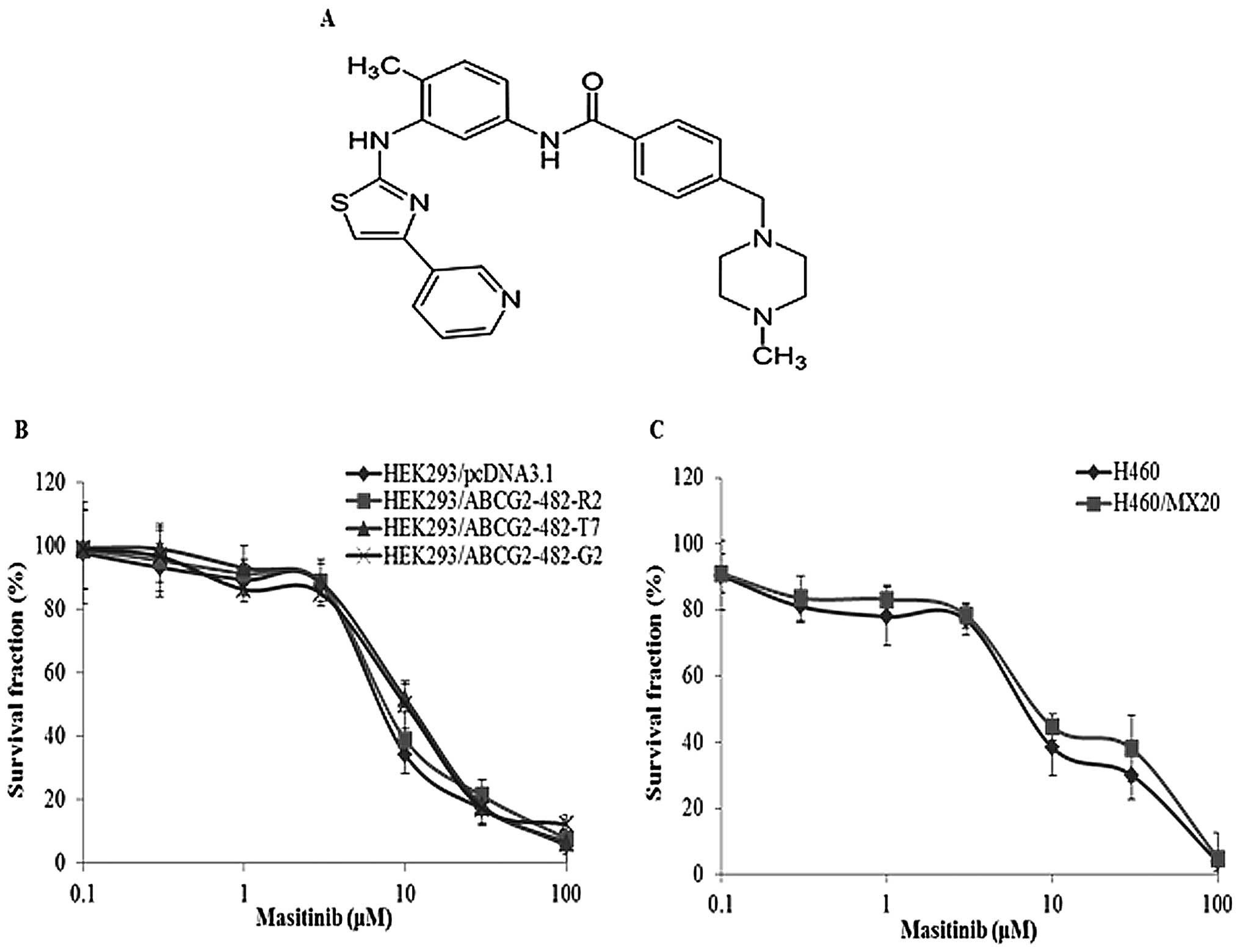
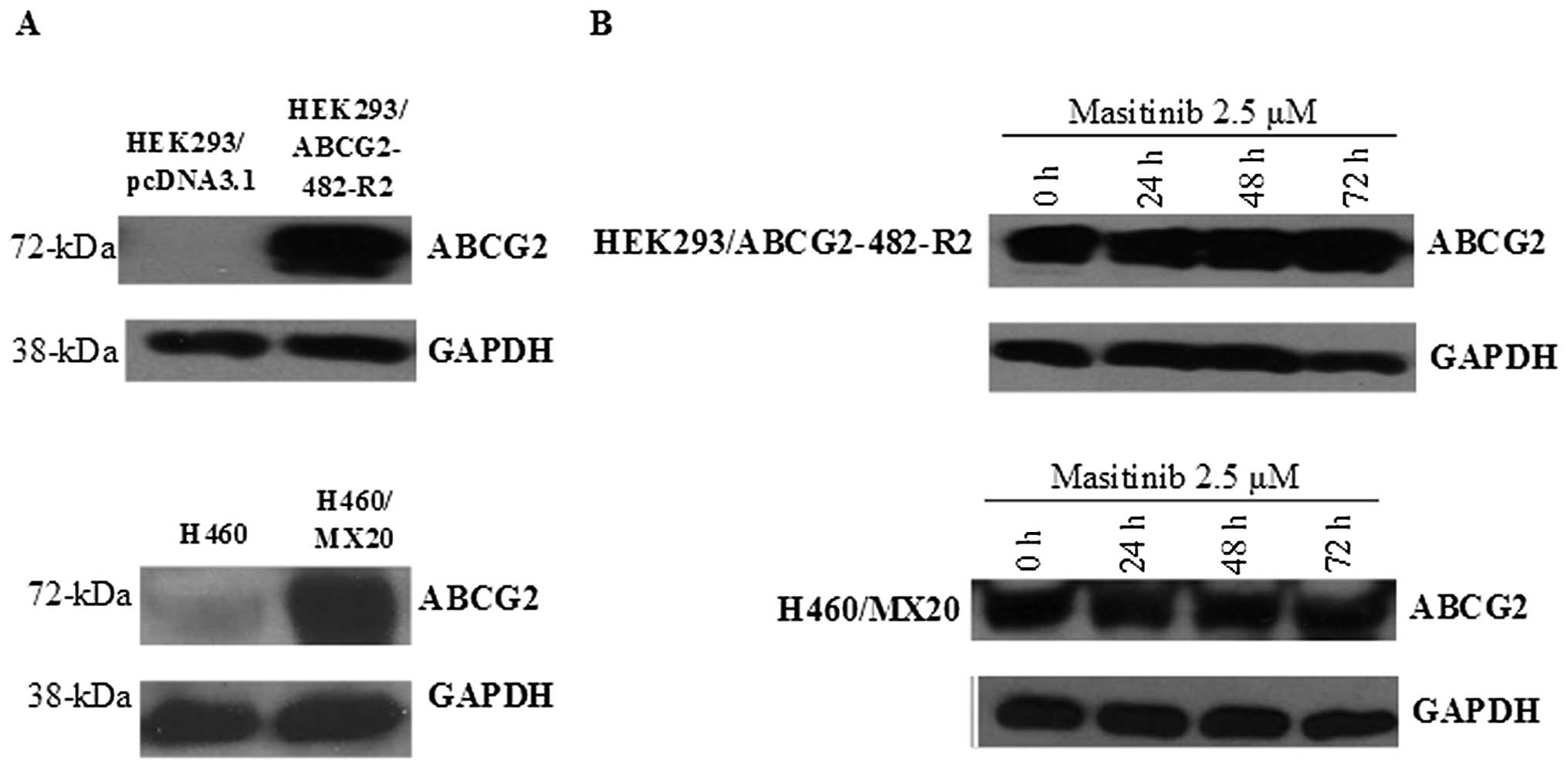
|
1.
|
Wu CP, Calcagno AM and Ambudkar SV:
Reversal of ABC drug transporter-mediated multidrug resistance in
cancer cells: evaluation of current strategies. Curr Mol Pharmacol.
