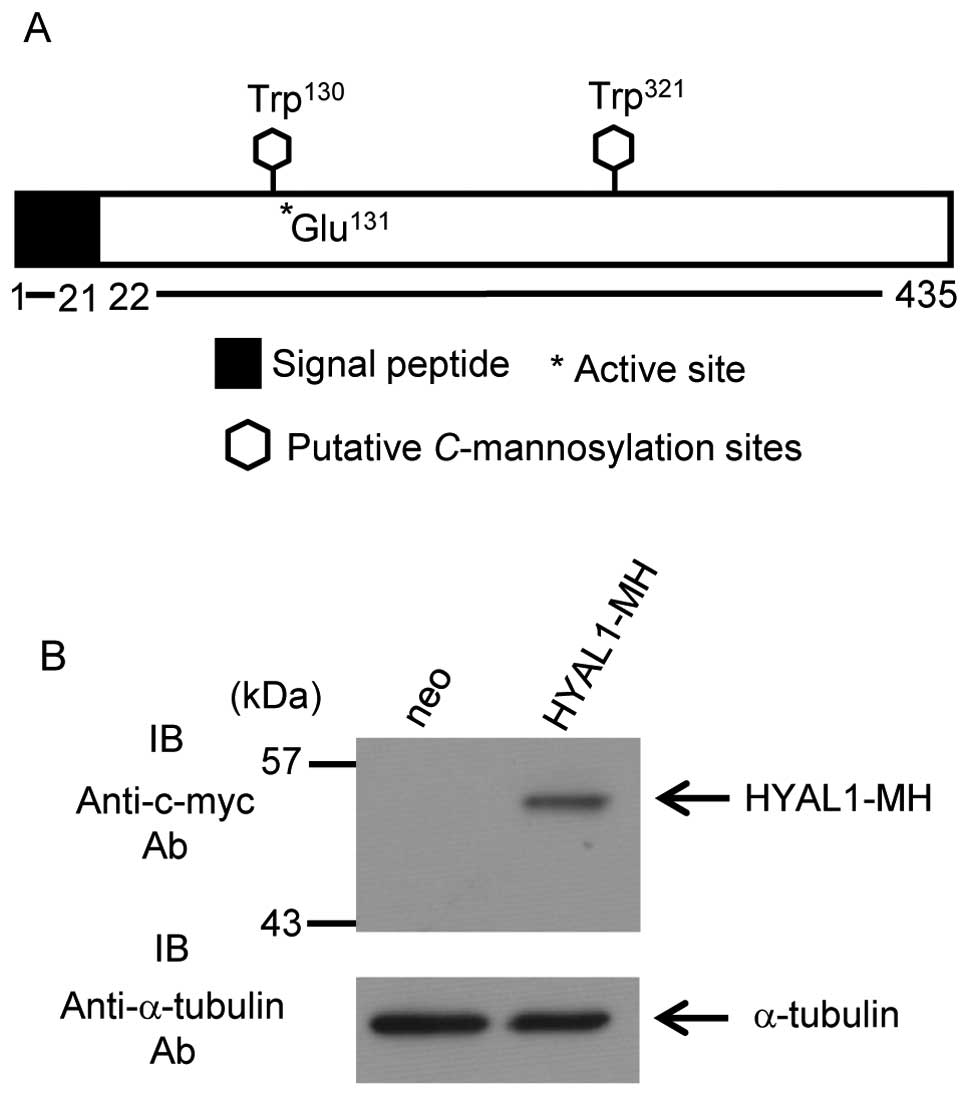
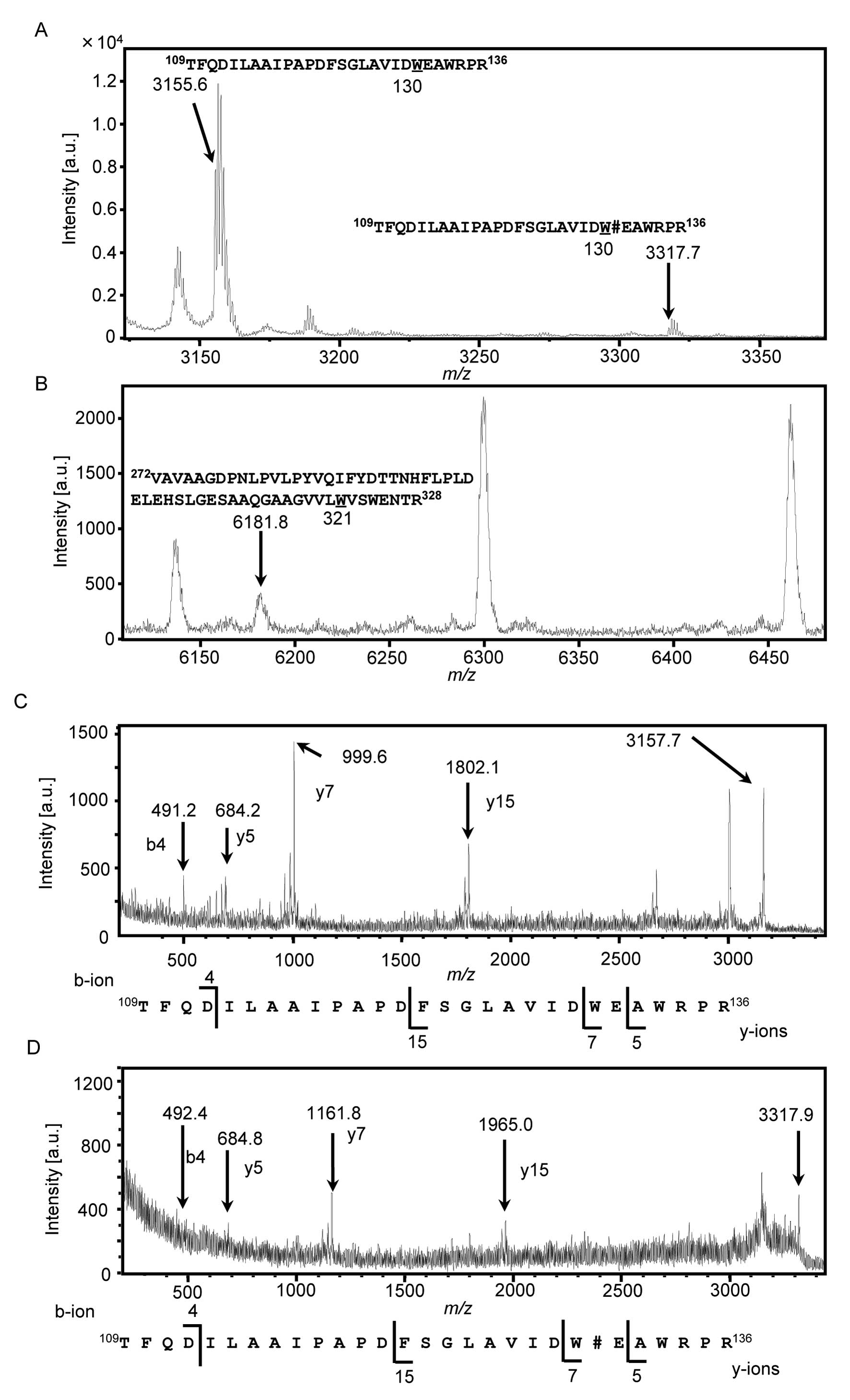
|
1.
|
Furmanek A and Hofsteenge J: Protein
C-mannosylation: facts and questions. Acta Biochim Pol. 47:781–789.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Doucey MA, Hess D, Cacan R and Hofsteenge
J: Protein C-mannosylation is enzyme-catalysed and uses
dolichyl-phosphate-mannose as a precursor. Mol Biol Cell.
9:291–300. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Krieg J, Hartmann S, Vicentini A, Gläsner
W, Hess D and Hofsteenge J: Recognition signal for C-mannosylation
of Trp-7 in RNase 2 consists of sequence Trp-x-x-Trp. Mol Biol
Cell. 9:301–309. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Julenius K: NetCGlyc 1.0: prediction of
mammalian C-mannosylation sites. Glycobiology. 17:868–876. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Hofsteenge J, Müller DR, de Beer T,
Löffler A, Richter WJ and Vliegenthart JF: New type of linkage
between a carbohydrate and a protein: C-glycosylation of a specific
tryptophan residue in human RNase Us. Biochemistry. 33:13524–13530.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Gonzalez de Peredo A, Klein D, Macek B,
Hess D, Peter-Katalinic J and Hofsteenge J: C-mannosylation and
