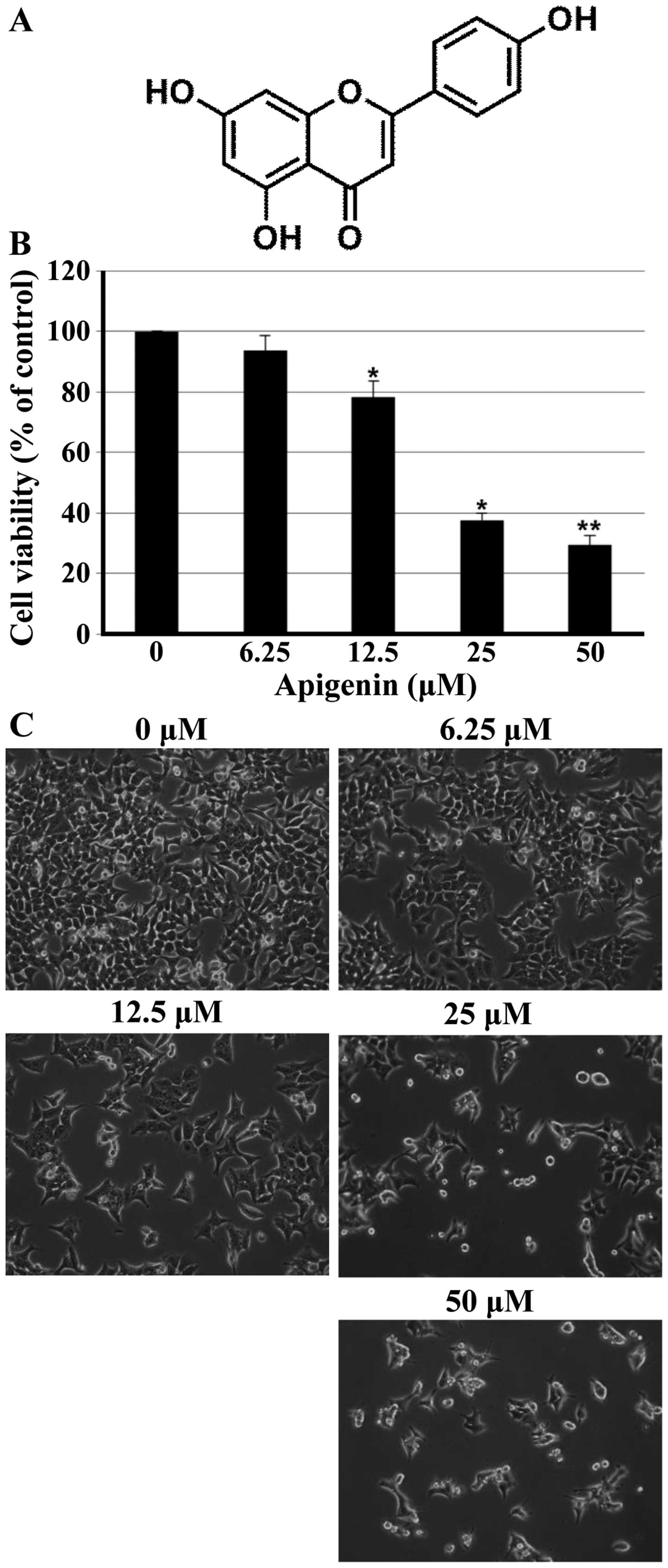
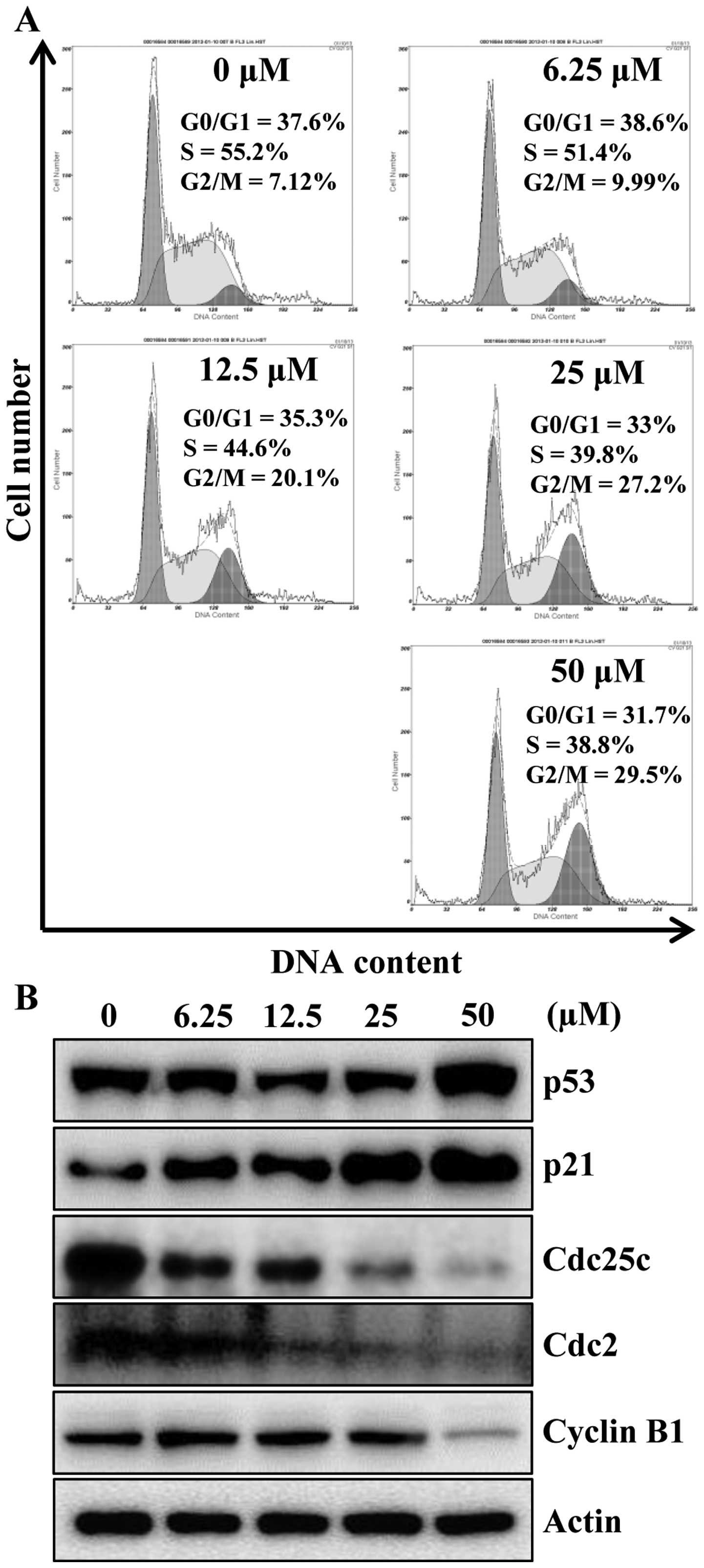
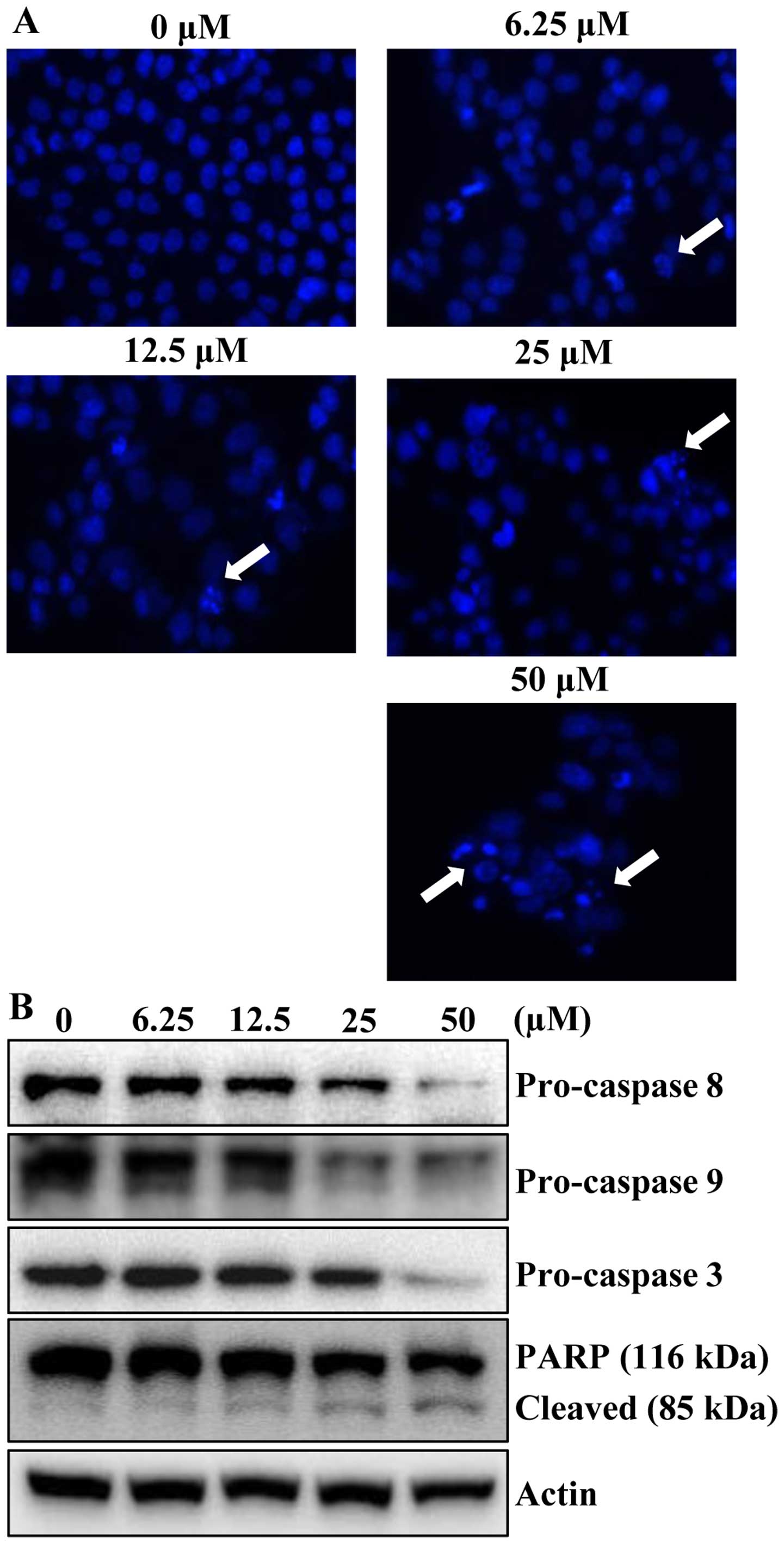
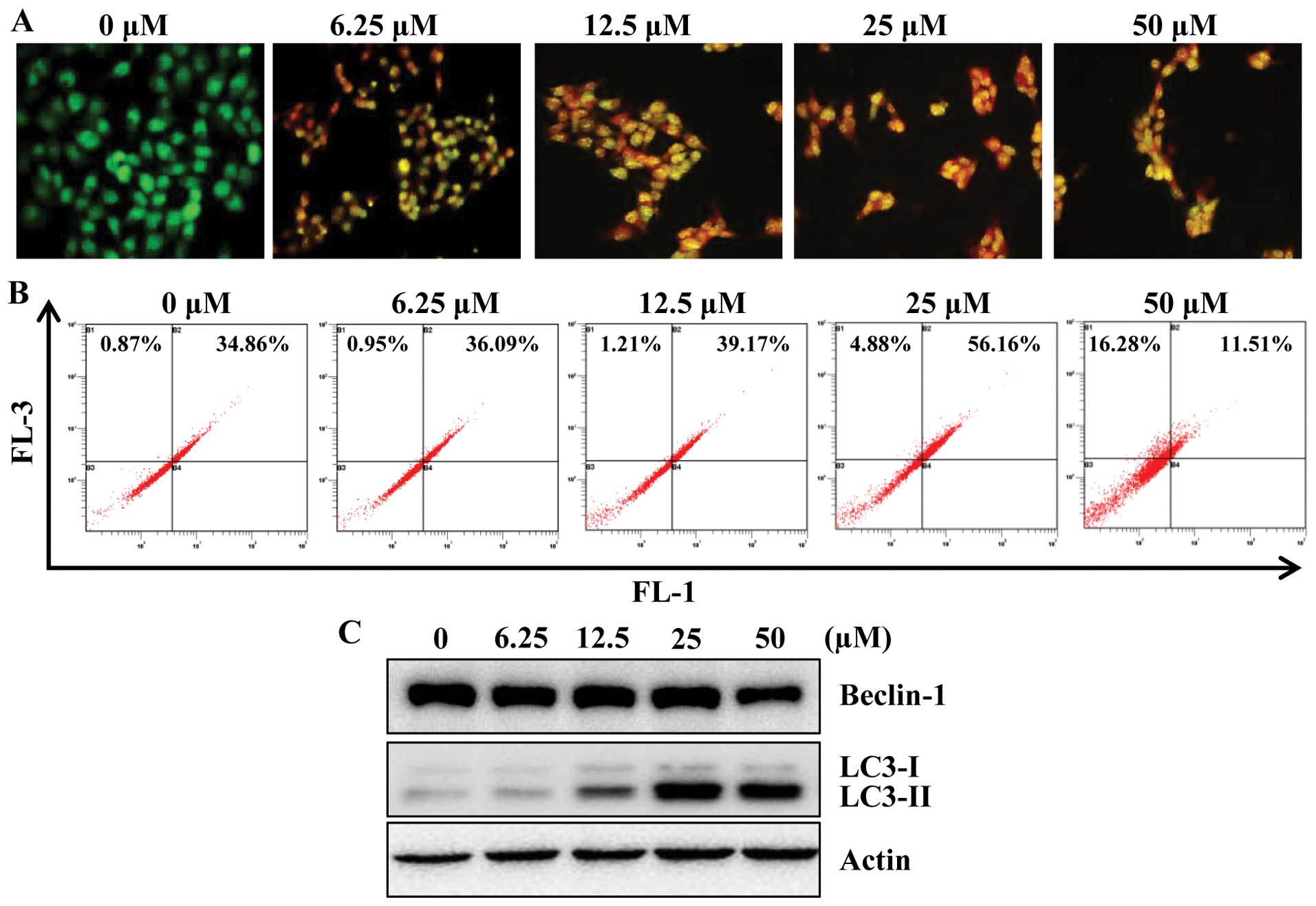
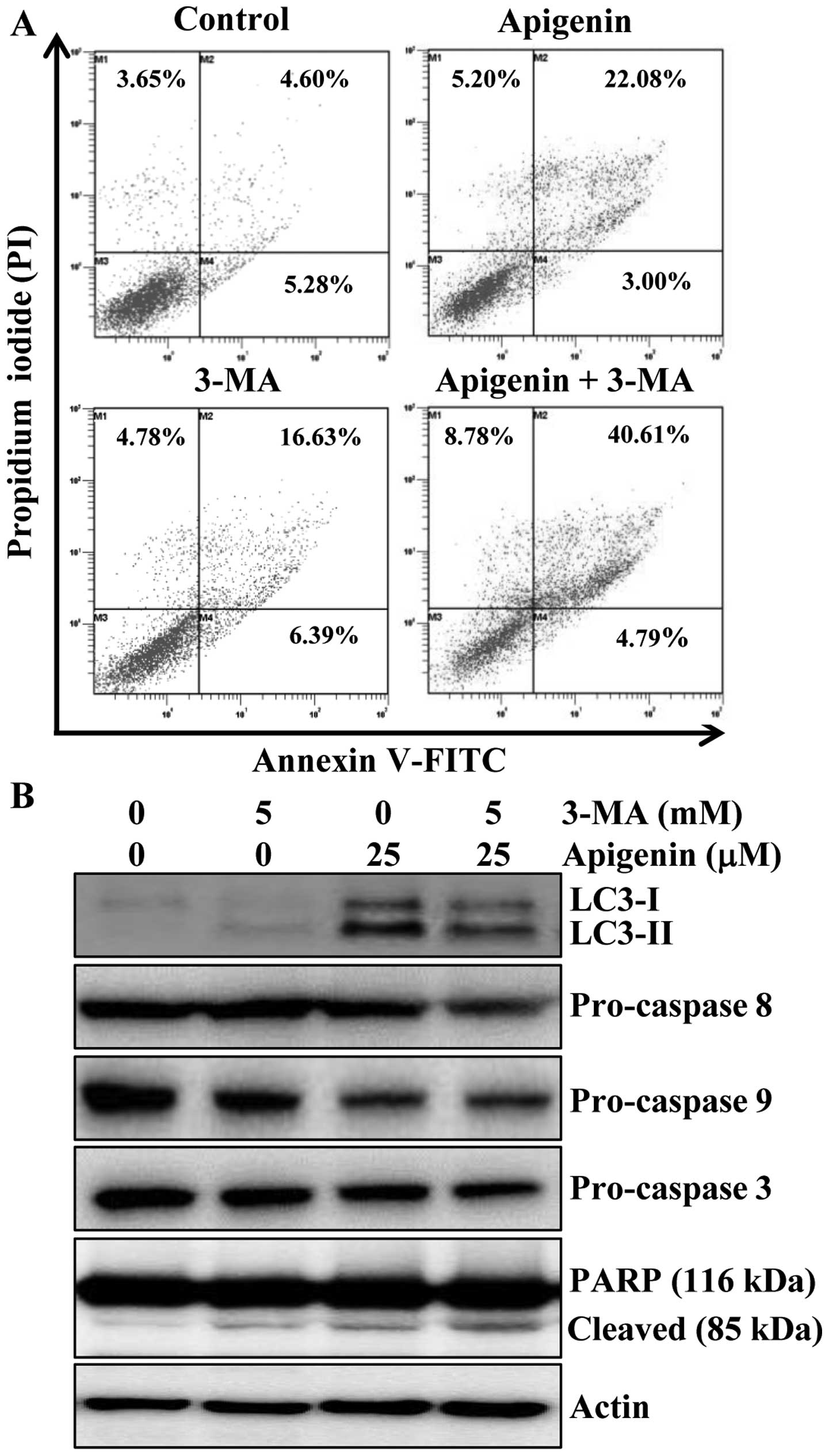
|
1.
|
Wang W, Heideman L, Chung CS, Pelling JC,
Koehler KJ and Birt DF: Cell-cycle arrest at G2/M and growth
inhibition by apigenin in human colon carcinoma cell lines. Mol
Carcinog. 28:102–110. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Wu DG, Yu P, Li JW, et al: Apigenin
potentiates the growth inhibitory effects by IKK-beta-mediated
NF-kappaB activation in pancreatic cancer cells. Toxicol Lett.
224:157–164. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Maggioni D, Garavello W, Rigolio R,
Pignataro L, Gaini R and Nicolini G: Apigenin impairs oral squamous