1:93–105. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Gottesman MM: Mechanisms of cancer drug
resistance. Annu Rev Med. 53:615–627. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Quintieri L, Fantin M and Vizler C:
Identification of molecular determinants of tumor sensitivity and
resistance to anticancer drugs. Adv Exp Med Biol. 593:95–104. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Liu YY, Han TY, Giuliano AE and Cabot MC:
Ceramide glycosylation potentiates cellular multidrug resistance.
FASEB J. 15:719–730. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Lowe SW, Ruley HE, Jacks T and Housman DE:
p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer
agents. Cell. 74:957–967. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Synold TW, Dussault I and Forman BM: The
orphan nuclear receptor SXR coordinately regulates drug metabolism
and efflux. Nat Med. 7:584–590. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Deeley RG, Westlake C and Cole SP:
Transmembrane transport of endo- and xenobiotics by mammalian
ATP-binding cassette multidrug resistance proteins. Physiol Rev.
86:849–899. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Bradbury PA and Middleton MR: DNA repair
pathways in drug resistance in melanoma. Anticancer Drugs.
15:421–426. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Ambudkar SV, Kim IW, Xia D and Sauna ZE:
The A-loop, a novel conserved aromatic acid subdomain upstream of
the Walker A motif in ABC transporters, is critical for ATP
binding. FEBS Lett. 580:1049–1055. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Liu FS: Mechanisms of chemotherapeutic
drug resistance in cancer therapy - a quick review. Taiwan J Obstet
Gynecol. 48:239–244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Gillet JP, Efferth T and Remacle J:
Chemotherapy-induced resistance by ATP-binding cassette transporter
genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1775:237–262. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Linton KJ and Higgins CF: Structure and
function of ABC transporters: the ATP switch provides flexible
control. Pflugers Arch. 453:555–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Sodani K, Patel A, Kathawala RJ and Chen
ZS: Multidrug resistance associated proteins in multidrug
resistance. Chin J Cancer. 31:58–72. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Tiwari AK, Sodani K, Dai CL, Ashby CR Jr
and Chen ZS: Revisiting the ABCs of multidrug resistance in cancer
chemotherapy. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 12:570–594. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Mao Q and Unadkat JD: Role of the breast
cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) in drug transport. AAPS J.
7:E118–E133. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Suzuki M, Suzuki H, Sugimoto Y and
Sugiyama Y: ABCG2 transports sulfated conjugates of steroids and
xenobiotics. J Biol Chem. 278:22644–22649. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Rocchi E, Khodjakov A, Volk EL, et al: The
product of the ABC half-transporter gene ABCG2 (BCRP/MXR/ABCP) is
expressed in the plasma membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
271:42–46. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Maliepaard M, Scheffer GL, Faneyte IF, et
al: Subcellular localization and distribution of the breast cancer
resistance protein transporter in normal human tissues. Cancer Res.
61:3458–3464. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Cooray HC, Blackmore CG, Maskell L and
Barrand MA: Localisation of breast cancer resistance protein in
microvessel endothelium of human brain. Neuroreport. 13:2059–2063.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Doyle LA, Yang W, Abruzzo LV, et al: A
multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:15665–15670. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Schinkel AH and Jonker JW: Mammalian drug
efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family: an
overview. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 55:3–29. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Dean M and Allikmets R: Complete
characterization of the human ABC gene family. J Bioenerg Biomembr.
