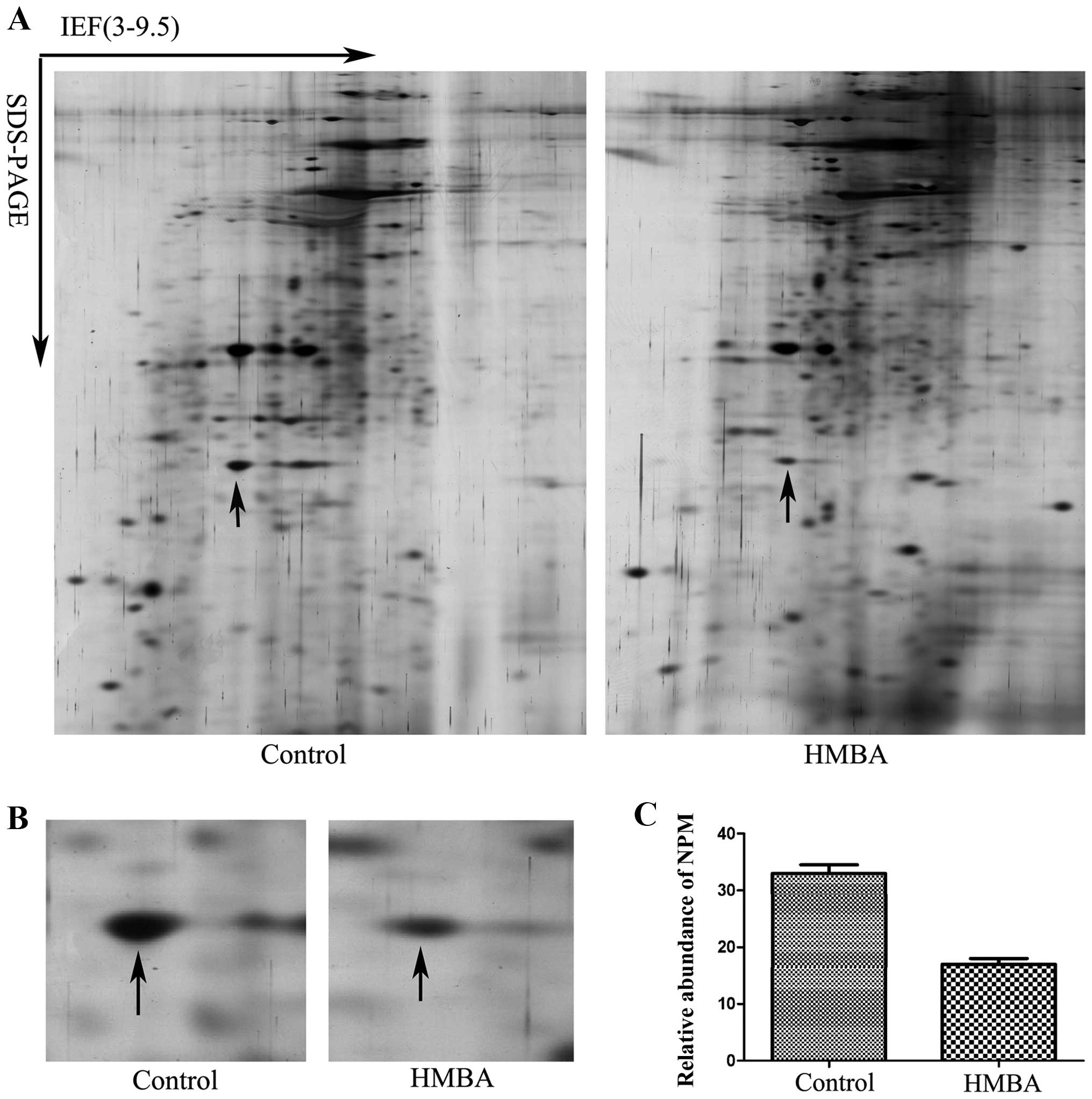
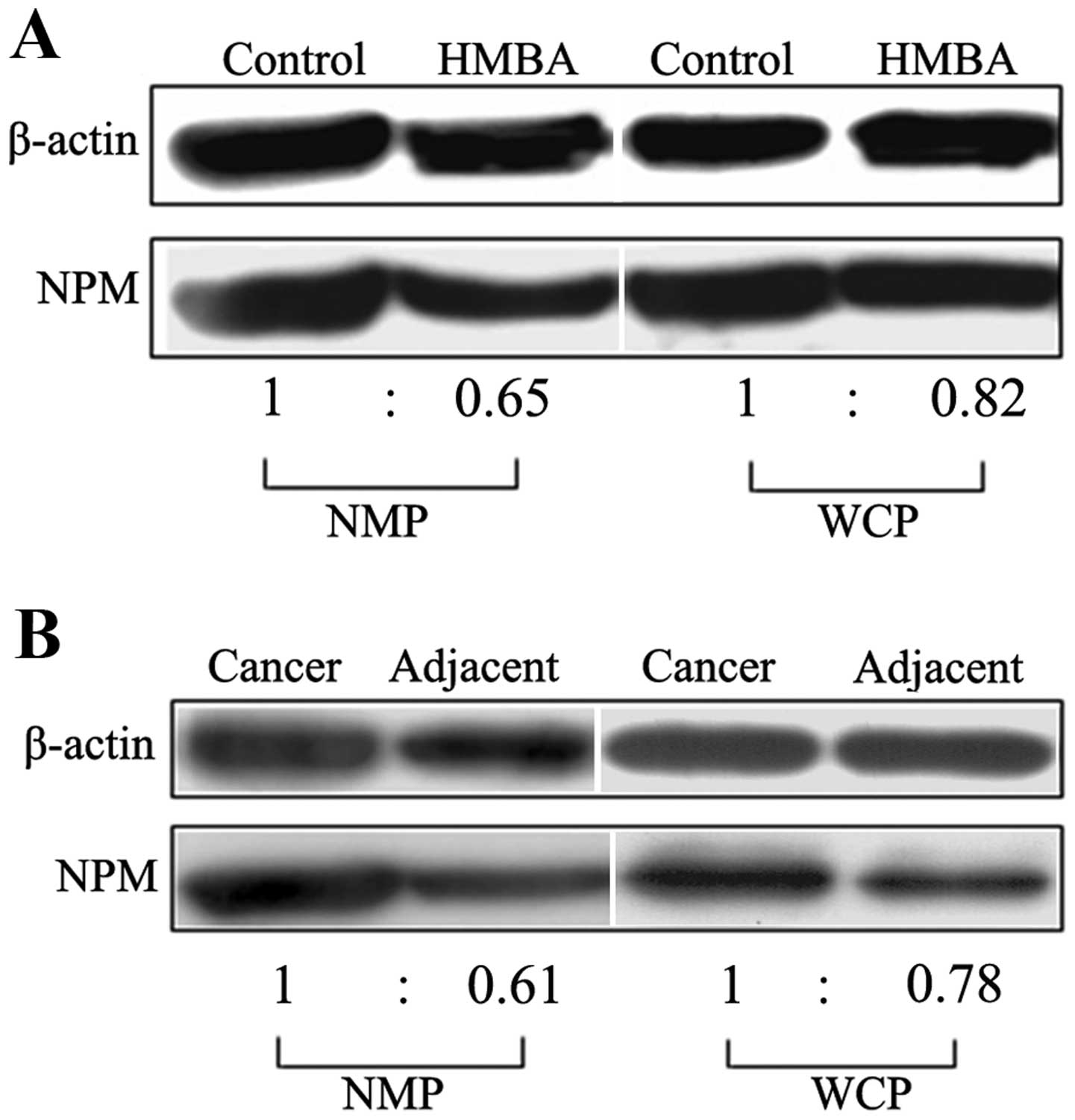
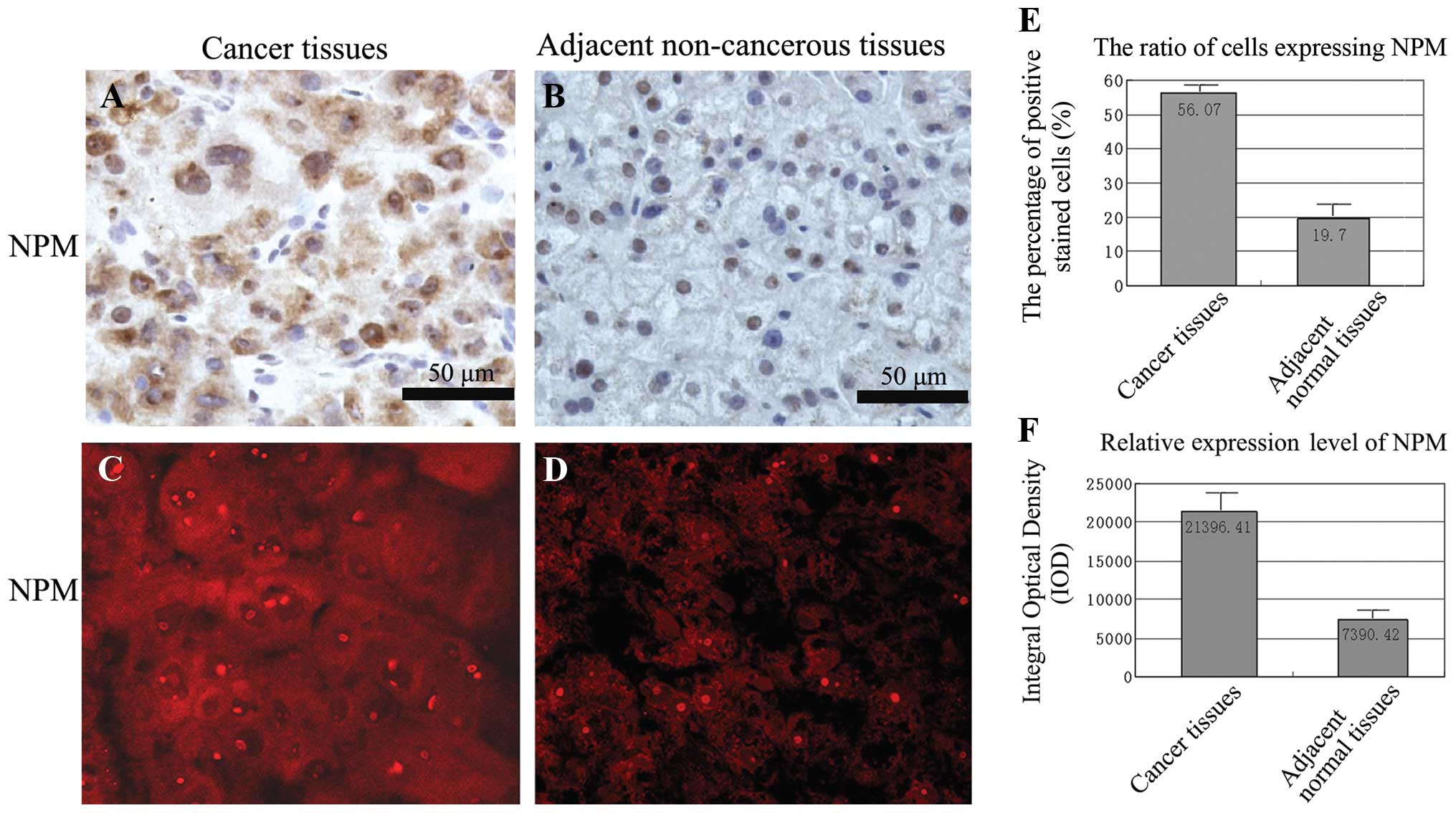
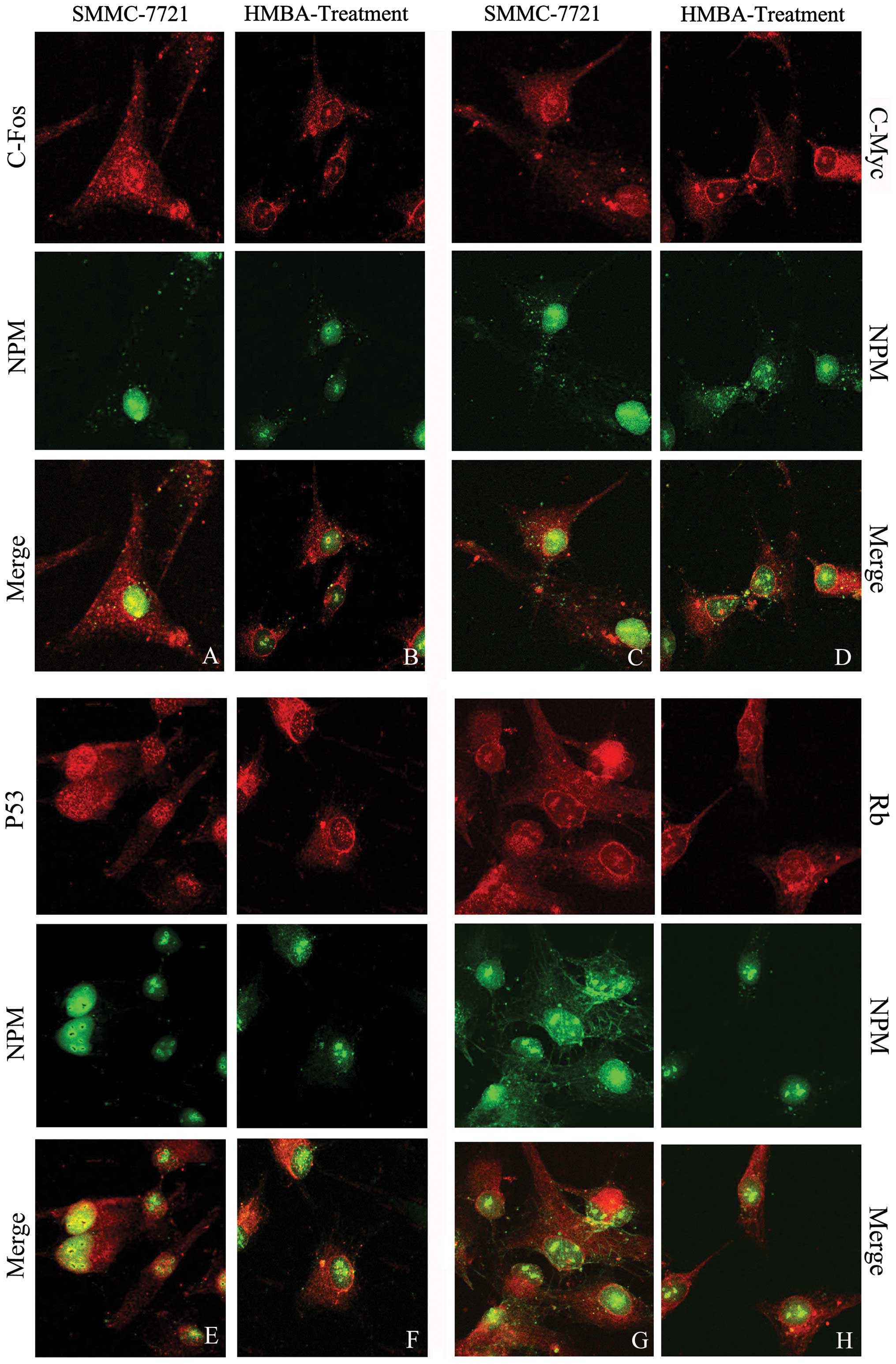
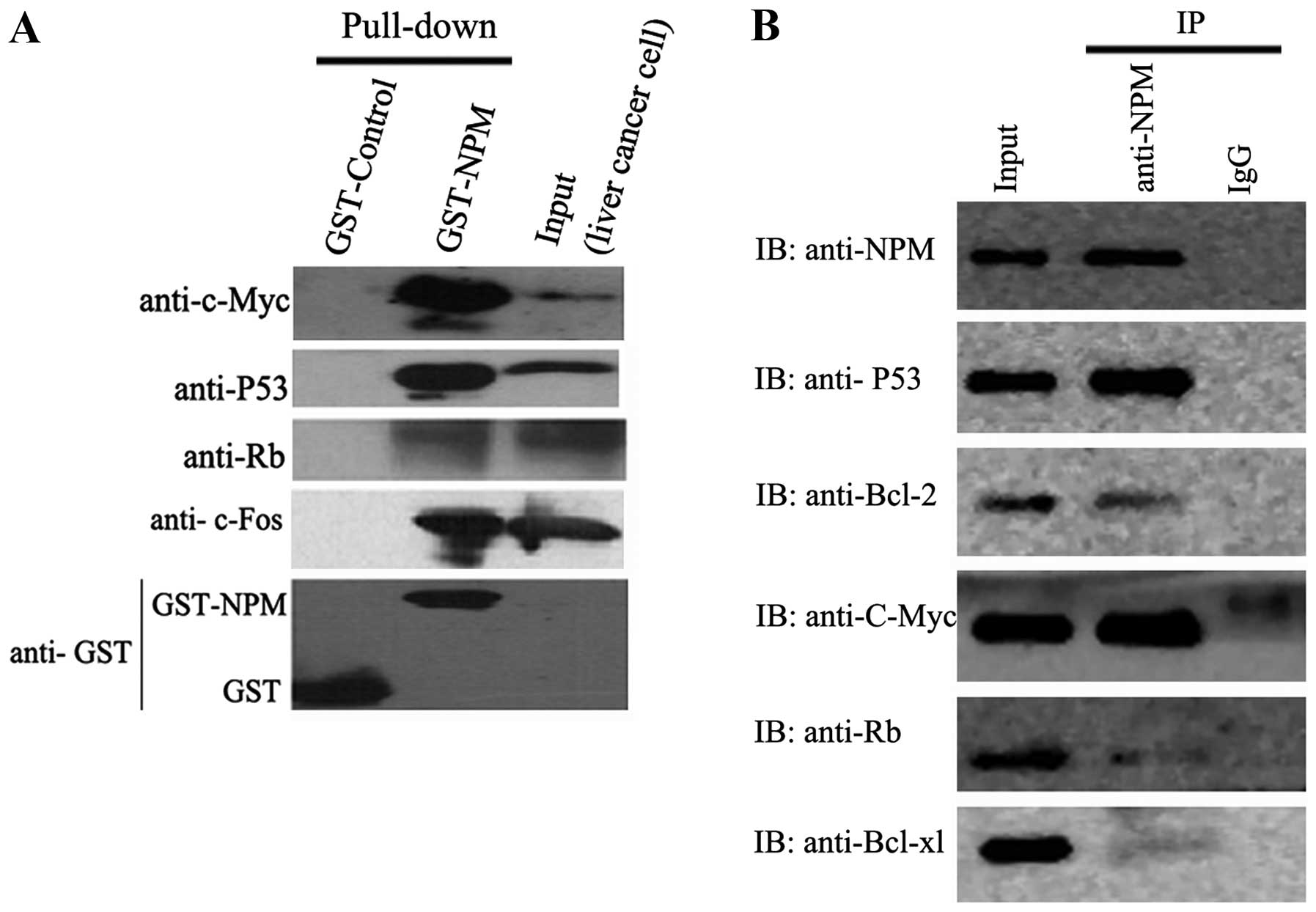
|
1.
|
Grisendi S, Mecucci C, Falini B and
Pandolfi PP: Nucleophosmin and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:493–505.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Lindström MS: Elucidation of motifs in
ribosomal protein S9 that mediate its nucleolar localization and
binding to NPM1/nucleophosmin. PLoS One. 7:e524762012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Lim MJ and Wang XW: Nucleophosmin and
human cancer. Cancer Detect Prev. 30:481–490. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Tsui KH, Juang HH, Lee TH, Chang PL, Chen
CL and Yung BY: Association of nucleophosmin/B23 with bladder
cancer recurrence based on immunohistochemical assessment in
clinical samples. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:364–370. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Hsu CY and Yung BY: Over-expression of
nucleophosmin/B23 decreases the susceptibility of human leukemia
HL-60 cells to retinoic acid-induced differentiation and apoptosis.
