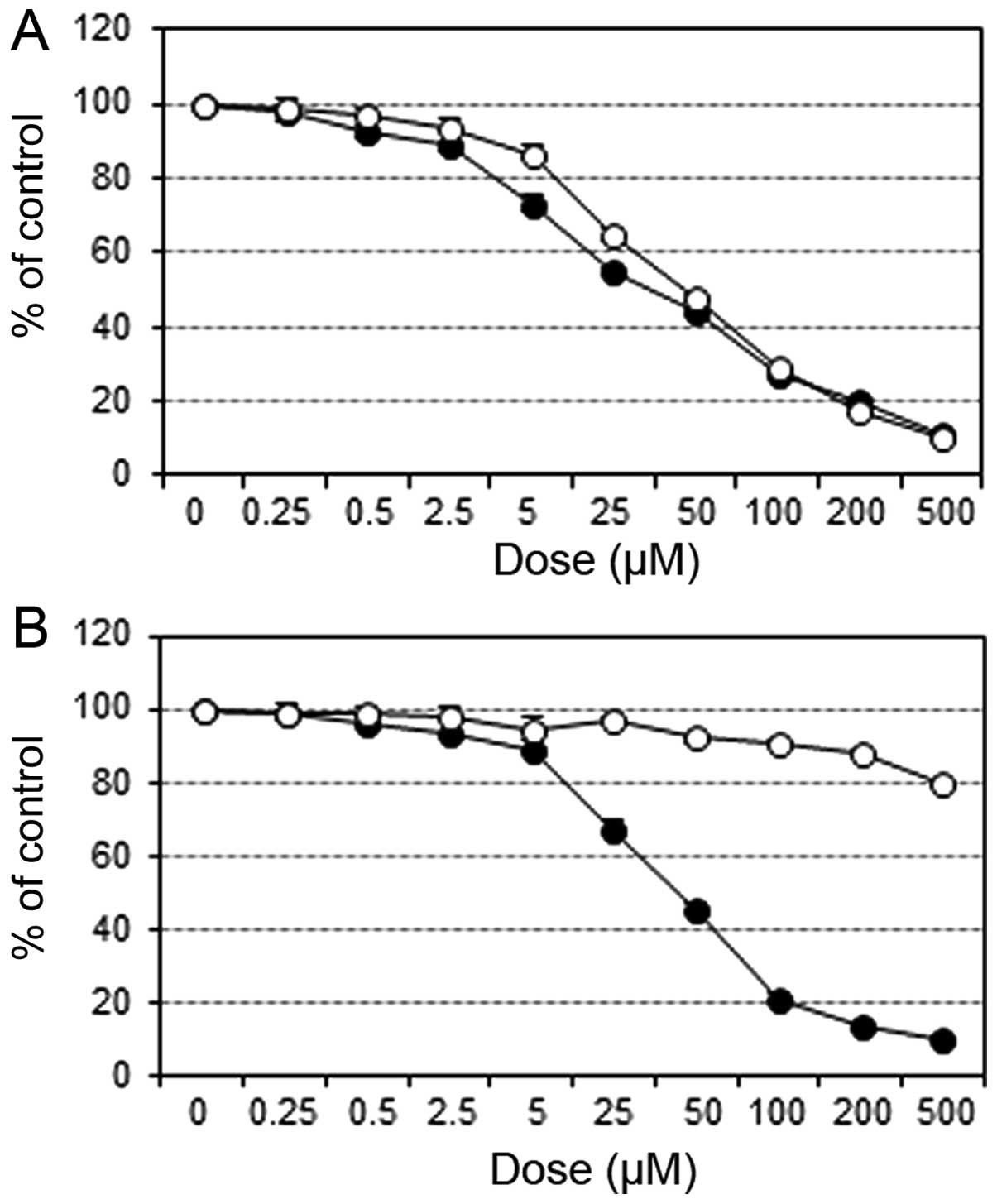
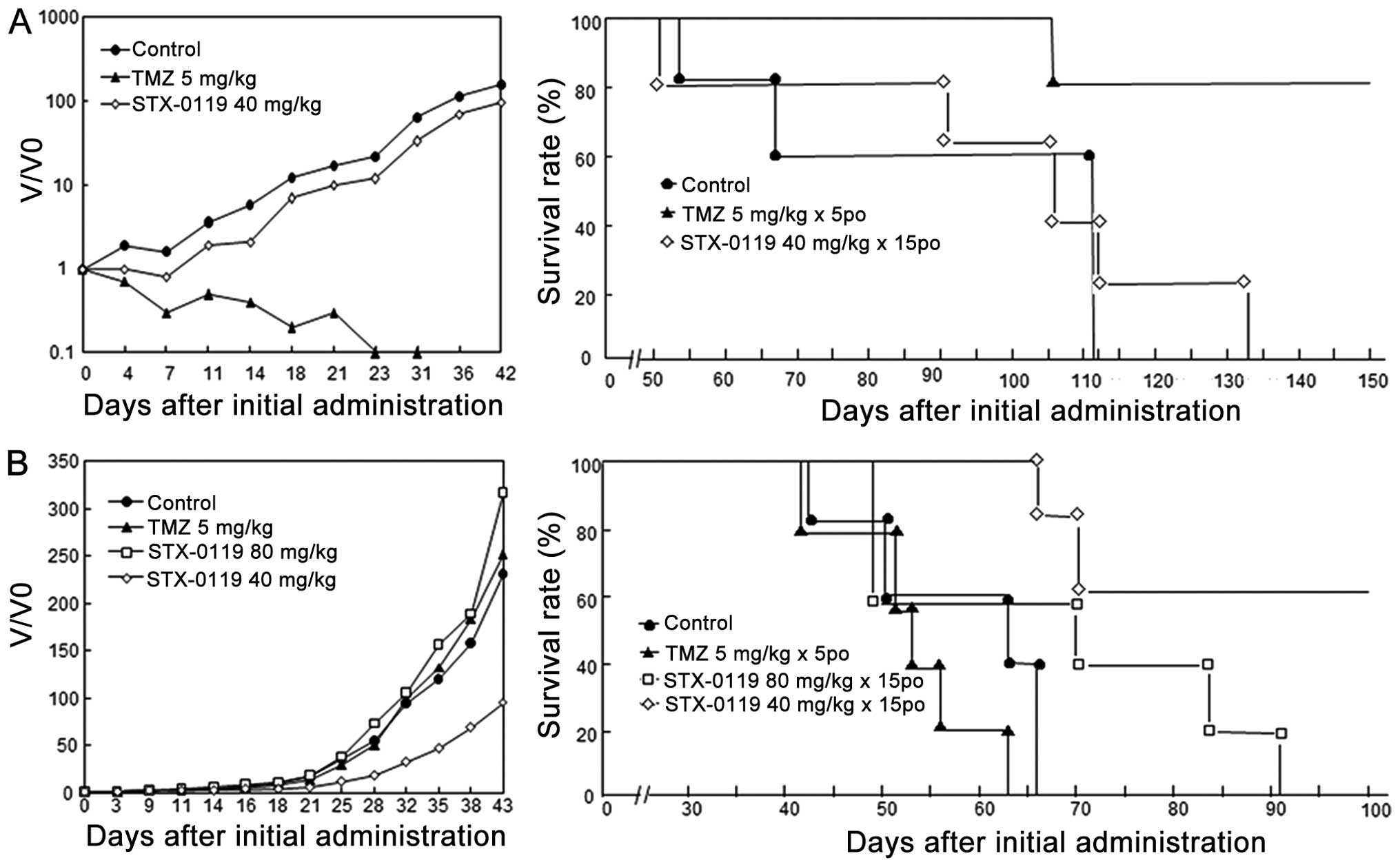
|
1.
|
Zhong Z, Wen L and Darnell JE Jr: Stat3
and Stat4: members of the family of signal transducers and
activators of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:4806–4810.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Bromberg J and Darnell JE Jr: The role of
STATs in transcriptional control and their impact on cellular
functions. Oncogene. 19:2468–2473. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Yu H, Kortylewski M and Pardoll D:
Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: role of STAT3 in the
tumor microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:41–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Wang T, Niu G, Kortylewski M, et al:
Regulation of the innate and adaptive immune responses by Stat-3
signaling in tumor cells. Nat Med. 10:48–54. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al:
Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for
glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Mirimanoff RO, Gorlia T, Mason W, et al:
Radiotherapy and temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma:
recursive partitioning analysis of the EORTC 26981/22981-NCIC CE3
phase III randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 24:2563–2569. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Brennan C, Momota H, Hambardzumyan D,
Ozawa T, Tandon A, Pedraza A and Holland E: Glioblastoma subclasses
can be defined by activity among signal transduction pathways and
associated genomic alterations. PLoS One. 4:e77522009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Cheng CK, Fan QW and Weiss WA: PI3K
signaling in glioma-animal models and therapeutic challenges. Brain
Pathol. 19:112–120. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Demuth T, Reavie LB, Rennert JL, et al:
MAP-ing glioma invasion: mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 and p38
drive glioma invasion and progression and predict patient survival.
Mol Cancer Ther. 6:1212–1222. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Pu P, Zhang Z, Kang C, Jiang R, Jia Z,
Wang G and Jiang H: Downregulation of Wnt2 and beta-catenin by
siRNA suppresses malignant glioma cell growth. Cancer Gene Ther.
16:351–361. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Purow BW, Haque RM, Noel MW, et al:
Expression of Notch-1 and its ligands, Delta-like-1 and Jagged-1,
is critical for glioma cell survival and proliferation. Cancer Res.
65:2353–2363. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, et al:
MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma.
