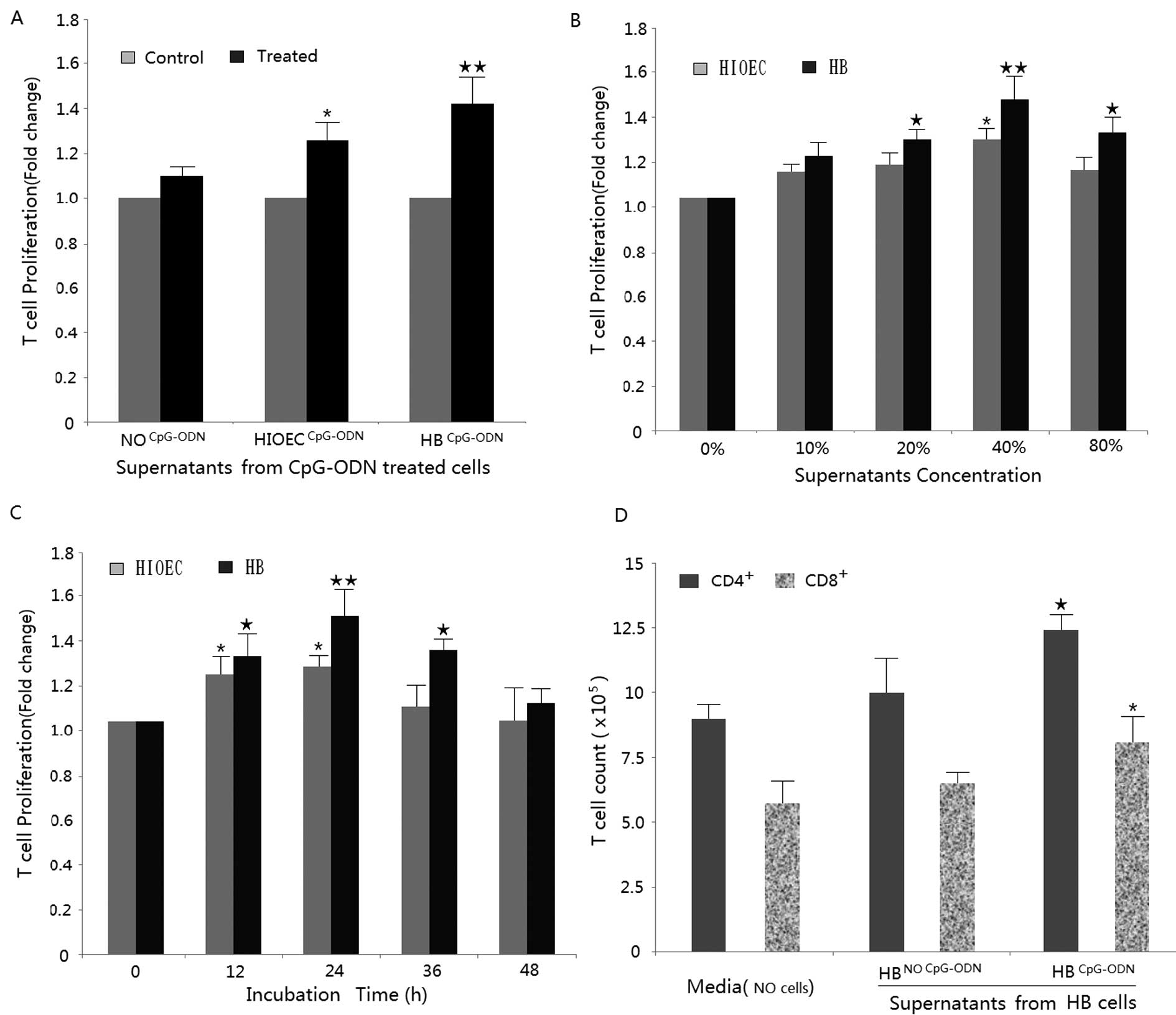
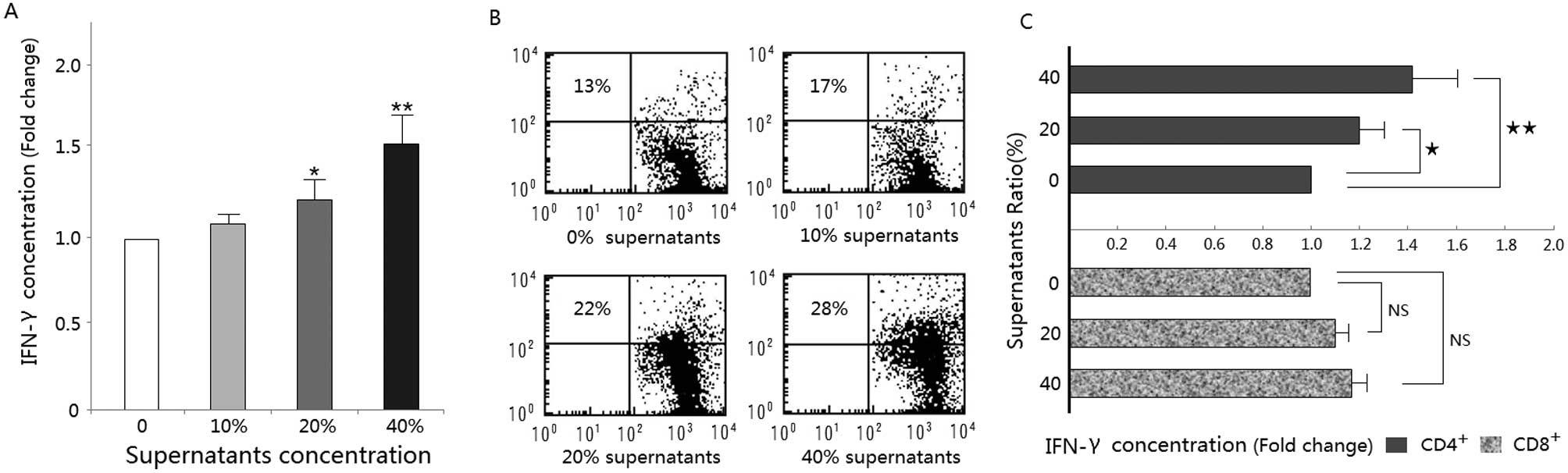
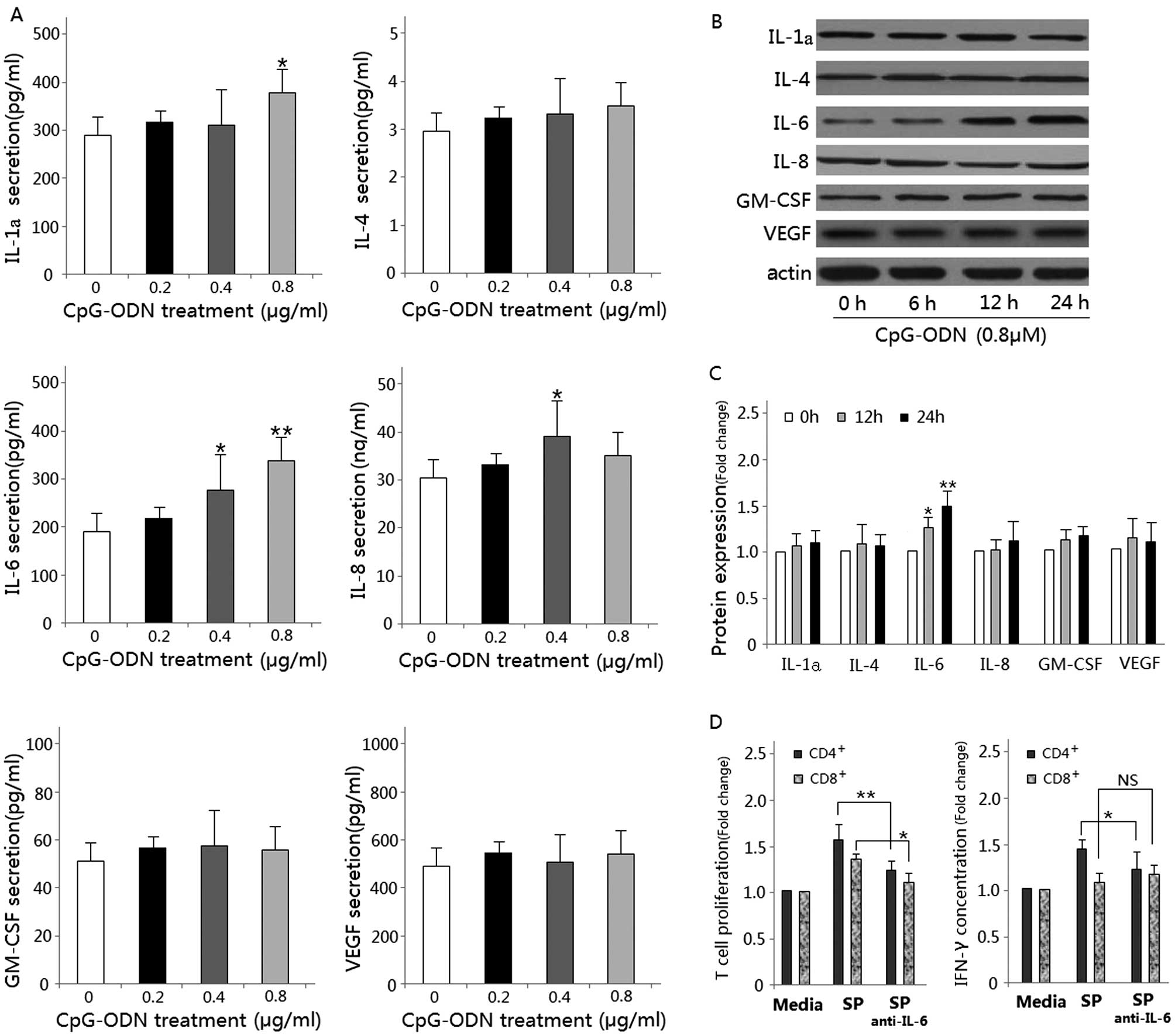
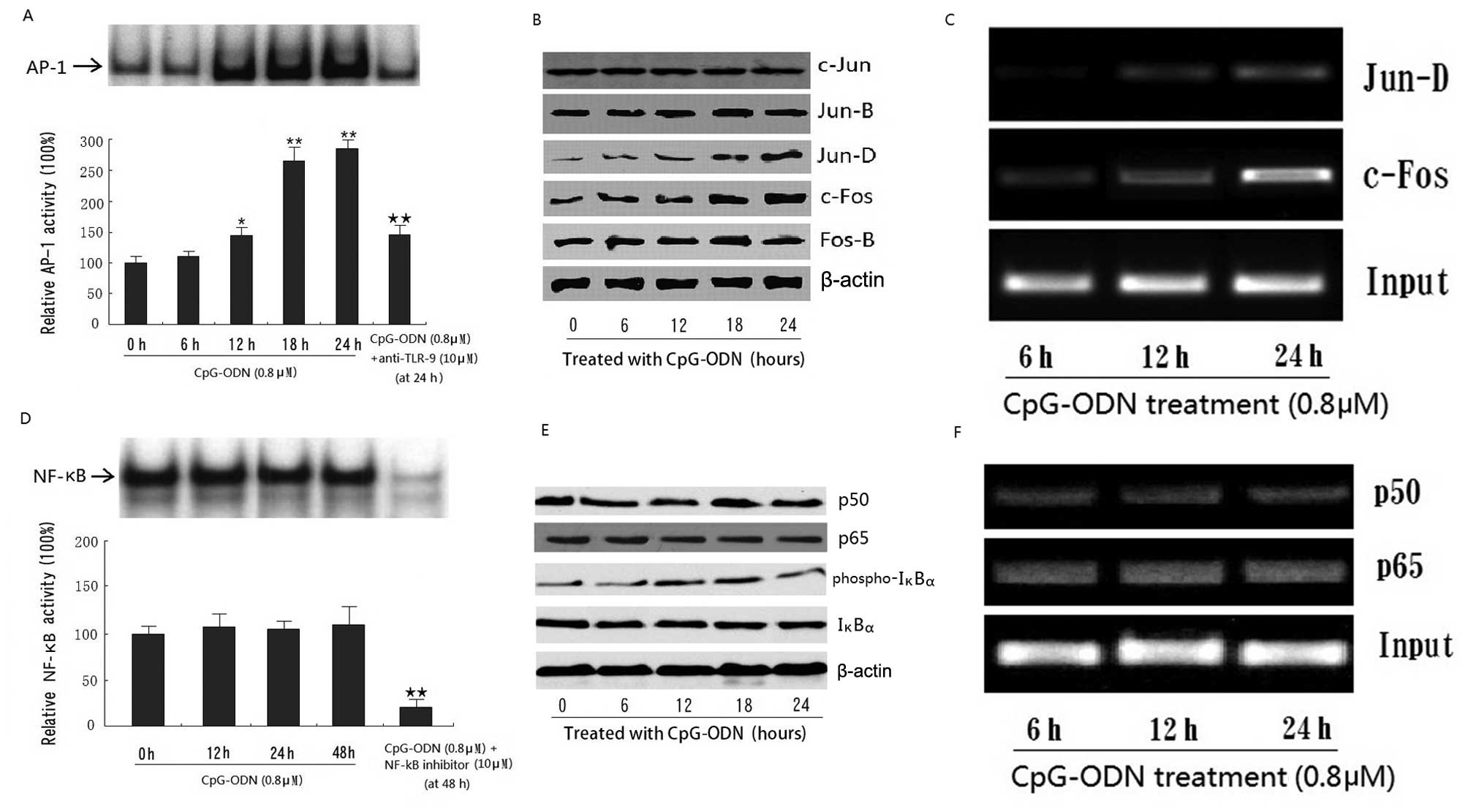
|
1.
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D and
Mathers C: GLOBOCAN 2008, cancer incidence and mortality worldwide:
IARC Cancer Base No. 10. International Agency for Research on
Cancer. http://globocan.iarc.fr.
Accessed July 20, 2012.
|
|
3.
|
Forastiere AA, Goepfert H, Maor M, Pajak
TF, Weber R, et al: Concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy for
organ preservation in advanced laryngeal cancer. N Engl J Med.
349:2091–2098. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Melief CJ: Cancer: immune pact with the
enemy. Nature. 450:803–804. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C
and Mantovani A: Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark
of cancer: links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis.
30:1073–1081. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, Park JM,
Li ZW, et al: IKKbeta links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a
mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell. 118:285–296. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Maeda S, Chang L, Li ZW, Luo JL, Leffert
H, et al: IKKbeta is required for prevention of apoptosis mediated
by cell-bound but not by circulating TNFalpha. Immunity.
19:725–737. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Rakoff-Nahoum S, Paglino J,
Eslami-Varzaneh F, Edberg S and Medzhitov R: Recognition of
commensal microflora by toll-like receptors is required for
intestinal homeostasis. Cell. 118:229–241. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
El-Omar EM, Ng MT and Hold GL:
Polymorphisms in Toll-like receptor genes and risk of cancer.
Oncogene. 27:244–252. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
O'Neill LA: Signal transduction pathways
activated by the IL-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor super family.
Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 270:47–61. 2002.
|
|
12.
|
Takeda K and Akira S: Toll-like receptors
in innate immunity. Int Immunol. 17:1–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Ruan M, Zun Z, Siyi L, Wenjun Y, Lizheng
W, et al: Increased expression of Toll-like receptor-9 has close
relation with tumour cell proliferation in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Arch Oral Biol. 56:877–884. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Min R, Siyi L, Wenjun Y, Shengwen L, Ow A,
et al: Toll-like receptor-9 agonists increase cyclin D1 expression
partly through activation of activator protein-1 in human oral
squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 103:1938–1945. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Sdek P, Zhang ZY, Cao J, Pan HY, Chen WT,
et al: Alteration of cell-cycle regulatory proteins in human oral
epithelial cells immortalized by HPV16 E6 and E7. Int J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 35:653–657. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Zhong LP, Pan HY, Zhou XJ, Ye DX, Zhang L,
et al: Characteristics of a cancerous cell line, HIOEC-B(a)P-96,
induced by benzo(a)pyrene from human immortalized oral epithelial
cell line. Arch Oral Biol. 53:443–452. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Ruan M, Ji T, Yang WJ, Duan WH, Zhou XJ,
et al: Growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in human oral
squamous cell carcinoma Tca-8113 cell lines by Shikonin was partly
through the inactivation of NF-κB pathway. Phytother Res.