33:475–479. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Miyake K, Mickley L, Litman T, et al:
Molecular cloning of cDNAs which are highly overexpressed in
mitoxantrone-resistant cells: demonstration of homology to ABC
transport genes. Cancer Res. 59:8–13. 1999.
|
|
24.
|
Chen ZS, Robey RW, Belinsky MG, et al:
Transport of methotrexate, methotrexate polyglutamates, and
17beta-estradiol 17-(beta-D-glucuronide) by ABCG2: effects of
acquired mutations at R482 on methotrexate transport. Cancer Res.
63:4048–4054. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Honjo Y, Hrycyna CA, Yan QW, et al:
Acquired mutations in the MXR/BCRP/ABCP gene alter substrate
specificity in MXR/BCRP/ABCP-overexpressing cells. Cancer Res.
61:6635–6639. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Dai CL, Liang YJ, Wang YS, et al:
Sensitization of ABCG2-overexpressing cells to conventional
chemotherapeutic agent by sunitinib was associated with inhibiting
the function of ABCG2. Cancer Lett. 279:74–83. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Pozza A, Perez-Victoria JM, Sardo A,
Ahmed-Belkacem A and Di Pietro A: Purification of breast cancer
resistance protein ABCG2 and role of arginine-482. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 63:1912–1922. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Ejendal KF and Hrycyna CA: Multidrug
resistance and cancer: the role of the human ABC transporter ABCG2.
Curr Protein Pept Sci. 3:503–511. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Padmanabhan R, Chen KG, Gillet JP, et al:
Regulation and expression of the ATP-binding cassette transporter
ABCG2 in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 30:2175–2187.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Evseenko DA, Paxton JW and Keelan JA:
Independent regulation of apical and basolateral drug transporter
expression and function in placental trophoblasts by cytokines,
steroids, and growth factors. Drug Metab Dispos. 35:595–601. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Chen ZS, Aoki S, Komatsu M, et al:
Reversal of drug resistance mediated by multidrug resistance
protein (MRP) 1 by dual effects of agosterol A on MRP1 function.
Int J Cancer. 93:107–113. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Dai CL, Tiwari AK, Wu CP, et al: Lapatinib
(Tykerb, GW572016) reverses multidrug resistance in cancer cells by
inhibiting the activity of ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member
1 and G member 2. Cancer Res. 68:7905–7914. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33.
|
Kathawala RJ, Wang YJ, Ashby CR Jr and
Chen ZS: Recent advances regarding the role of ABC subfamily C
member 10 (ABCC10) in the efflux of antitumor drugs. Chin J Cancer.
Oct 9–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
34.
|
Deng W, Dai CL, Chen JJ, et al: Tandutinib
(MLN518) reverses multidrug resistance by inhibiting the efflux
activity of the multidrug resistance protein 7 (ABCC10). Oncol Rep.
29:2479–2485. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Szakacs G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA,
Booth-Genthe C and Gottesman MM: Targeting multidrug resistance in
cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:219–234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Yang D, Kathawala RJ, Chufan EE, et al:
Tivozanib reverses multidrug resistance mediated by ABCB1
(P-glycoprotein) and ABCG2 (BCRP). Future Oncol. Dec 3–2013.(Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
37.
|
Shen T, Kuang YH, Ashby CR, et al:
Imatinib and nilotinib reverse multidrug resistance in cancer cells
by inhibiting the efflux activity of the MRP7 (ABCC10). PLoS One.
