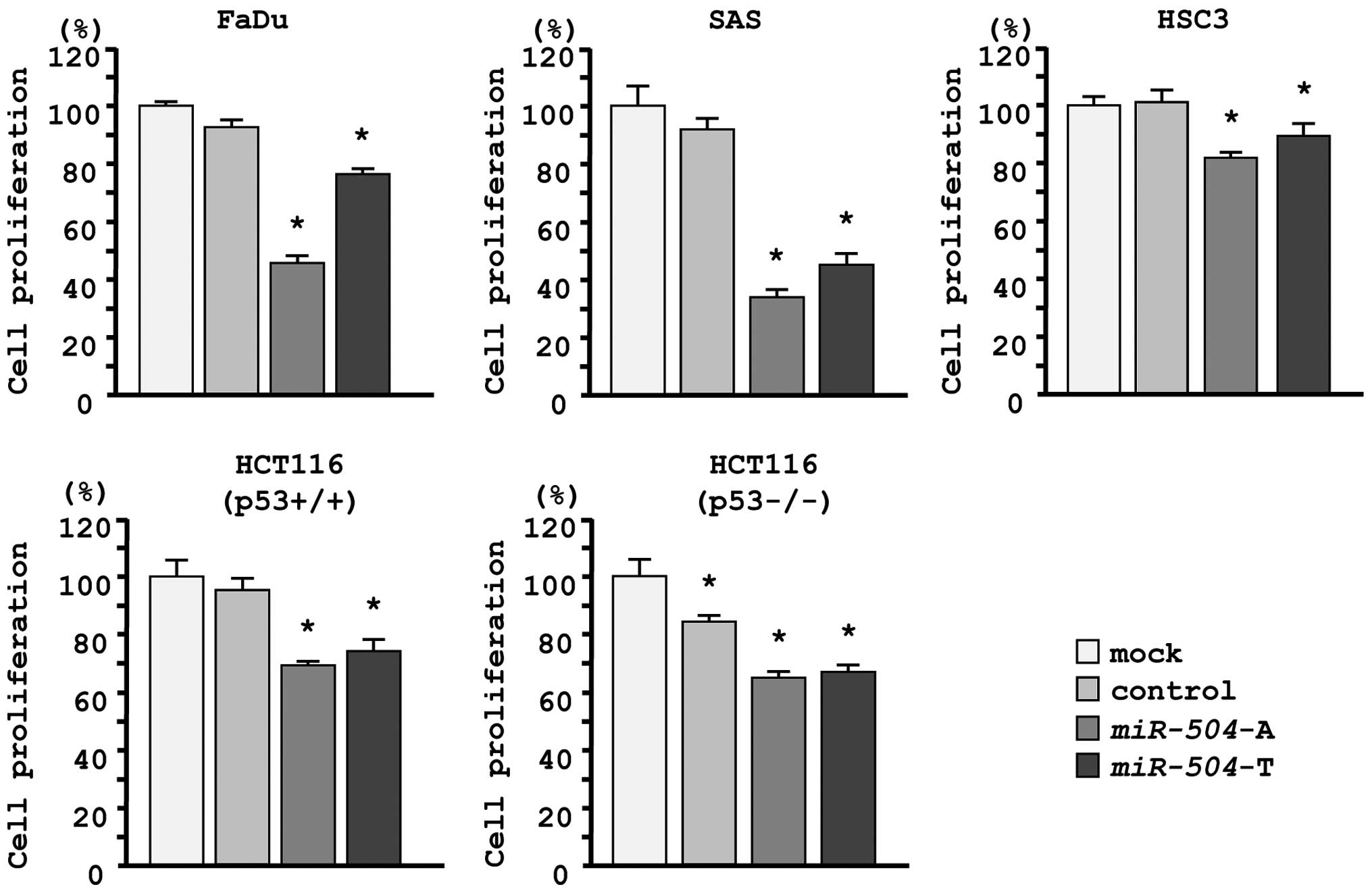
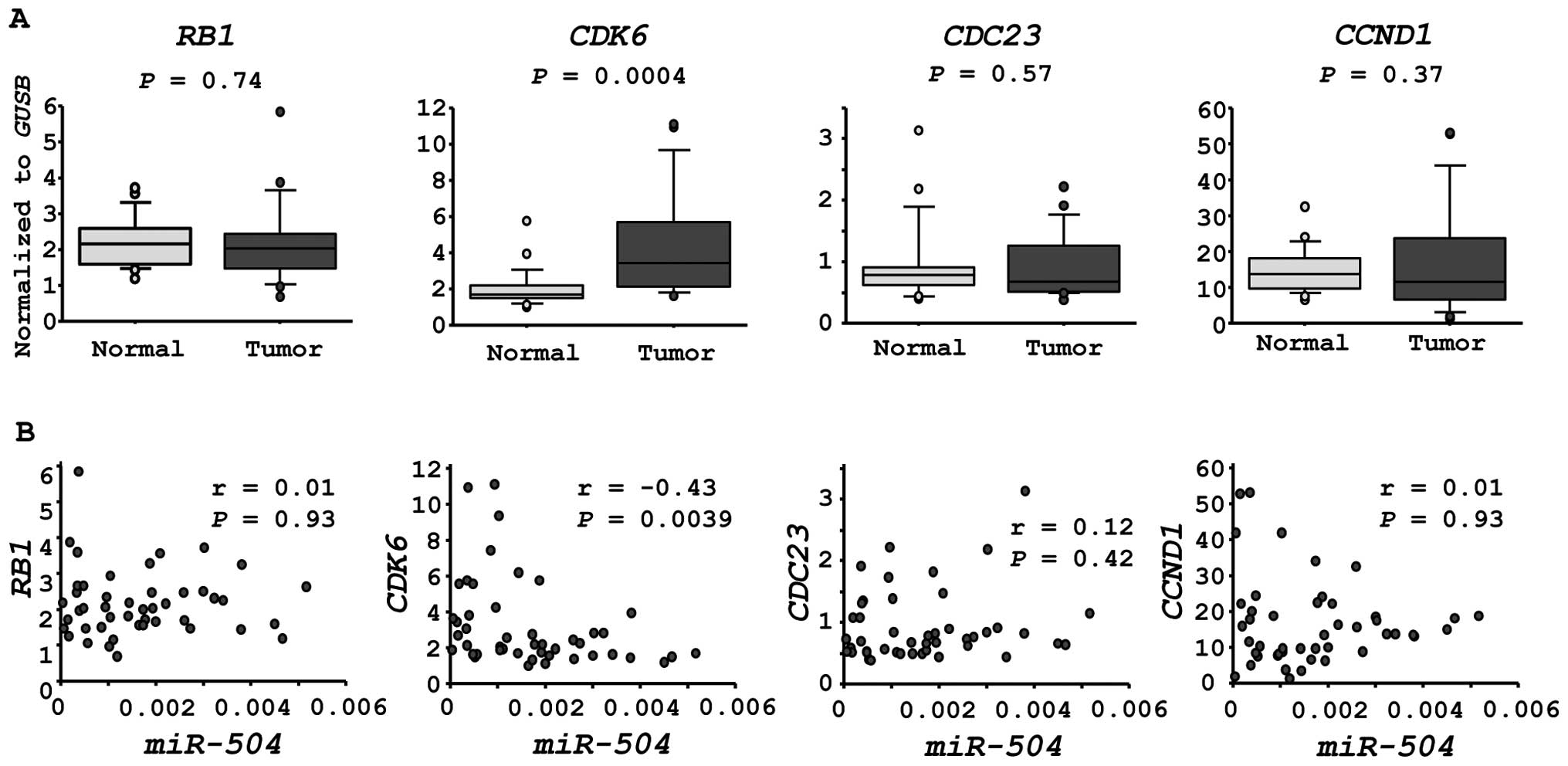
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ and Brakenhoff
RH: The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:9–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Davies L and Welch HG: Epidemiology of
head and neck cancer in the United States. Otolaryngol Head Neck
Surg. 135:451–457. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Hoffman HT, Karnell LH, Shah JP, et al:
Hypopharyngeal cancer patient care evaluation. Laryngoscope.