N Engl J Med. 352:997–1003. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Murat A, Migliavacca E, Gorlia T, et al:
Stem cell-related ‘self-renewal’ signature and high epidermal
growth factor receptor expression associated with resistance to
concomitant chemoradiotherapy in glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol.
26:3015–3024. 2008.
|
|
14.
|
Hunter C, Smith R, Cahill DP, et al: A
hypermutation phenotype and somatic MSH6 mutations in recurrent
human malignant gliomas after alkylator chemotherapy. Cancer Res.
66:3987–3991. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Mukherjee B, McEllin B, Camacho CV, et al:
EGFRvIII and DNA double-strand break repair: a molecular mechanism
for radioresistance in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 69:4252–4259.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Ashizawa T, Miyata H, Ishii H, et al:
Antitumor activity of a novel small molecules STAT3 inhibitor
against a human lymphoma cell line with high STAT3 activation. Int
J Oncol. 38:1245–1252. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Vlachostergios PJ, Hatzidaki E, Befani CD,
Liakos P and Papandreau CN: Bortezomib overcomes MGMT-related
resistance of glioblastoma cell lines to temozolomide in a
schedule-dependent manner. Invest New Drugs. 31:1169–1181. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Jiang G, Wei ZP, Pei DS, Xin Y, Liu YQ and
Zheng JN: A novel approach to overcome temozolomide resistance in
glioma and melanoma: Inactivation of MGMT by gene therapy. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 406:311–314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Li GH, Wei H, Lv SQ, Ji H and Wang DL:
Knockdown of STAT3 expression by RNAi suppresses growth and induces
apoptosis and differentiation in glioblastoma stem cells. Int J
Oncol. 37:103–110. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
See AP, Han JE, Phallen J, et al: The role
of STAT3 activation in modulating the immune microenvironment of
GBM. J Neurooncol. 110:359–368. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Sherry MM, Reeves A, Wu JK and Cochran BH:
STAT3 is required for proliferation and maintenance of multipotency
in glioblastoma stem cells. Stem Cells. 27:2383–2392. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Liu Y, Li C and Lin J: STAT3 as a
therapeutic target for glioblastoma. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
10:512–519. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Jackson C, Ruzevick J, Amin AG and Lim M:
Potential role for STAT3 inhibitors in glioblastoma. Neurosurg Clin
N Am. 23:379–389. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Ashizawa T, Miyata H, Iizuka A, et al:
Effect of the STAT3 inhibitor STX-0119 on the proliferation of
cancer stem-like cells derived from recurrent glioblastoma. Int J
Oncol. 43:219–227. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Kohsaka S, Wang L, Yachi K, et al: STAT3
inhibition overcomes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma by
donregulating MGMT expression. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:1289–1299. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Villalva C, Martin-Lanneree S, Cortes U,
et al: STAT3 is essential for the maintenance of
neurosphere-initiating tumor cells in patients with glioblastomas:
a potential for targeted therapy? Int J Cancer. 128:826–838. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Pistollato F, Abbadi S, Rampazzo E, et al:
Intratumoral hypoxic gradient drives stem cells distribution and
MGMT expression in glioblastoma. Stem Cells. 28:851–862.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Yuki K, Natsume A, Yokoyama H, et al:
Induction of oligodendrogenesis in glioblastoma-initiating cells by
IFN-mediated activation of STAT3 signaling. Cancer Lett. 284:71–79.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Yoshino A, Ogino A, Yachi K, et al: Effect
of IFN-β on human glioma cell lines with temozolomide resistance.
Int J Oncol. 35:139–148. 2009.
|
|
30.
|
Motomura K, Natsume A, Kishida Y, et al:
Benefits of interferon-β and temozolomide combination therapy for
newly diagnosed primary glioblastoma with the unmethylated MGMT
promoter: A multicenter study. Cancer. 117:1721–1730. 2011.
|
|
31.
|
Senft C, Priester M, Polacin M, Schroder
K, Seifert V, Kogel D and Weissenberger J: Inhibition of the
JAK-2/STAT3 signaling pathway impedes the migratory and invasive
potential of human glioblastoma cells. J Neurooncol. 101:393–403.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Stechishin OD, Luchman HA, Ruan Y, et al:
On-target JAK2/STAT3 inhibition slows disease progression in
orthotopic xenografts of human glioblastoma brain tumor stem cells.
Neuro Oncol. 15:198–207. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Senft C, Polacin M, Priester M, Seifert V,
Kogel D and Weissenberger J: The nontoxic natural compound Curcumin
exerts anti-proliferative, anti-migratory, and anti-invasive
properties against malignant gliomas. BMC Cancer. 10:4912010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Yoshino A, Ogino A, Yachi K, et al: Gene
expression profiling predicts response to temozolomide in malignant
gliomas. Int J Oncol. 36:1367–1377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Johnson BE, Mazor T, Hong C, et al:
Mutational analysis reveals the origin and therapy-driven evolution
of recurrent glioma. Science. 343:189–193. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|