cell carcinoma growth in vitro inducing cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 43:1675–1682. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Das S, Das J, Samadder A, Boujedaini N and
Khuda-Bukhsh AR: Apigenin-induced apoptosis in A375 and A549 cells
through selective action and dysfunction of mitochondria. Exp Biol
Med (Maywood). 237:1433–1448. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Jayasooriya RG, Kang SH, Kang CH, et al:
Apigenin decreases cell viability and telomerase activity in human
leukemia cell lines. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:2605–2611. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
McVean M, Weinberg WC and Pelling JC: A
p21(waf1)-independent pathway for inhibitory phosphorylation of
cyclin-dependent kinase p34(cdc2) and concomitant G(2)/M arrest by
the chemopreventive flavonoid apigenin. Mol Carcinog. 33:36–43.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Zhu Y, Mao Y, Chen H, et al: Apigenin
promotes apoptosis, inhibits invasion and induces cell cycle arrest
of T24 human bladder cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 13:542013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Kim SH, Kang JG, Kim CS, et al: Apigenin
induces c-Myc-mediated apoptosis in FRO anaplastic thyroid
carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 369:130–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Mirzoeva S, Kim ND, Chiu K, Franzen CA,
Bergan RC and Pelling JC: Inhibition of HIF-1 alpha and VEGF
expression by the chemopreventive bioflavonoid apigenin is
accompanied by Akt inhibition in human prostate carcinoma PC3-M
cells. Mol Carcinog. 47:686–700. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Horinaka M, Yoshida T, Shiraishi T, Nakata
S, Wakada M and Sakai T: The dietary flavonoid apigenin sensitizes
malignant tumor cells to tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:945–951. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Xu Y, Xin Y, Diao Y, et al: Synergistic
effects of apigenin and paclitaxel on apoptosis of cancer cells.
PLoS One. 6:e291692011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Shao H, Jing K, Mahmoud E, Huang H, Fang X
and Yu C: Apigenin sensitizes colon cancer cells to antitumor
activity of ABT-263. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:2640–2650. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Chan LP, Chou TH, Ding HY, et al: Apigenin
induces apoptosis via tumor necrosis factor receptor- and
Bcl-2-mediated pathway and enhances susceptibility of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma to 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1820:1081–1091. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Mizushima N: Autophagy: process and
function. Genes Dev. 21:2861–2873. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Shintani T and Klionsky DJ: Autophagy in
health and disease: a double-edged sword. Science. 306:990–995.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Xie Z and Klionsky DJ: Autophagosome
formation: core machinery and adaptations. Nat Cell Biol.