107:1005–1017. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Bova R, Goh R, Poulson M and Coman WB:
Total pharyngolaryngectomy for squamous cell carcinoma of the
hypopharynx: a review. Laryngoscope. 115:864–869. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Godballe C, Jorgensen K, Hansen O and
Bastholt L: Hypopharyngeal cancer: results of treatment based on
radiation therapy and salvage surgery. Laryngoscope. 112:834–838.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Carthew RW and Sontheimer EJ: Origins and
mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 136:642–655. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Tran N, O’Brien CJ, Clark J and Rose B:
Potential role of micro-RNAs in head and neck tumorigenesis. Head
Neck. 32:1099–1111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12.
|
Caldas C and Brenton JD: Sizing up miRNAs
as cancer genes. Nat Med. 11:712–714. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Kikkawa N, Hanazawa T, Fujimura L, et al:
miR-489 is a tumour-suppressive miRNA target PTPN11 in
hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HSCC). Br J Cancer.
103:877–84. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, et al:
Tumour suppressive microRNA-874 regulates novel cancer networks in
maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 105:833–841.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Kinoshita T, Hanazawa T, Nohata N, et al:
Tumor suppressive microRNA-218 inhibits cancer cell migration and
invasion through targeting laminin-332 in head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 3:1386–1400. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Kinoshita T, Nohata N, Fuse M, et al:
Tumor suppressive microRNA-133a regulates novel targets: moesin
contributes to cancer cell proliferation and invasion in head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
418:378–383. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Kinoshita T, Nohata N, Watanabe-Takano H,
et al: Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 5 (ARPC5)
contributes to cell migration and invasion and is directly
regulated by tumor-suppressive microRNA-133a in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 40:1770–1778. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Kinoshita T, Nohata N, Yoshino H, et al:
Tumor suppressive microRNA-375 regulates lactate dehydrogenase B in
maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 40:185–193.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Mutallip M, Nohata N, Hanazawa T, et al:
Glutathione S-transferase P1 (GSTP1) suppresses cell apoptosis and
its regulation by miR-133alpha in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma (HNSCC). Int J Mol Med. 27:345–352. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, et al:
Caveolin-1 mediates tumor cell migration and invasion and its
regulation by miR-133a in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Int J Oncol. 38:209–217. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, et al:
Identification of novel molecular targets regulated by tumor
suppressive miR-1/miR-133a in maxillary sinus squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 39:1099–1107. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kinoshita T, et al:
Tumour-suppressive microRNA-874 contributes to cell proliferation
through targeting of histone deacetylase 1 in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 108:1648–1658. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Nohata N, Sone Y, Hanazawa T, et al: miR-1
as a tumor suppressive microRNA targeting TAGLN2 in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2:29–42. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Kano M, Seki N, Kikkawa N, et al: miR-145,
miR-133a and miR-133b: tumor-suppressive miRNAs target FSCN1 in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 127:2804–2814.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Hu W, Chan CS, Wu R, et al: Negative
regulation of tumor suppressor p53 by microRNA miR-504. Mol Cell.
38:689–699. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Yang MH, Lin BR, Chang CH, et al:
Connective tissue growth factor modulates oral squamous cell
carcinoma invasion by activating a miR-504/FOXP1 signalling.
Oncogene. 31:2401–2411. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Ichimi T, Enokida H, Okuno Y, et al:
Identification of novel microRNA targets based on microRNA
signatures in bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. 125:345–352. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Tabas-Madrid D, Nogales-Cadenas R and
Pascual-Montano A: GeneCodis3: a non-redundant and modular
enrichment analysis tool for functional genomics. Nucleic Acids
Res. 40:W478–W483. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Ma X, Yoshimoto K, Guan Y, et al:
Associations between microRNA expression and mesenchymal marker
gene expression in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 14:1153–1162. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle,
CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:153–166.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Musgrove EA, Caldon CE, Barraclough J,
Stone A and Sutherland RL: Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:558–572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Shapiro GI: Cyclin-dependent kinase
pathways as targets for cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol.
24:1770–1783. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|