22:407–415. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Kaomongkolgit R, Cheepsunthorn P, Pavasant
P and Sanchavanakit N: Iron increases MMP-9 expression through
activation of AP-1 via ERK/Akt pathway in human head and neck
squamous carcinoma cells. Oral Oncol. 44:587–594. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Toualbi-Abed K, Daniel F, Güller MC,
Legrand A, Mauriz JL, et al: Jun D cooperates with p65 to activate
the proximal κB site of the cyclin D1 promoter: role of PI3K/PDK-1.
Carcinogenesis. 29:536–543. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Woods KV, El-Naggar A, Clayman GL and
Grimm EA: Variable expression of cytokines in human head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma cell lines and consistent expression in
surgical specimens. Cancer Res. 58:3132–3141. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
St John MA, Li Y, Zhou X, Denny P, Ho CM,
et al: Interleukin 6 and interleukin 8 as potential biomarkers for
oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Arch
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 130:929–935. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Nagata M, Fujita H, Ida H, Hoshina H,
Inoue T, et al: Identification of potential biomarkers of lymph
node metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma by cDNA microarray
analysis. Int J Cancer. 106:683–689. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Okamoto M, Hiura K, Ohe G, Ohba Y, Terai
K, et al: Mechanism for bone invasion of oral cancer cells mediated
by interleukin-6 in vitro and in vivo. Cancer. 89:1966–1975. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
De Schutter H, Landuyt W, Verbeken E,
Goethals L, Hermans R, et al: The prognostic value of the hypoxia
markers CA IX and GLUT 1 and the cytokines VEGF and IL 6 in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated by radiotherapy +/−
chemotherapy. BMC Cancer. 5:422005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Okamoto M, Lee C and Oyasu R:
Interleukin-6 as a paracrine and autocrine growth factor in human
prostatic carcinoma cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 57:141–146.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Smith HA and Kang Y: The
metastasis-promoting roles of tumor-associated immune cells. J Mol
Med. 91:411–429. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Beetz A, Peter RU, Oppel T, Kaffenberger
W, Rupec RA, et al: NF-kappaB and AP-1 are responsible for
inducibility of the IL-6 promoter by ionizing radiation in HeLa
cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 76:1443–1453. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Romano M, Sironi M, Toniatti C,
Polentarutti N, Fruscella P, et al: Role of IL-6 and its soluble
receptor in induction of chemokines and leukocyte recruitment.
Immunity. 6:315–325. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Mishra A, Bharti AC, Saluja D and Das BC:
Transactivation and expression patterns of Jun and Fos/AP-1
super-family proteins in human oral cancer. Int J Cancer.
126:819–829. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Rao SK, Pavicevic Z, Du Z, Kim JG, Fan M,
Jiao Y, et al: Pro-inflammatory genes as biomarkers and therapeutic
targets in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Biol Chem.
285:32512–32521. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Lin CM, Chen YH, Ma HP, Wang BW, Chiu JH,
et al: Silibinin inhibits the invasion of IL-6-stimulated colon
cancer cells via selective JNK/AP-1/MMP-2 modulation in vitro. J
Agric Food Chem. 60:12451–12457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Houghton AN, Uchi H and Wolchok JD: The
role of the immune system in early epithelial carcinogenesis:
B-ware the double-edged sword. Cancer Cell. 7:403–405. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Huang B, Zhao J, Unkeless JC, Feng ZH and
Xiong H: TLR signaling by tumor and immune cells: a double-edged
sword. Oncogene. 27:218–224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34.
|
Anders CK, Hsu DS, Broadwater G, Acharya
CR, Foekens JA, et al: Young age at diagnosis correlates with worse
prognosis and defines a subset of breast cancers with shared
patterns of gene expression. J Clin Oncol. 26:3324–3330. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Hirsh V, Paz-Ares L, Boyer M, Rosell R,
Middleton G, et al: Randomized phase III trial of
paclitaxel/carboplatin with or without PF-3512676 (Toll-like
receptor 9 agonist) as first-line treatment for advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 29:2667–2674. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|