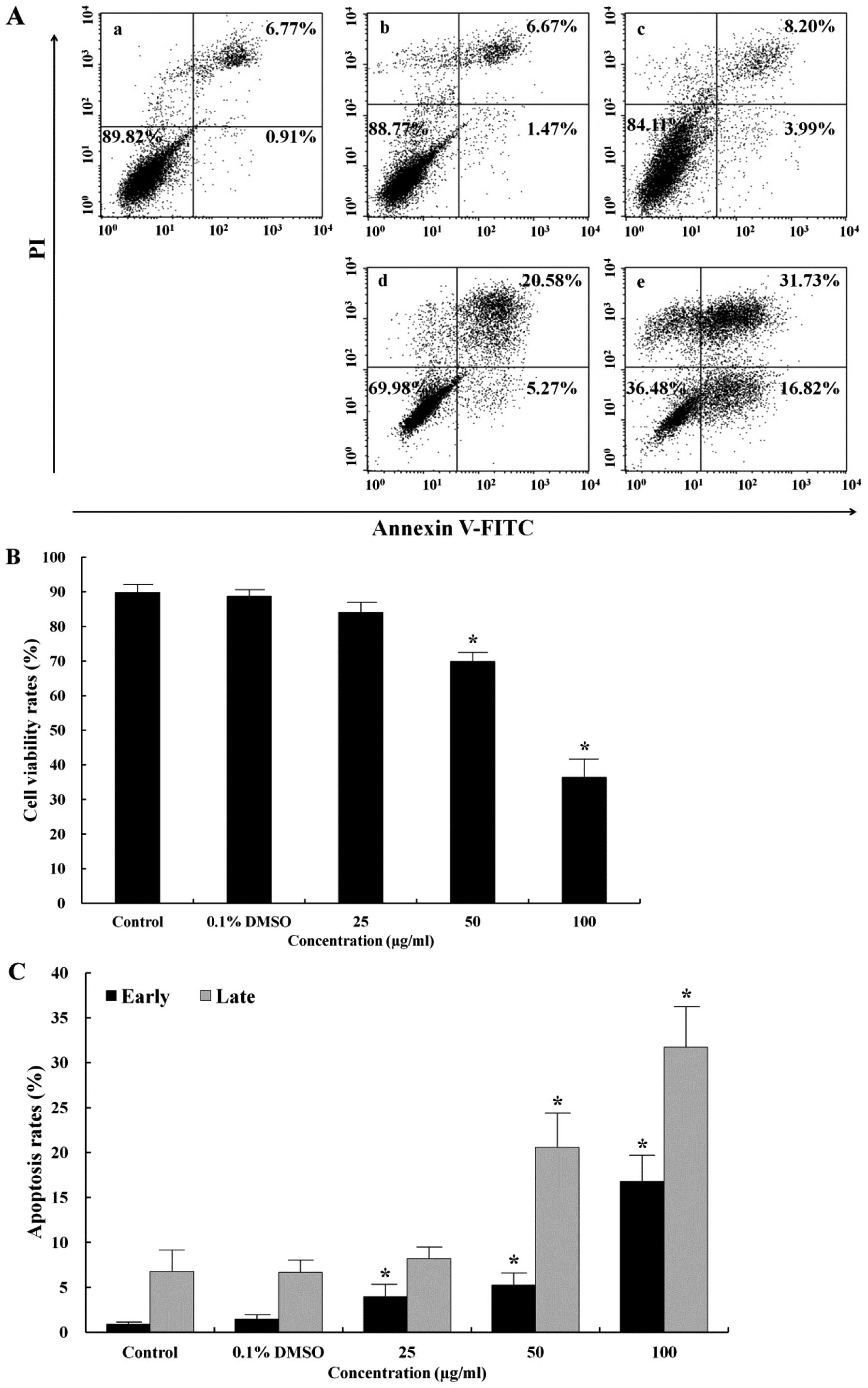
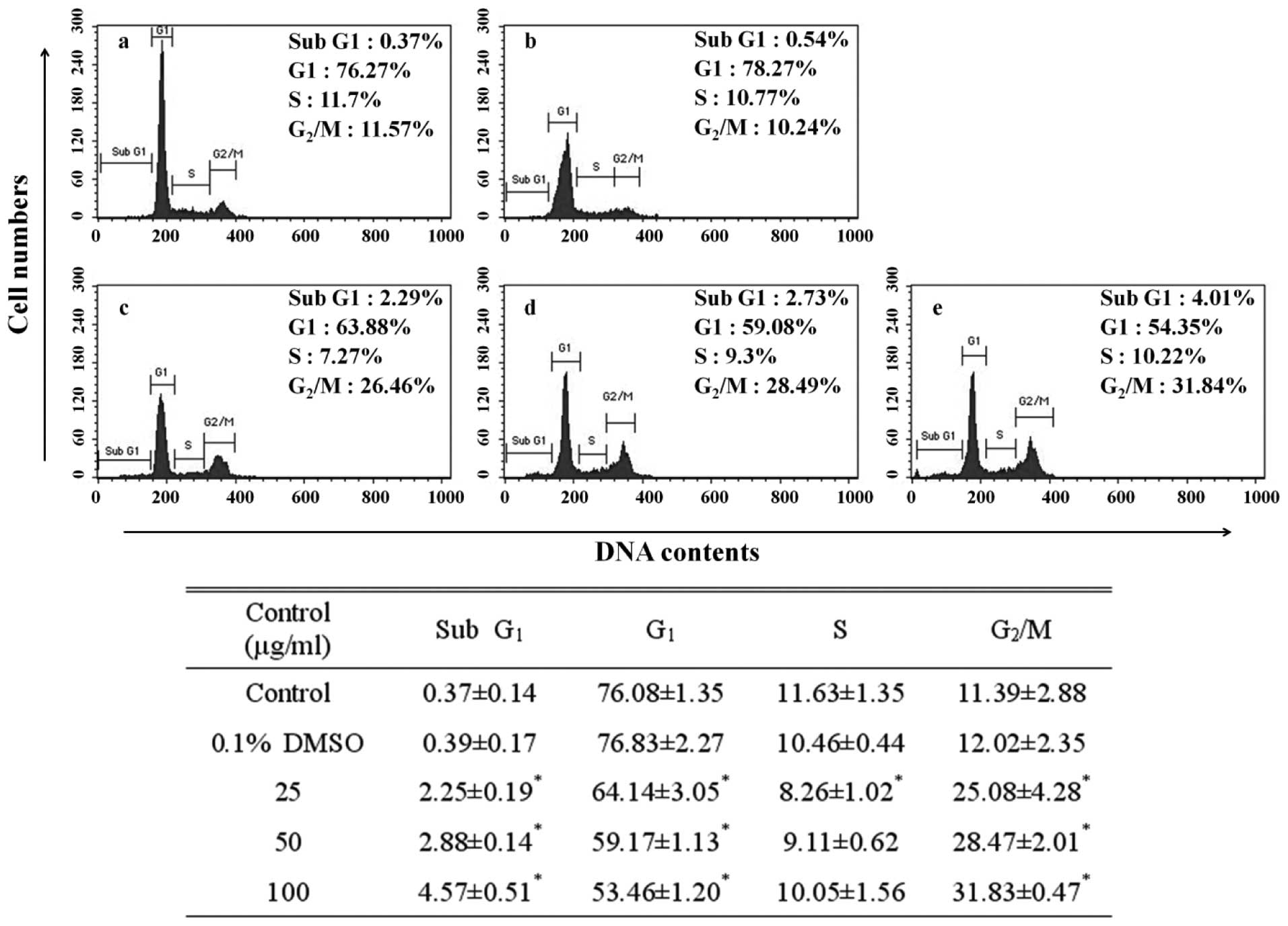
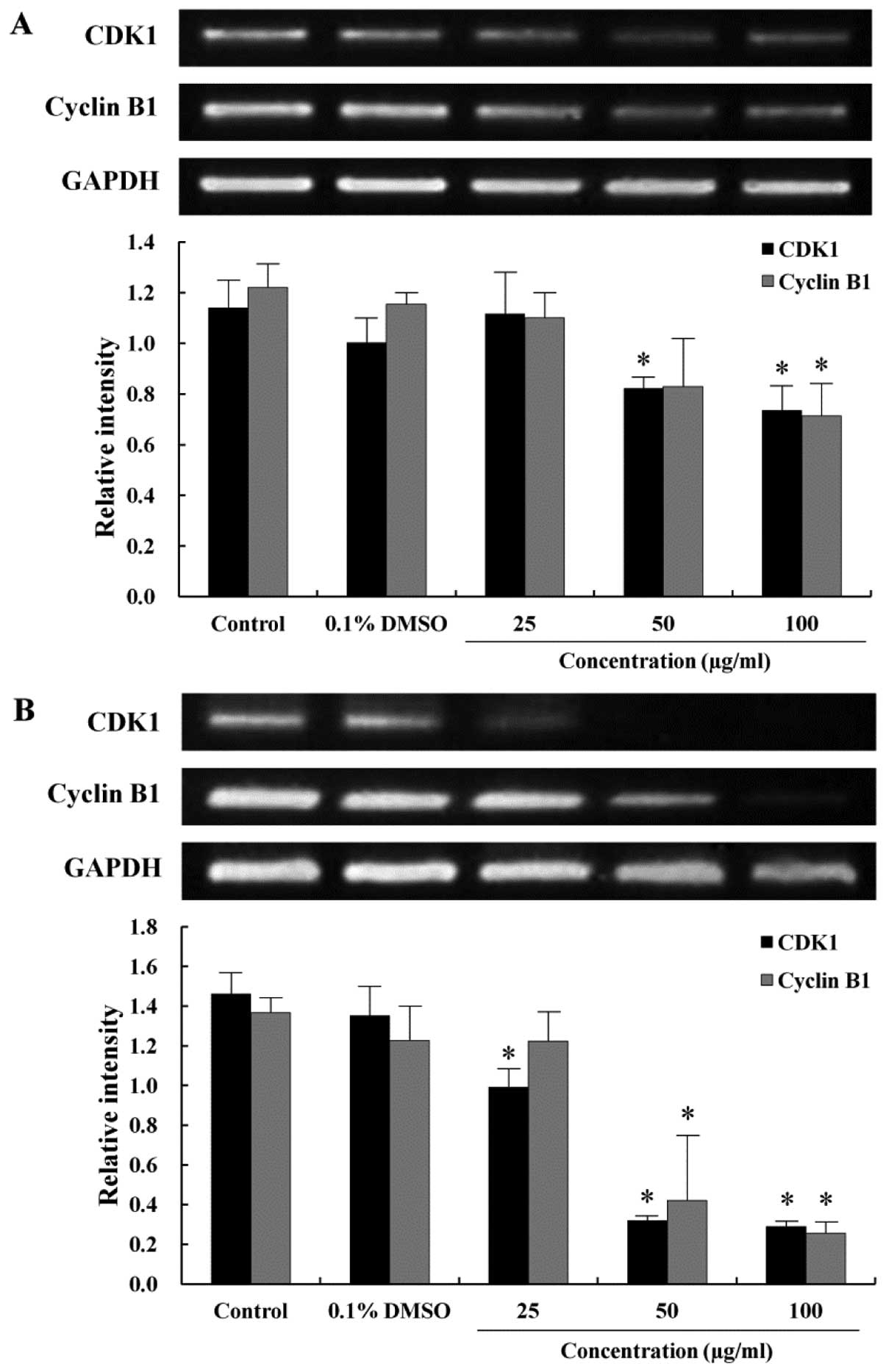
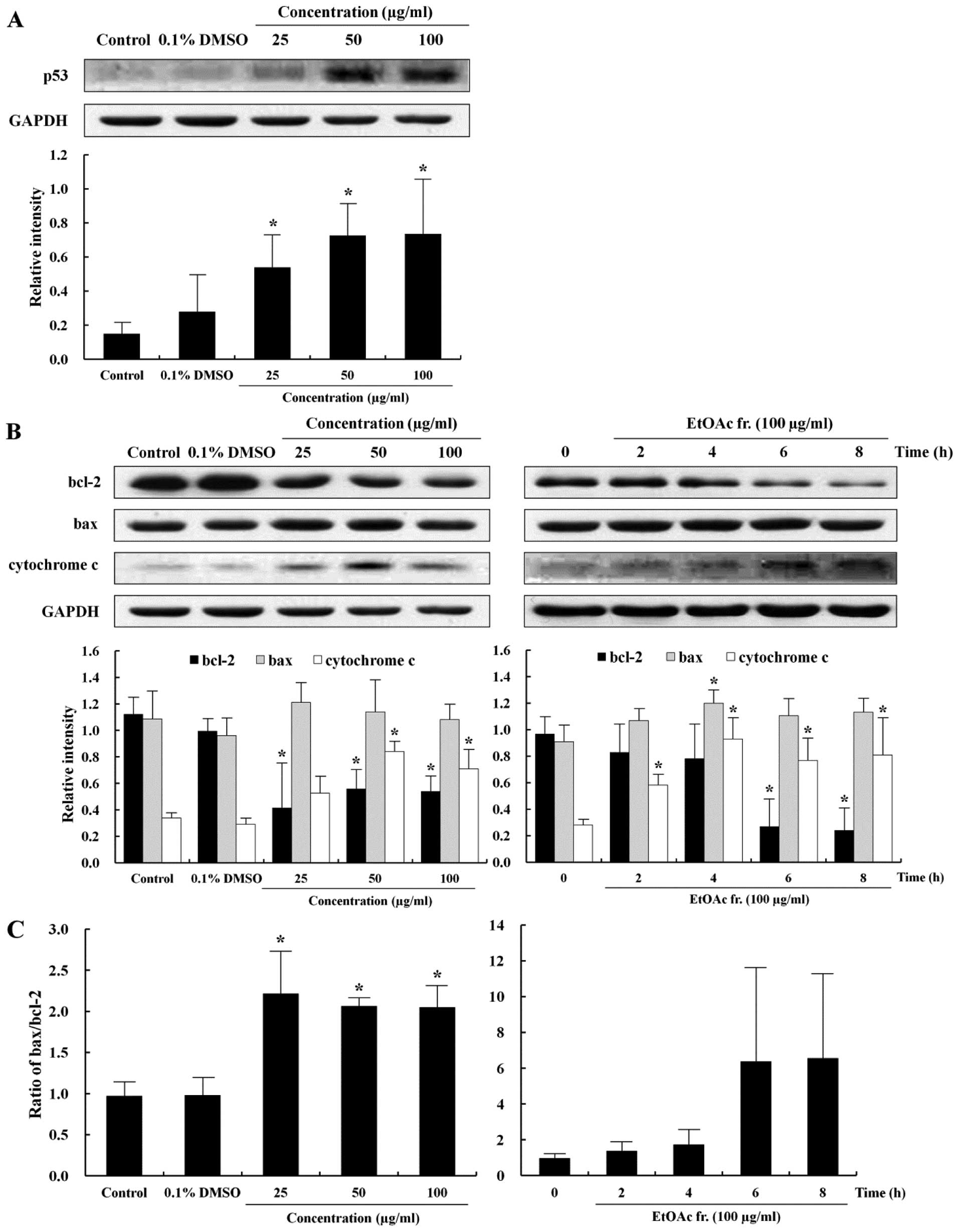