o-fucosylation of thrombospondin type 1 repeats. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 1:11–18. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Hofsteenge J, Huwiler KG, Macek B, Hess D,
Lawler J, Mosher DF and Peter-Katalinic J: C-mannosylation and
O-fucosylation of the thrombospondin type 1 module. J Biol Chem.
276:6485–6498. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Wang LW, Leonhard-Melief C, Haltiwanger RS
and Apte SS: Post-translational modification of thrombospondin
type-1 repeats in ADAMTS-like 1/punctin-1 by C-mannosylation of
tryptophan. J Biol Chem. 284:30004–30015. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Hamming OJ, Kang L, Svensson A, Karlsen
JL, Rahbek-Nielsen H, Paludan SR, Hjorth SA, Bondensgaard K and
Hartmann R: Crystal structure of interleukin-21 receptor (IL-21R)
bound to IL-21 reveals that sugar chain interacting with WSXWS
motif is integral part of IL-21R. J Biol Chem. 287:9454–9460. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Buettner FF, Ashikov A, Tiemann B, Lehle L
and Bakker H: C. elegans DPY-19 is a C-mannosyltransferase
glycosylating thrombospondin repeats. Mol Cell. 50:295–302. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Ihara Y, Manabe S, Ikezaki M, Inai Y,
Matsui I-SL, Ohta Y, Muroi E and Ito Y: C-mannosylated peptides
derived from the thrombospondin type 1 repeat interact with Hsc70
to modulate its signaling in RAW264.7 cells. Glycobiology.
