Kempkensteffen C, Schostak M, Miller K and Schrader M: Comparative
promoter methylation analysis of p53 target genes in urogenital
cancers. Urol Int. 80:398–404. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Tan L, Kwok RP, Shukla A, Kshirsagar M,
Zhao L, Opipari AW Jr and Liu JR: Trichostatin A restores Apaf-1
function in chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells. Cancer.
117:784–794. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21.
|
Schafer ZT, Parrish AB, Wright KM,
Margolis SS, Marks JR, Deshmukh M and Kornbluth S: Enhanced
sensitivity to cytochrome c-induced apoptosis mediated by PHAPI in
breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 66:2210–2218. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Johnson CE, Huang YY, Parrish AB, Smith
MI, Vaughn AE, Zhang Q, Wright KM, Van Dyke T, Wechsler-Reya RJ,
Kornbluth S and Deshmukh M: Differential Apaf-1 levels allow
cytochrome c to induce apoptosis in brain tumors but not in normal
neural tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:20820–20825. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Huang Q, Li F, Liu X, Li W, Shi W, Liu FF,
O’Sullivan B, He Z, Peng Y, Tan AC, Zhou L, Shen J, Han G, Wang XJ,
Thorburn J, Thorburn A, Jimeno A, Raben D, Bedford JS and Li CY:
Caspase 3-mediated stimulation of tumor cell repopulation during
cancer radiotherapy. Nat Med. 17:860–866. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Zimmerman MA, Huang Q, Li F, Liu X and Li
CY: Cell death-stimulated cell proliferation: a tissue regeneration
mechanism usurped by tumors during radiotherapy. Semin Radiat
Oncol. 23:288–295. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Joseph B, Marchetti P, Formstecher P,
Kroemer G, Lewensohn R and Zhivotovsky B: Mitochondrial dysfunction
is an essential step for killing of non-small cell lung carcinomas
resistant to conventional treatment. Oncogene. 21:65–77. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Gomyo Y, Sasaki J, Branch C, Roth JA and
Mukhopadhyay T: 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine upregulates caspase-9
expression cooperating with p53-induced apoptosis in human lung
cancer cells. Oncogene. 23:6779–6787. 2004.
|
|
27.
|
Krepela E, Prochazka J, Liu X, Fiala P and
Kinkor Z: Increased expression of Apaf-1 and procaspase-3 and the
functionality of intrinsic apoptosis apparatus in non-small cell
lung carcinoma. Biol Chem. 385:153–168. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Hoffarth S, Zitzer A, Wiewrodt R, Hahnel
PS, Beyer V, Kreft A, Biesterfeld S and Schuler M: pp32/PHAPI
determines the apoptosis response of non-small-cell lung cancer.
Cell Death Differ. 15:161–170. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Ekedahl J, Joseph B, Grigoriev MY, Muller
M, Magnusson C, Lewensohn R and Zhivotovsky B: Expression of
inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in small- and non-small-cell lung
carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 279:277–290. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Bartling B, Lewensohn R and Zhivotovsky B:
Endogenously released Smac is insufficient to mediate cell death of
human lung carcinoma in response to etoposide. Exp Cell Res.
298:83–95. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Checinska A, Giaccone G, Hoogeland BS,
Ferreira CG, Rodriguez JA and Kruyt FA: TUCAN/CARDINAL/CARD8 and
apoptosis resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells. BMC
Cancer. 6:1662006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Checinska A, Hoogeland BS, Rodriguez JA,
Giaccone G and Kruyt FA: Role of XIAP in inhibiting
cisplatin-induced caspase activation in non-small cell lung cancer
cells: a small molecule Smac mimic sensitizes for
chemotherapy-induced apoptosis by enhancing caspase-3 activation.
Exp Cell Res. 313:1215–1224. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33.
|
Cain K, Bratton SB, Langlais C, Walker G,
Brown DG, Sun XM and Cohen GM: Apaf-1 oligomerizes into
biologically active approximately 700-kDa and inactive
approximately 1.4-MDa apoptosome complexes. J Biol Chem.