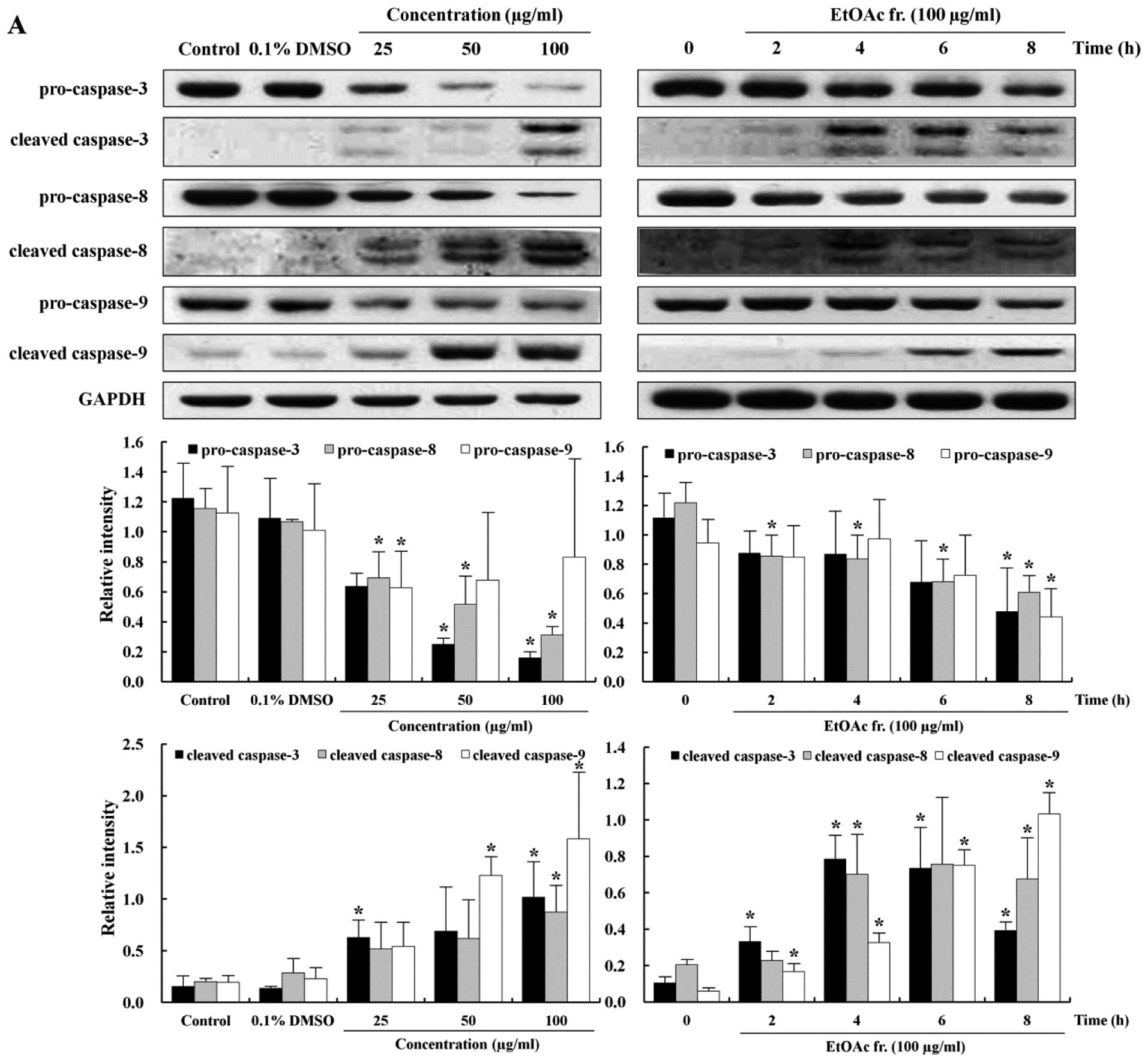
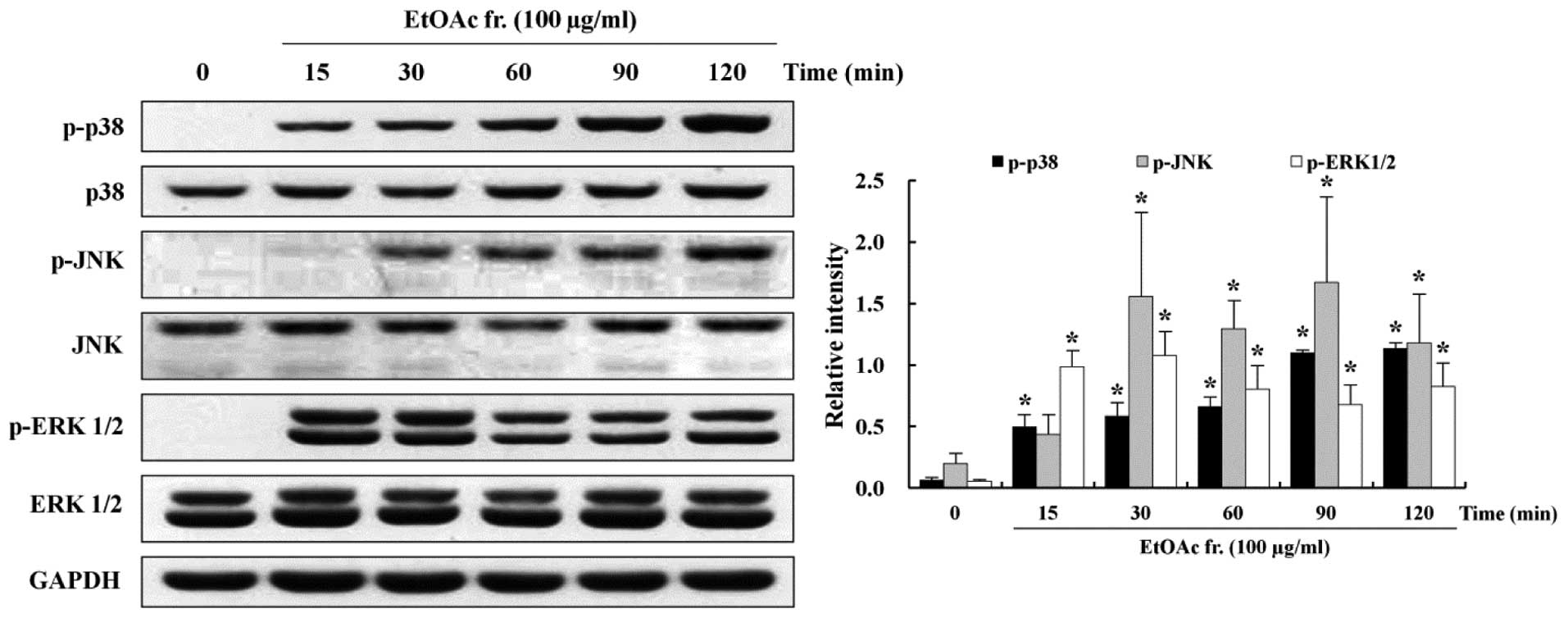
|
1.
|
Kelloff GJ: Perspectives on cancer
chemoprevention research and drug development. Adv in Cancer Res.
78:199–334. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Ryu DS, Baek GO, Kim EY, Kim KH and Lee
DS: Effects of polysaccharides derived from Orostachys
japonicus on induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell
death in human colon cancer cells. BMB Rep. 43:750–755.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Choi SY, Chung MJ, Seo WD, Shin JH, Shon
MY and Sung NJ: Inhibitory effects of Orostachys japonicus
extracts on the formation of N-nitrosodimethylamine. J Agric Food
Chem. 54:6075–6078. 2006.
|
|
4.
|
Jung HJ, Choi J, Nam JH and Park HJ:
Anti-ulcerogenic effects of the flavonoid-rich fraction from the
extract of Orostachys japonicus in mice. J Med Food.