20:1298–1310. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Muroi E, Manabe S, Ikezaki M, Urata Y,
Sato S, Kondo T, Ito Y and Ihara Y: C-mannosylated peptides derived
from the thrombospondin type 1 repeat enhance
lipopolysaccharide-induced signaling in macrophage-like RAW264.7
cells. Glycobiology. 17:1015–1028. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Overall CM and Lopez-Otin C: Strategies
for MMP inhibition in cancer: innovations for the post-trial era.
Nat Rev Cancer. 2:657–672. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Simizu S, Ishida K, Wierzba MK and Osada
H: Secretion of heparanase protein is regulated by glycosylation in
human tumor cell lines. J Biol Chem. 279:2697–2703. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Simizu S and Niwa Y: Practical molecular
targets for suppression of metastasis. For Immunopathol Dis Therap.
4:43–51. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Chao KL, Muthukumar L and Herzberg O:
Structure of human hyaluronidase-1, a hyaluronan hydrolyzing enzyme
involved in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Biochemistry.
46:6911–6920. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Tan JX, Wang XY, Su XL, Li HY, Shi Y, Wang
L and Ren GS: Upregulation of HYAL1 expression in breast cancer
promoted tumor cell proliferation, migration, invasion and
angiogenesis. PLoS One. 6:e228362011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Tan JX, Wang XY, Li HY, Su XL, Wang L, Ran
L, Zheng K and Ren GS: HYAL1 overexpression is correlated with the
malignant behavior of human breast cancer. Int J Cancer.
128:1303–1315. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Imundo L, Leduc CA, Guha S, Brown M,
Perino G, Gushulak L, Triggs-Raine B and Chung WK: A complete
deficiency of hyaluronoglucosaminidase 1 (HYAL1) presenting as
familial juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Inherit Metab Dis.
34:1013–1022. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Kuroda M, Funasaki S, Saitoh T, Sasazawa
Y, Nishiyama S, Umezawa K and Simizu S: Determination of
topological structure of ARL6ip1 in cells: identification of the
essential binding region of ARL6ip1 for conophylline. FEBS Lett.
587:3656–3660. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Yasukagawa T, Niwa Y, Simizu S and Umezawa
K: Suppression of cellular invasion by glybenclamide through
inhibited secretion of platelet-derived growth factor in ovarian
clear cell carcinoma ES-2 cells. FEBS Lett. 586:1504–1509. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Miyazaki I, Simizu S, Okumura H, Takagi S
and Osada H: A small-molecule inhibitor shows that pirin regulates
migration of melanoma cells. Nat Chem Biol. 6:667–673. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Simizu S, Umezawa K, Takada M, Arber N and
Imoto M: Induction of hydrogen peroxide production and Bax
expression by caspase-3(-like) proteases in tyrosine kinase
inhibitor-induced apoptosis in human small cell lung carcinoma
cells. Exp Cell Res. 238:197–203. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Simizu S, Suzuki T, Muroi M, Lai NS,
Takagi S, Dohmae N and Osada H: Involvement of disulfide bond
formation in the activation of heparanase. Cancer Res.
67:7841–7849. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Niwa Y, Suzuki T, Dohmae N, Umezawa K and
Simizu S: Determination of cathepsin V activity and intracellular
trafficking by N-glycosylation. FEBS Lett. 586:3601–3607. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Guntenhöner MW, Pogrel MA and Stern R: A
substrate-gel assay for hyaluronidase activity. Matrix. 12:388–396.
1992.
|
|
27.
|
Zhang L, Bharadwaj AG, Casper A, Barkley
J, Barycki JJ and Simpson MA: Hyaluronidase activity of human Hyal1
requires active site acidic and tyrosine residues. J Biol Chem.
284:9433–9442. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Yamaguchi H, Kidachi Y, Kamiie K, Noshita
T and Uetsu H: Structural insight into the ligand-receptor
interaction between glycyrrhetinic acid (GA) and the high-mobility
group protei B1 (HMGB1)-DNA complex. Bioinformation. 23:1147–1153.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Susana DL, Lídia MG, Teresa AFC, Henrique
FC, Rui M and Rita CG: Structure based virtual screening for
discovery of novel human neutrophil elastase inhibitors. Med Chem
Comm. 3:1299–1304. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30.
|
Wilkins MR, Gasteiger E, Gooley AA,
Herbert BR, Molloy MP, Binz PA, Ou K, Sanchez JC, Bairoch A,
Williams KL and Hochstrasser DF: High-throughput mass spectrometric
discovery of protein post-translational modifications. J Mol Biol.
289:645–657. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Frost GI, Csóka AB, Wong T, Stern R and
Csóka TB: Purification, cloning, and expression of human plasma
hyaluronidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 236:10–15. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Azuma M, Kabe Y, Kuramori C, Kodo M,
Yamaguchi Y and Handa H: Adenine nucleotide translocator transports
haem precursors into mitochondria. PLoS One. 3:e30702008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Fukiage C, Nakajima E, Ma H, Azuma M and
Shearer TR: Characterization and regulation of lens-specific
calpain Lp82. J Biol Chem. 277:20678–20685. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|