275:6067–6070. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Kim HE, Du F, Fang M and Wang X: Formation
of apoptosome is initiated by cytochrome c-induced dATP hydrolysis
and subsequent nucleotide exchange on Apaf-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 102:17545–17550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Kim HE, Jiang X, Du F and Wang X: PHAPI,
CAS, and Hsp70 promote apoptosome formation by preventing Apaf-1
aggregation and enhancing nucleotide exchange on Apaf-1. Mol Cell.
30:239–247. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Müller-Hermelink
HK and Harris CC: Pathology & Genetics: Tumours of the Lung,
Pleura, Thymus and Heart. IARC Press; Lyon: 2004
|
|
37.
|
Detterbeck FC, Boffa DJ and Tanoue LT: The
new lung cancer staging system. Chest. 136:260–271. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38.
|
Srinivasula SM, Datta P, Fan XJ,
Fernandes-Alnemri T, Huang Z and Alnemri ES: Molecular determinants
of the caspase-promoting activity of Smac/DIABLO and its role in
the death receptor pathway. J Biol Chem. 275:36152–36157. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Schägger H and von Jagow G: Tricine-sodium
dodecyl sulfatepolyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the
separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal
Biochem. 166:368–379. 1987.
|
|
40.
|
Krepela E, Dankova P, Moravcikova E,
Krepelova A, Prochazka J, Cermak J, Schützner J, Zatloukal P and
Benkova K: Increased expression of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins,
survivin and XIAP, in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
35:1449–1462. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia
AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ and
Klenk DC: Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal
Biochem. 150:76–85. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42.
|
Bratton SB, Lewis J, Butterworth M,
Duckett CS and Cohen GM: XIAP inhibition of caspase-3 preserves its
association with the Apaf-1 apoptosome and prevents CD95- and
Bax-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 9:881–892. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Shiozaki EN, Chai J, Rigotti DJ, Riedl SJ,
Li P, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Fairman R and Shi Y: Mechanism of
XIAP-mediated inhibition of caspase-9. Mol Cell. 11:519–527. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Scott FL, Denault JB, Riedl SJ, Shin H,
Renatus M and Salvesen GS: XIAP inhibits caspase-3 and -7 using two
binding sites: evolutionarily conserved mechanism of IAPs. EMBO J.
24:645–655. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Eckelman BP, Salvesen GS and Scott FL:
Human inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: why XIAP is the black sheep
of the family. EMBO Rep. 7:988–994. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Denault JB, Eckelman BP, Shin H, Pop C and
Salvesen GS: Caspase 3 attenuates XIAP (X-linked inhibitor of
apoptosis protein)-mediated inhibition of caspase 9. Biochem J.
405:11–19. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Chua BT, Guo K and Li P: Direct cleavage
by the calcium-activated protease calpain can lead to inactivation
of caspases. J Biol Chem. 275:5131–5135. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48.
|
Allan LA and Clarke PR: Apoptosis and
autophagy: regulation of caspase-9 by phosphorylation. FEBS J.
276:6063–6073. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49.
|
Kim J, Parrish AB, Kurokawa M, Matsuura K,
Freel CD, Andersen JL, Johnson CE and Kornbluth S: Rsk-mediated
phosphorylation and 14-3-3varepsilon binding of Apaf-1 suppresses
cytochrome c-induced apoptosis. EMBO J. 31:1279–1292. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50.
|
Martin MC, Allan LA, Lickrish M, Sampson
C, Morrice N and Clarke PR: Protein kinase A regulates caspase-9
activation by Apaf-1 downstream of cytochrome c. J Biol Chem.
280:15449–15455. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51.
|
White SR: Apoptosis and the airway
epithelium. J Allergy (Cairo). 2011.948406:2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Srinivasula SM, Hegde R, Saleh A, Datta P,
Shiozaki E, Chai J, Lee RA, Robbins PD, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Shi Y
and Alnemri ES: A conserved XIAP-interaction motif in caspase-9 and
Smac/DIABLO regulates caspase activity and apoptosis. Nature.
410:112–116. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|