10:702–706. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Lee HS, Ryu DS, Lee GS and Lee DS:
Anti-inflammatory effects of dichloromethane fraction from
Orostachys japonicus in RAW 264.7 cells: Suppression of
NF-κB activation and MAPK signaling. J Ethnopharmacol. 140:271–276.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Je Ma C, Jung WJ, Lee KY, Kim YC and Sung
SH: Calpain inhibitory flavonoids isolated from Orostachys
japonicus. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 24:676–679. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Park HJ, Young HS, Park KY, Rhee SH, Chung
HY and Choi JS: Flavonoids from the whole plants of Orostachys
japonicus. Arch Pharm Res. 14:167–171. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Ryu DS, Lee HS, Lee GS and Lee DS: Effect
of the ethylacetate extract of Orostachys japonicus on
induction of apoptosis through the p53-mediated signaling pathway
in human gastric cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 35:660–665.
2012.
|
|
9.
|
Singh SV, Herman-Antosiewicz A, Singh AV,
Lew KL, Srivastava SK, Kamath R, Brown KD, Zhang L and Baskarah R:
Sulforaphane-induced G2/M phase cell cycle arrest involves
checkpoint kinase 2-mediated phosphorylation of cell division cycle
25C. J Biol Chem. 279:25813–25822. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Harris SL and Levin AJ: The p53 pathway:
positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene. 24:2899–2908. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Vazquez A, Bond EE, Levine AJ and Bond GL:
The genetics of the p53 pathway, apoptosis and cancer therapy. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 7:979–987. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Shiozaki EN and Shi Y: Caspases, IAPs and
Smac/DIABLO: mechanisms from structural biology. Trends Biochem
Sci. 29:486–494. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Tsujimoto Y: Bcl-2 family of proteins:
life-or-death switch in mitochondria. Biosci Rep. 22:47–58. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Dhanalakshmi S, Agarwal P, Globe L and
Agarwal R: Silibinin sensitizes human prostate carcinoma DU145
cells to cisplatinand carboplatin-induced growth inhibition and
apoptotic death. Int J Cancer. 106:699–705. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Brooks G: Cyclin, cyclin-dependent
kinases, and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors: detection methods
and activity measurements. Methods Mol Biol. 296:291–298.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Vermeulen K, Berneman ZN and Van
Bockstaele DR: Cell cycle and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 36:165–175.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Sebolt-Leopold JS: Development of
anticancer drugs targeting the MAP kinase pathway. Oncogene.
19:6594–6599. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Sebolt-Leopold JS and Herrera R: Targeting
the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade to treat cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 4:937–947. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Jeong JH, Ryu DS, Suk DH and Lee DS:
Anti-inflammatory effects of ethanol extract from Orostachys
japonicus on modulation of signal pathways in LPS-stimulated
RAW 264.7 cells. BMB Rep. 44:399–404. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Lee HS, Bilehal D, Lee GS, Ryu DS, Kim HK,
Suk DH and Lee DS: Anti-inflammatory effect of the hexane fraction
from Orostachys japonicus in RAW 264.7 cells by suppression
of NF-κB and PI3K-Akt signaling. J Funct Foods. 5:1217–1225.
2013.
|
|
21.
|
Kaufmann SH and Henqartner MO: Programmed
cell death: alive and well in the new millennium. Trends Cell Biol.
11:526–534. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Ryu DS, Kim SH and Lee DS:
Anti-proliferative effect of polysaccharides from Salicornia
herbacea on induction of G2/M arrest and apoptosis in human
colon cancer cells. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 19:1482–1489.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Nakanishi M, Shimada N and Niida H:
Genetic instability in cancer cells by impaired cell cycle
checkpoints. Cancer Sci. 97:984–989. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Elledge SJ and Harpae JW: CDK inhibitors;
on the threshold of checkpoints and development. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 6:847–852. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Vousden KH: Apoptosis. p53 and PUMA: a
deadly duo. Science. 309:1685–1686. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Lavin MF and Gueven N: The complexity of
p53 stabilization and activation. Cell Death Differ. 13:941–950.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Ai Z, Lu W and Qin X: Arsenic trioxide
induces gallbladder carcinoma cell apoptosis via down regulation of
bcl-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 348:1075–1081. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Wang JB, QI LL, Zheng SD and Wu TX:
Curcumin induces apoptosis through the mitochondria-mediated
apoptotic pathway in HT-29 cells. J Zhejizng Univ Sci B. 10:93–102.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Lavrik I, Golks A and Krammer PH: Death
receptor signaling. J Cell Sci. 118:265–267. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30.