4:e75202009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Tiwari AK, Sodani K, Wang SR, et al:
Nilotinib (AMN107, Tasigna) reverses multidrug resistance by
inhibiting the activity of the ABCB1/Pgp and ABCG2/BCRP/MXR
transporters. Biochem Pharmacol. 78:153–161. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Shi Z, Peng XX, Kim IW, et al: Erlotinib
(Tarceva, OSI-774) antagonizes ATP-binding cassette subfamily B
member 1 and ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2-mediated
drug resistance. Cancer Res. 67:11012–11020. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Vermersch P, Benrabah R, Schmidt N, et al:
Masitinib treatment in patients with progressive multiple
sclerosis: a randomized pilot study. BMC Neurol. 12:362012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Rommer PS and Stuve O: Management of
secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: prophylactic
treatment-past, present, and future aspects. Curr Treat Options
Neurol. 15:241–258. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Humbert M, de Blay F, Garcia G, et al:
Masitinib, a c-kit/PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor,
improves disease control in severe corticosteroid-dependent
asthmatics. Allergy. 64:1194–1201. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Lee-Fowler TM, Guntur V, Dodam J, Cohn LA,
DeClue AE and Reinero CR: The tyrosine kinase inhibitor masitinib
blunts airway inflammation and improves associated lung mechanics
in a feline model of chronic allergic asthma. Int Arch Allergy
Immunol. 158:369–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Tebib J, Mariette X, Bourgeois P, et al:
Masitinib in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis: results
of a multicentre, open-label, dose-ranging, phase 2a study.
Arthritis Res Ther. 11:R952009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Walker UA: More about masitinib. Arthritis
Res Ther. 11:1202009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46.
|
Georgin-Lavialle S, Lhermitte L, Suarez F,
et al: Mast cell leukemia: identification of a new c-Kit mutation,
dup(501–502) and response to masitinib, a c-Kit tyrosine kinase
inhibitor. Eur J Haematol. 89:47–52. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Paul C, Sans B, Suarez F, et al: Masitinib
for the treatment of systemic and cutaneous mastocytosis with
handicap: a phase 2a study. Am J Hematol. 85:921–925. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Le Cesne A, Blay JY, Bui BN, et al: Phase
II study of oral masitinib mesilate in imatinib-naive patients with
locally advanced or metastatic gastro-intestinal stromal tumour
(GIST). Eur J Cancer. 46:1344–1351. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Mitry E, Hammel P, Deplanque G, et al:
Safety and activity of masitinib in combination with gemcitabine in
patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 66:395–403. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Gottesman MM, Fojo T and Bates SE:
Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters.
Nat Rev Cancer. 2:48–58. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Kruh GD, Guo Y, Hopper-Borge E, Belinsky
MG and Chen ZS: ABCC10, ABCC11, and ABCC12. Pflugers Arch.
453:675–684. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Robey RW, Honjo Y, Morisaki K, et al:
Mutations at amino-acid 482 in the ABCG2 gene affect substrate and
antagonist specificity. Br J Cancer. 89:1971–1978. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Carmichael J, DeGraff WG, Gazdar AF, Minna
JD and Mitchell JB: Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based semiautomated
colorimetric assay: assessment of chemosensitivity testing. Cancer
Res. 47:936–942. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Hazai E and Bikadi Z: Homology modeling of
breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2). J Struct Biol. 162:63–74.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Alqawi O, Bates S and Georges E:
Arginine482 to threonine mutation in the breast cancer resistance
protein ABCG2 inhibits rhodamine 123 transport while increasing
binding. Biochem J. 382:711–716. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
Sun YL, Kathawala RJ, Singh S, et al:
Zafirlukast antagonizes ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member
2-mediated multidrug resistance. Anticancer Drugs. 23:865–873.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Litman T, Brangi M, Hudson E, et al: The
multidrug-resistant phenotype associated with overexpression of the
new ABC half-transporter, MXR (ABCG2). J Cell Sci. 113:2011–2021.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Schellens JH, Maliepaard M, Scheper RJ, et
al: Transport of topoisomerase I inhibitors by the breast cancer
resistance protein. Potential clinical implications. Ann NY Acad
Sci. 922:188–194. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Jonker JW, Smit JW, Brinkhuis RF, et al:
Role of breast cancer resistance protein in the bioavailability and
fetal penetration of topotecan. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:1651–1656.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60.
|
Nakamura Y, Oka M and Soda H: Gefitinib
(‘Iressa’, ZD1839), an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine
kinase inhibitor, reverses breast cancer resistance
protein/ABCG2-mediated drug resistance. Cancer Res. 65:1541–1546.