Int J Cancer. 88:392–400. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Li QF, Shi SL, Liu QR, Tang J, Song J and
Liang Y: Anticancer effects of ginsenoside Rg1, cinnamic acid, and
tanshinone IIA in osteosarcoma MG-63 cells: nuclear matrix
downregulation and cytoplasmic trafficking of nucleophosmin. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 40:1918–1929. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Liang Y, Li QF, Zhang XY, Shi SL and Jing
GJ: Differential expression of nuclear matrix proteins during the
differentiation of human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells induced by
retinoic acid. J Cell Biochem. 106:849–857. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Tang J, Niu JW, Xu DH, Li ZX, Li QF and
Chen JA: Alteration of nuclear matrix-intermediate filament system
and differential expression of nuclear matrix proteins during human
hepato-carcinoma cell differentiation. World J Gastroenterol.
13:2791–2797. 2007.
|
|
9.
|
Derenzini M, Sirri V, Trere D and Ochs RL:
The quantity of nucleolar proteins nucleolin and protein B23 is
related to cell doubling time in human cancer cells. Lab Invest.
73:497–502. 1995.
|
|
10.
|
Michishita E, Kurahashi T, Suzuki T, et
al: Changes in nuclear matrix proteins during the senescence-like
phenomenon induced by 5-chlorodeoxyuridine in HeLa cells. Exp
Gerontol. 37:885–890. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Hsu CY and Yung BY: Down-regulation of
nucleophosmin/B23 during retinoic acid-induced differentiation of
human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Oncogene. 16:915–923.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Dergunova NN, Bulycheva TI, Artemenko EG,
et al: A major nucleolar protein B23 as a marker of proliferation
activity of human peripheral lymphocytes. Immunol Lett. 83:67–72.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Subong EN, Shue MJ, Epstein JI, Briggman
JV, Chan PK and Partin AW: Monoclonal antibody to prostate cancer
nuclear matrix protein (PRO:4-216) recognizes nucleophosmin/B23.
Prostate. 39:298–304. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Nozawa Y, Van Belzen N, Van der Made AC,
Dinjens WN and Bosman FT: Expression of nucleophosmin/B23 in normal
and neoplastic colorectal mucosa. J Pathol. 178:48–52. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Zhang Y: The ARF-B23 connection:
implications for growth control and cancer treatment. Cell Cycle.
3:259–262. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Ulanet DB, Torbenson M, Dang CV,
Casciola-Rosen L and Rosen A: Unique conformation of cancer
autoantigen B23 in hepatoma: a mechanism for specificity in the
autoimmune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:12361–12366. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
You BJ, Huang IJ, Liu WH, Hung YB, Chang
JH and Yung BY: Decrease in nucleophosmin/B23 mRNA and telomerase
activity during indomethacin-induced apoptosis of gastric KATO-III
cancer cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 360:683–690.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Gjerset RA: DNA damage, p14ARF,
nucleophosmin (NPM/B23), and cancer. J Mol Histol. 37:239–251.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Li Z, Boone D and Hann SR: Nucleophosmin
interacts directly with c-Myc and controls c-Myc-induced
hyperproliferation and transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:18794–18799. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Yung BY: c-Myc-mediated expression of
nucleophosmin/B23 decreases during retinoic acid-induced
differentiation of human leukemia HL-60 cells. FEBS Lett.
578:211–216. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Arabi A, Rustum C, Hallberg E and Wright
AP: Accumulation of c-Myc and proteasomes at the nucleoli of cells
containing elevated c-Myc protein levels. J Cell Sci.
116:1707–1717. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Grandori C, Gomez-Roman N, Felton-Edkins
ZA, et al: c-Myc binds to human ribosomal DNA and stimulates
transcription of rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I. Nat Cell Biol.
7:311–318. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Maiguel DA, Jones L, Chakravarty D, Yang C
and Carrier F: Nucleophosmin sets a threshold for p53 response to
UV radiation. Mol Cell Biol. 24:3703–3711. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Colombo E, Marine JC, Danovi D, Falini B
and Pelicci PG: Nucleophosmin regulates the stability and
transcriptional activity of p53. Nat Cell Biol. 4:529–533. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Lin CY, Liang YC and Yung BY:
Nucleophosmin/B23 regulates transcriptional activation of E2F1 via
modulating the promoter binding of NF-kappaB, E2F1 and pRB. Cell
Signal. 18:2041–2048. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|