9:1102–1109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Liang XH, Jackson S, Seaman M, et al:
Induction of autophagy and inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1.
Nature. 402:672–676. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Ng G and Huang J: The significance of
autophagy in cancer. Mol Carcinog. 43:183–187. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Gozuacik D and Kimchi A: Autophagy as a
cell death and tumor suppressor mechanism. Oncogene. 23:2891–2906.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Jung KW, Park S, Kong HJ, et al: Cancer
statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence
in 2009. Cancer Res Treat. 44:11–24. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Shin A, Kim KZ, Jung KW, et al: Increasing
trend of colorectal cancer incidence in Korea, 1999–2009. Cancer
Res Treat. 44:219–226. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Huerta S, Goulet EJ and Livingston EH:
Colon cancer and apoptosis. Am J Surg. 191:517–526. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Kundu M and Thompson CB: Autophagy: basic
principles and relevance to disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 3:427–455.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Lin JF, Tsai TF, Liao PC, et al: Benzyl
isothiocyanate induces protective autophagy in human prostate
cancer cells via inhibition of mTOR signaling. Carcinogenesis.
34:406–414. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Cheng P, Ni Z, Dai X, et al: The novel
BH-3 mimetic apogossypolone induces Beclin-1- and ROS-mediated
autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis.
4:e4892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Cao X, Liu B, Cao W, et al: Autophagy
inhibition enhances apigenin-induced apoptosis in human breast
cancer cells. Chin J Cancer Res. 25:212–222. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Paglin S, Hollister T, Delohery T, et al:
A novel response of cancer cells to radiation involves autophagy
and formation of acidic vesicles. Cancer Res. 61:439–444.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Klionsky DJ, Abeliovich H, Agostinis P, et
al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for
monitoring autophagy in higher eukaryotes. Autophagy. 4:151–175.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31.
|
Carew JS, Nawrocki ST and Cleveland JL:
Modulating autophagy for therapeutic benefit. Autophagy. 3:464–467.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Shukla S and Gupta S: Apigenin-induced
cell cycle arrest is mediated by modulation of MAPK, PI3K-Akt, and
loss of cyclin D1 associated retinoblastoma dephosphorylation in
human prostate cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 6:1102–1114. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Van Dross RT, Hong X and Pelling JC:
Inhibition of TPA-induced cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression by
apigenin through downregulation of Akt signal transduction in human
keratinocytes. Mol Carcinog. 44:83–91. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
King JC, Lu QY, Li G, et al: Evidence for
activation of mutated p53 by apigenin in human pancreatic cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1823:593–604. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 apoptotic
switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene. 26:1324–1337.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Harhaji-Trajkovic L, Vilimanovich U,
Kravic-Stevovic T, Bumbasirevic V and Trajkovic V: AMPK-mediated
autophagy inhibits apoptosis in cisplatin-treated tumour cells. J
Cell Mol Med. 13:3644–3654. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Nishikawa T, Tsuno NH, Okaji Y, et al:
Inhibition of autophagy potentiates sulforaphane-induced apoptosis
in human colon cancer cells. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:592–602. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Galluzzi L, Aaronson SA, Abrams J, et al:
Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring
cell death in higher eukaryotes. Cell Death Differ. 16:1093–1107.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39.
|
Fang J, Xia C, Cao Z, Zheng JZ, Reed E and
Jiang BH: Apigenin inhibits VEGF and HIF-1 expression via
PI3K/AKT/p70S6K1 and HDM2/p53 pathways. FASEB J. 19:342–353. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Shingu T, Fujiwara K, Bogler O, et al:
Inhibition of autophagy at a late stage enhances imatinib-induced
cytotoxicity in human malignant glioma cells. Int J Cancer.
124:1060–1071. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Li J, Hou N, Faried A, Tsutsumi S and
Kuwano H: Inhibition of autophagy augments 5-fluorouracil
chemotherapy in human colon cancer in vitro and in vivo model. Eur
J Cancer. 46:1900–1909. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Li J, Hou N, Faried A, Tsutsumi S,
Takeuchi T and Kuwano H: Inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA enhances
the effect of 5-FU-induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Ann
Surg Oncol. 16:761–771. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|