2005.
|
|
61.
|
Shukla S, Robey RW, Bates SE and Ambudkar
SV: Sunitinib (Sutent, SU11248), a small-molecule receptor tyrosine
kinase inhibitor, blocks function of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC)
transporters P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and ABCG2. Drug Metab Dispos.
37:359–365. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62.
|
Mi YJ, Liang YJ, Huang HB, et al: Apatinib
(YN968D1) reverses multidrug resistance by inhibiting the efflux
function of multiple ATP-binding cassette transporters. Cancer Res.
70:7981–7991. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Nicolle E, Boumendjel A, Macalou S, et al:
QSAR analysis and molecular modeling of ABCG2-specific inhibitors.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 61:34–46. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64.
|
An Y and Ongkeko WM: ABCG2: the key to
chemoresistance in cancer stem cells? Expert Opin Drug Metab
Toxicol. 5:1529–1542. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65.
|
Chen YJ, Huang WC, Wei YL, et al: Elevated
BCRP/ABCG2 expression confers acquired resistance to gefitinib in
wild-type EGFR-expressing cells. PLoS One. 6:e214282011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66.
|
Natarajan K, Xie Y, Baer MR and Ross DD:
Role of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) in cancer
drug resistance. Biochem Pharmacol. 83:1084–1103. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67.
|
Kerr ID, Haider AJ and Gelissen IC: The
ABCG family of membrane-associated transporters: you don’t have to
be big to be mighty. Br J Pharmacol. 164:1767–1779. 2011.
|
|
68.
|
Robey RW, Medina-Perez WY, Nishiyama K, et
al: Overexpression of the ATP-binding cassette half-transporter,
ABCG2 (Mxr/BCrp/ABCP1), in flavopiridol-resistant human breast
cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 7:145–152. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69.
|
Robey RW, Ierano C, Zhan Z and Bates SE:
The challenge of exploiting ABCG2 in the clinic. Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 12:595–608. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70.
|
Woodward OM, Kottgen A and Kottgen M: ABCG
transporters and disease. FEBS J. 278:3215–3225. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71.
|
Xu J, Peng H and Zhang JT: Human multidrug
transporter ABCG2, a target for sensitizing drug resistance in
cancer chemotherapy. Curr Med Chem. 14:689–701. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72.
|
Hang D, Dong HC, Ning T, Dong B, Hou DL
and Xu WG: Prognostic value of the stem cell markers CD133 and
ABCG2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis
Esophagus. 25:638–644. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73.
|
Li J, Li ZN, Du YJ, Li XQ, Bao QL and Chen
P: Expression of MRP1, BCRP, LRP, and ERCC1 in advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer: correlation with response to
chemotherapy and survival. Clin Lung Cancer. 10:414–421. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74.
|
Tsunoda S, Okumura T, Ito T, et al: ABCG2
expression is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology. 71:251–258. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75.
|
Bunting KD: ABC transporters as phenotypic
markers and functional regulators of stem cells. Stem Cells.
20:11–20. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76.
|
Kim M, Turnquist H, Jackson J, et al: The
multidrug resistance transporter ABCG2 (breast cancer resistance
protein 1) effluxes Hoechst 33342 and is overexpressed in
hematopoietic stem cells. Clin Cancer Res. 8:22–28. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77.
|
Kusuhara H and Sugiyama Y: ATP-binding
cassette, subfamily G (ABCG family). Pflugers Arch. 453:735–744.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78.
|
Ding XW, Wu JH and Jiang CP: ABCG2: a
potential marker of stem cells and novel target in stem cell and
cancer therapy. Life Sci. 86:631–637. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79.
|
Sung JM, Cho HJ, Yi H, et al:
Characterization of a stem cell population in lung cancer A549
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 371:163–167. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|