|
Fujita E, Egashira J, Urase K, Kuida K and
Momoi T: Caspase-9 processing by caspase-3 via a feedback
amplification loop in vivo. Cell Death Differ. 8:335–344. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Seger R and Krebs EG: The MAPK signaling
cascade. FASEB J. 9:726–735. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Meier P, Finch A and Evan G: Apoptosis in
development. Nature. 407:796–801. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33.
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Schwartz GK and Shah MA: Targeting the
cell cycle: a new approach to cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol.
23:9408–9421. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Koff A, Giordano A, Desai D, Yamashita K,
Harper JW, Elledge S, Nishimoto T, Morgan DO, Franza BR and Roberts
JM: Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the
G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science. 257:1689–1694. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Fisher DE: The p53 tumor suppressor:
critical regulator of life & death in cancer. Apoptosis.
6:7–15. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37.
|
Moll UM and Zaika A: Nuclear and
mitochondrial apoptotic pathways of p53. FEBS Lett. 493:65–69.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Erster S, Mihara M, Kim RH, Petrenko O and
Moll UM: In vivo mitochondrial p53 translocation triggers a rapid
first wave of cell death in response to DNA damage that can precede
p53 target gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 24:6728–6741. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Jiang X and Wang X: Cytochrome c-mediated
apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 73:87–106. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40.
|
Nagata S: Fas ligand-induced apoptosis.
Annu Rev Genet. 33:29–55. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41.
|
Willis SN and Adams JM: Life in the
balance: how BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 17:617–625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Pop C, Timmer J, Sperandio S and Salvesen
GS: The apoptosome activates caspase-9 by dimerization. Mol Cell.
22:269–275. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Zhou Z, Sun X and Kang YJ: Ethanol-induced
apoptosis in mouse liver: Fas- and cytochrome c-mediated caspase-3
activation pathway. Am J Pathol. 159:329–338. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Jin UH, Song KH, Motomura M, Suzuki I, Gu
YH, Kang YJ, Moon TC and Kim CH: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester
induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia
U937 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 310:43–48. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Zheng Y, Zhou M, Ye A, Li Q, Bai Y and
Zhang Q: The conformation change of Bcl-2 is involved in arsenic
trioxide-induced apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation in
SGC7901 human gastric cancer cells. World J Sur Oncol. 8:312010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Cho SH, Chung KS, Choi JH, Kim DH and Lee
KT: Compound K, a metabolite of ginseng saponin, induces apoptosis
via caspase-8-dependent pathway in HL-60 human leukemia cells. BMC
Cancer. 9:4492009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Martin GS: Cell signaling and cancer.
Cancer Cell. 4:167–174. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48.
|
Freeman SM and Whartenby KA: The role of
the mitogen-activated protein kinase cellular signaling pathway in
tumor cell survival and apoptosis. Drug News Perspect. 17:237–242.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Lin A and Dibling B: The true face of JNK
activation in apoptosis. Aging Cell. 1:112–116. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Lunghi P, Giuliani N, Mazzera L, Lombardi
G, Ricca M, Corradi A, Cantoni AM, Salvatore L, Riccioni R and
Costanzo A: Targeting MEK/MAPK signal transduction module
potentiates ATO-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells through
multiple signaling pathways. Blood. 112:2450–2462. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51.
|
Mansouri A, Ridgway LD, Korapati AL, Zhang
Q, Tian L, Wang Y, Siddik ZH, Mills GB and Claret FX: Sustained
activation of JNK/p38 MAPK pathways in response to cisplatin leads
to Fas ligand induction and cell death in ovarian carcinoma cells.
J Biol Chem. 278:19245–19256. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|